Many kidney diseases occur with excessive accumulation of protein molecules in the secretions, which normally should not be there. In this case, proteins begin to accumulate in the tubules of these organs, gradually enveloping them from the inside. As a result, special elements are formed, each of which is shaped exactly like a renal tubule, since it is its copy or cast. These formations are called cylinders.
In addition to protein, blood components can be detected in their composition - red or leukocytes, fat molecules and epithelial tissue cells. Today we will discuss what the appearance of casts in the urine means, and what diagnostic significance the formation of these components in the secretions has.
What are cylinders - general information
These particles are formed from protein and various cellular structures. They are part of numerous inclusions that together form urine sediment. The cylinders necessarily have a characteristic shape, but in size they can differ significantly from each other. Doctors call an increase in the amount of such elements in the patient’s fluid secreted by cylindruria.
A prerequisite for the formation of cylindrical elements is the high acidity of urine. When the pH of the secreted liquid deviates too sharply towards the acidic side, a large number of such components are detected in the fresh sediment. But the presence of casts in urine with an alkaline reaction is extremely rare. In addition, the increased concentration of colloidal particles (including proteins) and the surface tension of the secretions play a significant role in the formation of these structures.
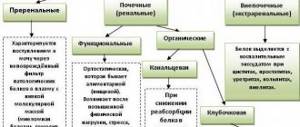
These components are divided into two types - false and true. The first type includes leukocyte, urate and mucous elements. True casts in urine:
- lipid (fat);
- hyaline;
- waxy;
- granular;
- pigmented;
- epithelial;
- red blood cell particles;
- cylindroids.
There are many cylindrical particles. They are divided into types, each of which appears only with a specific disease. And only hyaline casts are almost always present in the urine of healthy people, but in small concentrations.
The norm for a healthy person of any age is to contain a small number of hyaline casts in urine - only 1-2 bodies in the field of view of the microscope. Other similar components should not be present at all in normal urine. If quite a lot of cylindrical elements (including hyaline) appear in the discharge, this is already a sign of pathology.
Important! The most threatening is the formation of such components in the secretions of pregnant women. For them, the normal indicators are the same as for other patients - this is 1 or 2 hyaline elements in the field of view. These values may increase slightly with stress, toxicosis, physical activity and nephropathy.
Causes of the disease
Cylindrical structures are formed from protein or other cellular and biological elements (non-protein forms). The presence of cylinders in the biofluid indicates the development of a pathological process in the kidney associated with impaired functionality. For the formation of cylindrical molecules, the following conditions are required:
- high amount of protein in urine;
- acidic pH of the biofluid (in an alkaline environment, cylindrical structures are not formed).
Normally, only small amounts of hyaline proteins may be present (traces).
The reasons for the appearance of the elements include prolonged physical or emotional stress, a long diet with a predominance of food containing animal protein. Cylindrical elements appear not only with nephritis (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis), but as a result of infectious diseases, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, severe intoxication with poisons and drugs.
Appearance of hyaline casts
Such pathological casts in the urine are formed from specific proteins that are synthesized by the epithelial tissue of the renal tubules. They are easy to determine by microscopic examination of the sediment of the secreted liquid. These are colorless, transparent or translucent particles with regular, rounded tips.
Most often, these components are detected in the male half of the population. In them, the reason for the formation of hyaline cylinders in the urine is the presence of a large amount of meat in the menu. This is a protein food that causes natural proteinuria and significantly increases the acidic pH of the secretions. These inclusions appear in large quantities after hard work or sports.
Similar elements are often found in the urine of children. An increased content of hyaline casts in the urine of a child indicates infectious pathologies that do not have a direct effect on the kidneys. Basically, these are well-known childhood diseases:
- measles;
- chicken pox;
- polio;
- mumps (colloquially mumps);
- whooping cough;
- rubella.
Education mechanism
During plasma filtration, substances that enter the kidneys are either excreted (removed) from the body or reabsorbed into the blood. Regulation of selective excretion and selective absorption occurs due to nervous and humoral mechanisms. All of them have an impact on:
- tone of glomerular arterioles (through regulation of volumetric blood flow and filtration pressure);
- mesanginal cell tone;
- activity of the absorptive function of specialized cells - podocytes.
Substances retained in the tubules stick together, forming cylindrical conglomerates. Therefore, the formation of cylinders is preceded by:
- inhibition of absorption;
- decrease in the rate of passage of urine through the tubules;
- excessive permeability of the septa of the glomeruli of the kidney (normally, proteins should not penetrate into the cracks). Occurs when it is destroyed or inflamed.
