Antibiotics are one of the main means of treating cystitis. Whatever the stage of the disease, you have to deal with its infectious nature. The main goal of treatment is to suppress pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation of the bladder mucosa. Several antibacterial drugs are used for this, but the advisability of their use depends on many factors. Experts prescribe doxycycline for cystitis only in certain cases. Let's consider the conditions under which this remedy is most effective and when its use is not recommended.
About the properties of the drug
Doxycycline belongs to the group of semisynthetic antibiotics with a wide range of bacteriostatic and antibacterial effects. Pharmacodynamic properties are due to the ability to suppress protein synthesis in microbial cells, disrupting their transport to cell membranes, inhibiting cellular respiration and replication processes.
Gram-positive and gram-negative flora, including pathogenic strains with developed resistance to other antibiotics, exhibit high sensitivity to the drug.
Doxycycline copes well with representatives of the simplest flora, but is less active against Proteus, rod-shaped bacteria, microbes of the Serratia genus, enterobacteria and enterococci. It has a gentle effect on the natural intestinal flora.
Pharmacokinetic properties are manifested:
- almost 100% bioavailability;
- penetration into various tissues and biological fluids of the body;
- cumulative tendency with repeated use;
- relatively long (up to 18 hours) period of elimination from the body.
The drug is metabolized by the liver enzyme system and is excreted from the body in urine and in small quantities with feces.
In the pharmacological network, Doxycycline can be purchased in the form of capsules, dispersible tablets and powder (lyophilisate) intended for the preparation of infusion solutions.
The main substance in capsules is doxycycline hyclate, and in the form of hydrochloride - in lyophilisate.
Actions in case of overdose
The norms for taking the drug must be observed in accordance with the instructions. If they are exceeded, negative effects may occur. Clinical symptoms are as follows:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- rash;
- headache;
- impaired reaction to light.
If signs of overdose appear, you should stop taking the drug. It is necessary to rinse the stomach and take sorbents (activated carbon) inside. You should definitely call an ambulance, as clinical manifestations may worsen and lead to complications.
Overdose
If the dosage of the active component is violated, side effects increase.
To prevent the absorption of doxycycline, anatacids and magnesium sulfate are prescribed orally. Hemodialysis will not be effective in this case.
Indications
Despite the fact that in recent years the possibilities of antimicrobial treatment have expanded significantly due to the emergence of new antibacterial drugs, Doxycycline continues to be the drug of choice and one of the promising antibiotics used in the complex treatment of infectious and inflammatory pathologies not only in the field of urological diseases, but also in other areas of practical medicine.
- Medicine "Nitroxoline": rules of use for bladder disease and patient reviews
The drug can be prescribed both as monotherapy and in complex treatment of a wide variety of pathologies:
- acute and chronic bronchitis clinic;
- with infectious and inflammatory damage to the lung tissue and urinary tract;
- in the treatment of pleurisy and gonorrhea;
- for infectious postoperative complications after abdominal operations (sepsis, peritonitis);
- for purulent skin infections and infectious lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- in the treatment of tick-borne borreliosis and ophthalmological diseases.
Reviews from doctors
Mikhail, 57 years old, Moscow
This antibiotic is widely used in veterinary medicine. I often prescribe the drug to treat a disease caused by a tick bite. Colleagues often recommend medication in gynecology if the disease is caused by ureaplasma or chlamydia. A high recovery rate among women infected with sexually transmitted infections.
Alexey, 34 years old, Omsk
Prescribed a drug for the treatment of acne in adolescents. The patients were satisfied with the results of the therapy, but it was often necessary to prevent dysbiosis for several months after completing the course of treatment with Doxycycline.
Instructions: how to take Doxycycline for cystitis?
Antibacterial agents are drugs that must be used exactly as prescribed by the doctor. Even the attached abstract is not always correct, because urologists take into account any features of the clinical picture, for example, the patient’s weight, concomitant ailments, previously used antibiotics, the form and type of inflammatory process in the organ, and so on. Following precise dosing is the key to successful treatment.
