Detection of leukocytes in urine is a common event in laboratory practice. It is difficult to choose the only normal habitat for these cells. They perform a very serious task in the body. Spreading through the blood vessels, leukocytes “patrol” the entire human body. They are the first to encounter foreign substances (agents, allergens, microorganisms), disseminate information and cause a response.
Leukocytosis in the blood shows the severity of protective properties (immune strength). A decrease in the number of protective cells is considered a poor prognostic sign. The presence of leukocytes in urine is normally allowed only in limited quantities, in the form of single cells.
Their ability to penetrate tissue and organize a local reaction is known to doctors. But, to judge the nature of the accumulation of leukocyte cells in the urine, to determine what this means for a particular person, one has to take into account another diagnostic value - they are always messengers of inflammation.
Causes of increased levels of leukocytes in the blood
Normally, the human body should have 4-9 billion (from 4 E10 to 9 E10) leukocytes in 1 liter of blood. An increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood, or leukocytosis, can be either physiological, that is, occurring in completely healthy people in some situations, or pathological, when its cause lies in some disease.
Physiological leukocytosis is observed:
- after intense psycho-emotional or physical stress;
- after eating, and the number of leukocytes in this case does not exceed 10-12 billion per liter of blood.
- after a long stay in cold water or taking hot baths;
- in women a few days before the onset of menstruation;
- during the second half of pregnancy.
- inflammatory diseases such as appendicitis, pleurisy, pancreatitis, pneumonia, meningitis, otitis media, arthritis, etc.;
- 3-4 degree burns;
- heart attacks;
- excessive blood loss, kidney problems, leukemia and uremia.
Tests that determine the level of leukocytes
There are several ways to detect leukocyturia (increased levels of leukocytes in the urine.
General analysis
Helps identify various diseases in the early stages, including hidden inflammatory processes. The level of leukocytes is examined in urinary sediment from a portion of urine collected in the morning on an empty stomach. The study is prescribed during regular medical examinations for patients infected with staphylococcus, as well as for suspected diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary canals.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
It is prescribed after a general blood test if there were a lot of leukocytes in it. The number of leukocytes is counted in 1 ml of liquid. Only the average portion of urine taken in the morning on an empty stomach is taken for examination. Allows you to identify latent diseases of the urinary system.
Research on Amburge
Detects inflammatory kidney diseases and chronic urinary tract infections. The number of leukocytes deposited in 1 minute is counted. To take urine for analysis, you must completely empty your bladder in the morning on an empty stomach.
Exactly 3 hours later the biomaterial is collected. The average portion of the excreted liquid is subject to study. In the interval between the first and second urination, it is permissible to eat and drink.
Rofe method
Urine is collected according to the same scheme as in the Amburger study, only the leukocytes that have settled in 1 hour are subject to counting.
Stansfield-Webb method
This study is carried out without the use of a centrifuge. Urine should be collected for 24 hours in a large container. For analysis, 1 mm3 of liquid is taken.
Addis-Kakovsky test
You need to collect urine for 24 hours. To prevent the material from deteriorating, it is necessary to store it in the refrigerator. The volume of urine excreted in 12 minutes is analyzed. Using a special formula, the number of white blood cells in the sediment is calculated.
Pyrogen test
Helps identify hidden leukocyturia. The patient is injected into a vein with the drug Pyrexal. It provokes the release of leukocytes from the inflamed area into the urine. Then urine is collected for analysis within 3 hours. A day later, another control portion of urine is taken.
Prednisolone test
After the first urination, prednisolone is administered intravenously. It works the same way as Pyrexal. Biological fluid is collected after 3 hours and after 24 hours.
Two-glass sample
The material is collected in two different containers at the beginning of urination and at the end. They don't take the middle portion. White blood cells in the first glass indicate infection of the prostate or urinary tract. The presence of white blood cells in the second container means that the infection is in the bladder, kidneys and ureters.
Three-glass sample
Urine is collected in three containers. The middle portion should be larger than the rest. A high concentration of white bodies in the first glass indicates a disease of the urethra. If they are found in the last two containers, the bladder is inflamed. The presence of white bodies in all samples indicates infection of the kidneys.
Rules for submitting urine for analysis
In order for the research result to be correct, the following rules must be adhered to.
- Material for research is always collected in the morning, since in the evening the number of leukocytes in the body increases.
- Before collecting material, you should not eat or drink for about 10 hours.
- 24 hours before the procedure you need to stop taking medications, alcohol, and spicy foods. These foods can affect the chemical composition of your urine.
- The day before, you should not eat food that can color your urine or diuretics.
- Urine for analysis is taken no earlier than a week after cystoscopy or retrograde urography.
- You should refrain from significant physical activity for a couple of days before the test.
- The liquid container must be sterile and dry.
- Before collecting material, you must thoroughly wash your genitals without using soap or other hygiene products. Dirt and detergent particles may interfere with test results.
- Women should insert a tampon before urinating.
- When collecting liquid, the container should not touch the genitals.
- After taking material for research, it is necessary to deliver it to the hospital as quickly as possible. The analysis must be completed within two hours. If you linger, bacteria will actively multiply in the urine.
- During transportation, the container with urine should not be shaken vigorously, exposed to direct sunlight or hypothermia, otherwise the material may deteriorate. The optimal temperature is from + 5 C to + 20 C.
- You cannot take a urine test for the presence of leukocytes during sexually transmitted infections. White blood cells will enter the urine from the genitals.
- Urine tests are not performed on women during their periods. Menstrual blood can get into the material, which may lead to thoughts of bleeding in the urinary system.
