The first manifestation of cystitis is associated with frequent urge to go to the toilet and slight urine discharge. But there are also symptoms that accompany it, such as, for example, fever. The disease will mean that the walls of the bladder are under the influence of pathological microflora. In this case, the temperature during cystitis and the deviation itself can lead to undesirable consequences.
Therefore, it is very important to get rid of such symptoms as quickly as possible. Also, do not forget about all the inconveniences that a person will experience in this state. Whether there is a fever with cystitis depends on the form of the pathology. The more acute the pathology, the more intense the symptoms will appear.
Is there a fever with cystitis?
There should usually be no increase in temperature with this disease. But if an exacerbation occurs, then the temperature during cystitis indicates that the infection is spreading far beyond the bladder, and the upper urinary tract is also involved. In addition, the patient begins to experience severe pain in the lower abdomen. The inflammatory process in its initial stage is characterized by an abrupt increase in temperature from 37 to 38 degrees.
You should know that it is not recommended to lower the temperature below 38 degrees. Untreated cystitis can turn into a latent form, in which the temperature can constantly remain at around 37 degrees. This contributes to the fact that the disease becomes chronic, complications arise and genital infections develop.
How to get rid of fever
The process of cystitis development and temperature are always interconnected. If the disease is not accompanied by a complication, then it may not rise at all. However, with the development of the inflammatory process, its indicators begin to increase. Therefore, if the patient has a fever, then most likely the inflammation has spread beyond the bladder.
Only a doctor can prescribe treatment, since self-prescribed drugs may not only not eliminate the disease, but also cause serious complications.
It is necessary to bring down the temperature only when it is above 38 degrees in a child and 38.5 degrees in an adult. Before this, you don’t need to do anything, since in this way the body fights the infection on its own. In this case, the doctor can prescribe painkillers and antipyretic medications:
- Ibuprofen;
- Paracetamol;
- Papaverine.
The main prescription of the attending physician will be to drink plenty of fluids. This helps remove the pathogen from the body naturally. Decoctions of medicinal herbs (birch buds, chamomile, corn silk, bearberry, etc.) are suitable for this. In the pharmacy you can find special herbal preparations (Nephrophyte) that will be effective in this case. In addition, you can drink cranberry juice or weak tea with lemon.
When treating children, the doctor will prescribe antipyretic drugs in the form of syrup or rectal suppositories.
Additionally, you need to adhere to a certain diet. Any foods that can irritate the mucous membrane of the bladder (marinades, smoked meats, spicy, salty foods) should be excluded from the diet.
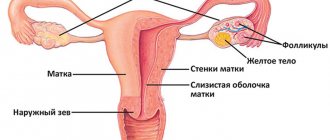
Causes of cystitis
Cystitis is one of the most common inflammatory diseases that occur in the female body. The development of this pathological process in most cases occurs for the following reasons:
- due to the penetration of chlamydia microbes or infections such as Trichomonas into the body;
- for chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- fungal infections;
- tuberculosis infection of the genital area;
- as a result of hypothermia.
There are quite a large number of causes for the occurrence of cystitis.
These are not all the reasons that can lead to the development of cystitis in the female body, but regardless of this, if even minor symptoms indicating this disease appear, you should immediately contact a medical institution, since even the slightest delay can lead to serious complications, including the transition of the disease to a chronic form, which will be quite problematic to get rid of.
What to do if the temperature rises sharply?
Many patients are interested: if there is a temperature with cystitis, can it reach 39 degrees or higher? Unfortunately, this is not uncommon, and in this case there is a high probability of kidney inflammation - pyelonephritis. Therefore, if the temperature during cystitis exceeds 38 degrees, you should immediately consult a doctor. You should know: with cystitis, body temperature rarely exceeds 37.5 degrees.
The following situations also happen: the patient received the necessary treatment, was tested again, and it turned out that he is healthy, but the temperature continues to stay within 37.5 degrees. In this case, we may be talking about a malfunction in the immune system, so you need to consult an immunologist.
Possible complications
If a person has any signs of illness, it is important to see a doctor immediately. If treatment is started in a timely manner, the infection can be quickly cleared from the bladder. When the kidneys are involved in the inflammatory process, the temperature rises sharply.
With cystitis in women, the temperature may rise due to the presence of a urogenital infection. In them, cystitis often becomes a secondary pathology that develops against the background of such female diseases as:
- vaginitis;
- colpitis;
- andexit.
In this case, the patient will require comprehensive treatment aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. Only after eliminating the main infection can you completely get rid of cystitis, otherwise the disease will constantly worsen.
There may be cases when, after completing the full course of treatment, low-grade fever does not disappear. This condition is a reason to consult a doctor, as it may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the body.
If this continues for several months and the temperature rises only during the day, but at night its readings are within normal limits, then the problem may be hidden in the immune system. What to do in this case, only a doctor can tell you after a complete examination of the body.
What to do if the temperature rises sharply?