A decrease in urine flow rate may occur with:
- heart failure;
- renal artery stenosis;
- a decrease in the lumen of the tubules due to inflammatory or tumor processes.
Long-term retention of substances that can stick together to form cylinders can occur when:
- poisoning;
- infections (high body temperature plays the main role);
- taking a number of medications (for example, antibiotics, Aspirin).
As mentioned above, casts in the sediment are formed when there is a high level of protein (proteinuria) and acidic urine.
Grainy or granular elements
These components in the secreted liquid are formed by protein molecules. In an acidic environment, proteins stick together and epithelial cells adhere to their surface. They die or change as a result of degeneration of the kidney tubules. This is how granular casts appear in the urine. Unlike hyaline bodies, granular inclusions are much darker in color and less transparent.
Granular formations in urine are formed as a result of pathological processes that are characterized by damage to small renal tubules and an increase in protein concentration in the secretions:
- Nephropathy caused by diabetes mellitus.
- Glomerulonephritis in the chronic stage.
- Amyloidosis of filtering organs.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Infectious diseases occurring with an increase in temperature.
Hyaline (grainy) casts in the urine of a child
If a patient has casts in the urine, what does this mean? The attending physician will answer this question. Looking ahead a little, it should be noted that we will be talking about the renal tubules, since urine is produced there.
What do casts in urine mean?
The kidneys play an important role in the human body - the role of filters. They are located in the lumbar region and are connected to arteries, veins and drainage tubules through which urine enters the bladder. The kidneys cleanse the blood, maintain salt balance and the ratio of other substances needed by our body.
These organs have a complex structure, but they act very effectively. They consist of many small capillaries - nephrosis, woven into glomeruli, which have afferent and efferent arterioles.
Primary urine is formed in Bowman's capsule, which is similar to a cup. Each kidney consists of one million nephrons. They are connected to each other so tightly that if they were stretched out in length, it would be equal to the length of 5 thousand cars lined up in a row.
Nephrons purify the blood entering the glomeruli. A renal artery approaches each kidney, through which blood is pumped and flows back through a vein. What remains is purified fluid, which enters the renal tubule. The walls of the tubule absorb substances that are beneficial to our body. And the residual liquid turns into urine, in which breakdown products unnecessary for the body remain.
All toxic substances are eliminated from the human body by the kidneys through the urinary tract. The liquid containing this waste is urine. During the day, the kidneys filter 100-200 liters of liquid (primary urine).
To begin with, it would be good to understand some of the terms that will be most often encountered later. The renal tubule is a tube that has the following segments:
- proximal,
- loop of Henle, or thin bend,
- distal,
- connective.
All these tubules and tubes perform one characteristic function - they transport substances through the cells, dissolving them and subjecting them to reverse absorption, returning them through the capillaries to the blood (glucose, amino acids, water).
Other substances (urea, uric acid, drugs) pass through the tubules and are eliminated from the body. Normally, this entire transport process is regulated by the kidneys by acid-base balance.
What does the presence of casts in urine mean? When the kidneys become diseased, protein begins to accumulate in the kidney tubules. Enveloping them from the inside and passing through these channels, they take their shape, resembling a cylinder. An accurate impression of the canal is created. That is why they are called cylinders, and their sediment in urine analysis is called cylindruria.
Cylinders are one of the indicators of a general urine test. In conclusion, a laboratory examination is one of the indicators of a urine test, which informs doctors that there is an inflammatory process in the kidneys and urinary tract.
If a person is healthy, then there should be no casts in the urine. They can only exist if the urine is acidic. There is no cylindrical factor in alkaline urine.
If the analysis showed the presence of cylinders, then this always indicates the renal origin of the disease. Depending on the composition, they take one or another shape, size, color. Therefore, when all the features of the cylinders are indicated in a urine analysis, the doctor, by determining their origin, can find out about the appearance of a particular disease in a particular patient.
If, according to the results of a laboratory analysis, there are cylinders in the urine, this shows the reaction of the kidneys to a general infection, intoxication and the presence of changes in the kidneys themselves. But if the test shows a small number of cylinders, this can be considered normal.
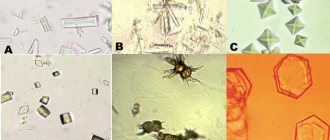
What types of casts are there in urine?