So, how should you take Doxycycline for cystitis in women? The pharmacological medicine itself is considered a long-acting medicine, and therefore, as a rule, it is enough to take only one pill per day. For example, if a patient took an antibiotic at eleven in the morning, then the next use should occur at the same time the next day.
How can changing the time you take your medication be dangerous? The concentration of the active ingredient in the patient's bloodstream should remain unchanged throughout the entire treatment period. Even a slight decrease in it, associated with untimely use of Doxycycline, leads to the development of resistance to the drug in the bacteria, and therapy as a result may be ineffective. In addition, further use of drugs in this series will not make any sense, and the urologist will be forced to prescribe the patient antibacterial agents of an alternative group, to which pathogens do not yet have resistance.
As the time between taking capsules decreases, the patient may suffer from an overdose, which leads to side effects. It is precisely patients who violate the therapeutic course that can get a negative impression from the treatment of cystitis with the help of this medication.
It is important to find out in advance how to take Doxycycline for cystitis in women. It is necessary to stock up on water, since the capsule must be taken with at least one glass of liquid. You should also not take the medication on an empty stomach. It is better to choose a meal time for this. The products themselves do not affect the absorption of the active component.
How long does cystitis treatment with this drug last on average? Most often, it is enough to drink it for only five days, but sometimes, for example, in the presence of a chronic form of the disease, this period can be extended.
What else does the instructions for use of Doxycycline for cystitis tell us?
Doxycycline
Doxycycline belongs to the antibacterial drugs of the tetracycline series. Widely used in the treatment of pathologies of the urinary, respiratory tract, stomach and intestines and other diseases.
Compliance with the requirements contained in the instructions for use is mandatory in order to prevent the development of complications of therapy.
The article contains average prices for the drug, reviews from patients and doctors, as well as current analogues of Doxycycline in Russia.
Compound
The active substance is a chemical compound derived from Tetracyclines - Doxycycline (international name - Doxycyclinum) in the form of hydrochloride or monohydrate. The amount per dose is 100 or 200 mg.
Other components are lactose, yellow dyes, Ca salts, Sodium EDTA (in ampoules).
Release form
The drug is produced in the following forms:
- Capsules for oral use. The package contains 10 or 20 yellow capsules containing 100 mg of active ingredient and the original version of the official instructions.
- powder for the preparation of solution for injection - Doxycycline lyophilisate. Contains 100 or 200 mg of active substance. The number of ampoules in a package is 5 or 10.
pharmachologic effect
Doxycycline belongs to the pharmacological group of antibacterial drugs that have a systemic effect on the body. According to the mechanisms of action, the drug is a bacteriostatic drug that inhibits the synthesis of protein elements in bacterial cells.
The pharmacological actions of Doxycycline are as follows:
- bacteriostatic effect on bacteria;
- impact on staphylococci, E. coli, clostridia, rickettsia, streptococci, gonorrhea pathogen, Salmonella rickettsia, mycoplasma, chlamydia and many other pathogens.
The wide spectrum of activity of the drug allows it to be used to treat many pathologies caused by sensitive pathogens.
During pregnancy and lactation
Doxycycline is contraindicated for use while pregnant. It is important to remember that the drug quickly penetrates into mother's milk and causes darkening of the baby's tooth enamel.
Therefore, the use of Doxycycline during breastfeeding (active lactation) should be discussed with your doctor.
During the period of treatment with Doxycycline during breastfeeding, the child should stop drinking mother's milk in order to avoid dangerous complications.
With alcohol
Ethyl alcohol that comes into contact with the drug in case of interaction with alcohol leads to a decrease in its effectiveness. During the period of therapy, it is important to exclude the interaction of Doxycycline and alcohol due to their low compatibility.
Analogs
Doxycycline can be replaced, in consultation with your doctor, with the following analogues (foreign or domestic Russian):
- Doxibene;
- Unidox Solutab;
- Vibramycin;
- Doxa-M-Ratiopharm;
- Doxycycline Solutab (soluble form, which is a modern analogue of Doxycycline of the new generation);
- Doxycycline from different manufacturers (Darnitsa (cheaper), Teva, Nycomed, Stada, Belmed, Kredofarm, etc.).