Folk remedies for lowering the level of leukocytes in the blood
As mentioned above, an increased level of leukocytes in the blood can be a consequence of serious diseases, so if problems with leukocytes arise, you should immediately consult a hematologist. However, if the cause of leukocytosis is ARVI, influenza and other similar diseases, then it is possible to lower leukocytes in the blood using folk remedies using a decoction of linden blossom, which is brewed at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. linden blossom to 1 cup of boiling water, put on fire and boil for 10 minutes. Then the broth is filtered and drunk 2-3 glasses instead of tea.
Symptoms
A urine test is done as prescribed by a doctor or during a medical examination.
You can take it yourself if the following symptoms occur:
- strong smell of urine;
- painful and unpleasant sensations when urinating;
- frequent discharge;
- temperature increase;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- general weakness;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- spasms below alive
- bloody discharge from the urethra;
- cloudiness;
- color change.
Reasons for changes in the level of leukocytes in urine
Normally, a urine test for women should show 0-6 leukocytes, and 0-3 for men. If, as a result of a urine test for leukocytes, deviations from the norm were recorded, this means that some inflammatory processes are occurring in the body. In this case, two situations are possible: leukocyturia - an increase in the level of leukocytes in the urine, which requires taking immediate measures to reduce leukocytes, and leukopenia, when the opposite picture is observed. Leukocyturia usually indicates that the patient has diseases of the urinary system such as pyelonephritis, cystitis or urethritis. In addition, if we are talking about men, an increased level of leukocytes in the urine can signal problems with the prostate gland. At the same time, such a result of a urine test for leukocytes is a reason to suspect that the patient has kidney damage due to amyloidosis, tuberculosis or glomerulonephritis. As for leukopenia, this is a sign of infectious, often chronic diseases, and can also be a consequence of prolonged stress.
Which doctor should I contact?
To determine the number of leukocytes in urine, you should contact a physician who will issue a referral for testing. If a woman is pregnant, then the first doctor to whom you need to make an appointment is an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Further, therapy directly depends on the cause of this condition - in case of kidney problems, therapy is continued by a nephrologist, in case of bladder diseases, treatment is carried out by a urologist, and inflammatory processes in the genital organs are treated by a gynecologist.
If, after taking the tests, an excess of leukocyte counts was revealed, then this may mean the presence of any pathology of the genitourinary tract associated with such manifestations as:
- infections;
- inflammatory processes;
- cystitis.
The most dangerous thing that exceeding the indicators can mean is cancer.
You should not worry when identifying high indicators, because they can reflect not only pathological changes in the human body. For example, the reasons for a high level of leukocytes in the urine may be the following factors:
- change in external temperature;
- change of diet;
- Increased physical activity and pregnancy can also lead to temporary changes in tests.
Repeated clinical examination of urine makes it possible to refute or confirm the diagnosis.
Detection of leukocytosis is possible through laboratory tests and personal observations of one’s health. Signs of this type of pathology may include the following:
Recommended topic:
Heat
- increased body temperature;
- prostration;
- lethargy and constant feeling of fatigue;
- pain in muscles, joints;
- pain in the throat, ears, and changes associated with deterioration in the functions of these organs, which should lead to consultation with a doctor.
Only regular detection of an increase in the level of leukocytes requires additional examination and consultation with other specialists. The most undesirable diagnosis comes from an oncologist, because it is leukocytes that can recognize the appearance of tumors in various parts of the body.
The individuality of the female body allows us to determine laboratory parameters using a smear. This study finds fungus, colpitis, urethritis, imbalance in the environment of the genital organ, and various sexually transmitted infections.
Ways to reduce the level of leukocytes in urine
After patients are told that urine tests indicate that he has leukocyturia, the first thing they are usually interested in is how to lower the leukocytes in the urine. However, it should be understood that this will only be possible if the underlying disease is cured. Antibiotics are most often used to combat infections that cause an increase in the number of white blood cells in the urine. The exception is cystitis. In this case, it is possible to reduce leukocytes in the urine using folk remedies, without the use of medications. For example, it is recommended to increase the amount of fluid consumed during the day and take warm medicinal baths with a decoction of eucalyptus and chamomile, taken in a 1:1 ratio.
How are leukocytes counted?
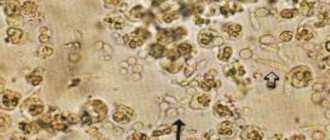
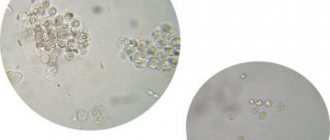
The most common way to determine leukocytes in urine is sediment microscopy. The liquid taken for analysis is poured into a test tube and centrifuged. Then one drop is placed under a special cover glass in Goryaev’s camera and examined at sufficient magnification.
The camera allows you to divide the field of view into equal squares; you need to count the cells in three of them
Laboratory technicians use small hand-held adding machines, look through a microscope, and press one with their finger.
When interpreting the analysis, medical professionals use terms that indicate how much the cells being studied cover the field of observation. The sharply increased number is indicated by such conclusions as:
- “leukocytes entirely”;
- "take up the entire field of view."
If the number of cells is insignificant, then their number is given or in the conclusion they are called “single”.
In the Nechiporenko analysis, the calculation is carried out using a similar method, but for a volume of 1 ml.
Additional laboratory research methods include:
- Kakovsky-Addis test - material for analysis is taken from the daily volume of urine;
- Amburge - calculation is made for allocation in one minute.
The color stripe method allows you to quickly identify leukocyturia. It is based on the activity of the enzyme esterase of granulocyte cells. It is quite suitable for mass medical examinations. However, it does not give an exact quantity and must be confirmed by microscopic examination.