There are several types of casts, and each of them reports the specifics of the disease and whether the infection is a genitourinary tract disease or a kidney disorder is occurring.
Types of casts in urine:
- hyaline,
- grainy,
- waxy,
- erythrocyte,
- leukocytes,
- pigmented.
Hyaline casts in urine are serum proteins that coagulate and are filtered through the glomeruli, the site where blood is filtered to form primary urine and protein metabolism occurs. Further, not being absorbed in the proximal sections of the tubules, but passing through their distal distant sections, these proteins acquire a cylindrical shape.
The reaction of the tubular fluid is acidic, and this environment promotes blood clotting and, accordingly, the formation of hyaline casts. They are not present in an alkaline environment. Therefore, if the analysis shows the presence of hyaline formations, this indicates the patient’s nephrotic syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by swelling of the arms and legs.
Granular casts in the urine arise from altered tissue cells of the proximal tubules and have the form of grains and granules. Hence their name. If the analysis showed that they are present, this indicates diseases such as glomerulonephritis (diseases of the glomeruli of the kidneys), amyloidosis (kidney disease due to diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, etc.), diabetic glomerulosclerosis (a disease caused by diabetes mellitus) and others viral diseases that occur with fever. The study shows the characteristic granularity of such formations.
Waxy - consist of a homogeneous, structureless material similar to wax, yellow in color. They are formed in the sections of the tubules, due to changes in the tubular layer of these sections. This sediment occurs with malignant kidney tumors.
Erythrocyte is a protein with red blood cells. Talks about a tumor, renal infarction, thrombosis and high blood pressure.
Leukocyte is an indicator of pyelonephritis (disease of the renal pelvis).
Pigmented are blood pigments with a brownish, brown color. In the analysis, this is an indicator of different types of hemoglobinuria (hemolytic diseases during blood transfusion, when blood incompatibility occurs).
Erythrocyte (blood) components
Such cylinders are determined in a urine test if the patient has various tumors in the kidneys. Their appearance is the result of the combination of proteins with red blood cells. Erythrocyte inclusions may not be detected during urine examination, because they are very fragile. Their shade can vary from yellowish to brownish. These cylinders have clearly defined boundaries.
The main reason for their formation is blood in the discharge. And this symptom often indicates benign and malignant tumors, renal vein thrombosis, glomerulonephritis or infarction of this organ.
Cylindruria: biofluid analysis and diagnosis
The norm is the presence of single elements in the general urine analysis. If the number of cylinders is increased, this condition is called cylindruria. The norm of hyaline elements in urine, when 1-2 are not detected in all fields of view. Cylindruria is the first signal of the development of a severe infection. Urinalysis with physicochemical assessment is an effective and simple way to study a number of diseases. Primary requirements:
Confirmation of the diagnosis of cylindruria can be obtained by ultrasound, MRI or CT scan of the kidneys.
- for patients with problems of the urinary system, it is done repeatedly;
- no special patient preparation is required;
- Urine for analysis is collected during the patient’s normal routine;
- In the dynamics of the study, the nature of the course of diseases is studied.
To confirm the diagnosis, in addition to submitting urine for analysis, ultrasound, X-ray with contrast, MRI or CT scan of paired organs are indicated. If these methods fail or there is a suspicion of a tumor, an endoscopic kidney biopsy is performed. Kidney tissues are selected for subsequent histological and cytological examination.
Epithelial inclusions
These components in urine sediment appear from specific Tamm-Horsfall protein molecules, to which epithelial cells attach. These cylinders in the urine are formed as a result of strong adhesion of dead epithelial structures to proteins. Such elements can have a chaotic arrangement or be included in the base of a cylindrical body in layers. Their cells have a large volume, rounded nuclei, but the content of cytoplasm in them is quite insignificant.
Epithelial casts in urine are detected if a patient develops necrotic changes in the tubules, with a viral form of hepatitis and cytomegalovirus. Also, similar disorders in the patient occur due to poisoning with toxins - diethylene glycol, mercury vapor, salicylate.
When a general urinalysis (UCA) revealed the presence of casts in the urine, what does this mean for the patient? This is usually how various diseases of the urinary organs manifest themselves – most often the ureters and kidneys.
What do casts represent in urine analysis?