All substitutes differ in manufacturers and release forms (soluble forms are available). Some sources indicate that Doxycycline, which should be dissolved in water before taking, is more effective. This form has less negative effects on the digestive system.
Other possible substitutes for Doxycycline may be the following (belong to the same group of drugs):
- Oletethrin (Tetracycline and Oleandomycin, combined);
- Tetracycline (more toxic). Doxycycline has differences, being a safer drug with fewer side effects;
- Tigecycline (Tygacil).
Doxycycline can be stored for three years from the date of manufacture. After the expiration date, the drug is not allowed to be used.
Terms of sale and storage
Doxycycline is an active antibacterial drug, available from pharmacies only with a prescription written by a doctor in Latin. It is important that the INN of the drug is indicated on the prescription form (in Russian or Latin).
Doxycycline is stored in rooms where the temperature does not exceed 25⁰C, and there is no access to moisture or direct light. The product should be kept out of reach of children.
special instructions
In order to prevent thrush (candidiasis), it is necessary to prescribe antifungal agents (Fluconazole, Nystatin) and probiotics simultaneously with the use of Doxycycline.
During treatment with the drug, no adverse reactions occur that affect the ability to drive.
Persons with lactose intolerance should take the medicine with caution.
If any manifestations occur that indicate disturbances in the functioning and integrity of the stomach and intestines, you should discontinue the drug and consult a doctor.
Price
The cost of Doxycycline 100 mg No. 10 is from 13.5 rubles. Doxycycline 100 mg No. 20 costs from 24.5 rubles.
Validity of prescription for cystitis
The basis for prescribing doxycycline for cystitis in women was its clear advantage over similar drugs, which is due to:
- How to take Furazolidone for cystitis: instructions and reviews
- minimal impact on the natural intestinal flora;
- better absorption into the blood (absorption);
- longer action;
- a stronger therapeutic effect when taking a minimum dose of the drug, due to its cumulative property;
- the possibility of a one-time daily dose of the established dosage.
Treatment regimen and special recommendations
The treatment regimen and dose of the drug are individual. The treatment order is determined according to the form of the disease and the severity of clinical manifestations. The main condition is compliance with the precisely established time of taking the drug for the entire period of the treatment course.
- In the acute form of the disease, Doxycycline for cystitis is prescribed according to a specific regimen - twice a day. The daily dose is 200 mg (morning - 100 mg and evening 100 mg) on the first day of illness. The safe, maximum permissible daily dose of the drug is 300 mg. On each subsequent day - 100 mg/day for a week.
- For chronic cystitis, the treatment regimen includes taking the drug twice a day - the total daily dose is 200 mg. This treatment regimen is maintained throughout the entire treatment course - from one to 1.5 weeks.
For cystitis, the genesis of which is due to the influence of gonococcal or staphylococcal infections, shock therapy is indicated. In this case, the dosage of the drug is doubled, and therapy is carried out according to a special scheme:
- On the 1st, 2nd and 3rd days of illness, the medicine is taken in the amount of 600 mg/day, dividing the dose of 100 mg into six doses at equal intervals.
- Day 4 – 500 mg in 5 doses of 100 mg.
- Day 5 – 400 mg in 4 doses of 100 mg.
- Days 6 and 7 – 300 mg in 3 doses of 100 mg.
The use of doxycycline can cause irritation of the mucous tissues of the digestive system, so the drug should be taken simultaneously with meals, with plenty of liquid.
For whom antibiotics are contraindicated?
Doxycycline is not prescribed:
Patients with lactase deficiency. For lactose intolerance. Patients with leukopenia. For porphyrias. For liver failure (severe). Patients with intolerance to Doxycycline and other tetracycline antibiotics, auxiliary components of the drug. Children under 12 years of age and/or lighter than 45 kg. For the treatment of pregnant women. Women during breastfeeding.
Doxycycline should not be taken during pregnancy
The drug is not used in pediatric practice, since the active substance, when interacting with calcium ions, forms insoluble complexes that are deposited in bone tissue (skeleton, tooth enamel, dentin).