The most acceptable and modern way is to use an analyzer, which, being an automatic machine, allows you to more accurately evaluate the result.
Why might the number of leukocytes in a smear be increased?
At each visit to the gynecologist, women have a smear taken for flora, which is examined, including the level of leukocytes. It is believed that normally, in a healthy woman, 15-20 leukocytes can be detected in the field of view of a microscope. If this amount is exceeded, then it can be argued that an inflammatory process is occurring in the genital area, which is caused by infections transmitted during sexual intercourse, as well as vaginitis or colpitis. In this case, there is usually a need for additional immunological, bacteriological and other studies, the results of which often indicate that the identified infections were present in the body for quite a long time and made themselves felt when immunity decreased for one reason or another. Such phenomena are especially often observed in pregnant women - hormonal changes in the body and changes in the immune system cause the activation of various kinds of pathogenic processes.
Leukocyturia in pregnant women
An increase in the level of leukocytes in a woman’s urine during pregnancy is considered acceptable if the number of white cells does not exceed 10 in the field of view.
Physiological (natural) leukocyturia occurs as a result of an increase in the total blood volume of a pregnant woman.
Since a woman’s body during pregnancy must nourish not only itself, but also the growing fetus, a new circle of blood circulation is created that connects mother and child through the placenta.
Despite the fact that all blood cells - both white and red - are produced in greater quantities than before conception, their growth is disproportionate to each other.
For example, the number of white blood cells increases by about 40 percent, while red blood cells increase by only 12 to 15 percent.
This process is considered normal if the main indicators remain normal. The high level of leukocytes in a woman’s body during pregnancy is explained by the fact that the fetus does not have its own immunity, so it is protected from harmful elements by the mother’s white cells.
Leukocytes accumulate mainly in the uterine lining to protect the fetus from possible attacks by foreign agents.
After birth, the child’s body quickly loses the mother’s white blood cells and produces its own - this process takes a short period of time.
If a pregnant woman has been diagnosed with pathological leukocyturia, it can be transmitted to the child, so it is important to carry out appropriate treatment in a timely manner.
In addition, an increase in white blood cells is also associated with preparation for childbirth. Giving birth to a child is a complex process that makes a woman vulnerable to infection for a certain period of time.
Therefore, a large number of leukocytes in a woman’s body prevents possible diseases.
Leukocytes are also responsible for the speed of blood flow - if necessary, they make the blood more viscous. This ability of white cells protects the mother in labor from heavy blood loss during childbirth.
Video:
Pathological leukocyturia is recognized when there are 11 leukocytes or more in the urine of a pregnant woman.
In such cases, doctors urgently prescribe a full examination of the expectant mother to identify the exact cause of the pathology. Sometimes the best solution for mother and child is hospitalization and inpatient therapy.
How to lower white blood cells in a smear?
If the situation is not critical and you can get by with folk remedies, then in order to lower the leukocytes in the vaginal smear, you can recommend resorting to twice-daily douching with a warm decoction of chamomile (2 tablespoons of raw material per 1/2 liter of water). You can also take warm sitz baths from time to time with a decoction of oak bark, St. John's wort, chamomile, nettle and red root. To do this, all these ingredients are mixed in equal proportions and brewed in an opaque container (4 tablespoons of dry collection in 3 liters of boiling water). It should be remembered that the bath water should be within 40-45 degrees so as not to cause burns to the genitals and skin.
10 minutes Author: Lyubov Dobretsova 3296
Urine is no less informative biomaterial than blood, and at the same time, thanks to the study of the fluid secreted by the kidneys, it is possible to more specifically determine the location of the pathology.
Since urine is formed and passes through the urinary system, its composition in most cases indicates the presence of diseases of these organs. Inflammatory processes of the urinary system are one of the main groups of diseases that are typical for patients of different genders and ages.
What other tests can you take?
The Nechiporenko test is prescribed to a patient with leukocyturia to confirm the presence of pathology. This research method does not replace, but complements a general urinalysis (UCA). The Nechiporenko test helps to identify a hidden inflammatory process in the renal pelvis and renal filters, hypertension, prostatitis and other pathological conditions.
According to Zimnitsky, urine is collected all day long. Biomaterial sampling is ideally done every 3 hours. The study is carried out if renal failure is suspected. Helps assess the functional state of the kidneys - their ability to concentrate and dilute urine.
Why do leukocytes increase in urine?
It is no longer a secret to anyone that white blood cells or leukocytes are the cells responsible for the body’s protective function. Therefore, when foreign objects (pathogenic microorganisms or toxic substances) enter the human body, they rush to the site of introduction of pathogens and absorb them.
Consumption and digestion, leading to neutralization of the activity of harmful agents, is called phagocytosis. After absorbing foreign objects, most leukocytes die, forming pus-like accumulations.
In the area of the latter, under the influence of released enzymes, blood circulation and functional activity of cells change, which in turn leads to swelling, fever and other signs of the inflammatory process. Due to the rapid death of leukocytes due to phagocytosis, the synthesizing organs begin to intensively produce them, which is manifested in analyzes by an increase in the indicator.
If an increase in white cells in the blood can be the result of many diseases, the localization of which is sometimes quite difficult to detect, then an increase in leukocytes in the urine is a clear sign of pathologies of the urinary system. This confidence is explained by the fact that urine is formed and excreted in these organs, therefore, the infection in it appears precisely from them.
Norm for women
As soon as a girl reaches adulthood and does not cross the threshold of 50 years, her leukocyte counts in her urine should always be within the same limits
. The ideal value for the number of white cells in urine is 0, but this indicator occurs in only 1 patient out of 100.
