Category: Online analyzes
Features of decoding a general urine test in adults, children and pregnant women
A general urine test is a clinical test necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. In laboratory conditions, the physicochemical parameters of this biological fluid are determined, and the sediment is diagnosed separately.
Disturbances in the functioning of the body are primarily manifested in the composition of urine. By noticing deviations from the norm in time, you can avoid severe forms of disease.
Features of urine collection
Submitting urine for analysis requires virtually no effort on the part of the person. The liquid must be collected immediately after sleep in a washed jar. The genital area must be washed before the procedure to prevent bacteria from entering.
For the most accurate results, you should not drink alcohol or diuretics the day before the urine test. Fresh fruits and vegetables can unduly change the color of the liquid. The medical restriction is that cystoscopy should be performed no later than a week before the test.
Women during their menstrual cycle should not allow menstrual blood to enter their urine.
The laboratory accepts a fixed volume of urine, the approximate norm is 50 ml. The collected test must be delivered to the clinic no later than 2 hours after collection.
- If you can’t get urine out within this period of time, you need to put the jar in the refrigerator. The analysis result can be obtained within the next day.
Interpretation of general urine analysis in adults, norms
Each indicator in the urine test result card either corresponds to the norm or indicates a specific disease. For laboratory diagnostics, not only the composition of the liquid is important, but also the color, consistency, and smell.
Table: general urine test norm and interpretation of results in adults
Below the table, all the analysis indicators and possible diseases indicated by a deviation from the norm (increase/decrease) are described in detail.
| Index | Analysis result |
| Color | light yellow |
| Transparency | transparent |
| Density | 1010 – 1022 g/l |
| pH reaction | sour 4 - 7 |
| Smell | Unsharp |
| PRO (protein) | 0.033 g/l |
| GLU (glucose) | 0.8 mmol/l |
| KET (ketone bodies) | no (negative) |
| BIL (bilirubin) | No |
| URO (urobilinogen) | No |
| Hemoglobin | No |
| LEU (leukocytes) | 0 - 3 (m) \ 0 - 6 (w) |
| BLD (red blood cells) | (m) single \ (f) 2 - 3 |
| Epithelium | to 10 |
| Cylinders | No |
| Salts | No |
| NIT (nitrates and bacteria) | No |
| Fungus | No |
Let's look at each indicator separately.
Urine color
Decoding the urine test begins with assessing the color of the liquid. In adults, the norm is shades from light yellow to rich straw. Other color variations indicate disturbances in the functioning of organs. The deviations are as follows:
- Pale urine indicates excessive fluid intake, pancreatic dysfunction (diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus) and renal failure.
- The ocher color is classic dehydration from intoxication or heart failure.
- Brown urine is a liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis), destruction of red blood cells after certain infections, especially after malaria.
- A bright red tint indicates the presence of blood in the urine. May be caused by the presence of stones in the bladder, kidney infarction, pyelonephritis (acute course), urinary tract cancer.
- A faded red color indicates abundant consumption of “coloring fruits”: beets, carrots, grapes, black currants. Doesn't pose any danger.
- Red-brown urine is a consequence of taking sulfonamides.
- A grayish tint with a pronounced sediment - kidney stones, tuberculosis or kidney infarction, rapid destruction of red blood cells. The use of streptocide and pyramidon also gives this shade.
- Black color - Michelli's disease (hereditary form of anemia), melanoma.
The color of urine is affected by the food taken the day before it is taken. To find out the exact result, it is not advisable to eat colored fruits or take the above medications.
Transparency level
The urine should not become cloudy within 2 hours after collection. A slight presence of mucus and epithelial cells is acceptable. Loss of transparency is possible if the liquid contains:
- Leukocytes – cystitis, pyelonephritis;
- Red blood cells – prostatitis, urolithiasis, cancer;
- Protein cells – glomerulo- and pyelonephritis;
- Bacteria – bacterial cystitis, pyelonephritis;
- Excessive amount of epithelium – renal failure;
- The loss of chalk sediment is urolithiasis.