Many patients are interested: if there is a temperature with cystitis, can it reach 39 degrees or higher? Unfortunately, this is not uncommon, and in this case there is a high probability of kidney inflammation - pyelonephritis. Therefore, if the temperature during cystitis exceeds 38 degrees, you should immediately consult a doctor. You should know: with cystitis, body temperature rarely exceeds 37.5 degrees.
The following situations also happen: the patient received the necessary treatment, was tested again, and it turned out that he is healthy, but the temperature continues to stay within 37.5 degrees. In this case, we may be talking about a malfunction in the immune system, so you need to consult an immunologist.
Why does the temperature rise
One of the most common questions from patients is: is there a fever with cystitis and what is the reason for this? If the body temperature has increased, this indicates the presence of pathogens in the body and the beginning of the inflammatory process. It is these processes that cause the symptoms of cystitis.
When urinating, the infection that affects the urinary system is partially eliminated each time. Therefore, the temperature during cystitis cannot be too high. Usually it rises to 37-38 degrees. However, there are complex forms of the disease - phlegmous or gangrenous, when its indicators can rise higher.
This is due to high intoxication of the whole body.
- It becomes cloudy.
- You can note the presence of mucus or even blood in it.
Such symptoms indicate damage to the walls of the bladder and if treatment is not started in time, they may rupture. These forms of the disease are rarely diagnosed, but to prevent them, it is recommended to consult a doctor if any unpleasant signs occur.
A fever with cystitis may indicate that the infection has spread beyond the bladder.
- improper treatment or untimely completion;
- advanced form of the disease;
- development of pyelonephritis.
If symptoms of cystitis last more than 7 days, the disease may become chronic. In such situations, the infection often spreads to the kidneys, which leads to severe intoxication. The temperature may be 40 degrees. The patient's general condition worsens significantly, pain spreads to the lower back, nausea, chills and increased sweating occur.
Symptoms of cystitis
Symptoms of cystitis manifest themselves in a painful state of the urinary system and the inability to comfortably empty the bladder:
- symptoms of a sharp burning sensation when emptying the bladder;
- frequent urination and emptying does not occur completely;
- symptoms of difficulty urinating;
- the head of the urethral canal is red and swollen;
- constant nagging pain above the pubis;
- a small amount of blood in the urine, and there is also a purulent sediment in it.
Fluctuations in temperature depend on the form of the disease and the area of infected organs:
- inflammatory process in the mucous part - the temperature may not rise;
- inflammation in the muscles of the bladder - the temperature may be within normal limits;
- phlegmonous form of cystitis - the temperature rises to 37.5 degrees;
- gangrenous form of the disease - an increase in temperature within 38 degrees, sometimes up to 39 degrees;
- pyelonephritis - temperature can reach up to 40 degrees;
- if the infection has covered a large area of infection of the organs of the urinary system and the kidneys are infected, in this case the temperature of 38 degrees will remain for no less than 7 calendar days.
Does cystitis cause fever in adults and children?
Fever with cystitis occurs quite rarely. This can be explained by the fact that the disease most often occurs in a chronic form. With inflammation of the bladder, patients may feel discomfort during urination and nagging pain in the lower abdomen. The temperature can rise only during periods of hypothermia and exacerbation of the disease. In other cases it is within normal limits.
A high temperature with cystitis serves as an indicator of the spread of infection. It most often occurs in children and women. After infection with cystitis, frequent urination is observed, dizziness and pain occur. Most often, body temperature does not exceed 37-38 degrees. If the inflammation has spread to other organs, for example, the kidneys, then the temperature can rise to 39 degrees.
Fever with cystitis usually lasts about a week. After this period of time, the disease, in the absence of proper treatment, becomes chronic. A person feels better, but exacerbations of cystitis can occur at any time. In addition, the infection begins to spread throughout the genitourinary system and lead to disruptions in its functioning.
Causes of fever with cystitis
Most often, a high temperature indicates the spread of infection in the body. To accurately determine the cause, it is necessary to undergo tests to identify the bacteria that caused the disease. Quite often there may be a fever with cystitis if the cause of the disease is genital infections or there is a malfunction of the genitourinary system.
Normally, an infection that has entered the bladder is washed out during urination. If some process is disrupted, bacteria begin to accumulate in the body, which causes the temperature to rise. Hormonal imbalances, weakened immunity and frequent fatigue have a beneficial effect on the spread of pathogenic microorganisms.
From cystitis of the phlegmonous and gangrenous form, a high rise in temperature is observed. Frequent urination with impurities of pus and blood and severe pain are also characteristic. These forms of the disease can lead to rupture of the bladder wall if left untreated. Only a specialist can tell you what to do in this case after receiving the analysis results.
Very often, a high temperature indicates an infection in the kidneys. In such cases, body temperature can reach 40 degrees. The patient experiences severe pain, it is difficult for him to move, and a decrease in pain is not observed even in a supine position. Treatment is only possible in a medical setting.
Diagnosis of cystitis
In order to establish an accurate diagnosis and the form of the disease and the stage of development of the disease, as well as the area affected by the infection, symptoms alone are not enough; it is necessary to take tests and undergo a series of diagnostic examinations:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- cystoscopic examination;
- enzyme immunoassay;
- PCR is a diagnostic test.
