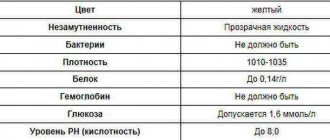
Tests for pregnant women Urine tests
07/11/201801/24/2019 Chernenko A. L. 1201 Views pregnancy, sugar, diabetes mellitus
In this article we study sugar in urine during pregnancy. Glucose in urine during pregnancy is one of the most important and mandatory tests, allowing timely detection of the development of such a dangerous condition as gestational diabetes in pregnant women.
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is the most common type of metabolic disorder in pregnant women. Despite modern treatment methods, this condition is accompanied by a high (about eighty percent) rate of complications in pregnant women and the fetus.
The term gestational diabetes mellitus refers to hyperglycemia that first appeared or was detected during pregnancy. In the absence of timely treatment, GDM can cause the development of severe gestosis of pregnancy, termination of pregnancy, severe asphyxia of the child, etc.
Timely determination of sugar in the urine during pregnancy makes it possible to identify the development of GDM in the early stages and begin comprehensive treatment aimed at preventing the development of complications.
- 1 Glucose levels during pregnancy
- 2 Normal levels of sugar in urine during pregnancy
- 3 Sugar in urine during pregnancy - causes and consequences
- 4 Which doctor treats endocrine disorders in pregnant women?
- 5 What are the dangers of high sugar during pregnancy?
- 6 Sugar in urine during pregnancy - what are the symptoms?
- 7 What treatment is required?
Norms
The results of a laboratory test of urine for glucose levels are assessed according to three criteria:
- sugar content less than 1.7 mmol/l is normal;
- from 1.7 to 2.7 mmol/l - permissible glucose level;
- more than 2.79 - sugar is above normal, glucosuria.
It turns out that sugar in urine during pregnancy should not be higher than 2.7 mmol/l. If glucose in the urine of an expectant mother increases for the first time or its amount is slightly higher than normal, there is no need to panic. This does not always indicate the presence of the disease, so it is better to retake the tests and listen to the recommendations of the attending physician.
Why does glucose appear in urine?
When sugar is determined during general and biochemical urine analysis, the presence of glucosuria is indicated. It is possible in two cases.
- In the first case, sugar increases in the blood so much that the kidney tubules are simply unable to absorb such an amount from the urine. The critical level for the appearance of glucose in urine occurs when blood levels are 8.8 -8.9 mmol/l. Although it may be lower than these values in some kidney diseases.
- In the second case, the cause of glycosuria is the inability of the kidney tubules to properly reabsorb sugar.
Causes of increased sugar in urine
During filtration, glucose from the primary urine is almost completely returned to the blood, so it is not normally found in the secondary urine that is excreted.
The appearance of sugar in the urine during pregnancy can have various reasons:
- presence of diabetes mellitus - true or gestational;
- endocrine disorders, for example, hyperthyroidism;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- traumatic brain injury causing metabolic disorders.
Of the listed reasons, most often the pathology lies in the kidneys. In this case, glucose increases only in the urine, and blood tests show normal levels.
Sometimes the reasons for the appearance of blood sugar during pregnancy lie in poor nutrition, for example, overeating or excess consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates. In this case, it is strongly recommended to adjust your diet.
There are also factors that can increase your risk of developing diabetes during pregnancy. These include:
- woman's age over 30 years;
- development of gestational diabetes in previous pregnancies;
- more than three miscarriages or a history of stillbirth;
- the birth of a child with gross malformations from a previous pregnancy;
- a child from a previous birth had a birth weight of more than 4.5 kg;
- multiple births;
- polyhydramnios;
- hereditary predisposition to diabetes.
If the expectant mother has one or more risk factors, she is advised to consult an endocrinologist and carefully monitor her sugar levels during pregnancy. It should be noted that in 97% of women, gestational diabetes goes away after childbirth, and in only 3% it turns into chronic diabetes. Read more about gestational diabetes →
What affects sugar levels?
It has long been a known fact that while carrying a child, the load on the female body increases several times, hormonal levels change and the functioning of some systems becomes more complicated. All this is certainly reflected in biological fluids, so the test results of pregnant women often contain various deviations.
If sugar or glucose is detected in the urine during pregnancy, then this condition (glucosuria), depending on the level of concentration, requires at least careful monitoring and, at a maximum, appropriate therapy.