For cystitis in pregnant women, antibiotics are not used due to the toxic effect on the fetus: the drug causes a delay in skeletal development and fatty infiltration of the liver. If a nursing woman needs to take an antibiotic, breastfeeding should be stopped for the duration of therapy.
Possible side effects
Despite the high efficiency and effectiveness of the drug, patient reviews of doxycycline for cystitis are, for the most part, full of negativity, noting:
- nausea, vomiting, development of diarrhea and pain in the abdomen;
- with associated problems - exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases;
- decreased or increased blood pressure, cramps and muscle pain;
- dysbacteriosis, headaches, dizziness and problems with coordination.
Indeed, the list of pitfalls is quite extensive. Undesirable effects can occur in any organs of the body and its systems. Therefore, without the advice of a specialist, self-administration of the drug is strictly prohibited.
What adverse reactions to expect
The list of side effects of the drug is extensive. Doxycycline provokes side effects from almost all body systems and sensory organs.
Doxycycline may cause high blood pressure
Taking the drug can cause metabolic problems and the development of anorexia. From the digestive system, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, colitis and enterocolitis, esophagitis, dysphagia, gastritis and peptic ulcer may occur. During the course of treatment, blood pressure may decrease and heart rate may increase. Possible functional disorders of the hematopoietic system: increased destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia), decreased platelet content (thrombocytopenia) or leukocytes (leukopenia), increased number of eosinophils (eosinophilia). Sometimes there is liver dysfunction, cholestasis. Arthralgia and myalgia (pain in joints and muscles, respectively) may develop. The concentration of nitrogen in the urine increases. Frequently occurring adverse reactions include dysbacteriosis, inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the mouth (stomatitis), tongue (glossitis), rectum (proctitis), and vagina in women (vaginitis).
Patients taking Doxycycline may complain of tinnitus, blurred vision, headache and loss of appetite, caused by increased intracranial pressure. Dizziness, loss of balance and coordination occur.
Liver problems may sometimes occur when taking Doxycycline.
Due to the high risk of side effects, antibiotics should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
What is the drug for?
The human body has a permanent microflora. It is divided into beneficial and opportunistic. The latter is found on the skin, in the tonsils and intestines, and is present on the mucous membrane of the genitourinary tract. Opportunistic microorganisms can cause inflammatory diseases when the desired bacteria no longer “restrain” their growth and reproduction. This occurs when the immune system is weakened (hypothermia, colds) or dysbacteriosis.
- Palin: instructions for use, price, substitutes, reviews
Other causative agents are infectious pathogens. For their introduction into the body, contact with a patient or a carrier of the virus is necessary. Such microorganisms are not normally found in a healthy person. These include pathogens of syphilis, gonorrhea, dysentery, and salmonella.
The disease occurs with a local inflammatory reaction and recognizable diagnostic symptoms. The condition is characterized by generalized systemic exposure to toxins, manifested by the clinical manifestations of infectious intoxication. Symptoms such as:
- fever;
- chills;
- muscle aches;
- pain in the eyeballs;
- weakness;
- dizziness.
Local symptoms disrupt the functioning of the organ, while general symptoms can lead to death due to severe intoxication. The use of the antibiotic doxycycline to treat such diseases is due to the need to destroy pathogenic bacteria.
Short description
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus and bacteroides are resistant to the action of Doxycycline. These are causative agents of nosocomial infections. The medicine is active against the following microorganisms:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- clostridium;
- Neisseria (the causative agent of gonorrhea);
- coli;
- causative agent of dysentery;
- salmonella;
- Treponema (the causative agent of syphilis);
- mycoplasmas;
- chlamydia.
The drug is effective for most inflammatory diseases of the respiratory and genitourinary tract.
What kind of remedy is this
The drug has a broad antimicrobial effect on gram-positive microorganisms that change color when using a special dye:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- clostridia (opportunistic anaerobic bacteria, part of the normal flora, but if they multiply excessively, they can pose a health hazard; they can cause clostridiosis - botulism, tetanus, toxic infections, etc.);
- actinomycetes, with a gram-positive reaction having a structure close to gram-negative (fungal microorganisms that have pathogenic forms that create health problems);
- listeria (intracellular parasitic microorganisms that can cause abscesses and meningitis).