Enzyme immunoassay and PCR are carried out if the test results contain the presence of microorganisms of sexually transmitted infections.
The use of bacteriological research in the examination allows us to determine which bacteria are in the urinary area.
Ultrasound of the bladder and ultrasound of the kidneys can determine the area of spread of the disease.
Features of the course of the disease in pregnant women
During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes hormonal changes, the vaginal microflora is disrupted, and immunity decreases. If she suffers from chronic cystitis, then the inflammatory process begins to worsen.
During this period, taking any medications is strictly prohibited, but in this condition they should be taken in minimal quantities. Only anti-inflammatory medications administered directly into the bladder are allowed. After the birth of a child, a woman needs to see a doctor as soon as possible to begin intensive treatment.
Causes of temperature with cystitis in women
Does cystitis cause fever? This symptom is not key in this disease, but it can still create discomfort for the patient in the following cases:
- with an unfinished disease;
- the acute form of the disease provokes fever and general weakness due to intoxication;
- development of pyelonephritis.
The specificity of this pathology is due to pain in the lumbar region and directly in the area of the bladder itself. Periodic spasms characteristic of the disease against the background of high pressure in the bladder provoke an urgent need to empty its cavity.
These processes indicate an acute form of the disease. At the progression stage, the temperature with cystitis in women can reach up to 38 degrees. In this case, the use of antipyretic drugs is permissible. If the temperature during cystitis is 37, then the intervention of medications is inappropriate.
Treatment should be approached with all responsibility and strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician. Otherwise, pathological processes in the body will progress and over time the disease will become chronic. More radical therapeutic measures will be required to eliminate the consequences.
Clinical manifestations
The most common symptoms of cystitis include:
- numerous, palpable urges to urinate, during which liquid is released in small volumes;
- burning sensation in the urethra when urinating;
- discomfort, pain in the pelvis, pubis, lower abdomen, genitals (for men);
- hyperthermia of different stages (depending on the severity of the disease), general ailments, signs of intoxication of the body.
The shade of urine changes, it becomes darker. Visually, cloudiness, sediment, and purulent accumulations are detected in it. During severe stages, hematuria and the presence of blood particles in the urine may be noted.
Causes of cystitis
The causative agents of this disease are staphylococcal, intestinal and streptococcal bacteria, ureaplasma, viruses, Trichomonas, fungal infections, chlamydia and other microorganisms. Factors that can provoke cystitis are hypothermia, injury to the bladder mucosa, recent surgery, stagnation of venous blood in the pelvis, vitamin deficiency, and hormonal disorders.
A common cause of the disease in women is the anatomical features of the structure of the urethra, which is shorter and wider than the male one. As a result, any infection can easily rise up, since this organ is located very close to the anus and vagina. That is why the temperature in acute cystitis in women rises much more often, because the body begins to fight the harmful infection.
Men most often suffer from cystitis due to inflammation of the testicles and prostate gland, infections of the genital organs and kidneys, and a significant decrease in immunity. In addition, the disease can be triggered by kidney stones, radiation damage, the presence of a cancerous tumor in nearby organs, and allergies.
Causes of the disease
The main one is bacterial infection. Its most common causative agent is E. coli, which can cause up to seventy percent of cases of disease. The functions of sexually transmitted infections are still being researched.
But it has already been established that promiscuous intimate relations and neglect of protective measures significantly increase the chances of infection in the lower ureteral tract and the possible development of cystitis. For those who love anal copulation, the risk of contracting the disease increases significantly - this method of contact favors the spread of intestinal infection from the anus and perineum to the urethra.
For infectious inflammation preceding cystitis, certain predisposing circumstances are necessary. These include:
- Hypothermia . They are not considered the direct cause of the disease, but are one of the main factors. Therefore, it is recommended not to sit on a cool surface and wear clothes appropriate to the weather conditions.
- Blood circulation disorders in the pelvic area . An inflammatory process in the bladder can occur due to circulatory disorders, which are caused by prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position. If you have a sedentary job, it is recommended to warm up once every hour.
- Hormonal abnormalities . There is a decrease in female hormones.
- Stagnation of urine, disturbances in urination . You should not postpone trips to the toilet for a long time. Fluid that remains in the bladder for a long time is an excellent place for infections that precede cystitis and factors for the formation of stones.
- Failure to comply with hygiene requirements . Women should perform all hygienic movements from front to back, which will help avoid the penetration of intestinal bacteria into the urethra and further into the bladder. It is recommended to constantly adhere to simple requirements - wash your hands before and after visiting the toilet, promptly replace (every two hours) hygiene products on menstrual days.
Temperature in acute cystitis
As noted earlier, acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system is caused by the presence of an infectious pathogen in the body, as a result of which cystitis causes fever. As a rule, with acute cystitis, the temperature lasts no more than 7-10 days. Much depends on the correctness of the chosen course of treatment.
With timely diagnosis of this pathology, cystitis can be eliminated relatively quickly and without serious consequences for the body. If you strictly follow all the recommendations of your doctor, then you don’t have to worry about the development of chronic cystitis.