In the normal state, sugar in the urine is practically absent or contained in small quantities. And if sometimes its presence is detected during pregnancy, then this cannot be considered a manifestation of diabetes mellitus.
Moreover, in almost half of expectant mothers in the 2nd or 3rd trimester, the results of a urine test reveal an increase in glucose concentration, which is called gestational diabetes, or diabetes during pregnancy. In most cases, this pathology goes away on its own immediately after childbirth, without requiring medical intervention.
Most often, gestational diabetes develops due to increased stress on the body, due to which the latter is not able to respond to incoming glucose as before. More specifically, the pancreas becomes unable to produce enough insulin to utilize excess sugar, so the body must excrete it in the urine.
This obstacle is created by hormones that begin to be produced by the placenta, and from 20-24 weeks of gestation and block the effects of insulin. High glucose levels simultaneously disrupt both metabolisms - both mother and fetus. The fact is that sugar penetrates through the placenta into the child’s circulatory system, which means it requires increased activity from his pancreas.
Therefore, the organ is subjected to increased stress, forced to produce more insulin. Excess insulin makes it possible to absorb excess glucose, turning it into fat, which helps to increase the weight of the fetus to a large size.
Reference! A child's accelerated metabolism requires a larger volume of oxygen, but its supply is limited. As a result of such disorders, the fetus experiences a constant lack of oxygen, and as a result, hypoxia develops.
In addition, during pregnancy, the kidneys also often suffer from increased stress. During their normal functioning, glucose first passes through the renal filter and enters the primary urine, and then is absorbed back into the blood through the renal tubules.
Therefore, sugar is no longer detected in secondary urine. If the kidneys do not cope with their task, then part of the glucose is not absorbed, but remains, which makes it possible to detect it during analysis. Most often, this condition develops in the third trimester.
Glucosuria is most common in late pregnancy
Is it dangerous?
If a woman’s condition is ignored and the necessary treatment is not carried out, the disease can have serious consequences. Glucosuria can negatively affect not only the general well-being and health of a woman, but also the condition of her unborn baby.
Complications of gestational diabetes include:
- blurred vision;
- kidney problems;
- arterial hypertension;
- swelling and numbness of the limbs, pain in the legs;
- development of gestosis, preeclampsia.
But the most severe complication of glucosuria for the expectant mother is fetal macrosomia, that is, a pathological increase in its body weight and height. The course of natural childbirth can be complicated by the large size of the baby - the weight of such newborns is usually more than 4.5 kg, which can cause difficulty in removing it during pushing.
For the mother, fetal macrosomia can result in premature onset of labor, uterine bleeding and injuries to the birth canal. The baby is at increased risk of developing birth injuries. This situation does not have any absolute contraindications to natural childbirth, but most often delivery is carried out by cesarean section. Read more about the pros, cons and consequences of a cesarean section →
Also, consequences for the fetus against the background of glucosuria during pregnancy can include neurological disorders in the future, pathologies of the respiratory system and jaundice, and, less often, mental retardation. To avoid this, a pregnant woman needs to undergo tests in a timely manner and regularly visit a doctor at the antenatal clinic.
Negative consequences
Sugar by itself in urine cannot harm the fetus. It can have a bad effect on the health of the fetus when there is a lot of it in the blood. Glucose is one of the substances necessary for the development of the baby, and penetrates through the placenta into his blood.
Macrosomia
- Hyperglycemia leads to the development of fetal macrosomia (pathological increase in its weight and height).
- Damage to organs of various physiological systems (cardiovascular, bone, central nervous, etc.) is observed.
- Perinatal mortality is high (death of the fetus or newborn from the 22nd week of pregnancy to seven days after birth).
Pregnancy with hyperglycemia occurs with complications (miscarriages, polyhydramnios, late toxicosis), which most negatively affects the woman’s health.
Insulin
Symptoms
It is possible to accurately determine the sugar content in urine only in laboratory conditions. But a woman can notice the first signs of the disease on her own; to do this, it is enough to be attentive to her health.
Symptoms of renal glycosuria during pregnancy are:
- increased thirst, constant dry mouth;
- frequent urination;
- increased blood pressure;
- unexplained fatigue, drowsiness;
- weight changes, often upward;
- increased appetite.