Also act on gram-negative flora:
- meningococci;
- gonococci (causative agents of gonorrhea);
- Klebsiella (can cause pneumonia, urogenital diseases, sepsis, acute intestinal infections);
- enterobacteria;
- hemophilus influenzae bacterium (causes acute conditions accompanied by the development of ulcers in various organs, damage to the respiratory system and the central nervous system).
Suppresses the activity of flora that is immune to penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics.
Disturbance of normal flora occurs to a lesser extent when using doxycycline than with other antibiotics.
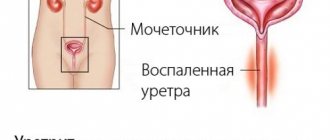
Indications for cystitis
The main indication for taking antibiotics in general and Doxycycline in particular in the treatment of cystitis is the presence of an infection in the urethra or bladder. Taking this antibiotic is an effective way to quickly destroy almost all types of pathogenic bacteria, viruses or microbes.
That is, the use of the medicine is advisable if the disease is infectious in nature, regardless of the form in which it occurs.
In addition to the initial presence of infectious agents in the genitourinary system, which become the causative agents of cystitis, the drug can be recommended by doctors if the nature of the disease is non-infectious. During the development of cystitis, the internal balance of the flora is disrupted, which is the reason for the development of pathogenic microorganisms. This is especially common in women suffering from a chronic type of disease.
Treatment with antibiotics, including Doxycycline, is also carried out in case of the development of secondary cystitis, which arose as a result of the presence of any infection in the body. For example, in men, cystitis often develops after an incompletely treated urogenital infectious disease, absolutely any, not necessarily venereal.
Infection of the body by fungi, for example, progressive thrush, is also the reason why antibiotics are used in therapy.
Thus, the use of Doxycycline is advisable for almost any type of cystitis, including non-infectious chronic types of disease.
Ampicillin is also a very good drug. Read more.
Recommendations for taking the medicine
Among patients treated with Doxycycline for cystitis, individual photosensitivity reactions are likely to occur, which should be taken into account. Even a small amount of time in the sun can cause the formation of age spots and redness of the skin. Visiting the solarium, of course, is also prohibited.
If the patient develops dental tissue, then taking this medicine can affect the formation of its color. The condition of the teeth may be accompanied by a dark shade for a long period. Most often this relates to adolescents with cystitis. Women who take oral contraceptives should be aware that Doxycycline reduces the effect of these drugs, and thus the onset of an unwanted pregnancy is quite likely.
Brief overview of the drug
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent. Available in the form of hard yellow capsules, the inside is a yellow-green powder with white patches, which is the norm. The main effect of the drug is bacteriostatic (stops the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microflora). Activity is manifested against the following cystitis pathogens:
- staphylococcus;
- streptococcus;
- enterobacteria;
- coli;
- proteas;
- Klebsiella;
- mycoplasma;
- chlamydia.
Release forms and composition
The drug is produced in 2 dosage forms. 1 capsule and 1 ampoule of lyophilisate contain 0.1 g of active ingredient.
Oral capsules
The product is available in blisters of 5 yellow capsules in each.
Lyophilisate for the preparation of solution for infusion
The lyophilization product (a method of soft drying of a substance in which the dried active component is frozen) is produced in ampoules of 5 pcs. in cardboard packaging.
How does Doxycycline interact with other medications?
When prescribing any drugs, you should be aware of their interactions with other drugs. "Doxycycline" is not used in conjunction with antacids based on aluminum, calcium and magnesium salts, as well as with medications for the treatment of anemia (iron-containing).
Barbiturates reduce the half-life of the antibiotic, thereby impairing its effectiveness. Combination with penicillins reduces the potency of both drugs. Estrogen-based medications (oral contraceptives) increase the frequency of bleeding and also reduce the reliability of contraceptives while taking Doxycycline.
Pregnancy and lactation
Doxycycline is strictly contraindicated for pregnant women and breastfeeding. The active substances of the antibiotic penetrate the child’s body through the placental bloodstream or through mother’s milk. As a result, adverse effects and complications may appear:
- Delays and disorders of intrauterine development.