Otherwise, the temperature after cystitis may occur again some time after the end of treatment. In this case, it is recommended to consult your doctor again and undergo diagnostics. You may have to slightly correct the course of treatment and repeat it.
Treatment of cystitis
To get rid of this disease, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
maintain bed rest; drink as much warm water as possible; take the necessary medications; follow a diet.
If a fever occurs due to cystitis, antipyretic, painkillers and antibacterial drugs are prescribed. For severe pain, it is recommended to take medications that relieve spasm of the bladder muscles - “Drotaverine”, “No-shpu”, “Papaverine”. They are presented both in the form of tablets and suppositories. An ordinary heating pad placed on the lower abdomen can eliminate the pain.
For cystitis, diuretic herbs such as bearberry and lingonberry leaf help well. Blueberry, lingonberry and cranberry fruit drinks are considered especially useful. There are also ready-made herbal preparations - Fitolysin paste, Cyston and Canephron tablets. Warm herbal baths or washing the external genitalia with warm water and soda can help relieve the condition.
In case of acute cystitis, it is not recommended to consume marinades, pickles, and spices, but fruits and dairy products are considered very healthy.
If the disease is chronic, the doctor will prescribe procedures to help restore the flow of urine. It is imperative to diagnose and eliminate foci of infection in the body. Antibacterial therapy is possible only after the necessary laboratory tests - urine culture and identification of the pathogen, as well as determining its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Symptoms of cystitis
A clear clinical picture is expressed in acute inflammation of the bladder. After suffering infectious diseases, injuries or hypothermia, severe pain in the lower abdomen, urination problems, frequent urges, burning, and cramping are typical. There may be blood in the urine. In analyzes of the secreted fluid, white blood cells and possibly even pus appear. The stronger the inflammation, the more pronounced the disease is. In the chronic form, it proceeds sluggishly, reminding itself during periods of exacerbation.
The frequency of the urge to urinate depends on the degree of the inflammatory process. Urologists believe that pain increases with each visit to the toilet. In this case, women experience severe pain in the lumbar back. Pain with cystitis, caused by contraction of the bladder muscles and increased intravesical pressure, torments the patient day and night. Cystitis in a child is accompanied by frequent urination, darkening and cloudiness of urine, elevated temperature up to 38-39º C and sweating, anxiety and irritability, headache, chills. Possible urinary incontinence and nausea. Very young children hold their tummy and cry, thus expressing pain. Parents should sound the alarm if a baby under the age of 12 months urinates more than twice within an hour. In children and pensioners, symptoms are often not obvious.
Symptoms of the disease
Cystitis is an inflammation that occurs in the walls and mucous membrane of the bladder. The disease is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate primarily through the urethra. Provoking factors include reduced immunity, hypothermia, congestive processes in the pelvic area, hormonal changes in the body and surgical operations.
A person can suspect the development of cystitis by discovering symptoms characteristic of the disease.
Its main features:
- frequent urination;
- after going to the toilet, the patient feels incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- false urge to urinate;
- sharp pain occurs during urination;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- increased body temperature;
- blood in urine.
The stronger the inflammatory process, the more pronounced the symptoms of the disease will be.
If you notice any signs of cystitis, it is important to immediately consult a doctor who will conduct an examination (blood and urine tests, cystoscopy) and prescribe the necessary treatment. Therapy for cystitis should be comprehensive. In addition to the use of medications, the doctor will prescribe physiotherapy and sitz baths, which will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms and speed up recovery.
Infectious form
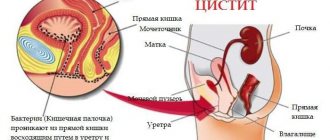
The vast majority of cases of cystitis are associated with infection of the bladder with opportunistic microflora. Due to the physiological characteristics of the structure of the female urogenital system, the infection quite easily penetrates the bladder from external organs. Less commonly, it is possible for a kidney infection to penetrate or be carried through lymph and blood.
Cystitis can also begin when infected with Trichomonas, chlamydia during unprotected sexual intercourse. In case of weakened immunity, inflammation of the bladder can also be provoked by such representatives of opportunistic microflora as Candida fungi, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, etc.
Acute cystitis is characterized by rapid development of symptoms. Within a few hours after exposure to the triggering event, urination becomes more frequent. The volume of urine excreted is reduced. The process of urine excretion is accompanied by pain. The intensity of these symptoms increases rapidly. With cystitis, the temperature can rise to 38 ºС if it is acute. Most often, the acute period lasts 3–4 days, then the intensity of the symptoms weakens and the temperature drops. During this period, you need to drink plenty of fluids. This ensures the washing away of waste products of bacteria or another type of infection that causes intoxication of the body.
Among traditional medicine there are a huge number that help cure the disease. Most of them include herbal components with anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects. In the treatment of this disease, decoctions of chicory, bearberry, St. John's wort, knotweed, dill seeds, yarrow and many other plants are used. You can use mono-decoctions or various herbal preparations, including natural antiseptics and diuretics. Warming the lower abdomen or perineum with a heating pad or warm bath increases blood flow, improving blood supply to the genitourinary system.