The clarity of urine is largely influenced by the health of the kidneys. In addition, cloudiness may appear if hygiene is not observed when taking the analysis. Therefore, if pathological abnormalities are detected, it is recommended to conduct a repeat study with another portion of urine.
Urine smell
The test taken may have a subtle odor. The appearance of a specific aroma indicates inflammatory and putrefactive processes in the urinary tract:
- The presence of acetone notes in the smell indicates diabetes;
- The similarity of the smell to feces indicates the presence of a fistula from the rectum;
- Ammonia is felt in the urine due to fermentation processes caused by cystitis;
- The rotten smell is caused by gangrene of the urinary tract.
Urine has a very unpleasant aroma if garlic or horseradish has been ingested.
Specific Gravity (SG)
The normal relative density of urine in an adult is from 1.005 to 1.028. The increased specific gravity is caused by a lack of fluid intake or its excessive waste by the body (vomiting, diarrhea, fever, excessive physical activity with increased sweating).
This process can be caused by diabetes mellitus and toxicosis during pregnancy. Decreased urine output is called oliguria.
A reading below normal is caused by kidney failure. Also, a high ratio can be justified by consuming a large volume of fluid or taking diuretics. A more accurate picture of the specific gravity will be shown by the Zimnitsky test - analysis within 24 hours - 8 portions are collected every 3 hours.
Urine pH (acidity level)
Acidity in the body changes throughout the day, which is why the test is taken on an empty stomach. During filtration, the kidneys remove hydrogen ions from the blood. The normal pH value of urine is 4-7.
If the PH value is above 7:
- Increased amount of potassium and parathyroid hormones in the blood;
- Lack of animal food;
- Metabolic, respiratory alkalosis;
- Urinary tract infection.
The acidity level increases when taking medications based on adrenaline and nicotinamide.
If the PH value is below 4:
- Decreased amount of potassium in the blood;
- Dehydration, fasting, fever;
- Diabetes;
- Abundant consumption of meat products.
The acidity level decreases when taking diacarb, aspirin, and methionine.
Protein in urine (PRO)
Normally, there should be no protein in the urine (PRO neg). Decoding neg – the absence of any component in the general analysis result card. Traces of protein are found after intense physical exertion or hypothermia.
- A stable positive PRO factor indicates chronic pyelonephritis and hypertension.
Glucose in general urine analysis (GLU)
The presence of sugar in the urine indicates problems with the pancreas. The patient is usually diagnosed with acute pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, or excessive presence of carbohydrates in the diet.
Ketone bodies (KET)
This indicator is disrupted in people who change their diet to lose weight. The positive effect of the diet is noticeable if ketones are present in the urine. This is due to the fact that the body synthesizes its own fat reserves.
- Medical causes: diabetes mellitus, acute pancreatitis, glycogen storage disease.
Bilirubin (BIL)
There is no bilirubin in a healthy adult body. Its presence indicates liver disease:
- Cirrhosis;
- Viral hepatitis;
- Cholestasis;
- Subhepatic jaundice.
Alcohol and other toxic substances consumed the day before have a similar effect on the analysis results. In chronic alcoholism, pathological changes are persistent.
Urobilinogen (URO)
The presence of urobilinogen indicates that bile enters the small intestine in excess. Characteristic diseases are constipation, jaundice and initial liver damage.
Hemoglobin in urine analysis
Normally, this indicator should be negative. If hemoglobin, which appears during the breakdown of red blood cells, enters the urine, then the patient has one of the following pathologies:
- Extensive heart attack;
- Malaria;
- Crash syndrome (muscle damage due to injury);
- Poisoning by sulfides or mushrooms;
- Bleeding in the urinary system.
Hemoglobin is present in small amounts in the urine normally after a blood transfusion.
Red blood cells (BLD)
The BLD transcript must have no more than 3 units of red blood cells in women and no more than 1 in men. If an accumulation of red blood cells is found in the urine, then there are serious problems with the kidneys:
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Nephrotic syndrome, kidney infarction;
- Urolithiasis disease.