With various pathologies of the urinary system, protein, epithelial cells, and fatty particles are often found in the urine. Sticking together, they form oblong-shaped conglomerates. It is precisely such unions that are called cylinders. Such particles line the inside of the kidney tubules. Cylindruria is necessarily preceded by an increase in protein levels in the urine. Also, the resulting conglomerates are preserved exclusively in an acidic environment. Therefore, sometimes casts are present in urine sediment, but are not detected due to destruction in its alkalized environment.
If traces of cylindrical particles are detected in the preparation, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the patient. An objective examination is carried out, including palpation of the kidneys, percussion and auscultation of the heart, and palpation of the abdomen.
Waxy bodies in urine
Waxy elements in the discharge appear with dystrophic or atrophic changes in the kidney tissue. Their structure contains a homogeneous substance that does not have a clear structure and is most similar to wax. The place of its formation is considered to be distant parts of the kidney tubules.
Wax casts in the urine are formed due to necrobiosis - the death of the epithelial tissue lining the inner surface of the nephrons. This phenomenon is considered a consequence of severe diseases of the filtering organs: chronic functional kidney failure, malignant glomerulonephritis in the subacute stage, and other pathologies in the later stages of development. The detection of waxy inclusions in urine is an unfavorable sign.
In a normal state, the fluid secreted by a person has a slightly acidic reaction. The presence of pathological particles in the urine may be indicated by a sharp increase in its acidity level and increased protein content.
What do casts in urine indicate: hyaline, granular, waxy?
The appearance of casts in the urine is called cylindruria. They are a kind of sediment in the liquid during urination, which has a cylindrical shape.
Various types of cylinders make it possible to recognize diseases of the lower zone of the genitourinary tract (urethritis, etc.), as well as developing disorders of the functional capabilities of the kidneys.
Cylinders detected during a urine test, which include red blood cells, indicate acute diffuse glomerulonephritis. If bacterial casts were detected in the urine, this indicates the presence of bacterial pyelonephritis. In addition, the cylinders carry only those harmful microorganisms that provoked the onset of the disease.
Casts in urine - what does this mean?
Depending on what pathological processes occur in the human urinary system, different pathological cylinders appear in the urine. Therefore, the laboratory assistant indicates which cylinders were found in the general urine analysis, namely:
- Hyaline cylinders - can stand out against the background of a person’s overall health; during microscopy of urinary sediment, there should normally be no more than 1-2 cylinders in the field of view.
- Granular casts are a protein cast of the tubules with an admixture of renal epithelial cells.
- Waxy cylinders are formations of a homogeneous translucent mass.
- Erythrocyte casts indicate the renal origin of hematuria (with acute glomerulonephritis, chronic glomerulonephritis, kidney cancer, fornical bleeding, etc.).
- Epithelial casts in the absence of kidney pathology are not detected in the urine. The appearance of epithelial casts indicates severe degenerative changes in the tubular apparatus of the kidneys. Occurs in nephrosis and severe lesions (sublimate, etc.).
- Pseudocylinders are formed from mucus and are similar to hyaline casts. They can form from a precipitate of uric acid salts: they are red in color, resembling pigmented blood cylinders.
What does it mean? The appearance of casts of any type in the urine is an alarming signal indicating that the functional units of the kidneys - nephrons - are under attack.
Hyaline casts in urine
They are formed from denatured protein in the renal tubules under the influence of the acidic reaction of urine. Extremely delicate, pale, transparent formations, barely noticeable in bright light; for better diagnosis, the sediment can be tinted with methylene blue, gentian violet, eosin, and iodine tincture. Their surface may be slightly granular due to the deposition of amorphous salts or cellular debris, which may make it difficult to differentiate them from granular casts.
Normally, the number of hyaline casts does not exceed 1-2 in the preparation; they appear during physical activity, increased body temperature, the constant presence of protein in the urine, nephrotic syndrome, measles, rubella, chickenpox, influenza, parainfluenza, adenoviral infection, polio, mumps, HIV /AIDS and other infectious diseases (whooping cough, scarlet fever, diphtheria, meningococcal infection, tuberculosis) accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Grainy casts in urine
This is a cast of a kidney tubule, consisting of a protein that has coagulated in acidic urine, to the surface of which dystrophically altered tubular epithelial cells have adhered. As a result of this, the flowers acquire a granular appearance, and their color is darker in comparison with hyaline flowers.