In other cases, the presence of leukocytes up to 5 units in the field of view
. This figure is twice as high as in men, since in women white bodies constantly enter the urinary canal from the vagina, where they are found in large numbers.
Norms and deviations
Before discussing diseases that affect the organs of the urinary system, accompanied by a high content of leukocytes in the excreted fluid or leukocytosis, the features of the reference values should be studied in detail.
Firstly, normal indicators differ among people depending on gender and, secondly, among different age categories. In addition, there are several conditions in which the level of these cells may also increase. The following values are considered to be signs of health in adults: for men, 1-3 cells in the field of view of the microscope and for women – 5-7.
Ideally, no white blood cells should be detected in the sample at all. In newborns and pregnant women, normal levels are 8-10 units, which is due to minor deviations in the activity of their urinary system. And this is not regarded as a pathology.
Higher values already indicate varying degrees of infectious or inflammatory process, and the greater the deviation from the norm, the more serious and dangerous it is for the patient. So, for example, indicators of 20-25 U indicate minor inflammation, most often characteristic of infection of the lower urinary tract - urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) or cystitis (inflammation of the bladder).
When receiving microscopy results with leukocytes of 75-100 units, we can safely say that the infection has spread through the upper urinary tract. Diseases that can increase the content of white cells for such indicators are nephritis (inflammation of the kidney), pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis) and glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidney).
In the case where the analysis of the biomaterial showed that there are a lot of leukocytes in the smear and are described in the form with the word “entirely”, this means that it is not possible to count their number.
As a rule, their number exceeds 250-500 units in the field of view, which clearly indicates generalized inflammation of the urinary system. Often, such high rates are observed with kidney tuberculosis involving other organs of the urinary tract.
Features of pathogenesis
Physiological characteristics play an important role in women’s predisposition to various diseases, including during pregnancy. For example, a significant increase in the number of white blood cells occurs with pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys. This problem very often affects pregnant women due to the growing uterus, which puts pressure on the kidneys, as a result of which the body malfunctions and, as a result, leukocytes in the urine increase during pregnancy.
This pathological condition is characterized by focality of the lesion. Inflammation affects the interstitial tissue, then the renal tubules. If the disease is not treated, they will die. In the early stages of the disease, pathological processes affect blood vessels, which can cause arterial hypertension.
Pathological changes are of an increasing nature. This is explained by the long-term course of the disease, which, due to the onset of pregnancy, can clearly manifest itself. Pyelonephritis has dangerous consequences for a pregnant woman. The 1st trimester with pyelonephritis can often result in a miscarriage or defects in the development of the baby. In the third trimester, the disease causes gestosis - a particularly dangerous condition that poses a direct threat to the fetus. The prognosis will be favorable if the woman is prescribed correct and timely treatment.
With cystitis, women experience pain above the pubis, urination becomes painful and frequent, and there is itching and burning in the urethra. Inflammatory processes in this part of the body also lead to an increase in white blood cells in the urine. If the case is not complicated, drugs like Canephron are prescribed, which treat the disease without any side effects.
The number of leukocytes increases during pregnancy and with thrush. Candida fungus affects the vaginal mucosa, resulting in inflammatory processes. With thrush, white blood cells are a signal of danger for the child, since bacterial infections often develop against the background of this disease. As a result, intrauterine infection of the fetus may occur.
Causes of leukocyturia
There are many factors that can lead to an increase in the content of white blood platelets in the secreted fluid, and not all of them are caused by the development of the disease. Also, non-pathological reasons for which leukocytes in the urine are elevated have long been identified.
Physiological factors
The most common causes of non-pathological leukocytosis in urine are pregnancy, conditions before and after childbirth, and the newborn period in infants. During conception and further development of the embryo in the first trimester of pregnancy, white blood cells rush to the uterus to maximally protect the fetus from possible infections.
Considering that the uterus is located in close proximity to the urinary organs and leukocytes are able to penetrate their membrane, it becomes clear why they can be displayed in the analysis.
Moreover, due to pregnancy and in the absence of infection, the excess of the indicator in this case is insignificant, only a few units, and therefore should not cause concern to the attending physician and the woman herself.
Before and after childbirth, the content of white blood cells also often increases, which is associated with the body’s insurance for the upcoming event and the period after it, in order to protect it from possible infections.
If the indicator increases slightly, that is, up to 10-12 units, then there is no need to worry, whereas with values reaching 30-50 cells in the field of view, you should definitely check the kidneys. The same applies to newborn babies, whose urinary system is not yet fully formed and is capable of passing a little more leukocytes into urine.
Leukocyturia, or the presence of white blood cells in the urine, in a child is often temporary and goes away as soon as his organs begin to function at the proper level. However, the appearance of a large number of the described cells indicates the presence of pathology and requires immediate examination and treatment.
Pathological causes
The most common diseases of the urinary tract include infectious lesions of the lower and upper tracts, which can be either primary or secondary.
The first type includes independent diseases that develop as a result of direct entry of a pathogen into an organ, and the second includes diseases that arise, for example, as complications after a cold, sore throat, etc.
Lower urinary tract infections
This group includes urethritis and cystitis, which are not considered life-threatening diseases for the patient, but can still cause him a lot of suffering. Leukocytosis in the urine with them is generally moderate, however, if these pathologies for any reason are not completely cured, there is a high probability that the infection through the ureters will spread to the kidneys, and the course of the disease will worsen.
Upper urinary tract involvement
Nephritis, pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis are much more severe for the patient and require longer conservative treatment. Often he has to be hospitalized in a hospital in order to be able to regularly monitor his condition and carry out complex therapy.
