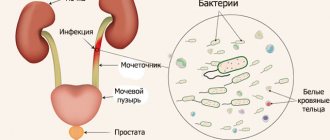
Pregnant women need to undergo a whole range of tests throughout pregnancy. A variety of laboratory tests allow you to quickly and timely detect pathological processes in the body. A urine culture tank during pregnancy is prescribed during registration, before childbirth, and for diseases of the genitourinary system. This analysis is one of the main and effective studies of the urine of the expectant mother.
With its help, it is possible to identify and identify pathogens of urinary infections, as well as determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics. The pathology can be present in the mother’s body for a long time and asymptomatically, and become more active during pregnancy. In such cases, only urine culture will help detect the pathogenic pathogen. Based on the results of the analysis, doctors determine the onset of the disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment to the woman.
Reasons to donate a urine culture tank
A urine culture test during pregnancy helps to find a chronic or latent form of an infectious disease of the genitourinary system.
The study is mandatory for all women, including those who do not complain about their health and feel well. In the absence of timely treatment, the infection spreads further, affecting the renal structures. As a result, the pregnant woman develops pyelonephritis, a bacterial inflammation of the kidneys. This disease also occurs when the number of pathogenic microorganisms increases due to decreased immunity and stagnation of urine in the bladder.
Pyelonephritis often causes intrauterine infection of the child, leads to spontaneous abortion, and in the third trimester causes premature birth.
An obstetrician-gynecologist must prescribe a bacteriological examination of urine to the expectant mother if:
- Her body temperature rises slightly but steadily.
- A pregnant woman is bothered by pain and itching when urinating.
- Dull, aching painful sensations appear in the lumbar region and lower abdomen.
- There is a frequent urge to empty the bladder, often false or with minimal discharge.
It is better to cure the disease at the incubation stage, undergo safe and effective therapy, so as not to risk the health of the woman and the fetus. If even before conception the body had diseases of the urinary system, then during pregnancy bacteriological analysis should be taken much more often.
Indications for analysis
Pregnant women are prescribed general laboratory urine tests monthly. A pregnant woman is referred to a culture tank if an increased level of leukocytes, sugar, red blood cells, protein or bacteria is detected in the urine.
During possible treatment, the patient needs to take a culture test several times so that the doctor can monitor the dynamics of the healing process. Pregnant women also undergo this type of diagnosis:
- with hereditary pathologies;
- working in hazardous industries;
- with past abortions;
- having children with congenital abnormalities;
- related marriages.
The purpose of the analysis is to determine the nature of the pathogenic agent and its prevalence. This is necessary for optimal therapy to restore microflora in the birth canal and relieve the inflammatory process.
Decoding
What does a urine sterility test show? It is important to know that the urinary tract is completely sterile. Therefore, if you maintain hygiene, then no infections will be found in your urine. The analysis may contain a small amount of non-pathogenic microflora, which is quite clear, because it can come from the vagina or urethra.
There is absolutely no need to worry if the following are found in your urine:
- coli;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci.
It's not a matter of presence, but of quantity and type. No need to worry in advance. From the results of bacterial culture it will be clear:
- is there a pathogen;
- if so, which one;
- how to carry out treatment.
In addition, when prescribing therapy, a general blood and urine test is taken into account. Now briefly about how the analysis is carried out:
- place the collected material in a nutrient medium;
- sent to an incubator for one day;
- the resulting colonies are sown in Petri dishes;
- leave for a day;
- divided by type;
- propagate for another day;
- Only after all these stages are bacteria checked for vulnerability.
As a result of the analysis, a CFU indicator is written out, which we will talk about in the next section.
Preparation for the study and interpretation of the results obtained
Before carrying out the procedure, the doctor must instruct the woman how to collect and submit the urine culture tank to a nutrient medium during pregnancy correctly. This will help avoid data distortion and repeated analysis. There is absolutely nothing difficult about this, and if you are faced with such a study for the first time, then check with your doctor how this process should occur.
Pregnant women need to collect urine cultures in accordance with a certain algorithm. If you perform all the steps correctly, the doctor will not have to doubt the reliability of the data obtained. To do this, follow these steps.
- To collect clean urine for bacterial culture during pregnancy, first of all, a woman needs to make a small cotton swab and insert it into the vagina. This will prevent mucus and other genital contents from getting into the urine container.
