What is a stent and how to install it
To prevent stagnation of urine in the kidneys, a special flexible plastic tube is placed in the ureter, which allows urine output to normalize. But not every patient knows what a stent is. This is a special tube made from polyurethane, silicone or PVC. Regardless of the type of material, hydrophilic materials are necessarily sprayed onto it during production, which is necessary for better compatibility of the tube with the tissues of the urinary organs.
Depending on the structural features of the urinary organs, gender and age of the patient, the dimensions of the tube can vary from 12 cm to 30 cm in length with a diameter of 1.5 mm to 6 mm. To relieve the patient from discomfort and increase the mobility of the tube, its ends are shaped like a spiral. On one side the tube is placed in the bladder, on the other - in the renal pelvis.
Before the operation, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination: donate blood and urine for a general clinical analysis, as well as undergo an instrumental examination to make a correct diagnosis.
Installation of a stent in the kidney and bladder is carried out after the patient has been given local or general anesthesia. Depending on the method of installing the tube in the ureter, the procedure can be performed using retrograde or anterograde methods. The first involves inserting a plastic tube through the lower urinary organs. To install a stent using the second method, the surgeon makes a small incision in the abdominal cavity through which the catheter is installed.
Preparing for surgery
Preparing for the procedure is quite simple. The day before the stent is installed, you should stop taking any food or liquid. The bladder should not be full in order for the cystoscope to have free access. Before administration, patients are given a special enema to cleanse the intestines. A few days before the operation, you must completely stop consuming alcohol-containing products. The doctor will prescribe antibiotics that affect the organs of the genitourinary system to exclude the occurrence of bacteriuria. Such drugs are Furagin or Furadonin. It is recommended to take sedatives before the procedure to reduce stress levels.
Indications and contraindications for stenting
A stent is placed in the ureter when its lumen narrows, blood pressure increases, which is caused by an increase in intrarenal pressure, and during preparatory procedures before various types of surgical interventions in the pelvic organs. The main goal of this procedure is to normalize urination.
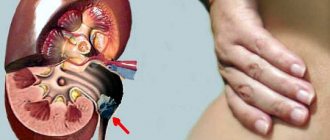
The main reason for installing a stent is urolithiasis and blockage of the ureter with stones. Also, an obstacle to the passage of urine can be a blood clot, a malignant or benign tumor in the ureter. Swelling of the ureteral tissues as a result of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs, as well as after surgical manipulations on them, can lead to impaired diuresis and stagnation of urine in the kidney.
A urologist may recommend installing a stent in the kidney if there are adhesions in the ureter or if the lumen of the organ is abnormally narrow. Installation of a catheter is necessary for cancer of the lymphatic system, as well as organs that are located in the pelvis near the ureters. Fibrosis of fatty tissue is another indication for stenting.
General view of the stent
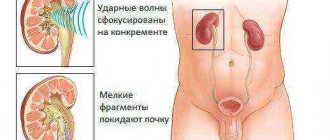
The stenting procedure is carried out using shock wave methods for crushing kidney stones, which helps prevent blockage of the ureters with large fragments. During complex surgical operations, installation of a catheter is necessary to maintain normal and timely diuresis, as well as to determine the location of the ureters.
Stent installation is contraindicated in case of respiratory diseases, renal failure, extensive damage to the renal vessels, low platelet levels, as well as allergic reactions to medications used during stenting.
How to avoid discomfort with a stent
For those women scheduled for stenting, there is no need to be afraid. You just need to find out more useful information in this area from your doctor. Women who have undergone the procedure and given birth give pregnant women recommendations:
- relax on the couch, walk less, and if necessary, go somewhere by car. This is not the best recommendation for a pregnant woman, since doctors recommend that they move, but in case of kidney problems, the situation takes a slightly different course, and other recommendations must be followed. You need to check with your doctor for more information;
- To make yourself feel better, you need to stay in the knee-elbow position more often. For example, while reading, browsing websites of children's clothing stores, etc.;
- increase the volume of liquid you drink to the permitted limits. Some expectant mothers take Brusniver several times a day to get rid of inflammatory processes in the urinary organs, including the kidneys;
- For some pregnant women, doctors prescribe Urolax, which increases immunoglobulin A in the urine. This drug is expensive, but after it the bladder hurts less in the morning.