Reasons for the increase
Since there is no limit for a low level of leukocytes in the urine (since their complete absence is ideal), problems in patients can only arise due to its increase. This phenomenon has even been given a separate name - leukocyturia.
Unfortunately, normally, an increase in leukocytes in the urine practically does not occur, so when it appears, you should be wary and be prepared to organize therapy for a specific pathology.
Leukocyturia can be caused by a considerable number of diseases occurring in the human body. However, the most common ones are the following:
- all forms of cystitis, glomerulonephritis, or
- carbuncle or similar ailments characterized by the appearance of pustular neoplasms in the kidneys
- tuberculosis of the urinary tract
- nephritis
- hydronephrosis of the kidneys
- urolithiasis disease
- reproductive system infections
- a whole range of sexually transmitted diseases
It is impossible to find out why leukocytes in urine are elevated on your own. To carry out such a procedure, it is necessary to submit, perform, carry out, examine a smear from the urethra, or give preference to intravenous urography.
Only a doctor should prescribe one or another type of diagnosis, since only he will be able to choose the most optimal examination option for a particular patient.
Symptoms and possible complications
In order to live long and without health problems, it is advisable for every person to systematically conduct examinations of the body in a clinic. A mandatory procedure for this is urine collection. Despite the universality of this practice, only a few adhere to it.
Many people prefer to go to the hospital only when unpleasant symptoms of a particular pathology appear. In the case of an increase in leukocytes in the urine, the signs of this phenomenon will be different and directly depend on what caused the pathology.
Most often, with leukocyturia, some of the symptoms presented below appear:
- strong and unpleasant odor of urine
- pain when urinating or increased frequency;
- slightly less often – fever, chills of the genital organs, inflammation in the reproductive system
If you notice such symptoms, you must immediately consult a doctor, explain the situation to him and carry out the necessary diagnostics. The latter will help organize the correct course of therapy and relieve the patient from the unpleasant signs of leukocyturia as soon as possible.
An increase in white blood cells should not be ignored, since the development of diseases that cause the pathology is not only dangerous to health, but also extremely unpleasant for the patient himself.
Treatment method
The treatment method for leukocyturia is determined by the attending physician based on the cause of the anomaly. As a rule, “excess” leukocytes in the urine are eliminated by eliminating the infection that caused this or that ailment of the genitourinary system.
In 70% of cases of leukocyturia, treatment is possible exclusively with medications. In most of them, the full course of pathology therapy does not exceed 3 weeks.
You can prescribe medication yourself only if you know exactly:
- what pathology provoked leukocyturia
- what is it caused by (bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc.)
- how severe is its course?
It is taking into account the factors presented above that the correct course of therapy is determined when it comes to drug treatment of leukocyturia. It is worth noting that this ailment is not one of those that can be cured in any way using traditional methods, so it is advisable to exclude such treatment methods in the first place.
It is worth understanding that in the presence of tumors in the kidneys that cause an anomaly, it is often necessary to resort to surgical methods of treatment. Depending on the etiology of the disease, operations of varying complexity may be prescribed. In any case, they are all aimed at getting rid of foreign formations in organs and returning them to normal functioning.
Leukocytes (or white blood cells) are a heterogeneous group of cells that differ in appearance and functions, the peculiarity of which is the presence of a nucleus and the absence of their own color.
Leukocytes carry out specific and nonspecific protection of the body from both external and internal pathogenic factors.
White blood cells come in several types. Regardless of the specific variety, they can actively move, penetrate through capillary walls into tissues, from which they absorb and digest particles of foreign origin. This process is called phagocytosis, and the cells that carry it out are called phagocytes.
If there are a large number of foreign bodies in the body, the size of phagocytes increases significantly, as a result of which they are destroyed, releasing special substances that lead to a local inflammatory reaction. These substances are able to attract new white blood cells to the site of inflammation. In the process of destroying foreign bodies and damaged cells, a large number of leukocytes die, which form an accumulation of pus in the body and are excreted from it in several ways - including with urine.
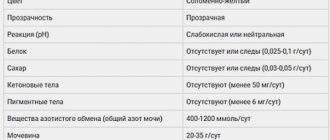
Normal and elevated levels of leukocytes in urine
The Nechiporenko method of urine analysis is also used, in which the normal value is the content of 4000 leukocytes per 1 ml.
In some pathological conditions, the upper threshold is exceeded. If it reaches 20, this condition is called leukocyturia.
An excessive increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine (more than 60), which is accompanied by the presence of purulent discharge, is evidence of the presence of pyuria - a pathological process of a purulent-inflammatory nature in a certain genitourinary organ. As a rule, a change in the composition of urine can be seen even with the naked eye: it loses transparency, becomes noticeably cloudy, and threads and flakes are visible in it.
- In newborns and older children, it ranges from 1 to 8 units in the field of view. As a rule, for boys the norm is less: up to 5 units.
- In many cases, the number of leukocytes in a completely healthy baby remains within 1-2 in the field of view.
- In newborns, leukocytes are detected in urine sediment after centrifugation. Recently, special analyzers have been used for this purpose.
Reasons for increasing the number of leukocytes in urine
Leukocyturia can develop as a result of:
- prostatitis;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- presence of stones in the ureter;
- glomerulonephritis;
- manifestations of GVHD (graft-versus-host disease) as a result of kidney transplantation.
Pyuria is mainly an indicator of certain pathological conditions:
- the presence of a focus of inflammation;
- allergic reaction;
- helminthic infestations;
- genitourinary infections;
- systemic connective tissue diseases.