Granular casts in the urine appear against the background of diseases accompanied by damage to the kidney tubules and proteinuria (protein in the urine): chronic glomerulonephritis, renal amyloidosis, diabetic nephropathy, pyelonephritis, viral diseases accompanied by fever.
Waxy casts in urine
Waxy casts consist of a homogeneous, structureless, wax-like material of a yellowish color; are formed in the distal sections of the tubules due to degeneration and atrophy (necrobiosis) of the tubular epithelium of these sections, which is usually observed in severe acute kidney damage (for example, in subacute malignant glomerulonephritis) or in the late stage of renal diseases and chronic renal failure. Therefore, their detection in urine is regarded as a prognostically unfavorable symptom.
Leukocyte casts
Particularly characteristic of pyelonephritis, to a lesser extent for lupus nephritis and some other diseases.
Epithelial casts
They are of renal origin and appear with necrosis of the renal tubules and heavy metal poisoning. The appearance of these casts is an indicator of allograft rejection (a few days after surgery).
Red blood cell casts
Present in the urine in acute progressive glomerulonephritis and some other renal diseases (renal infarction, renal vein thrombosis), as well as in polyarthritis, severe hypertension.
Cylinders
Cylindrical formations consisting of mucus. Single cylindroids can sometimes be found in the urine of a healthy person. A significant amount of them can be detected during inflammatory processes in the urinary tract.
(Visited 5,760 times, 1 visits today)
Cylinders - the reasons for their occurrence in secretions
These structures have a special shape - they resemble small threads formed from mucus. The ends of these elements are regular, round on both sides.
Cylinders in urine are detected at the final stages of nephrotic damage to the filtering organs. As we have already found out, all cylinders in the urine can be detected and preserved for a long time only when the acidity of the excreted liquid is high. When it is alkalized, these components are destroyed without a trace. Therefore, if microscopic examination of urine is carried out during urination, practically no cylindroids are detected in the sediment.
Such inclusions can easily be confused with pseudocylindroids. These false particles are formed by mucous clots and may externally resemble hyaline or pigment casts.
Other types of cylinders
Casts in urine
In addition to the types of casts described above, erythrocyte or leukocyte casts can be found in the urine. They are compounds of red and white blood cells and protein. This occurs when the integrity of the vessels of the renal glomeruli is violated. There are also urate, mucus and coma casts.
Leukocyte elements
This is a commonly found type of cylinder. Such components in the urine are detected during a general analysis in patients suffering from serious infectious or inflammatory kidney damage.
Leukocyte casts in urine are found in allergic forms of nephritis, pyelonephritis, acute streptococcal glomerulonephritis and other kidney infections. These inclusions include a protein molecule and white blood cells - leukocytes. These particles are easily confused with epithelial cells during microscopy. That is why the staining method is used to identify such structures during OAM.
Urate casts are often detected in the urine. In their structure, they resemble granular inclusions, but unlike the latter, they are easily destroyed under the influence of high temperatures. These formations are considered false and are often detected in concentrated urine.
In what cases is analysis prescribed?
A general analysis of urine is carried out for almost all diseases, for preventive purposes or to monitor the results of treatment. In addition to detecting cylinders, clinical examination of urine provides characteristics of transparency, acidity, and specific gravity of the liquid. The analysis also helps determine the presence of bile pigments, red blood cells, white blood cells, glucose, hemoglobin, and protein in the patient’s urine.
A urine test is considered a simple test, but deciphering it requires a lot of specific knowledge. The composition of urine is affected not only by the functioning of the kidneys, but also by the functioning of other organs and metabolism. Also, the specific components of urine determine the functioning of the reproductive system, but in any case, the study shows the condition of the patient’s kidneys and excretory system.
On a note! For preventive purposes and for timely diagnosis of diseases, doctors recommend taking a urine test once a year.
How to prepare and pass urine: recommendations
Proper conduct of the study itself and collection of biomaterial will help to obtain reliable results. The rules for collecting urine include several important aspects.
Recommendations for urine collection:
- Forget about mayonnaise jars and other “homemade” containers for storing urine. Only special sterile containers are suitable for collecting material. Thus, the entry of foreign substances into the patient’s urine is minimized, which can distort the test results. Also, compliance with this rule increases the shelf life of biomaterial and helps preserve it during transportation;
- Hygiene procedures are a mandatory aspect. Sebaceous secretions and sweat should not get into the urine. Antibacterial agents cannot be used, otherwise the results of the study may be distorted;
- Do not use specific medications or food products that may distort the results of the study. The specific list of substances is indicated by the doctor. The night before, avoid eating any coloring foods (beets, carrots). Remember, the color of urine is also important during analysis;
- Before conducting a urine test, do not drink alcohol, and the water regime cannot be changed either (drink water as usual). It is not recommended to be sexually active 12 hours before the test, or to collect urine during menstruation.