- Ureteral blockage symptoms
The main recommendation for women planning pregnancy is to treat any diseases, including pyelonephritis, in a timely manner. There are cases when women knew about their chronic pyelonephritis and consulted with a urologist and gynecologist even before pregnancy, but doctors assured them that there would be no problems with pregnancy.
In fact, problems are possible, and doctors must take all measures to prepare a woman’s body for pregnancy and childbirth. If pyelonephritis is detected in a pregnant woman, the woman is given a stent, she needs to get more recommendations in order to alleviate the condition and not harm the baby.
About the benefits of the knee-elbow position, which serves as a prevention of compression of the ureter by the growing uterus. If women were warned about this, there would be fewer kidney problems.
Stenting during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a catheter is installed only according to strict indications: in case of blockage of the ureters due to urolithiasis and infectious and inflammatory pathologies of the urinary system. Timely stenting can reduce the likelihood of complications in a pregnant woman, as well as the risk of intrauterine anomalies in the fetus. A kidney stent during pregnancy helps a woman carry a healthy baby and give birth on time. The catheter is removed after childbirth. Next, the young mother is prescribed drug therapy, which is often strictly contraindicated during pregnancy.
Features of stenting in pregnant women
The expectant mother may develop various diseases associated with the urinary system. Treatment with antibiotics and medications in such cases is not allowed. A stenting operation is needed, which will help get rid of some diseases and maintain the normal course of pregnancy. The stent itself will not interfere with the woman.
In preparation for surgery, all possible laboratory tests are prescribed, including a blood test for STDs. If inflammation is detected in the kidneys, a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed. Before the stenting operation, the pregnant woman will be selected the optimal option for using anesthesia.
Stenting scheme for pregnant women
During surgery, the girl is placed on her stomach, which is absolutely harmless to the fetus. Anesthesia is administered. Next, a cystoscope is inserted into the body, which will show the opening of the ureter. Next, the stent itself is installed, and the cystoscope is removed from the body.
The entire intervention process is controlled using a monitor. After the operation, a picture is taken that shows how the tube was positioned in the body. If everything is fine, the operation ends. It rarely lasts more than 30 minutes.
The first few days after the operation, the girl should be under the supervision of a doctor.
Advantages and disadvantages
The stenting procedure has many advantages: it allows you to normalize urination, while it is minimally invasive and does not last long. Kidney stenting helps normalize diuresis and avoid many negative consequences of impaired urine outflow.
Along with the advantages, installing a catheter also has disadvantages. During the first two days after surgery, the patient may experience discomfort and burning when urinating. The patient may be tormented by a constant feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. In the first two days, a slight presence of blood in the urine is normal. All these unpleasant symptoms should go away within 48 hours after insertion of the catheter. If this does not happen, such symptoms are a reason for an urgent visit to the doctor.
The appearance of pain, blood in the urine, and discomfort most often results from improper stenting, poor-quality materials and insufficient preoperative examination.
Urinary catheter
Possible complications
Each body reacts differently to the appearance of a foreign object in the tissues. After stenting, the following complications may occur:
- sensations of pain or burning;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- elevated temperature
- dysuretic symptoms (frequent urge to urinate);
- swelling of the bladder mucosa or ducts.
As a rule, patients have lower back pain, but after some time the above symptoms disappear. However, there are more serious consequences when monitoring the patient's condition is necessary, and in some cases it may be necessary to remove the stent from the ureter. Such cases include:
- development of the infectious process;
- improper installation of drainage;
- displacement of the structure;
- narrowing of the lumen due to swelling or spasm;
- closure of the lumen due to the deposition of salts on the walls of the stent;
- rupture of the ureter during installation of a drainage system;
- Vesicoureteral reflux.
The stent is also removed if there is an increase in the amount of blood in the urine, allergic reactions to the implanted structure, or a critical increase in body temperature for a long time.