These symptoms may not specifically indicate diabetes, but they should not be ignored. You should inform your doctor about any changes in your health.
Symptoms of glycosuria
Its main symptom is polyuria or increased urine production. It is considered normal when the daily volume of urine excreted in an adult is in the range of 1000-1200 milliliters. With polyuria, this volume increases to two liters, in some cases it can reach three. Urination becomes more frequent.
When glucosuria is the result of high blood sugar, other typical diabetic symptoms are added (diabetes causes the largest percentage of glucosuria). These include:
- constant thirst;
- increased appetite;
- skin problems (boils, dryness, itching, poor wound healing);
- fatigue and feeling of weakness;
- decreased vision;
- cramps of the calf muscles.
Which doctor should I contact if my urine sugar level increases?
If the concentration of glucose in the urine during pregnancy is higher than the normal level, the gynecologist at the antenatal clinic will prescribe additional tests for the patient: a blood test for sugar levels and determination of daily diuresis. With the results of these tests, he refers the pregnant woman for a consultation with an endocrinologist.
The specialist conducts a comprehensive examination, finds out the cause of the disease, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, prescribes treatment. Gestational diabetes should not be ignored, as this condition is dangerous for both the woman and her unborn child. In addition, glucosuria during pregnancy is dangerous for the development of true diabetes in the future.
What are the dangers of high sugar during pregnancy?
Gestational diabetes mellitus is accompanied by the development of such severe complications as:
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- late gestosis of pregnancy (preeclampsia and eclampsia);
- fetal shoulder dystocia and clavicle fractures during childbirth (these complications are caused by the large weight of the fetus);
- severe fetal asphyxia;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- hyperinsulenism and postnatal hypoglycemia in the baby;
- neurological disorders in the baby;
- distress syndrome in a newborn;
- increased risk of perinatal mortality;
- development of Erb's palsy in a child;
- hyperbilirubinemia;
- polycythemia;
- development of diabetic fetopathy (high weight of the fetus, enlargement of its liver and spleen, heart damage, the appearance of edema, etc.), etc.
It should also be noted that half of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus subsequently develop type 2 diabetes mellitus.
With the development of diabetic fetopathy, the child has a high risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, an endocrinologist prescribes a general blood test called a “sugar curve.” This test shows the body's sensitivity to glucose and makes it possible not only to determine the amount of glucose in the blood, but also to consider how the body reacts to a sugar load.
The study is carried out in several stages after the 24th week of pregnancy. The procedure is done on an empty stomach and 2 hours after drinking water with diluted glucose. If the amount of sugar in the blood during pregnancy is normal, but its amount in the urine remains elevated, we are talking about disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, and not about diabetes. If sugar is really elevated, treatment is necessary. Read more about normal blood sugar levels during pregnancy →
Pathological glycosuria
Such glucosuria develops for reasons that are either extrarenal in origin or renal (renal).
Extrarenal pathologies
These include diseases that develop outside the kidneys. The group of such pathologies includes diabetes mellitus (DM). There may be two types during pregnancy. The first type is true diabetes, which was present before pregnancy, but, for example, proceeded in a latent form and was not diagnosed for one reason or another.
The second type is gestational, which is associated exclusively with pregnancy.
Insulin is the main regulator of carbohydrate metabolism
True diabetes
There are two types of it: insulin-dependent and insulin-resistant.
- The first type occurs when the pancreas (PG) loses the ability to produce the required amount of the hormone insulin, which is the main regulator of carbohydrate metabolism. A deficiency of insulin in the blood increases the concentration of glucose in it.
- The second type develops when there is enough insulin, but the tissues lose sensitivity to it. This happens, for example, with obesity. The fat layer becomes a barrier that prevents the interaction of the hormone and tissues.
Pregnant women with diabetes should be under special medical supervision from early pregnancy until later, or rather until the birth of the child. It is advisable for such patients to have a glucometer at home that allows them to monitor glucose at home.
Gestational diabetes is possible only during pregnancy
Gestational diabetes
It develops in pregnant women who have not previously had any abnormalities in blood sugar. In most cases, it goes away after childbirth, but can progress to insulin-resistant type diabetes.
There is no single point of view regarding the etiology of the gestational type among specialists; most experts are inclined to the hormonal version. Hormonal changes and shocks in the body raise glucose in the blood, and the pancreas cannot cope with the increased production of insulin.