Examination and diagnosis
To make a diagnosis, you need to take several tests. Urine and blood are usually examined, which can be used to identify almost any disease. Women have a special medical examination to examine their bladder. It is called cystoscopy. A special instrument is inserted through the urethra, and the urethra is also examined with it.
Treatment is prescribed in combination. Along with medications, the use of herbal medicine is indicated. Antibiotics are used for five to ten days. The most suitable groups are nitrofurans and fluoroquinolones. Infusions of medicinal herbs can be taken orally and made into baths.
Cystoscopy may be required to determine the correct treatment.
The success of the course of treatment largely depends on compliance with all the doctor’s recommendations. During the treatment period, it is recommended to take diuretics. The ban on alcohol is very strict, because antibiotics will not bring the desired result, and such a mixture can cause irreparable harm to your body.
An increase in temperature to 37 C or higher indicates the existence of an inflammatory process in the body. With characteristic symptoms, cystitis can be diagnosed. The acute form requires hospitalization, comprehensive examination and treatment. Prevention of any disease consists of a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and exercise.
The video below will tell you how to deal with high fever:
Increased temperature with cystitis
A common disease of the bladder - cystitis - is provoked by pathogens that, when they enter the mucous membrane of the organ, cause inflammation. Severe pain, constant urge to urinate and fever during cystitis is the body’s protective reaction to the penetration of infection into the genitourinary system. The disease more often affects women due to the anatomical features of the body.
Why does the temperature rise
In the acute form of cystitis, which develops as a result of hypothermia, decreased immunity or sexual contact, the patient’s temperature may rise. To determine the cause of this symptom, it is necessary to establish the nature of the pathology.
If the genitourinary system is healthy, then microbes are eliminated from the body in the urine. When the organs of men and women, and sometimes small children, malfunction, viruses and bacteria accumulate in the bladder and, when the body’s protective functions are weakened, provoke an attack of acute cystitis with blood and hyperthermia.
Elevated temperature always accompanies inflammatory processes and shows that the body is fighting the spread of infection. During the acute phase of cystitis, it rises spasmodically. At the thermometer mark of +37...+38°C it is not knocked down; the body must cope with the fever itself.
With phlegmonous and gangrenous forms of cystitis, or if it causes pyelonephritis, body temperature can rise to 39°C.
The appearance of fever and blood in the urine during inflammation of the bladder requires consultation with a urologist, and for women, also with a gynecologist. Self-medication may be ineffective, and the disease quickly develops into a chronic form.
How to properly lower your temperature
Before going to the clinic, you need to lower your temperature if it is above 38°C. This must be done in advance so as not to distort the symptoms and picture of the disease. You can bring down the temperature with inexpensive drugs from the group of analgesics-antipyretics, for example, Paracetamol. They can also be taken when the patient has an exacerbation of cystitis without fever. These medications reduce pain due to bladder inflammation.
In addition to medications, a person needs to drink a lot of fluids: this way the body will clear the infection faster. For cystitis, it is better to drink acidic drinks, such as tea with lemon, fruit drinks.
Temperature during inflammatory processes in the urinary area
A rise in temperature during cystitis means that the inflammatory process has spread to all organs of the urinary system. In the initial (acute) form of the disease, the temperature during cystitis can be up to 38 degrees, and sometimes up to 38.5. In children with this disease - up to 39 degrees. If the temperature during cystitis rises higher than 38.5, what should you do? It is necessary to take an antipyretic drug:
- Nuroven (syrup for small children);
- Ibuprofen (suspension for children under 3 years of age);
- Paracetamol.
These drugs reduce body temperature and also have analgesic properties, which has a positive effect on well-being during cystitis. It’s even better to use suppositories that have antipyretic and inflammatory effects. Suppositories quickly dissolve in the body, which contributes to their rapid action.
It is also necessary to take a large amount of fluid, firstly, drinking plenty of fluids reduces the fever, and secondly, drinking plenty of fluids creates a need for frequent urination. The infection leaves the body along with urine.
Sour drinks and fruit drinks that contain vitamin C are very useful - cranberry juice, lingonberry juice, drinks and teas with lemon added.
Decoctions of medicinal herbs that have diuretic properties will not only help cleanse the urinary system of infection through frequent urination and relieve cystitis, but will also replenish the body’s lack of vitamins and microelements.
The disease cystitis and temperature up to 38.5 do not need to be brought down by any drugs.
Temperature with cystitis - what to do? Brief information
In most cases, an increase in temperature is a completely harmless symptom that disappears along with the main problem. You can determine the tactics of behavior using the following tips:
- It is not recommended to bring down a temperature in the range of 37-37.9 C, which occurs against the background of acute cystitis. The inflammatory process itself should be treated, and the accompanying symptoms will go away on their own.
- A temperature of up to 38 C, which appears after the signs of untreated cystitis have disappeared or weakened, does not need to be knocked down. It is necessary to carefully check the condition of the body for the development of chronic inflammation of the bladder and damage to other organs.