- The liquid should be collected in the morning. The first few milliliters must be flushed down the toilet, after which the “middle” portion must be collected in a container.
- The sample container must be delivered for testing within 2 hours.
The jar in which you will collect the urine test for a clinical test for sterility in pregnant women must be sterile, so it is better to buy it at the pharmacy. Of course, you can sterilize containers at home, but it will be more difficult. For example, you can hold a glass jar over the spout of a boiling kettle for a few seconds, and then wait until it dries. Only then will it be possible to collect a urine test for sterility during pregnancy.
In order for a urine test for tank culture during pregnancy to give reliable results, it is necessary to wash yourself with laundry soap before collecting urine. For this purpose, you can also resort to using a solution of baking soda.
Do not forget about the time during which it is necessary to deliver the material to the clinic. If you do not do this within 2 hours, you will have to collect your urine again the next morning. Based on the data obtained, the doctor will decide on the use of certain therapeutic techniques, so you must know how to correctly collect material for research.
Data interpretation
Correct interpretation of data obtained after urine culture during pregnancy is of great importance. It is an indicator of the functioning of the urinary system of the expectant mother. Test results are measured in CFU and are interpreted as follows.
- If the CFU level per 1 ml of urine does not exceed the 1 thousand mark, this is the norm for urine culture in patients during pregnancy. This amount of microbes does not require medical intervention.
- The interval between 1000 to 100,000 units indicates the presence of slight deviations. However, the result is often questioned, so the patient may be prescribed a repeat test to determine pathogenic microflora.
- If the number of colony-forming units is more than 100 thousand, then these are rather unfavorable indicators, indicating the presence of serious kidney diseases or diseases of the urinary system. The patient is prescribed an antibiogram to select an antimicrobial substance to combat the detected pathology.
The main task of the laboratory technician conducting the research is to accurately determine the type of pathogen, since this is directly related to the choice of therapy methods (if any are needed). The most common type of bacteria is staphylococcus in bacterial culture during pregnancy. Even a gynecologist can bring it in when examining a patient. And even if a woman independently purchased a special, sterile gynecological kit, this cannot be a complete guarantee that this type of microorganism will not penetrate her body.
For this reason, if you notice tingling in the lower abdomen, suspicious nagging pain, or copious mucous discharge of a yellowish or reddish color, you should immediately consult a doctor. Staphylococcus can affect not only the bladder, causing cystitis, but also the genitals. And this is already extremely dangerous, since there is a high probability of infection of the child, which can affect the health after birth!
What to do if bacteria are found
A bad analysis is a problem that needs to be dealt with, but it should not cause panic in the expectant mother. Excessive nervous tension can negatively affect the condition of the fetus. However, the infection cannot be ignored either due to the risk of the following complications:
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- placental insufficiency, in which the normal process of nutrient exchange between mother and child is disrupted;
- deterioration of a woman’s kidney function.
Advice! Detection of bacteria in the urine should be a reason to initiate appropriate treatment. Thanks to the availability of a sufficient number of effective antibacterial drugs, it is possible to eliminate infections of the urinary system in pregnant women. The main thing is not to ignore the problem, but to seek qualified help in a timely manner.
Detection of bacteria in the urine should be a reason to initiate appropriate treatment. Doctors have three groups of antimicrobial drugs that are safe for mothers and children:
- Penicillins. Preference is given to Amoxicillin and Ampicillin. Both products have a wide spectrum of action and destroy most known pathogenic bacteria.
- Cephalosporins. Another group of popular and safe antibiotics during pregnancy. Due to the presence of 4 generations of drugs, the doctor individually selects the drug depending on the type of pathogen. Popular representatives are Cefazolin, Cefatoxime, Ceftriaxone.
- Macrolides. A group of antibiotics that are active against intracellular microorganisms (chlamydia, mycoplasma). “Erythromycin” and “Azithromycin” are the most popular representatives among macrolides, which have proven themselves in the treatment of urinary tract infections in pregnant women.
Thanks to the availability of a sufficient number of effective antibacterial drugs, eliminating infections of the urinary system in pregnant women is a completely feasible task. The main thing is not to ignore the problem, but to seek qualified help in a timely manner. In parallel, symptomatic therapy can be prescribed.