Other extrarenal causes
Extrarenal glycosuria can also be caused by:
- acute pancreatitis;
- pathologies of central origin (meningitis, hemorrhagic stroke, brain tumors, etc.);
- some endocrine diseases (hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, etc.);
- febrile conditions;
- exposure to toxic substances.
Renal pathologies
There are primary and secondary glycosuria.
- Primary glycosuria, also called renal diabetes, occurs when the mechanism of sugar reabsorption in the proximal tubules of the kidneys is disrupted.
- The secondary form of pathology develops in various kidney diseases (chronic pyelonephritis, glycogen storage disease, acute renal failure, etc.).
Treatment
Despite the fact that glucosuria in expectant mothers is in most cases a temporary phenomenon, ignoring it is very dangerous. Timely detection of an increase in sugar levels in urine and blood during pregnancy and additional research can quickly identify the cause of the disease and make an accurate diagnosis. There is usually no need to take medication for gestational diabetes.
The basis of treatment is adherence to a diet, thanks to which glucose in the urine during pregnancy will be maintained at an optimal level. To do this, the expectant mother should limit her consumption of sugar, salt, sweets and honey as much as possible.
It is recommended to follow the principles of separate nutrition, that is, not to combine the consumption of fats and carbohydrates during one meal. You also need to avoid fast food, potatoes, and baked goods as much as possible. It is advisable to consume more non-starchy fruits and vegetables rich in fiber.
In addition to diet, glucosuria requires giving up a sedentary lifestyle. Physical activity also lowers sugar in the urine and blood. Hiking, light gymnastics, swimming - all this not only improves a woman’s well-being, but also strengthens her health, relieving lower back pain, constipation and sleep disorders, which often affect pregnant women.
In some cases, diet and exercise cannot adequately reduce glucose levels in the body, so the endocrinologist prescribes special medications to the woman. Insulin injections are usually prescribed.
There is no need to be afraid of drug treatment, since, firstly, insulin does not penetrate the placental barrier to the fetus, and, secondly, after childbirth, the woman’s body returns to normal and the need for the drug disappears. Despite this, the woman will need monitoring from an endocrinologist even after the birth of the baby in order to prevent the development of possible complications.
Symptoms
An accurate determination of glucose in urine is possible after laboratory tests. But the presence of the first signs of problems in a woman can be traced independently.
Signs of renal glucosuria in pregnant women:
- constant consumption of fluids, as dry mouth is noticeable;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- blood pressure increases;
- general malaise in the form of drowsiness and fatigue;
- sudden weight gain;
- taking carbohydrates in large quantities.
These initial signs are not direct evidence of diabetes, but you need to pay attention to them to prevent complications. For this purpose, the doctor must fully monitor the well-being of the expectant mother.
Forecast
If elevated sugar is detected in the urine during pregnancy, in most cases the situation has a positive prognosis. In 97% of women, gestational diabetes goes away on its own shortly after giving birth. This situation is not uncommon, so there is no need to panic.
If the cause of increased sugar in the urine in pregnant women is any disease, the prognosis is generally positive. Properly selected treatment can eliminate most pathologies.
Of course, you will have to maintain the amount of glucose at a normal level throughout pregnancy. To do this, the expectant mother will need to follow a special diet. Strict adherence to all medical recommendations will avoid complications.
Author: Olga Rogozhkina, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for Mama66.ru
Diagnosis of high sugar in urine
It is difficult not to notice glucosuria: before each visit to the gynecologist, the expectant mother takes a general urine test - it reveals the sugar level.
However, if alarming signs appear between visits to the doctor, a woman can check the secreted fluid herself - using test strips: the strip is immersed in a container with a fresh portion of urine, the end is painted a certain color, which is compared with the color indicators on the packaging scale.
Pharmacies sell test strips that make it easy to determine the level of sugar in urine without leaving home.
It is possible that to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will also prescribe:
- daily sugar loss test; during the day, starting at 6 a.m., the patient walks little by little into a sterile container; then the resulting liquid is mixed, 100 ml is poured separately and submitted to the laboratory; you must also indicate the total amount of urine excreted per day;
- Zimnitsky test (if kidney inflammation is suspected) - shows how sugar levels change during the day; 8 containers are filled with urine every 3 hours, the containers are stored closed in the refrigerator, and after collecting the biomaterial they are taken for research;
- test for the body's tolerance to glucose - in this case, blood is taken from a vein, twice with an interval of two hours, after the first blood draw the woman drinks syrup; if it is found that the body copes with the absorption of glucose, then the problem is not diabetes, but problems with the kidneys or liver.