- Fatty infiltration.
- Allergic reactions.
- Liver diseases.
Therefore, if Doxycycline is prescribed to a nursing woman for severe cystitis, the child is temporarily transferred to artificial feeding for the period of treatment.
Methods of using antibiotics
Doxycycline capsules for cystitis in women are prescribed according to an individual regimen. Depending on the diagnosis, one course lasts on average a week, but does not exceed 10 days.
In case of an acute attack of bladder inflammation, the first day is prescribed 2 capsules once or 1 capsule in the morning and evening with an interval of 12 hours. The following days drink 1 capsule per day.
Chronic cystitis with frequent relapses requires an increased dose. Prescribe 200 mg (2 drops) 1-2 times a day.
Important!
Doxycycline irritates the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach; with long-term treatment, it can provoke the development of ulcers and erosions. To prevent this, the drug is taken after meals. Instead of eating, you can drink a glass of milk or kefir, which does not affect the degree of absorption of the substance.
Take the medicine with plenty of liquid. It is better to use it in the first half of the day. Consumption immediately before bed increases the risk of irritation of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
During therapy, it is necessary to observe the exact dosage and interval between doses of the antibiotic. For the effectiveness of cystitis treatment, it is important that the concentration of the active substance in the blood is constant. Its decrease leads to the development of bacterial resistance. This situation requires discontinuation of the drug and the prescription of more potent antimicrobial agents. If you take capsules more often, this will lead to an overdose and the following negative consequences:
- non-infectious kidney damage;
- pancreatitis;
- excess calcium in the blood.
Doxycycline begins to act 1.5-2 hours after administration, when the concentration of the substance in the blood plasma reaches its maximum. During the first days of antibacterial therapy, a woman experiences severe pain, pain during urination decreases, and the number of false urges to empty the bladder decreases.
The inflammatory process is quickly eliminated, the signs of cystitis are stopped. During this period, a woman should not stop taking the drug, so as not to provoke the re-development of cystitis. Noticeable improvement occurs within 3-4 days. It is necessary to complete the entire course of treatment, even if the symptoms of the disease have disappeared.
Doxycycline: instructions, composition, indications, action, reviews and prices
Doxycycline is prescribed for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of various organs. This is a tetracycline antibiotic that is effective against a wide range of infectious agents.
The therapeutic effect of the drug allows the use of doxycycline as a drug therapy for diseases of the respiratory tract, digestive and genitourinary systems. Indications for use are determined by the attending physician.
Independent use of the drug is fraught with the development of complications.
Antibiotics are serious prescription medications. The use of such drugs is allowed only if there are strict indications.
Doxycycline capsules
The standard dosage of the active component in one capsule is usually 100 milligrams. This dosage formula promotes rapid absorption of the substance in the gastrointestinal tract. Prescription is possible in children after twelve years of age, if the child’s body weight is more than 45 kilograms.
Package
Doxycycline tablets
The standard dosage of the active component in one capsule is usually 100 milligrams. The special shell of the tablet formula improves the absorption of the substance in the desired part of the digestive tract.
Doxycycline as a lyophilisate
Lyophilisate is a dry form of a medicinal substance used to prepare a solution. Options for the concentration of the active component: 100 or 200 milligrams.
It is used for intravenous administration by injection.
Therapeutic effect
According to the classification, the medicinal substance belongs to semisynthetic antibiotics from the tetracycline group. Wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity. It is considered bacteriostatic in its action.
After absorption and distribution in the body, the chemical compound enters the bacterial cell and inhibits protein production.
As a result, the infectious agent cannot perform basic functions, including production and pathogenic activity.
Activity spectrum
additional information
- In its antimicrobial effect, the drug surpasses the effect of natural antibiotics of the tetracycline group.
- Unlike other medications, the long-term therapeutic effect of the drug is maintained when using small doses.
- Doesn't have much effect on the state of the intestinal microbiome.