Other causes of increased white blood cell count:
1. Pregnancy can cause an increase in the number of white blood cells. Often this condition develops against the background of an infectious process in the vagina. The rapid development of leukocyturia and the presence of accompanying symptoms should be especially alarming. In this case, it is necessary to conduct a diagnosis in order to exclude an inflammatory process in the bladder.
2. Kidney infections - as a rule, the pathological process begins in the urinary tract, bladder and then spreads to the kidneys. The likelihood of developing a pathological process increases significantly under two circumstances:
- weakened immunity;
- bladder catheterization.
Inflammatory kidney diseases can occur in acute or chronic form.
They are accompanied by the following characteristic symptoms:
- pain in the lumbar region (localized on one or both sides);
- change in urine color;
- temperature increase.
3. Urinary tract infections:
- urethritis;
- cystitis;
- prostatitis.
The characteristic symptoms are:
- pain in the suprapubic area;
- pain when urinating.
4. Sexually transmitted diseases cause an inflammatory process in the genitourinary organs, leading to an increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine.
5. Retention of urine in the bladder leads to weakening of its walls, the development of a pathogenic environment that provokes infectious diseases and subsequent leukocyturia.
6. Narrowing or blockage of the urinary ducts is also accompanied by an increase in the number of white blood cells. The reason for the narrowing, in turn, can be:
- stones in the urinary ducts or kidneys;
- tumors of the pelvic organs;
- prostate hypertrophy
- injuries.
7. Sometimes the level of leukocytes increases with tuberculous kidney disease or amyloidosis.
The most common causes of an increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine in children are infectious diseases and inflammatory processes. Most often, this symptom indicates the presence of the following pathologies:
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- inflammation of the external genitalia;
- inflammatory process in the kidneys;
- metabolic disorders;
- enterobiasis (one of the types of helminthiasis);
- allergies.
Rules for taking the analysis
Often, a high level of leukocytes in the urine is just a consequence of improper urine collection and further analysis. This is indicated by the absence of symptoms of any other diseases.
In women, leukocytes can enter the urine from the vagina, and in men, from the urethra (their high concentration is observed in these parts of the body even in absolute health).
When taking the analysis, the following rules must be observed:
- Before collecting urine, take a shower or perform thorough genital hygiene with soap.
- Women should close the vaginal opening with a sterile tampon, and then spread the labia with their fingers so that urine does not come into contact with them.
- Collect urine in the morning.
- Use a completely sterile container to collect the sample.
- Release the first portion into the toilet.
- Collect a middle portion of urine for analysis.
- these are white bodies that perform an important function - they protect the body from pathogens. They absorb and break down foreign cells. Production is carried out by the bone marrow and immune system. White blood cells are present in small quantities in the blood and urine, but a large number of them indicates an inflammatory focus in the body.
Determine the quantity by passing a general analysis and. Nechiporenko's test allows you to assess the content of formed elements in the average portion of urine. This laboratory test helps differentiate inflammatory diseases from non-inflammatory ones.
In addition, it can be performed to detect bacteria and their sensitivity to antibiotics. If the white blood cell count is high, leukocyturia is diagnosed.
Norm of leukocytes in urine:
- Normally, a woman’s white blood cell count should be within 5 units in the field of view.
- Men have no more than 3 units.
- The number in children is slightly higher and amounts to 8-10 units.
When diagnosing, a quantitative count of leukocytes is carried out and, taking this into account, three degrees of leukocyturia are distinguished:
- Mild degree. The number of white cells is slightly higher than normal.
- Moderate degree. Diagnosis is made when leukocytes are detected in the amount of 50-90 units.
- High degree. In this case, pyuria is diagnosed, the number of cells significantly exceeds the norm.
If the level is high, dynamic control of leukocytes is indicated, so tests are taken within 2-3 days.
What to do with leukocyturia?
Initially, it should be understood that leukocytosis in the urine is not an independent disease - it is a separate symptom that means the presence of problems in the body of varying degrees. Therefore, in order to reduce the content of white blood cells, it is necessary to find out the reason for their increase.
As a rule, detecting leukocyturia is quite simple if you conduct a general urine test, which will show all changes in the composition of the excreted fluid. Then, based on its data, the doctor will, in all likelihood, prescribe subsequent diagnostics aimed at determining the location of the pathological focus and the characteristics of the course of the disease.
After diagnosing pathologies of the urinary system, the therapist will send the patient for consultation and therapy to specialized specialists, such as a urologist, nephrologist, gynecologist, etc. If leukocyturia is detected, ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, kidneys, excretory urography, cystoscopy, x-ray of the bladder and other instrumental techniques can be performed.
How to take a urine test correctly?
To ensure that the data in the analyzes is not distorted, the following rules must be adhered to:
- For a general analysis, morning urine accumulated in the bladder overnight is taken.
- The genitals are carefully washed.
- The containers should not contain traces of cleaning agents (it is better to use disposable dishes).
- To avoid introducing bacteria from the external genitalia into a clean container, first release some urine into the toilet and then fill the bowl. It is advisable that the container does not come into contact with the skin.
- Prepared urine is stored for up to 2 hours in a cool place.
- Sterile urine bags are purchased for infants.
A couple of days before doing a general urine test, you will need to give up foods that change the color of urine, alcohol, vitamins, dietary supplements and diuretics. The doctor must be informed about the use of any medicine, since the drug contains substances that change test data. Do not visit the bathhouse or sauna, reduce physical activity. You cannot do tests during menstruation, fever or high blood pressure.
Methods for correcting indicators
Once the cause of the increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine has been established, appropriate treatment is prescribed. Under no circumstances should you take any action on your own, assuming that this will help reduce the number of white bodies.