How to pass a general urine test correctly
To reduce the likelihood of an erroneous result, follow these rules:
- during the day before collecting biomaterial, exclude from your diet spicy foods, smoked foods (they are not recommended for pregnant women at all), as well as fruits and vegetables of bright colors that color the urine and increase sugar in it - for example, tomatoes, beets;
- do not take diuretics or herbal decoctions for swelling on the day before the test;
- do not be nervous, do not subject your body to heavy physical activity; do not go to the sauna or bathhouse;
- the analysis is taken on an empty stomach;
- in the morning, before collecting urine, wash yourself and blot your external genitalia with a clean towel; the fact is that there is a protein on the vaginal mucosa, which, if hygiene is not observed, gets into the urine and distorts the test results;
- flush the initial portion of urine down the toilet, collect the rest (100–150 ml) in a sterilized glass jar or disposable container;
Sterile plastic containers for collecting urine are sold in pharmacies; sometimes they are given to patients along with a referral for a general urine test
- When collecting liquid, the container should not touch the skin.
Hurry up with the delivery of biomaterial to the study site; Urine for analysis can be stored for no more than two hours.
Why do glucose levels drop during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, glucose levels may also decrease. This condition is no less dangerous for the mother and fetus. The main threat is the lack of energy to properly maintain the functioning of the mother’s body and the development of the child.
Reasons for low glucose in pregnant women:
- lack of protein and glucose in the daily diet of a pregnant woman;
- early or severe toxicosis;
- increased physical activity;
- fasting or eating small portions with long breaks;
- sweet carbonated drinks. They provoke a rapid but short-term increase in glucose. As a result, not all of the insulin is used to metabolize sugar. Its increased amount leads to a decrease in glucose levels;
Glucose levels in pregnant women increase with the consumption of fast carbohydrates, such as sweet sodas. - dysfunction of the liver and pancreas;
- the presence of a tumor of any etiology.
The presence of these reasons should also be reported to the gynecologist. Their timely elimination will avoid a drop in glucose in the blood of a pregnant woman.
Normalization of glucose levels at elevated levels
If the glucose concentration in the tests increases, a complex of therapy is prescribed by the endocrinologist. Taking into account the woman’s position, gentle therapy is selected. It consists of taking medications, using folk remedies and following a diet.
Drugs for pregnant women
During pregnancy, insulin is used to reduce sugar levels. It is harmless to mother and child and allows you to quickly normalize glucose concentration.
The drug is administered intramuscularly using a pen syringe. The dosage is selected taking into account the amount of glucose in the analysis. To do this, you need to purchase a glucometer. The measurement is taken after waking up, before eating and 2 hours after eating. And also before bed.
The use of glucose-lowering tablets is prohibited. They disrupt the formation and development of the fetus. The rules for using the glucometer and calculating the dosage are explained by the treating specialist.
Folk remedies
You can normalize the concentration of sugar by using folk decoctions and infusions.
Recommended recipes:
- infusion of white mulberry bark and leaves. You need to place the prepared mixture (40 g) in 400 ml of boiling water. After 2 hours you can use it. The infusion is divided into 3-4 doses and drunk during the day;
- A decoction of unpeeled oats. Boil 20 g of oats in 300 ml of water for 15 minutes. The decoction should be drunk throughout the day. Consume before meals;
- Decoction of blueberry leaves. Place 20 g of crushed leaves in 200 ml of boiling water and cook for 4 minutes. The product is divided into 2 doses. Consume before meals;
- Infusion of bay leaf. Place 10 laurel leaves in 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 24 hours in a thermos. Consume before meals. The serving is divided into 4 doses;
- Tea made from dry or fresh currant leaves. Steam like regular tea. Drink no more than 300 ml of this tea during the day.
When selecting products, it is necessary to take into account the likelihood of allergic reactions. And also some decoctions may have a diuretic effect, which is not desirable for a pregnant woman. It is recommended to discuss the choice of funds with a specialist.