Renal and ureteral stenting is a surgical procedure that can have unpleasant consequences.
The most common patient complaints are:
- discomfort during urination (pain, burning);
- frequent false urge to defecate;
- blood impurities in the urine;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- pain in the groin, lower back, stomach.
After installing a stent in the ureter, complications may occur:
- development of inflammation. Inflammatory diseases appear as a result of insufficiently professionally performed surgical intervention, the body’s failure to accept the materials from which the stent is made, and infection. Manifested by the following symptoms: fever, changes in the composition of urine, pain when urinating. Treatment includes taking antibiotics;
- violations of stenting technology. Incorrect installation of the end of the tube or too hard stent material leads to the formation of hematomas and ruptures. Signs of incorrect surgery include pain and blood in the urine. Removal of the ureteral stent is required;
- design migration. If the procedure uses a tube without a curl at the end, which is inserted into the kidney, then there is a possibility of displacement. It is necessary to remove the stent from the ureter;
- tube destruction. The material may lose its integrity under the influence of urine. The development of complications is excluded by replacing the product; the old one must be removed;
- inlay (hammering). The tube is filled with salts, which prevent the free passage of urine. Occurs with prolonged wear. Patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids;
- ureteral erosion, fistula. Rare phenomena that occur during frequent surgical interventions.
Possible complications of stenting include deterioration in health.
Possible complications of stenting include the following:
- Vesicoureteral reflux is the backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureter and kidneys. Symptoms of this condition:
- heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen;
- dark cloudy urine;
- pain during urination, which radiates to the lower back;
- swelling;
- weakness;
- deterioration in general health;
- increase in body temperature.
- If an infectious-inflammatory process begins at the site of surgery, it is manifested by the following symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- cloudy dark urine mixed with pus and blood;
- pain in the process of urination.
- If the stent was installed incorrectly or is made of poor quality material, then swelling develops at the site of its installation, an inflammatory process begins, which is accompanied by a bacterial infection.
- Another complication may be rupture of the ureter. In this case, the patient feels a sharp pain, and there is blood in the urine.
- If the stent is poorly secured, it may move along the urinary tract.
- The stent may become clogged with urine particles that may collect on the inside of the tube.
- The tube material may be damaged by the aggressive environment of urine.
- Due to surgery, inflammation of the urinary canal may develop.
When the root cause of the disease (stones, tumor or inflammation) has been eliminated and the organ is ready to fully perform its functions, the stent can be removed. It is removed under local anesthesia. To do this, a cytoscope treated with a special gel is inserted into the urethra. When the cytoscope reaches the stent, it grabs it and brings it out.
Vesicoureteral reflux
Poor-quality production and an incorrectly installed renal stent provokes the backflow of urine from the lower urinary organs to the upper ones, and vesicoureteral reflux develops. This complication is accompanied by pain in the pelvic area and lower back, which intensifies during diuresis. The patient may complain of a feeling of heaviness and incomplete emptying of the bladder. The quality of urine deteriorates - sediment forms and blood appears. Urine reflux may be accompanied by a deterioration in the patient’s general condition.
Features of the procedure
Stenting is a manipulation that helps prevent complications in the course of diseases. It is prescribed not only to pregnant women, but also to children. Stenting is minimally invasive and does not require incisions in the skin. Patients tolerate the procedure easily; anesthesia is not required. When the stent is inserted, there is a feeling as if something cold or sour has come into contact with the diseased tooth. This sensation is localized not in the oral cavity, but in the kidney area.
The length of the stent (tube) varies between 12-30 cm, the curl at one end allows you to securely fix the device for the entire period of its stay in the body. The exact period for which the stent is installed is determined by the doctor.
The tubes are made of silicone, metal, polyurethane. The choice of material is based on the state of health, the presence of pathologies, and the duration of installation of the device.
The stent takes the desired shape, especially for silicone - it is not affected by aggressive environments, it is built into the body. For long-term treatment, metal tubes are installed - they are compressed, but expand in the body. The epithelium fixes such a stent in place. The stent is installed using a cystoscope - a device that is inserted into the urethra.