Leukocytes (LEU)
LEU decoding allows up to 6 leukocytes in the urine in women and up to 3 in men. It is this indicator that is considered an indicator of the presence of diseases of the urinary system and kidneys. The diagnosis of leukocyturia can be absolutely anything; an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is necessary.
Epithelial cells
Epithelial cells should normally be present in the analysis in small quantities - up to 10. A larger number indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. In laboratory conditions, you can find out the epithelium of which organ is present. This will help in making a diagnosis.
Casts, salts, bacteria and parasites are normally practically absent in urine. These indicators do not always indicate the presence of urinary tract disease. Rather, we are talking about violations of the rules when collecting urine.
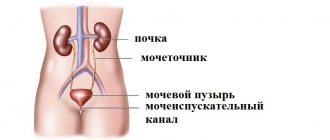
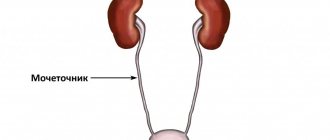
Mechanisms of urine formation and excretion
Urine contains water, certain electrolytes and end products of cellular metabolic processes, which enter the circulating blood and are excreted from the body by the kidneys. The mechanism of urine formation is regulated by nephrons, consisting of:
- from the glomerulus - a network of capillaries;
- Shumlyansky-Bowman capsule - a double-walled cup covering the glomerulus;
- tubule system - loop of Henle, proximal and distal segments, connecting canal and collecting duct.
The process of urine formation begins with the formation of glomerular ultrafiltrate (primary urine), which consists of the following:
- the blood entering the renal glomeruli undergoes filtration through a specific membrane of the nephrons and loses a significant part of the soluble beneficial elements, liquid and waste;
- Primary urine, which includes water, glucose, excess salts, amino acids, urea, low molecular weight compounds and creatinine, enters the renal capsules and tubules.
The second component of the mechanism of urine formation is the process of reabsorption - the movement of useful substances back into the circulating blood through the peritubular vessels. The complex process of secondary urine formation begins in the proximal segment of the tubular system and continues in the loop of Henle, the distal segment and the collecting ducts.
In the body of a healthy person, none of the vital elements are excreted in urine - they are completely returned to the blood.
The third process of urine formation is the formation of tubular secretion (secondary urine), in which ammonia, drug residues, potassium and hydrogen ions are secreted into the primary urine. This mechanism is very important for maintaining acid-base balance in the human body. The functional activity of the kidneys is regulated by the nervous system and humoral factors - hormones and protein breakdown products.
The release of urine is a reflex process - from the renal pelvis the substance enters the ureter, bladder and is released through the urethra
Features of a general urine test in pregnant women
Expectant mothers need to regularly undergo a general urine test. Decoding for pregnant women corresponds to the classical norms of an adult.
Inflammatory processes of the bladder are typical for every second woman carrying a fetus, which is why early diagnosis is important. Kidney pathology is more serious, therefore, examination in a hospital is necessary.
- It is especially important to promptly identify asymptomatic bacteriuria. In this condition, there are no clinical manifestations, but there are changes in the urine - bacteria are detected.
All this can lead to various obstetric complications, so timely use of approved antibiotics is required.
What is albumin?
Albumin is the main component of the liquid part of blood. Among all the major proteins, it occupies more than 50% of the total plasma volume. Its molecules have a low mass, bind water in the vascular bed, thereby maintaining constant plasma pressure and circulating blood volume.
In addition, albumin binds and is responsible for the metabolism of many minerals, trace elements, bilirubin derivatives and uric acid.
Every day, about 5 g of albumin passes through the kidneys, and most of it is absorbed back and remains in the body. No more than 1% is excreted in urine.
Doctors call an increase in plasma protein excretion in urine of more than 20 mg/l microalbuminuria - malb. If a patient loses more than 300 mg of protein per day, he is diagnosed with macroalbuminuria, which indicates the development of severe liver failure.
Features of deciphering a general urine test in children
Decoding a general urine test in a child corresponds to the principles of adult diagnosis. Features – more flexible indicators for children under 5 years of age. In the urine of a child, unlike an adult, the following are allowed:
- Protein;
- Glucose;
- Urobilinogen;
- Ketones;
- Bilirubin;
- Salt.