Urine culture tank during pregnancy
Bacteriological seeding is an analysis of biomaterial for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms. It is this type of examination that most accurately determines the presence of infections and their number. This study proceeds as follows: the biomaterial is placed in an environment comfortable for the growth of pathogenic organisms for 5–7 days, after which the result is observed. If any bacteria or fungi are detected, testing is carried out to see if they are responsive to medications and the most effective drug is selected.
Timely diagnosis of the disease during pregnancy is very important
Why is analysis prescribed?
Before the next visit to the antenatal clinic, the expectant mother each time takes a clinical urine test. Isn’t this enough, you say: and why is bacteriological culture necessary? The fact is that not all pathogenic microorganisms can be detected using a general urine test, especially if a woman has chronic diseases. But bacteriological culture helps to easily find pathogens even before any symptoms appear.
This is especially important for expectant mothers, because the earlier the disease is treated, the lower the risk of pregnancy complications.
How often is urine culture tested?
Throughout pregnancy, a woman will need to be tested for culture twice:
- when registering for pregnancy in a gynecology department, in order to promptly determine the presence of pathogenic microflora and subsequently treat it;
- at 36 weeks of pregnancy to determine the cleanliness of the genitourinary and birth canal, thereby preventing infection of the baby during childbirth.
Unscheduled, the doctor will definitely prescribe a bacteriological culture if a clinical analysis of the expectant mother’s urine shows the presence of protein (protein in urine very often indicates an inflammatory process) in order to determine the cause and subsequently eliminate it.
The main indications for unscheduled urine culture:
- kidney diseases;
- diabetes;
- control of therapy of prescribed medications;
- confirmation or refutation of the diagnosis;
- painful sensations when urinating;
- fever in the absence of other symptoms;
- immunodeficiency, etc.
Normal for healthy men and women
Urine is tested for sterility not only during pregnancy; this test can be prescribed for men and small children. It is important to know that the presence of a small number of bacteria is quite normal, they can be found even in a completely healthy person. As a result, the following indicators are indicated:
- color (light yellow and transparent);
- concentration (up to 1025 grams per milliliter);
- protein (up to 0.03 mol per liter);
- red blood cells (up to 1);
- CFU (up to 10 thousand per milliliter);
- there is no mucus;
- no crystals;
- there is no glucose;
- leukocytes (men - up to three, women - up to six).
A small clarification on the CFU content: if less than 1 thousand are found in the material, then the person is healthy, from 1 to 10 thousand - a retake is required, more than 10 thousand - a clear indication of the presence of infection.
Danger of intrauterine infection of the fetus
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is dangerous because bacteria multiply unnoticed by the pregnant woman; the woman is unaware of the infection and does not take measures to get rid of harmful microorganisms. The consequence of this situation is infection of the embryo in the womb of the mother or the baby during the passage of the birth canal.
Late detection of harmful microorganisms leads to the risk of termination of pregnancy - miscarriage. The fetus dies from intoxication with decay products. The degree of danger depends on the characteristics of the pathogen, type, quantity and drug resistance. The patient’s immunity and gestational age also play a role.
Studies reveal the consequences of IUI in newborns:
- cerebral hypoxia – oxygen starvation;
- hypotrophy – retarded growth and development;
- respiratory disorders - caused by immaturity of the lungs;
- edema is a consequence of kidney damage, etc.
Symptoms in infants are often mild, making diagnosis difficult. After 3-4 months, children exhibit:
- pneumonia – inflammation of lung tissue;
- conjunctivitis – inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye of various etiologies;
- urinary tract infections - damage by microbes to the genitourinary system;
- encephalitis – brain damage;
- meningitis – occurs in a severe form, with fatal complications;
- hepatitis is a disorder of the liver.
Until the first year of life, diseases of the kidneys, liver and lungs can be treated. After 2 years, delayed physical and intellectual development is recorded in sick children. In children under one year old and older, hydrocephalus manifests itself - a circulation disorder, an imbalance between the production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. The difficulty of adapting to a team is explained by brain dysfunction, which manifests itself in:
- behavioral disorders;
- excessive activity;
- speech impairment;
- enuresis, etc.
The future of such children does not seem optimistic due to impaired vision and hearing, mental disorders and epilepsy. Most become disabled. Developmental delays lead to inaccessibility to education.