The use of this medicine is less likely to cause complications associated with microflora disturbances. - Cross-resistance with other drugs of similar action from the group of penicillins and tetracyclines is possible.
The bacteriostatic effect helps stop the spread of the infectious process in the body.
This property is due to the ability of doxycycline to disrupt the binding of the transport substance to the cellular ribosome.
Side effect
The drug substance fights the infectious process and causes adverse effects in some patients. The severity of the side effect depends on the dosage form, dosage and condition of the patient.
A typical adverse effect is sensitivity to substances contained in the drug (allergy). The immune system recognizes chemical compounds as a threat.
It is necessary to exclude an allergy to the drug before starting therapy.
Possible Adverse Effects:
- Nervous system: toxic effects, increased pressure inside the skull. Symptoms of these conditions include dizziness, cephalalgia, lack of appetite, and vomiting.
- Immune system: skin rashes, autoimmune reactions, dermatitis, redness of the integumentary tissues, swelling, anaphylactic shock, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria and others.
- Gastrointestinal tract: loose stools, abdominal discomfort, vomiting, pseudomembranous colitis, ulcer formation, inflammation of tongue tissue, difficulty swallowing and others.
- Auditory and vestibular apparatus: the effect of background noise.
- Heart and blood vessels: inflammation of the pericardial sac, disturbance of the rhythm of heart activity, low blood pressure, erythema multiforme.
- Reproductive and excretory systems: increased levels of urea nitrogen.
- Visual apparatus: decreased visual acuity, the appearance of blind spots, double vision.
- Hematopoietic system: hemolytic anemia, increased concentration of eosinophils, decreased prothrombin index, decreased levels of leukocytes, neutrophils, platelets.
- Liver and gallbladder: dysfunction of the liver tissue, increased levels of liver enzymes, autoimmune damage to the organ, cholestatic syndrome.
- Local reaction to the injection: blood clot formation and inflammation of the vein.
- Additionally: increased sensitivity to light, superinfection, discoloration of teeth, fungal infections, disruption of the intestinal microbiome, pathology such as serum sickness, joint and muscle pain.
Most of the possible complications associated with antibacterial therapy are listed, but the specific list of reactions depends on the dosage form. You need to read the instructions and consult a doctor.
Absorption and excretion
Capsule and tablet forms of the drug are quickly absorbed in the digestive tract after the shell dissolves. Eating food has virtually no effect on the efficiency of absorption of the chemical compound.
The highest concentration of the active component in the blood plasma is observed 150 minutes after administration. Within half an hour, the substance penetrates into major organs, including the liver, spleen and sinuses. Converted in the liver.
Excreted by the digestive tract and excretory system.
Appointed by a specialist
Indications for use
- Infectious diseases of the respiratory tract: damage to the lung tissue, larynx, pharynx, bronchi and other parts.
- Infectious lesions of the paranasal sinuses, hearing aid and other ENT organs.
- Inflammatory and infectious processes in the excretory organs and reproductive system: inflammation of the bladder, kidney tissue, uterine mucosa, prostate gland and other organs.
- Infectious lesions of the abdominal organs: inflammation of the gallbladder and bile ducts, diarrhea and inflammation of the mucous membranes of bacterial origin.
- The main remedy for the treatment of bronchial inflammation in patients under the age of 65 with exacerbation of pathology without additional diseases.
- Microbial infection of soft tissues, including cellulitis, abscesses and infected wound surfaces.
- Additionally: damage to the visual apparatus, syphilitic infection, rickettsiosis, tick-borne infections, cholera, dysentery, bone damage and other diseases caused by pathogens sensitive to the drug.
The medicine is always prescribed by a doctor after initial diagnosis. Self-medication is prohibited.
Instructions for using Doxycycline
The purpose of prescribing an antibiotic is always determined by the attending physician. The specialist must correctly assess the patient’s symptoms and select the right medication.
The drug therapy regimen is drawn up taking into account the patient’s condition.
It is necessary to take the drug daily in a certain dose at the same time, otherwise there is a risk of infectious agents developing resistance to the active component.
The admission guidelines and additional information listed below are for reference purposes only. The exact method of using the antibiotic is explained to the patient by the attending physician. You should also read the instructions that can be found in the package.