Diet
The glucose level in pregnant women depends on the diet. Diet is a necessary condition for maintaining sugar in the required concentration. Meals should be in small portions and at regular intervals.
A woman should eat in portions, but not overeat. Lack or excess of food provokes changes in sugar in the body. A light dinner before bed is required. It is recommended to create a menu together with an endocrinologist for a week.
A pregnant woman's diet should consist of the following products:
- meat (beef, poultry);
- fish and other seafood;
- non-sweet dairy products;
- nuts, but in limited quantities;
- vegetables and fruits in any form.
Quickly digestible carbohydrates and sweet foods are excluded from the menu. The drinking regime is also limited to 2 liters per day. Fatty, salty and spicy foods are excluded, as they increase thirst.
Treatment of glycosuria
Treatment of glycosuria is aimed at eliminating the concomitant disease, and not the symptom itself. The main goal is to lower sugar levels to acceptable levels that will not harm the pregnant woman and the fetus.
Since glucosuria is accompanied by an exacerbation of the disease, appropriate short-term therapy is possible: administration of insulins, review and adjustment of doses of drugs used, etc. The use of multivitamins is also indicated.
Traditional methods of treatment are also beneficial, such as taking decoctions of raspberries, parsley root, dandelion, nettle, and birch buds.
Consequences of glucosuria
High sugar levels in the urine threaten the expectant mother:
- the formation of blood clots - due to diabetes, the speed of blood flow decreases, blood stagnates in the vessels;
- gestosis - if the level of estrogen is also reduced;
- miscarriage or miscarriage;
- complications during childbirth; Thus, a fetus that is too large has difficulty moving through the birth canal, and a woman will inevitably experience ruptures and large blood loss; It happens that the size of the baby does not correspond to the woman’s pelvis and a caesarean section is inevitable.
For a child, maternal glycosuria can result in:
- macrosomia - excess weight (more than 4.5 kg); after birth, metabolic disorders and the development of diabetes are possible;
- hypoxia (lack of oxygen); diabetes in a woman leads to polyhydramnios, which makes it difficult for oxygen to reach the fetus; Also, if there is an excess of amniotic fluid, the baby is often wrapped in the umbilical cord; during childbirth, the child can suffer asphyxia - suffocation;
- pathologies of internal organs - the heart, blood vessels, nerves, vision suffer;
- mental retardation;
- jaundice - due to high levels of the bile pigment bilirubin in the blood.
What are the dangers of gestational diabetes for a woman?
High sugar in the urine during pregnancy leads to the destruction of tissue of the placenta and ovaries, which can have serious consequences for mother and child. The production of the hormone estrogen is disrupted, and late toxicosis develops. Typically, this condition is diagnosed after the 20th week of pregnancy. In addition, women experience severe swelling, increased blood pressure, and rapid weight gain.
What are the dangers of high blood and urine sugar during pregnancy, and how dangerous is an increased level of glycemia? A high concentration of glucose causes aging of placental tissue, oxygen deficiency occurs, and fetal nutrition is disrupted. This can lead to spontaneous abortion or congenital abnormalities of the child.
Increased sugar in the body during pregnancy negatively affects the amniotic membranes, and polyhydramnios occurs as a negative consequence. The baby may take an incorrect position before birth, and the umbilical cord will be torsioned, which can lead to fetal hypoxia. If these abnormalities are detected, women undergo a caesarean section.
If a pregnant woman has constantly elevated blood sugar, metabolic processes are disrupted, the fetus grows very rapidly and reaches large sizes exceeding 4 kg. During the passage of the child through the birth canal, injury to the baby and mother can occur. To avoid complications, patients are prepared for caesarean section.
Gestational diabetes during pregnancy can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes, so women are at risk. They are recommended to be examined every 3 years for glycemic levels and impaired tissue sensitivity to insulin.
Women who already had diabetes before pregnancy are at risk of developing complications. The genitourinary system is often damaged, pyelonephritis, acute cystitis occurs, the functioning of the heart and blood vessels is disrupted, and vision is greatly deteriorated.
When does the risk of developing gestational diabetes increase?