To prevent dangerous consequences, a mandatory laboratory test of urine is prescribed, and if bacteria are detected, treatment is prescribed. Compliance with the doctor’s recommendations guarantees the pregnant woman’s recovery. If the doctor’s orders are not followed, the patient’s hemoglobin decreases, swelling and cramps appear, and blood pressure rises.
Causes of kidney inflammation
Various factors can provoke kidney inflammation during pregnancy. Pregnant women experience large-scale hormonal changes that cause venous dilatation of the ovarian vessels. As a result, compression of the ureter occurs, which disrupts urinary outflow, triggering the development of pathogenic microbes. In addition, as the fetus grows, the parameters of the uterine body increase, which leads to compression of the pathways through which urine is excreted. As a result, urinary stasis occurs. This picture is especially often observed in women who have a relatively narrow pelvis.
Also, inflammatory kidney damage develops against the background of a decrease in ureteric tone, an increase in the size of the ureters, which is caused by hormonal changes occurring in the pregnant body. As a result, urinary stasis and active development and reproduction of pathogenic microbes occur. But with timely detection of the pathology, specialists are able to rid the pregnant woman of the pathology without harm or consequences for the child.
Pyelonephritis in pregnant women is a pathology that has an extremely adverse effect on fetal development and maternal health. In the absence of timely therapy, there is a high risk of developing complications such as sepsis and purulent-necrotic renal damage, and various types of obstetric complications. Quite often, women who have suffered from pyelonephritis during pregnancy will in the future develop chronic renal inflammation, nephrosclerosis or nephrolithiasis, hypertensive pathology, etc.
According to statistics, pyelonephritis is in second place in the frequency of extragenital pathologies in pregnant women. More often the disease is detected during the first pregnancy. Pathology usually manifests itself in the second half of gestation; periods of 24-26 and 32-34 weeks are considered critical. Therefore, a urine test during pregnancy is mandatory. Most often, pathology develops due to excessive activity of Proteus and Escherichia coli.
What tests are taken?
To make sure that the pregnancy is proceeding without pathologies, a visual examination and diagnostic studies (for example, ultrasound) are not enough. After all, many diseases can only be shown by blood tests, urine tests, and vaginal smears.
The list of tests that are required at the antenatal clinic is known to many:
A clinical blood test shows the content of basic cells in it (you can evaluate the number of immature forms, the leukocyte formula, and its shift), as well as the amount of hemoglobin (important for diagnosing anemia) and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (can increase during various processes in the body, accompanied by inflammation, and during pregnancy). A biochemical blood test allows you to assess the correct functioning of internal organs. A coagulogram evaluates blood clotting parameters. General urine analysis
Color, density, acidity and sediment are assessed. Screening for infections (HIV, hepatitis, syphilis). It is carried out at least 3 times during pregnancy, at registration, in the middle of the second trimester and a couple of weeks before giving birth. Determination of antibodies in the blood to infectious diseases that threaten the development of the child (toxoplasmosis, rubella). Blood test for chromosomal diseases (evaluated in conjunction with the data of the first screening ultrasound). Study of the hormonal background of a pregnant woman (hormones of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands) according to indications. A smear for microflora from the vagina, cervical canal, as well as a smear for oncocytology. Bacteriological culture of urine. Produced, as a rule, against pathogenic environments.
All these tests will allow timely detection of pathology in the mother, which can affect the development of the fetus.
What is bacterial seeding
Bacterial culture is a special laboratory diagnostic procedure in which a nutrient medium is selected for a particular type of bacteria, and then these bacterial microorganisms are grown on it. The entire process takes place under special temperature conditions. A similar study is carried out to determine the type of microorganisms living in the area from which the smear or liquid was obtained.
Diagnostics shows the presence of certain pathogenic bacteria, the number of their colonies, and also helps to calculate the sensitivity of microbes to certain antibiotics, which allows you to speed up therapy as much as possible and increase its effectiveness. Diagnostics must be carried out under special sterile conditions, then its reliability will be as accurate as possible. Only such an analysis allows today to obtain complete information about the patient’s health status.