Inflammation
Poor quality materials during surgery and insufficient hygiene of instruments lead to the development of infection in the ureteral cavity. It causes swelling of the tissues of the urinary organs, which leads to impaired urine flow, accompanied by pain in the pelvic area and signs of general intoxication of the body. The properties of urine change: a cloudy sediment and blood appear. During laboratory tests, an increase in leukocytes and protein is noted.
Features of walling
Not everyone knows what kidney stenting is, how it is carried out and for what purpose, which is why the issue should be approached responsibly and as carefully as possible. Kidneys are a very important organ in the human body, it performs the function of purifying the blood from unnecessary substances that have entered the body, for example, toxins, harmful components, breakdown products from certain proteins, etc. At the same time, the kidneys are very sensitive to any changes , both the surrounding and internal environment. During pregnancy, all systems work at an increased rate, which cannot but affect the state of the excretory and other systems.
Ureteral stenting is necessary to stabilize the functioning of the kidneys, as well as correct the normal excretion of urine. This device is used in the fight against various ailments of the excretory system, including malignant formations. The procedure is also performed on pregnant women, subject to recommendations from the attending physician. The wall is a tube of a characteristic shape; it performs the only function - it prevents narrowing of the ureter.
The device is inserted directly into the area of possible complications, although it is often placed throughout the ureter. Kidney stenting is carried out using a special device, and due to the installation of a zigzag, it is fixed at the ends, which makes the stent completely immobilized. The installation procedure is absolutely safe for humans; it does not cause pain, since painkillers are used. After this manipulation, the person immediately returns to normal activities; the tube can remain in the body for 6 months. To avoid complications and unpleasant consequences, you should regularly maintain the device and be examined by a doctor so that he can promptly detect deviations from the norm or any changes in the body.
A kidney stent may be prescribed for a variety of reasons, most notably the following:
- The presence of hard formations in the kidney, such as stones or sand.
- Complications of various kinds after surgery.
- Development of malignant neoplasms.
- Pregnancy.
- Various hematomas.
The diameter and length of the device are selected by a specialist based on the results of diagnostic studies, as well as after a detailed study of the general clinical picture of the disease.
Stent removal
Several weeks or months after the stent is inserted into the kidney, it must be removed. Removal occurs only after achieving the set goals, when the need for a catheter is no longer necessary.
The catheter is removed by a surgeon using general or local anesthesia. The procedure for removing a stent is carried out using a cystoscope, which makes it possible to determine its location and reduce the likelihood of injury to the mucous tissues of internal organs. For painless removal, the urethra is lubricated with a special gel and removed.
Stenting is a procedure necessary to normalize diuresis, which is indicated for narrowing or blockage of the lumen of the ureter. Insertion of a catheter is necessary before certain types of surgery. It is installed through the lower or upper urinary organs, as well as into the renal artery. The wall is installed for several weeks. If installed incorrectly, it can lead to some unpleasant consequences.
Operation process
The stent is installed under local anesthesia. The entire procedure takes from 15 to 30 minutes. When performing surgery on children, general anesthesia is used. On the eve of stenting, the patient is recommended to undergo all laboratory and instrumental examinations. All manipulations are controlled using an X-ray scanner. Stages of renal artery stenting:
- Before installing the structure, contrast angiography is performed to examine the patient’s vessels.
- A thin elastic probe is inserted into the femoral artery. The procedure is performed through a small incision in the groin. Using a scanner, the movement of the probe to the renal artery along the aorta is monitored.
- A balloon is attached to the edge of the probe, on which a compressed stent is placed. When it hits a problem area, the balloon is inflated, thereby expanding the artery and straightening the structure.
- After which the balloon is deflated and removed, the straightened stent remains in the artery.
- A contrast agent is injected into the blood. X-rays are used to examine the patency of the structure.
Stages of urinary tract stenting:
- For pain relief, an anesthetic drug (lidocaine, novacaine) is injected into the urethra.
- The internal organs are examined and the ureteral orifice is searched using a cystoscope.