Tablet or capsule form
- Chronic form of an infectious process that affects the organs of the excretory system: two hundred milligrams per day.
- Disease caused by gonococcus: for damage to the urethra, the dose is five hundred milligrams (one dose of three hundred milligrams and two times one hundred milligrams six hours apart), one hundred milligrams every 24 hours in women, one hundred milligrams twice a day in male patients (on throughout the week).
If a complicated form of pathology is diagnosed, the course dosage is increased to 800 or 900 milligrams. - Syphilitic infection: three hundred milligrams every 24 hours for at least ten days.
- Chlamydial infections of the rectum, urethra and cervix: one hundred milligrams twice a day for at least 7 days.
- Bacterial damage to the excretory and reproductive systems in men: one hundred milligrams twice a day for a month.
- Chloroquine-resistant malaria: two hundred milligrams every 24 hours for a week along with other medications. One hundred milligrams per day is used for prevention.
- Acne: one hundred milligrams every 24 hours. The course of drug therapy is from six to twelve weeks.
- Travelers' diarrhea: two hundred milligrams once or in two doses on the first day and then one hundred milligrams each. No more than three weeks.
- Leptospirosis: one hundred milligrams twice every 24 hours for a week.
- Reducing the risk of complications after an abortion: one hundred milligrams 60 minutes before the procedure and two hundred milligrams half an hour after the abortion.
Adults should not use more than 600 milligrams of the drug per day. If the functioning of the excretory system is seriously impaired, dose adjustment is necessary.
Injection form
The doctor prescribes an injection of an antibiotic if no other use of the drug is possible and it is necessary to quickly create a high level of the active component in the tissues.
It is recommended to switch to oral medication over time if possible. The average recommended dose for adult patients is two hundred milligrams. This dose can be divided into two administrations 12 hours apart.
The duration of treatment and the final dosage are calculated by the doctor, focusing on the patient’s medical history.
For a child over eight years of age, a dose is prescribed based on body weight. With a body weight of more than forty-five kilograms, an adult dosage can be used.
Analogues of the drug
Doxycycline is the name of the active component and the release form of the drug in the form of capsules/lyophilisate. In the pharmacy you can find other drugs containing this chemical compound in different concentrations. Before using any analogue, you need to read the instructions and consult a specialist.
Known analogues:
- Xedocin in tablets of one hundred or two hundred milligrams.
- Vidoccin for the preparation of injection solution.
- Unidox Solutab in tablet form.
Analogue
Reviews and prices
Doctors of various profiles note the effectiveness and good tolerability of the antibiotic. Proper use is rarely accompanied by the development of serious complications.
The price of the drug starts from 30 rubles.
Doxycycline is a popular antibiotic prescribed to treat various pathological processes. Use as prescribed by a doctor helps eliminate the infection and prevent the development of complications.
| Product type | Antibiotics |
| Release form | Tablets, capsules, lyophilisate |
| Method of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| Other names | Xedocin, Vidoccin, Unidox Solutab |
Contraindications
It is prohibited to use an antibiotic if there are the following contraindications:
- Severe form of liver failure.
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- Porphyria is a condition represented by a disorder of pigment metabolism.
- Hypersensitivity to antibacterial drugs from the tetracycline group.
Compatibility with alcohol: alcoholic beverages negatively affect the body while using Doxycycline, therefore it is prohibited to drink such drinks while using the medicine.
Sources used:
- https://mycistit.ru/lekarstva/doksiciklin
- https://uromir.ru/vospalenie-mochevogo-puzyrya/lekarstva/doksiciklin.html
- https://fb.ru/article/474365/doksitsiklin-pri-tsistite-instruktsiya-po-primeneniyu-otzyivyi-prinimavshih
- https://saydiabetu.net/cistit/tabletki-doksiciklin/
- https://cistit911.ru/lekarstva/doksitsiklin-pri-tsistite-instruktsiya-po-primeneniyu.html
- https://1labhealth.ru/tsistit/lekarstva/doksitsiklin-pri-lechenii-tsistita-u-zhenshhin.html