Numerous studies have proven that almost half of infant mortality cases in the first weeks of life are caused by intrauterine infection. Microbes enter the fetal body from the mother's body, easily leaking through the placental protection. In most cases, pregnant women with fetal pathology also have latent urogenital pathologies. Infectious processes develop for quite a long time, and when conception occurs they are activated, which becomes a serious problem, fraught with fetal death. Therefore, urine culture during pregnancy is one of the most important diagnostic procedures that allows timely identification of a pathogenic pathogen.
Biomaterial for bacterial culture in pregnant women is taken from urine, vaginal mucosa or nose. Urine for pregnancy is taken twice: immediately upon registration for obstetric registration and at 36 weeks. If there are special indications, the study is carried out more often.
How is urine culture performed?
As is known, the urine of a healthy person contains various microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, etc.), including pathogenic ones, in a certain amount that does not exceed the maximum permissible values. As soon as, under the influence of any reasons (weakening of the immune system, entry of microorganisms into the body from the outside, etc.), pathogenic organisms begin to actively multiply, their number exceeds the permissible values, and an inflammatory process begins in the body.
When performing tank inoculation, a certain amount of analyzed urine is placed on a nutrient medium and kept for some time at a given temperature.
At the same time, the pathogenic organisms present in the analyzed sample begin to multiply. Based on the amount they reach after a given time, the laboratory technician determines whether there are excess amounts of any pathogenic microorganisms in the urinary organs or kidneys.
If any deviations are detected, the laboratory technician conducts additional studies on the resistance of existing microorganisms to various antibiotics to determine the most optimal medications for this case.
Carrying out this analysis takes much longer than it takes for a general urine test and other similar tests, since it takes several days to a week to grow certain microorganisms on a nutrient medium.
How long does the analysis take?
The main disadvantage of culture - the most accurate analysis - is the long wait for results, and during pregnancy there is no need for unnecessary worry. The reasons for this slowness are the additional need to establish the sensitivity of the infection to various antibacterial drugs and the workload of laboratory workers.
There is no exact figure. Each laboratory has its own deadlines set for research. Typically, bacterial urine culture takes 7-10 days in a local clinic. Paid laboratories are ready to provide results after 3-4 days.
How is urine culture done during pregnancy?
A urine inoculation tank is made as follows: a relatively small amount of biological material is applied directly to the nutrient medium. Then the test tubes are carefully placed in a special thermostat and left for a while. It is in the thermostat that ideal conditions are created for the reproduction and growth of bacteria.
Then the bacteria that are in the biomaterial under study will be determined, and the presence of pathogenic microorganisms among them will also be established. This analysis takes on average no more than 5 days. Bacterial urine culture will be carried out at least twice during pregnancy - the first time in the early stages and the second at the 36th week of pregnancy. In all cases, as soon as a pregnant woman is registered at the antenatal clinic, a urine culture is also prescribed to determine Staphylococcus aureus. If the expectant mother has kidney and bladder diseases, this test will need to be done a little more often. With the onset of pregnancy, hormonal changes occur, and certain physical changes are also observed, including dilation of the ureters. As a result, conditions are created for the development of various infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract. It is with the help of a urine culture tank that it becomes possible to identify the disease at an early stage, after which adequate treatment is prescribed. To obtain the most accurate result, during the process of collecting biological material for research, you must strictly adhere to several fairly simple rules:
- The material for analysis should be collected only in a sterile container; approximately the middle part of the first morning urine will be needed. It will be necessary to carry out hygiene of the external genitalia in advance.
- To get the most accurate result, urine collected for analysis must be submitted to the laboratory no later than an hour after collection.
- If a urine culture tank is given during pregnancy, the results will list all the microorganisms that are currently contained in the liquid being tested - protozoa, fungi, bacteria.
- Results will be determined in colony forming units per ml of liquid - CFU/ml. There is no need for treatment if a reading of less than 1000 CFU/ml is obtained. Provided that the resulting indicator is in the range of 1000-100000 CFU/ml, then this result is doubtful. If such a result is received, the doctor may order a repeat test.
- If the values exceed 100,000 CFU/ml, it means there is an infection or inflammation that requires immediate treatment. To determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to the medicinal drug, a study called an “antibactogram” will be carried out. Thanks to this study, the doctor will be able to prescribe the most effective treatment.
- Approximately three weeks after completing the prescribed medications, the woman should have a repeat urine culture to determine how effective the treatment was.