- The mark of 37-37.5 C after treatment for cystitis and the disappearance of all other symptoms may indicate impaired functioning of the immune system. There is no need to lower the temperature. It is recommended to make an appointment with an immunologist.
- A temperature above 38 C during cystitis is a symptom of a developed complication and a reason to urgently consult a doctor. The specialist will make the correct diagnosis by examining the patient’s complaints and conducting the necessary research. The temperature must be brought down using antipyretics; Ibuprofen and Paracetamol have proven to be the best.
The most reliable way to get rid of fever due to cystitis is to completely and promptly cure bladder inflammation. You should start therapy as early as possible: then the recovery process will be relatively simple and fast.
A decrease in body temperature is not a sign of the absence of infection in the body. If you refuse treatment, inflammation may occur again. Does cystitis cause an independent decrease in temperature? As in the case of refusal of treatment, body temperature may return to normal, but the infection will progress in the genitourinary tract. If the body is exposed to negative factors, cystitis may worsen again and the temperature will rise.
Even if it was possible to normalize body temperature at home, you should continue taking antibacterial drugs for the prescribed course. This will help avoid the appearance of chronic cystitis. The presence of infection in the body is easy to diagnose using tests.
With cystitis, the temperature is up to 37.9 C
The inflammatory process is provoked by an infection that has entered the body. It affects the bladder and naturally “causes interest” in the immune system. Defensive forces accumulate, and the body “fights” pathogens by raising the temperature. As a rule, it rises sharply, spasmodically and lasts for several days.
If the mark on the thermometer does not exceed 38 C, there is no need to worry: the body is just trying to cope with the infection. Of course, it is not recommended to let the situation take its course. You should definitely consult a doctor and, if necessary, take a course of antibiotics and herbal medicine. But you shouldn’t lower the temperature: as soon as the inflammatory process subsides, the mark on the degree scale will return to normal.
A separate case is when the temperature did not rise immediately. For example, a person suffered from typical symptoms of cystitis, such as:
- frequent urge to pee;
- pain when urinating;
- discomfort in the pelvic organs.
The patient did not undergo therapy under the supervision of a doctor, but either simply endured the symptoms or self-medicated. After some time, the signs of the disease disappeared - almost or completely, and instead they appeared increased body temperature.
If a jump to 37-37.9 C occurred against the background of untreated cystitis, then it makes sense to suspect that the disease has become chronic. Also, the possibility of further “spreading” of the infection and damage to other organs cannot be ruled out. You should undergo a full examination, paying special attention to the genitourinary system.
It happens less often that after high-quality and timely treatment of cystitis, the temperature remains at 37-37.5 C. There may be a malfunction in the immune system, which requires contacting an immunologist.
What do the temperature values mean?
Light form.
A woman or man’s temperature of no more than 37-37.5 degrees indicates that the disease is concentrated in the bladder, and not outside it, and proceeds without serious complications. This is a milder form of cystitis. In children in such a situation, the thermometer can show up to 39 degrees.
In acute form of the disease.
The temperature can jump sharply to 37-38 degrees, this indicates that the body is fighting the infection. In this case, the patient experiences pain in the abdominal area.
In severe forms of the disease.
The thermometer may show 39-40 degrees, the urine becomes cloudy, and there are blood impurities in it. This indicates the destruction of the walls of the bladder.
Complicated form.
If the indicator rises above 38 degrees, this indicates that the infection has affected other organs; the inflammatory process has begun in the kidneys and ureter. If pyelonephritis develops, the condition can deteriorate greatly, and the temperature can reach 40 degrees. In this case, the patient will feel chills, headache, nausea, and lower back pain.
In some cases, the patient continues to have a temperature of 37-38 degrees, and then the question arises: can this happen even after treatment, because all other tests are already normal. Such behavior of the body indicates problems with the immune system. Here you will need the help of an immunologist.
Normal or not?
How to understand the temperature limit for cystitis?
Within normal limits
When the immune system begins to fight the infection in the bladder, the temperature rises a couple of hours after the start of the treatment process. It can increase intermittently and is long-lasting.
- Normal temperature indicators for cystitis in women are from 37 to 38 degrees Celsius.
- In men, cystitis occurs in very rare cases, since the structure of the organs does not facilitate the penetration of infection into the bladder. But if this does happen, then the characteristic signs of the disease will be the same symptoms as in women.
- With cystitis in a child, the readings can rise to 37.5 degrees. Since children have weaker bodies and immune systems, treatment should not be left to chance. At the first signs, you should consult a doctor.
Within such limits, temperature during cystitis can be useful. This means the body's natural fight against the disease. Of course, this does not mean the patient is completely inactive. You need to treat cystitis itself, see a doctor, take medications.
You should not lower the temperature to 37-38 degrees, so as not to interfere with the body’s natural defense processes. It will go away along with the infection.
Deviation from the norm
But, in some cases, readings from 37 to 38 degrees Celsius may be abnormal. Many people prefer not to seek help from specialists. Often we act on the principle “it will go away on its own” or engage in poor-quality self-medication. So in the case when a person ignores the signs of cystitis and does not begin timely treatment, our body “trumpets” that the disease is becoming chronic.