- A catheter is inserted through the urethra.
- Using a cystoscope, a stent is placed into the lumen of the duct and secured.
- After installation of the structure, the bladder is emptied and the cytoscope is removed.
- After 24 hours, the installation and position of the stent are monitored using x-rays.
Removal is performed using a cystoscope without anesthesia; it may be accompanied by mild pain in the kidneys.
Stent during pregnancy
This procedure is especially relevant during the period of bearing a baby, when there is a threat to the life of the child or mother. The functioning of the kidneys and urinary system during pregnancy can malfunction, as it is under great stress. Many of the treatment procedures are contraindicated. Stenting is safe, allows you to delay necessary surgical interventions and reduce the progression of the disease.
The installation procedure is carried out lying on your back, it is safe for the child. A stent is not a contraindication to natural childbirth. After the baby is born, the structure is removed after a couple of weeks.
A special feature of the installation of the structure is enhanced control after the procedure. A timely installed stent allows you to maintain the health of the mother, fetus and safely carry the child to term.
Pros and cons of the operation
The main advantage of surgical intervention is that during stenting there is no need to make large incisions and damage tissue. The operation is performed using a minimally invasive method, which consists of the doctor making an incision directly where the stent will be installed. Another advantage is the short rehabilitation period and rare complications after surgery. If everything is done correctly during the procedure, patients do not complain about postoperative consequences; they will only need to take the medications prescribed by the specialist for the first few months.
However, renal stenting also has disadvantages. Sometimes restenosis occurs, which is a repeated narrowing of the ureter where the stent was installed. To avoid this, they resort to using a special tube, which is lubricated with a mixture of medications. In this case, the likelihood of narrowing the urinary duct is greatly reduced.
Benefits of kidney stenting
Before agreeing to undergo the procedure, many patients wonder why it is needed at all and what kidney stenting does. Unlike bypass surgery and open surgery, this procedure is minimally invasive. At the site where the catheter is inserted, the doctor makes only a small puncture.
The specialist will administer local anesthesia, so during the procedure the patient will be able to speak and tell the specialist what his or her health status is. Usually, after just a couple of days, the patient is discharged from the hospital, and he can soon return to his usual rhythm of life.
Stent placement usually does not cause any complications. In the first few months after the tube is placed, there is a high risk of blood clots forming around it. To prevent this phenomenon, patients are prescribed thinning drugs, in particular aspirin. The most serious complication, which occurs in twenty percent of cases, is restenosis. As a rule, it occurs when a drug-eluting stent is placed.
Method of performing stenting of the renal artery
Before the intervention, the patient must undergo general and special examination methods. Prescribe a CBC, OAM, LBC, coagulogram, ECG, chest x-ray, examination by a therapist and specialized specialists in the presence of concomitant pathology.
Of the special methods, the most important and informative is contrast angiography. It is a method of visualizing a vessel on an X-ray machine after injecting a contrast agent into a vein. Helps clarify the level and degree of narrowing of the renal arteries. If, during examination, inflammation of the walls of the renal vessels is detected in the patient, a course of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory treatment is first prescribed, after which stenting is performed.
In the absence of the contraindications noted above, the stent is installed immediately during contrast imaging. The minimally invasive intervention is performed by a vascular surgeon under X-ray control in an operating room. A small incision is made in the skin of the groin area in the projection of the femoral artery. A conductor with a vascular probe is inserted into it. At the end of the elastic probe there is a deflated balloon
Having passed into the aorta, the doctor finds the renal artery on the screen. At the point of greatest narrowing, the probe stops, and air is pumped into the cavity. The balloon inflates and expands the lumen of the vessel in which the stent is placed. The air is pumped out, the probe with the deflated balloon is removed. The introduction of contrast helps to ensure correct placement of the tube and its patency.
The patient can get out of bed on the first day after surgery. Physical activity is contraindicated in the immediate future after installation.
The service life of the stent is individual in each specific case. Its replacement is carried out in case of blockage, migration or development of inflammation at the site of contact with the vascular wall.