In order to obtain the most accurate analysis result, only morning urine is taken for research and collected only in a sterile container (can be purchased at any pharmacy).
Together with urine, all the end products of metabolism, as well as salts, excess fluid, enzymes, some hormones, and vitamins leave the body. Thanks to a general urine test, you can find out about the condition of both the kidneys and other organs (gastrointestinal tract, liver, heart). The reliability of the result will directly depend on the accuracy of compliance with the main conditions for collecting material for analysis:
- about a day before the test, it is forbidden to consume coloring foods, which include carrots and beets;
- the day before the test, you should avoid intense physical activity, as this may affect the level of protein concentration in the urine;
- the day before the test, it is prohibited to take not only diuretics and herbs, but also other medications;
- collected urine can be stored for no longer than 2 hours;
- before collecting material for analysis, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the external genitalia;
- For the study you will need at least 70 ml of urine.
How to get tested during pregnancy?
When collecting urine, a pregnant woman should cover the vaginal opening with a clean napkin during the procedure. In some cases, a sterile disposable catheter is used. This usually happens if the gestation period is significant.
It must be remembered that when preparing for the test, everyday hygiene procedures will not be enough. Additional measures have been developed:
- It is not recommended to use public toilets when taking the test.
- After each visit to the toilet, you must wash yourself using regular soap for children.
- Underwear or sanitary pads should be changed frequently.
- It will be better if the linen is made from natural materials. It is not recommended to use synthetics.
- Washed linen must be carefully ironed with a hot iron.
The need for analysis
Inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract occur quite often during pregnancy. The fact is that factors that provoke them often appear. These include:
- Decreased local and general immunity.
- Compression of the ureters in a pregnant woman by the uterus and a decrease in their tone under the influence of hormones.
- Impaired blood supply to the bladder, since during pregnancy there is a redistribution of blood flow in favor of the growing uterus.
All these changes lead to stagnation in the urinary system, the spread of flora from the vagina and anal canal through the urethra towards the kidneys. Inflammatory phenomena of the mucous membrane begin to manifest themselves with corresponding symptoms, and urine that has lost its sterility gives bacterial growth during the study.
Sowing during pregnancy and having it deciphered by a specialist will help prevent such a serious disease as pyelonephritis, which is accompanied by:
- Severe pain syndrome in the lumbar region.
- A sharp increase in temperature to 40 degrees.
- Symptoms of general intoxication of the body.
- Changes in the color and odor of urine.
This disease is dangerous because the fetus can be infected in utero. This sometimes leads to his death, which the mother may not even suspect for some time. If a miscarriage does not occur, then the fetal organs may suffer from those toxins that accumulate in the mother’s body during pyelonephritis and are able to penetrate through the placental barrier into the child’s blood. Such children are born with severe toxic damage to the liver, kidneys, and brain.
Taking antibiotics can have an extremely negative impact on the baby, without which it is simply impossible to cure pyelonephritis and restore the sterility of urine. Subsequently, such children will often experience dysbacteriosis, fungal diseases, pyoderma and allergic diseases.
As inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract progress, the filtration apparatus of the kidneys may be affected. This will lead to kidney failure, eclampsia and the need for emergency delivery, regardless of the stage of pregnancy, in order to save the life of both mother and child.
If a woman strictly follows all the prescriptions and recommendations of her doctor, takes all tests on time and correctly, and undergoes the necessary examinations, then she will certainly be able to avoid serious illnesses, maintain her health and give birth to a healthy and strong baby.
Physiological mechanisms leading to kidney inflammation
Poor culture results indicate the spread of infection in the pregnant woman’s kidneys. This is very dangerous for the expectant mother, as the filtration function of the organ is impaired. Kidney failure leads to a malfunction of the water-salt balance, to the retention of toxic substances and decay products in the body. During pregnancy, there is an increased risk of kidney inflammation, which is associated with physiological mechanisms.
Due to changes in hormonal balance, the muscle tone of the ureters decreases, and fluid stagnation occurs. Consequently, conditions are created for the development of pathogenic bacteria. Dilatation of the ovarian veins during pregnancy contributes to disruption of the outflow of urine. In the second trimester, the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the urinary tract, which also leads to congestion.