Characteristic signs of temperature with cystitis, which signals the transition to chronicity, is that it does not rise immediately. At first, symptoms of the disease, such as frequent urination, pain and stinging when going to the toilet, may go away. Then the temperature rises slightly, which lasts for a long time.
Then you definitely need to see a doctor, undergo an examination of the genitourinary system and choose the type of treatment. What if the patient underwent full treatment, adhered to medication, got rid of cystitis, but the temperature continues to range from 37 to 38 degrees. Could this be possible?
Maybe, but very rarely. This indicates that after taking antibiotics, the immune system is greatly weakened or lost. As we know, it sometimes happens that modern medicines cure one thing but cause harm to another.
The patient should consult an immunologist and take a course of vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
Danger
If the temperature during cystitis has exceeded the limit of 38 degrees, then this is not just a signal, it is a call for help.
- Pyelonephritis may await you. Infection from the lower urinary canals moves higher and higher, affecting the kidneys. The temperature rises to 40 degrees and the heat begins! Side effects may include severe vomiting and severe back pain (especially in the lower back). Under no circumstances should such indicators be left to chance. Only medical intervention can help here. This is the worst outcome of cystitis, which is best not to happen.
- An increase in temperature after 38 degrees also indicates the development of a severe, acute form of the disease. This happens rarely. The symptoms of inflammation worsen. Not just blood appears in the urine, but pus or viscous turbidity. Intoxication is tormenting. At this stage, the walls of the bladder are very weakened and susceptible to damage. If treatment is not prescribed in a timely manner, they may simply rupture.
- Paracystitis is considered not the worst, but also dangerous. The peri-vesical fatty tissue becomes inflamed. If it is deformed in the front part, then swelling may occur in the very bottom of the abdomen. If in the back, then problems with bowel movements appear. The temperature fluctuates around 39 degrees.
In all these cases, you need to urgently go to the hospital. The temperature can be lowered.
Conclusion
Thus, to the question whether there can be a fever with cystitis, the answer is yes. In this case, you should not waste time, but quickly consult a doctor, since this condition indicates a strong inflammatory process. Self-medication can lead to the disease becoming chronic, which is very difficult to get rid of.
Inflammation of the walls of the bladder - this disease is called cystitis. If you very often need to go to the toilet, and the portion of urine is very small, you can make a preliminary diagnosis. The inflammatory process occurs due to an infection in the bladder, affecting the mucous membrane. Fever and cystitis can lead to complications and the development of serious diseases.
Inflammation in the bladder is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature
The symptoms of this disease can be inconvenient and may cause changes to your regular schedule. In addition, you will feel pain in the lower abdomen. According to scientific research, this disease is observed more often in females than in males. Temperature with cystitis is not uncommon, but its indicators depend on the form of the disease.
It occurs due to the ingress of various bacteria. It can be:
Chlamydia and Trichomonas. Fungal and intestinal infections. Pathogens of tuberculosis. Chronic infection of the genitourinary system. Various bacteria and viruses.
The temperature can rise from 37 C to 38 C. Doctors call such indicators low-grade body temperature if this continues for a very long time.
Cystitis is often caused by bacteria entering the body.
It is possible to determine the cause of the increase in temperature only after establishing the nature of the occurrence of cystitis. If the genitourinary system works without failures, all microorganisms are excreted along with the urine. But if certain delays begin, viruses and infections will remain and accumulate. Women's bodies become vulnerable with weak immunity, overwork and hormonal imbalance.
Fever and acute cystitis occur after hypothermia, weakening of the body's protective functions and during sexual transmission. Cystitis has a number of characteristic symptoms:
The presence of blood in the urine, usually a small amount. Painful sensations when urinating and an unreasonably frequent urge to do so. When analyzing urine, leukocytes are found in it.
This disease can contribute to the development of a depressive state and a deterioration in general health. Every visit to the toilet for women becomes a kind of test.
What to do after hyperthermia
Our bladder has a huge positive property.
Due to its structure, it thoroughly cleanses the body of infections and removes them along with urine. But if malfunctions begin in the urinary canals, then the infection accumulates in the body. The process is aggravated by weak immunity and hormonal problems. The disease is characterized by painful urination, blood clots in the urine or white mucus (remnants of white blood cells).
Cystitis can occur either without an increase in temperature or with a gradual or sharp rise in temperature. It all depends on the degree of inflammation and the individual characteristics of the body.
In cases when all the body’s forces are thrown into the fight against the treatment of some disease (in this case cystitis), additional protective processes may be activated. This is how our immune system reacts to various types of infections.
Temperature is the body’s signal that the inflammatory process is serious and the body is trying to fight the infection. Thus, a high temperature during cystitis makes us understand that the disease has begun to spread further or is developing into an acute form.
If you do not immediately begin to fight the disease, it can rise further, affecting the kidneys. This is already very dangerous and requires immediate medical intervention.