No matter how absurd such a desire may sound, however, unfortunately, quite often people undergoing routine medical examinations in order to get “good” test results can, instead of treating diseases, look for various ways that will normalize this indicator.
There are no such ways! Rare cases in which the picture of a urine test can be corrected are if the sample of biomaterial was collected incorrectly and leukocytes from the mucous membrane of the genital organs got into it, or the increase was physiological and temporary. In the rest, a therapeutic course is required.
So, for simple and mild infections - cystitis and urethritis - anti-inflammatory drugs and a diet are prescribed, which involves avoiding salty, hot and spicy foods, which irritate the mucous membrane, aggravating the symptoms of the disease. In addition, the patient is recommended bed rest, and compliance with it will contribute to a speedy recovery.
In case of inflammatory processes in the kidneys, antibiotics are prescribed without fail. To treat infections that most often develop in the urinary tract, Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin and cephalosporin drugs are mainly used.
A diet prohibiting hot, salty and spicy foods is also prescribed. It is recommended that dishes be boiled, steamed, baked, that is, subjected to gentle processing, and under no circumstances fried or smoked. It is very important to maintain a drinking regime, and in the absence of renal failure, drink at least two liters of fluid per day.
Pathologies that require surgical intervention should be operated on as early as possible, as this will help reduce the likelihood of complications caused, for example, by urolithiasis or enlarged tumors. Failure to promptly seek medical help in these situations can cost the patient his life.
Mention should be made of traditional treatment methods. Of course, many herbs, such as bearberry and stinging nettle, are used in the treatment of urinary tract infections, but their role is secondary, that is, auxiliary. Placing all hopes on their healing power is extremely dangerous, especially in severe inflammatory processes.
Memo to patients. The first thing you need to do when you receive a test with elevated white blood cells is to repeat the test. If the results are identical, then be sure to contact a specialist for help. During the course of treatment, you must carefully follow all the recommendations of your doctor to avoid complications.
Almost every visit to the attending physician begins with a referral for tests, the delivery of which is necessary to determine the area of development of the disease and its complexity. A subsequent appointment with a doctor is based on the available test results and the indicators indicated in them, which sometimes exceed the norm, which indicates various diseases.
The most common tests are urine and blood, identifying the number of leukocytes. Each person has their own leukocyte norm, so for a woman they should not exceed 4 units, and for men – 1 unit. If these indicators are not normal, then treatment for leukocytes in the urine should be started.
Treatment
Drug therapy
Leukocyturia almost always requires therapy. Its goal is not only to lower the level of white blood cells, but also to remove infections and bacteria. The choice of medications and treatment tactics are determined by the diagnosis. Drug therapy includes the use of antispasmodics, analgesics, and anti-inflammatory drugs, which are prescribed by a doctor. For infectious leukocyturia, antibiotics are prescribed. If the increase in leukocytes is of an aseptic nature, then it would be more advisable to rest in bed and drink plenty of fluids, and irrigate or douche with aseptic preparations.
Treatment with traditional methods
Lingonberry decoction
There are also traditional medicine methods. To reduce the number of leukocytes in the urine, you need to drink a lot of mineral water and diuretics for a couple of days. A decoction of Lingonberry or Bearberry helps to reduce the number of leukocytes.
Corn silks should first be boiled, then poured with boiling water. Infusions from hop cones have proven themselves well in this matter. You can also drink a decoction of Stinging Nettle. Make salads with Nasturtium flowers and drink the juice from this plant. For kidney diseases, many doctors recommend eating berries and sea buckthorn juice - this is a natural storehouse of vitamins.
Diet
The diet for leukocyturia is based on reducing salt intake and reducing the amount of fluid you drink. In the initial stages, a fruit-sugar diet is prescribed for 2 days. Adults – 10-15 grams per dose, while the daily intake should not exceed 150-200 grams. Sugar intake is accompanied by drinking coffee, tea or natural juice. On the third day they switch to mixtures, cereals, vegetables, fruits and purees, jelly, crackers. In the chronic form, it is recommended to consume alkaline and acidic foods.
Elevated leukocytes in urine - treatment
It is impossible to determine on your own how to treat leukocytes; the doctor is dealing with this issue. Contacting your doctor with the available test results will allow you to give a superficial assessment of the patient’s condition; a more accurate picture of the disease is determined by a detailed study.
Most cases of detailed examination consist of a “3-glass analysis.” The unusual name represents taking a urine test in three containers. By examining urine samples from each glass, the number of leukocytes is determined.
By analyzing each sample, it is possible to identify urethritis or prostatitis by the dominance of leukocytes in one container. An increase in leukocytes in the last analysis determines cystitis. If the indicator increases in three tests, the doctor sends the patient for a detailed examination of the kidneys.
Drug treatment
Identifying the cause of the increase in leukocytes will make it possible to timely determine how to treat and prevent the development of the disease, as well as lead to a complete recovery of the patient. Studying the obtained tests and determining the infection will require the prescription of antibiotics. These drugs are prescribed depending on the characteristics of each individual organism, but a drug such as Furadonin is especially popular; it is recommended to use it 4 times a day. Also, when the number of leukocytes is high, Palin is often prescribed; you need to drink it 2 times a day (the drug is also prescribed during pregnancy).
The development of neoplasms in the body includes diagnosis and combined treatment of oncology with a combination of chemotherapy and leukopheresis, which allows removing excess leukocytes from the body, thereby cleansing it.
Leukocytosis also appears in blood tests.
This leukocytosis occurs:
- Physiological. It is observed in a child (newborn), a pregnant woman, and a healthy adult with changes in the emotional state. When changing your diet and general physical condition. Detection of this pathology is very difficult due to the occurrence of asymptomatic changes in the body. The treatment method takes place at home.