Such components are explained by the early age of children and the characteristics of their diet. Cellular inclusions (leukocytes, erythrocytes) must strictly comply with “adult” standards. The card with the results of a general urine test must be shown to the pediatrician without fail.
Chemical characteristics of urine composition
Modern laboratory centers are equipped with automatic analyzers that measure the chemical composition of urine. This type of research includes determining the level of several basic indicators.
Total protein
Normal urine contains a minimal amount of it (in the form of traces), which cannot be detected qualitatively. If protein is detected in the urine of a healthy person due to physiological reasons, this phenomenon is temporary and is observed after:
- excessive physical activity;
- strong emotional shocks;
- epilepsy attacks;
- abuse of protein foods.
Functional proteinuria is provoked by a hemodynamic disorder caused by fever, arterial hypertension, hypothermia, and heart failure.
Pathological proteinuria is divided into:
Chemical composition of urine
- for the kidney, associated with a febrile state, insufficiency of the functional activity of the heart muscle, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hypertension, kidney tuberculosis;
- extrarenal, caused by an admixture of protein that is released from the genitourinary tract during urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis, pyelitis, vulvovaginitis.
Glucose
Normal urine does not contain it. Glucosuria can be:
- physiological – when consuming foods with large amounts of carbohydrates, psycho-emotional stress, the use of certain medications, heavy metal poisoning;
- pathological – observed in diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome).
Ketone bodies
Acetone, acetoacetic and hydroxybutyric acids, which can be present in the urine of a healthy person when consuming a large amount of fatty and protein foods and a small intake of carbohydrates. The presence of high levels of ketones in urine is observed:
- with diabetes;
- prolonged fasting;
- severe infectious diseases;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- alcohol poisoning;
- neuro-arthritic pathology.
Indications
The indication for testing for UBC antigen in urine is bladder cancer. The study is prescribed for the primary diagnosis of the disease if the patient complains of blood in the urine, frequent urination or urge, or pain when urinating. The results of the study make it possible to establish a diagnosis and determine the stage of the pathological process. Urinalysis for UBC is performed periodically to monitor bladder cancer. The study is used to identify relapses, determine the effectiveness of the course of treatment, and make a prognosis.
A urine test for UBC antigen is not indicated in the acute phase of an inflammatory disease, bacterial or transient urinary tract infection. To obtain reliable results, it is recommended to wait at least two weeks after recovery. Also, you should not conduct the study immediately after cystoscopy, during treatment (especially intravesical) inflammation and infections. If these requirements are neglected, there will be a high probability of a false positive result. Bladder cancer antigen testing cannot replace cystoscopy, which must be performed in conjunction with this laboratory test or after it if a positive result is obtained. The level of UBC antigen in the urine allows the doctor to create an individual schedule for cystoscopic and other procedures. The advantage of this analysis is its cost-effectiveness and safety - the procedure is non-invasive, the preparation of results takes up to 7 days.
Preparation for analysis and collection of material
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
The level of UBC antigen is determined in the average portion of morning urine, which has been in the bladder for at least 3 hours. 24 hours before the collection procedure, it is necessary to suspend the use of diuretics, having previously discussed the safety of this measure with a doctor. Urine collection must be rescheduled if there are acute inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract or exacerbation of a chronic bacterial infection, if intravesical therapeutic procedures have recently been performed, or a cystoscopic examination of the bladder has been performed. You should drink the liquid as usual. Immediately before collecting the biomaterial, the patient toilets the external genitalia. An average portion of urine is placed in a sterile container with a lid. It must be delivered to the laboratory on the same day. It is allowed to store in the refrigerator at a temperature of +2 to +8 ° C for no more than 4-6 hours.
Determination of the level of UBC antigen in urine is performed using an enzyme immunoassay. It is based on the ability of the test compound to form specific complexes with antibodies. The mixture is washed, an enzyme is introduced into it, which gives color. Using a photocolorimeter, the optical density of the sample is determined and the antigen concentration is calculated based on the obtained values. The study takes several hours, the results are prepared the next day after the biomaterial is submitted.