- Age after 30 years (the tendency to diabetes increases with age)
- Body mass index (BMI) 30 or higher
- Having a large baby (weighing 4.5 or more) after a previous pregnancy
- History of gestational diabetes
- The presence of a disease - diabetes mellitus (is a separate condition - pregnancy with diabetes mellitus)
- Problems during previous pregnancies (frequent miscarriages, unknown causes of dead fetus, birth defects in children)
- Urinary tract inflammation
- Multiple pregnancy
Prevention
Prevention measures will help protect against high sugar levels during pregnancy. They consist of regularly undergoing urine and blood tests so that sugar does not increase.
Doctors advise women to eat right and pay attention to weight gain throughout the entire period of bearing a child. A woman is advised not to neglect physical exercise and do special exercises daily.
To avoid this, it is necessary to inform the antenatal clinic doctor about any, even minor, deterioration in the condition. If there is a recommended diet, you must strictly adhere to it.
A pregnant woman should undergo basic tests regularly. Light exercise and monitoring changes in body weight can help control glucose levels in the blood and urine.
If during pregnancy excess weight and unbalanced nutrition cause impurities in urine, then these parameters require urgent correction.
Some patients have a genetic predisposition to developing such problems. For example, diabetes is transmitted through the female line, so if you have sick relatives, it is important to take your health as seriously as possible, and not only while pregnant.
To minimize the risk of traces of glucose appearing in tests, you need to build the right diet. So, carbohydrates should be evenly distributed and consumed throughout the day. Proper nutrition is the main element of successful prevention.
It is recommended to eat 6 times a day: three medium portions and three small ones. 1-2 light snacks are possible, which are also included in the six meals. A smaller amount of carbohydrates is recommended than in normal life. The basis of nutrition should be complex carbohydrates and foods rich in fiber.
Skipping meals is highly undesirable. Following a diet will significantly reduce the load on the pancreas and virtually eliminate the release of sugars in urine.
A hearty breakfast includes nuts, eggs, cheese, but fresh fruit and bread should be limited. The emphasis is on increasing the amount of fiber entering the body.
Physical activity plays an important role in maintaining optimal glucose levels. Regular exercise will help prevent high blood sugar levels.
To avoid the appearance of sugar in the blood, it is necessary to carry out its prevention in a timely manner. The patient requires an even intake of carbohydrates throughout the day. A balanced diet for the fairer sex will limit the possibility of pathology occurring. A woman should eat six meals a day. Portions should be medium to small in size.
A woman is allowed to take carbohydrates in minimal quantities. The patient's snacks should contain foods that contain large quantities of fiber. A pregnant woman should eat without skipping meals. This will make it possible to reduce the load on the pancreas and eliminate the possibility of sugar in the blood.
A woman should have a hearty breakfast, which will help maintain blood glucose levels. A pregnant woman's diet should include porridge, bread, milk and fruit in minimal quantities. It is best to eat protein-rich foods - cheese, butter, nuts, eggs. A woman's daily diet should consist of fiber.
A woman should remember about feasible physical activity. Doctors recommend regular exercise. It is also necessary for the fairer sex to walk in the fresh air every day, regardless of the time of year.
Sugar in the urine is quite common in pregnant women. This pathological condition is characterized by the presence of pronounced symptoms.
When the first of these appear, a woman should seek help from a doctor. Treatment of the pathology consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, as well as regular monitoring of blood sugar levels.
After the birth of a child, the situation for the representative of the fair half of humanity stabilizes.
Treatment methods
What to do if you find high sugar during pregnancy, how to lower the level of glycemia in the blood of a pregnant woman? The doctor prescribes a low-carbohydrate diet, physical activity, and strictly monitors glycemic parameters.
How can you lower blood sugar during pregnancy? Meals should be fractional, you need to follow a sleep and rest schedule, most of the diet should consist of fresh vegetables, fruits, dietary meats, and fish. Calorie content is calculated based on 30 kcal per 1 kilogram of body weight.
What foods increase blood sugar in pregnant women, and what lowers glycemia during pregnancy? The prohibited category includes foods containing light carbohydrates that are quickly digested and enter the bloodstream. These are sweets, white bread, semolina, rice, grapes, banana, fruit juices, fresh juices, raisins, dates, alcoholic drinks. It is useful to eat cabbage, buckwheat, pearl barley, wheat, all green vegetables, most fruits, and dairy products. When prescribing therapy, the endocrinologist will help create a diet for the expectant mother.
If such measures do not help reduce hyperglycemia, regular insulin injections are prescribed. The dosage is determined by the doctor.