- Pathological. Signs: infection, inflammation, various neoplasms. Pathologies will require the use of medications prescribed by a doctor. Depending on what type of leukocyturia is detected, a specific drug is prescribed.
The attending doctor, depending on the disease, knows how to lower and how to reduce the level of leukocytes with a medicine suitable for the patient.
Diet
Drug therapy is prescribed by a medical specialist without fail, with the possibility of supplementing it with folk remedies. Some doctors recommend following a diet. Depending on the direction and form of the disease, it is recommended:
- reducing the number of meat dishes;
- exclusion of fatty foods;
- reducing calorie content in the general diet;
- increasing intake of seafood dishes;
- expanding the nutritious diet through legumes and dairy products, not forgetting to give preference to green crops;
- consumption of fruits and berries, which during the off-season can be replaced with a vitamin-mineral complex sold in the pharmacy chain;
- inclusion of cereals in the diet;
- consumption of juices and decoctions from the list of traditional medicine.
- Equal portions of knotweed, motherwort and field ivy herbs are carefully crushed and mixed together. A teaspoon of herbal powder is calculated per 200 ml of boiling water for infusion and intake before meals. It is allowed to add the same amount of dry mixture to one serving of the dish.
- Wormwood herb powder is infused in the following proportions: 3 teaspoons of herb per 500-600 ml of hot water. Preparing the infusion will not take more than 1 hour. The product is taken 15 drops before meals.
- Green beans, known to many, can normalize leukocyte counts in the shortest possible time; just take the juice from them and drink 1 teaspoon daily on an empty stomach.
- Melissa (200 grams) is diluted in 0.5 liters of water and consumed one tablespoon three times a day.
This diet allows you not only to reduce (bring to normal) indicators, but also to increase the level of leukocytes.
Treatment with folk remedies
Despite the prohibition of most doctors on the use of traditional medicine for various diseases, in the case of an increase in leukocytes, therapy with folk remedies is allowed. Of course, all personal intentions must be coordinated with the attending physician, because it is impossible to cure yourself. Coordination of the prescribed treatment with traditional medicine includes the following infusions:
Clinical picture
Increased white blood cells in the urine may be accompanied by a change in the color of the urine, which darkens and becomes cloudy. Loose mucus (squamous epithelium) is observed in the sediment. Often these symptoms let you know that there are a large number of white blood cells in the urine. The number of leukocytes in the urine after childbirth gradually decreases.
However, depending on the disease during pregnancy, white blood cells may be accompanied by some additional symptoms. For example, with cystitis, a woman is plagued by sharp pain when urinating and frequent trips to the toilet. With pyelonephritis, painful sensations in the kidneys are added to these symptoms, and the temperature may even rise. The clinical picture is complemented by the poor health of the pregnant woman. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as a change in urine color is noticed.
In complicated cases, red blood cells may increase in the urine along with leukocytes, which also confirm the ongoing pathological processes. The reasons for this are hidden in infectious diseases of the genitourinary system. Pyelonephritis, cystitis and other ailments can also lead to the appearance of protein in the urine, which should normally be absent. Additionally, the number of leukocytes in the blood during pregnancy also increases. What could be the consequences?
An increase in white blood cells can have serious consequences for the expectant mother and her baby if not treated promptly. Leukocyturia in early pregnancy, confirming kidney disease, indicates the need to take urgent therapeutic measures. Thanks to this, the woman will be able to carry the baby to term and give birth safely.
Dangers that may be hidden behind an increase in leukocytes in the urine:
- Gangrene of the bladder as a result of rapidly developing inflammation. A dangerous condition in which the integrity of the bladder is compromised and its contents enter the abdominal cavity.
- Chronic inflammation during pregnancy is fraught with painful attacks caused by the movement of stones in the kidneys and bladder. In such cases, even surgery may be prescribed.
- Late toxicosis (preeclampsia) at 38 weeks is fraught with various complications, including fetal death.
- Eclampsia is a convulsive syndrome that develops as a result of impaired blood flow in the placenta. At the same time, there is a high risk of having a child with pathology or miscarriage at any week of pregnancy.
An elevated white blood cell count is the first of many symptoms of these and other complications. Therefore, pregnant women should be attentive to their health and, at the slightest suspicion of unfavorable processes in the body, consult a doctor.
Prevention of pathology
Despite the pathological increase in indicators, you should not allow leukocytes in the urine to increase due to physiological changes. Among all the recommendations, special attention is paid to the state of the immune system. Preventing diseases and taking antiviral drugs will reduce the risk of increased white blood cells and strengthen the immune system.
Only the attending physician can answer how to completely get rid of the risks of increased leukocytes. It is he who will prescribe the patient a balanced diet, including a complex of vitamins and minerals that will allow the body to work without failures. In addition to a number of foods that need to be added to the diet, there are also elements that need to be avoided, such as alcohol, tobacco and the use of illicit drugs.
Prevention of chronic diseases, regular examination by medical specialists and compliance with their instructions, protecting yourself from viral patients, walking in the fresh air will help maintain normal leukocyte levels.
Causes
An increased number of bodies in the urine can be observed due to the following reasons:
- Infection in the genitals.
- Viral infections in the body.
- Oncology.
- Kidney pathologies.
- Lack of hygiene.
- Tuberculosis.
An increased number of leukocytes can be observed for several reasons.
Predisposing factors are:
- Vaginitis.
- Blood diseases.
- Reduced immunity.
- Stagnation in the urine.
- Venereal diseases.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the material in the laboratory, identifying the number and type of cells.