- There is no need to fight temperatures up to 38 degrees. You should pay attention to the disease of cystitis and its treatment. The temperature will indicate additional assistance from the body in treatment. When you heal your bladder, then the fever will subside.
- A low temperature after the disease disappears indicates a weakened immune system. What to do in this case? A complex of vitamins and a trip to an immunologist will help here.
- If cystitis has not been properly treated, but the symptoms of the disease have passed and the temperature has risen, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination of the genitourinary system. And only after a verdict is made, take appropriate medications.
- Before going to the doctor, do not lower your temperature under any circumstances. This may give false evidence of illness.
- At temperatures above 38 degrees, it must be lowered. Tablets such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen will help. They will help relieve fever and reduce pain. It is not recommended to take aspirin when there is blood in the urine. This medicine stimulates blood circulation, which can only worsen the patient's condition.
- If you have cystitis, you need to drink a lot of fluids to allow you to more thoroughly remove the infection and restore the body. Sour drinks are recommended for children (cranberry juices, teas with lemon and viburnum, orange and currant juices, etc.).
- Do not forget about the rules for preventing cystitis: maintain intimate hygiene; wash your genitals thoroughly; use protective equipment during sexual intercourse; during menstruation, it is better to use pads to prevent infections from multiplying in the blood inhibited by the tampon; don’t stand it when you want to go to the toilet; strengthen your immune system and exercise.
If you have a fever due to cystitis, the main thing is not to panic. It is important to study the reasons for its occurrence in your case. If you are not sure of the diagnosis, then contact the specialists again. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances and do not let the disease take its course!
In most cases, the disease occurs due to emerging microbes, but this is not the only reason. Identifying it is important in order to select the appropriate treatment. The following factors for the development of cystitis are identified:
- hypothermia of the body;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- holding back the urge to urinate;
- tight synthetic underwear;
- stressful situations;
- weakened immune system;
- inflammation of the anus;
- physical stress;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- early sexual life;
- hormonal changes.
In women, the occurrence of the disease is often associated with inflammation of the genital organs due to diseases such as gonorrhea, vaginitis, and candidiasis. This is how acute cystitis develops, accompanied by its characteristic symptoms.
If the infection has not passed beyond the bladder, there will be no significant changes on the thermometer. An increase in degrees on the scale is a protective reaction of the immune system to foreign bodies.
Inflammation will always be accompanied by an increase in basal temperature, because this is how the body expresses its readiness to fight viruses.
With a weakened immune system, which is typical for pathology, the patient is unable to fight the pests that come to him. This condition provides an increase in heat. Feverish syndrome defines the disease as acute, because the body is not yet accustomed to the emerging bacteria and goes on the attack. In most cases, with a chronic course, hyperthermia is absent.
| Indicators on the thermometer | Characteristics of the disease and the organs it affects |
| Within normal limits | Inflammation does not extend beyond the mucous membrane |
| May rise to 37C | Bladder muscle infection |
| Up to 37.5 | Phlegmonous cystitis |
| 38-39С | Gangrenous |
| Up to 40 C | Acute pyelonephritis |
| 38 C lasts for a week | Pathogenic microorganisms occupy most of the genitourinary system |
The temperature with cystitis in women occurs more often than in men, does not exceed 38 C and lasts up to 5-7 days. If after this period the signs of inflammation do not go away, the disease becomes chronic.
Among the pathogenic symptoms in children, a symptom such as temperature is often encountered with complications of the urinary tract, and it immediately becomes febrile. The course of the disease in a child differs from the development of pathology in adults. In babies under one year old, fever is almost the only pronounced sign of the disease.
In the presence of hyperthermia, it is important to focus on the child and the fight against the emerging virus, and not on the height of the mercury column.
Like all patients, children who suspect developing inflammation need to undergo urine and blood tests so that the pediatrician can provide timely assistance.
If you manage to reduce your fever at home, you don’t need to stop there. The absence of fever is not an indicator of complete healing; one should not think that all pathogens have disappeared. The basis of the treatment of the disease is the fight against pathogenic flora with the help of antibacterial drugs. To avoid relapses, the course of treatment should be continued until the tests are normal.
There is a close relationship between the etiology of hyperthermia and this disease - infection with viruses and harmful bacteria of the bladder mucosa. To avoid complications and protracted therapy, it is necessary to visit a urologist immediately after the appearance of characteristic signs.
Conclusion
Thus, to the question whether there can be a fever with cystitis, the answer is yes. In this case, you should not waste time, but quickly consult a doctor, since this condition indicates a strong inflammatory process. Self-medication can lead to the disease becoming chronic, which is very difficult to get rid of.
Due to the anatomical structure, bladder inflammation occurs in every fifth woman; it occurs less frequently in men and children. Unbearable pain and cramps, fever with cystitis torment the patient. The disease is provoked by microbes of E. coli, staphylococcus, Proteus, as well as ureaplasma, trichomonas, chlamydia, various fungi and viruses. The cause of the disease may be decreased immunity, impaired blood supply, and even failures in the excretory system.
Fluctuations in body temperature are one of the symptoms of inflammation in the bladder.