Women with a narrow pelvis are more likely to suffer from this disease.
Intrauterine infection
Kidney inflammation in a pregnant woman has a negative impact on the condition of the fetus and has a negative impact on the well-being of the expectant mother. The outcome of intrauterine infection depends on:
- type of bacterial pathogen;
- maternal immunity;
- integrity of the placental barrier;
- sensitivity of pathogenic microbes to fetal tissues;
- the period of pregnancy during which the infection occurred;
- presence of chronic diseases in women.
The main pathogens contributing to intrauterine infection:
- coli;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- enterococcus;
- mushrooms of the genus Candida.
Microorganisms from the group of parasites and viruses can also provoke developmental pathologies in a child:
- trypanosomes, trichomonas, toxoplasma;
- rubella, herpes, hepatitis, smallpox.
How to collect urine
Many women are interested in how to collect urine correctly? To obtain a specific result in pregnant women, urine donation must be carried out correctly. If certain rules are not followed, pathogenic bacteria can enter the urine, causing incorrect interpretation of the results during research.
Sterile urine is collected as follows:
- A cotton swab is carefully inserted into the vagina.
- The average portion of morning urine should be collected (it is during these hours that the concentration of pathogenic bacteria will be exceeded).
- The container with urine must be delivered to the center within the next 2 hours.
Urine for bacterial culture should be collected only in a sterile jar; it is advisable that it be purchased at a pharmacy, since it is almost impossible to sterilize it yourself at home. The woman also needs to wash herself, this will help prevent bacteria from getting into the jar she is using. To properly collect urine for culture, you first need to empty your bladder a little, and only then collect the liquid. These simple steps will help you avoid the wrong result.
How much urine do you need to give?
A urine test for sterility should be performed in the morning. Be sure to follow all recommendations when collecting material. A mandatory step is to wash with non-antibacterial soap and insert a tampon into the vagina. This will help to avoid the introduction of unnecessary bacteria, which could confuse the laboratory technician.
As mentioned earlier, you need to collect an average portion of urine (the first and last stream is released into the toilet). As a result of collecting the material, the jar should contain at least fifteen milliliters.
It is also important that the material must be sent to the laboratory immediately. No more than two hours should pass between collection and delivery. It is very important! In some cases, storing material in the refrigerator is permitted. However, urine must be delivered no later than six hours after collection.
Why take a urine culture test?
During pregnancy, research of this kind becomes one of the most important. Even if a general urine analysis reflects positive results, tank. culture can determine the chronic or asymptomatic type of infectious pathology of the genitourinary system. It is easier to stop the development of the disease than to treat its advanced form, risking the health of the baby or its loss.
Testing a pregnant woman's urine for bacteria helps:
- detect infectious pathogens;
- identify infections, identify their properties;
- carry out acceptable therapy, taking into account the stage of pregnancy. To do this, the susceptibility of the flora to antibiotics is determined;
- protect the fetus from infection and irreparable changes to its organs that are incompatible with the life of the fetus or newborn.
Testing a pregnant woman's urine for bacteria helps to detect pathology in time
Often pregnant women are affected by pyelonephritis, which develops through an ascending pathway or due to weakened immunity. The disease can provoke abortion or intrauterine pathologies of the fetus.
Actions in case of bad results
Bacteriological examination of urine is a reliable source of information about the health status of a pregnant woman. Thanks to this diagnostic method, doctors are able to detect the dangerous course of the disease in time, prevent it and minimize the risk of infection of the fetus.
A urine culture tank can show the presence of cystitis in a woman. The infection quickly affects the bladder and disrupts its functioning. The main causes of this disease are bacterial vaginosis, weakened immunity, and changes in hormonal levels. During pregnancy, cystitis must be treated without delay, because it is very dangerous for mother and child.
Poor urine culture results may also indicate inflammation of the urethra. This condition of a pregnant woman is caused by urethritis. Factors contributing to the development of the disease: urological infections, allergic reactions, impaired blood flow to the pelvic organs, lack of fluid, insufficient intimate hygiene.
The infection threatens to complicate the course of pregnancy, leads to various pathologies of fetal development and the occurrence of placental insufficiency. During childbirth, the baby, passing through the inflamed tract, may develop pneumonia or conjunctivitis. Urethritis is treated with gentle but quite effective drugs.