The appearance of cylindrical bodies in the patient’s urine indicates the presence of renal pathology. An increase in the norm is over 20 y in 1 ml of liquid. Each type of cylinder indicates a specific type of disease, which makes it easier to diagnose the disease in the patient.
Find out about the causes of cystitis in women and how to treat the pathology with a special diet.
The list and rules for the use of antibiotics for acute pyelonephritis can be seen on this page.
Go to the address and read about the benefits of chamomile and the use of the plant to treat the kidneys and urinary tract.
Pigment or hemoglobin
These casts in the urine are formed from hemoglobin residues. Since these elements contain iron, their color varies from dark red to brown. The formation of such particles indicates an extensive intravascular hemolysis process. During such a disorder, a large number of destroyed red blood cells are excreted in urine. Red blood components cannot pass through the filtration barrier in an intact state. Dead cells do not enter the general bloodstream, but collect in the spleen.
Pigment casts in the urine appear as a result of hemoglobinuria. This condition occurs as a result of toxic poisoning, transfusion of incompatible blood group, severe injuries with damage to organs and muscles.
Important! After such serious disorders, a person may experience anuria or functional failure of the kidneys. After normal urination has been restored, pigment particles are detected in the analysis of discharge.
Urine sediment
It is known that if fresh whole blood taken from a vein is mixed with a small amount of sodium citrate (to prevent it from clotting) and subjected to rotation in a centrifuge, the whole blood will separate as a result of centrifugal forces. At the top there will be a transparent, slightly opalescent liquid, or blood plasma, and at the bottom there will be heavy cellular elements, the main mass of which are red blood cells, or erythrocytes.
What happens if a similar experiment is carried out with fresh urine? Of course, there is no need to inject sodium citrate into it, because unlike blood, urine does not clot. But as a result of such centrifugation, the urine will still remain transparent, but sediment will be visible at the very bottom of the test tube. This is called urinary sediment, and it is necessarily present to one degree or another in every person, both healthy and sick.
Among the elements of urine sediment, the following are found in varying quantities:
- erythrocytes, or red blood cells. There may either be none at all, or very few of them. If you microscopy urine sediment, then in the field of view of a laboratory microscope, at a slight magnification (120 - 180) times, normally in women there are no more than 3 red blood cells, and in men - even less;
- white blood cells, or leukocytes normally, are also infrequent: no more than 6 cells in the field of view in women, and no more than 3 in men. This sexual selectivity is explained very simply: in women, the external genitalia are very close to the urethra, and it is from there that blood cells can enter the urine;
- epithelium is usually present in the urinary sediment, and this is understandable: after all, it is the epithelium that lines the inner surface of the urinary tract, the renal pelvis, and also the bladder;
- finally, a variety of casts may be present in the urinary sediment. Casts in urine - what does this mean?
Before we talk about what it is, and tell what types of casts in urine there are, we need to remember how the nephron, or the structural and functional unit of the kidney, is designed, capable of producing final urine from the blood.
By the way: if in the urinary sediment, in addition to the structures described above, bacteria, fungi, various salts in large quantities, and renal tubular epithelium are also isolated, then all this is evidence of various diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Treatment of cylindruria
In a healthy state, the discharge should not contain any casts other than hyaline elements (and then in limited quantities). The remaining components appear in urine due to infectious, tumor or inflammatory processes. Therefore, if they are detected, the underlying pathology must be treated immediately.
For different diseases, a specialist will prescribe different courses of therapy for you. For example, for the treatment of infectious lesions of the urinary system, the following is used:
- Antibiotics - their use is advisable for diseases of a bacterial nature (Monural, Ceftriaxone).
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - eliminate the inflammatory process in the affected area (Canephron, Cyston, Furagin).
- Analgesics – intended for symptomatic therapy. Reduce pain and alleviate the patient's condition (Analgin, Ketanov).
- Folk remedies are kidney preparations and decoctions. For this purpose, St. John's wort, knotweed, and chamomile are used. A collection with a diuretic effect – Nephrophyte – also helps relieve inflammation and pain.
- It is recommended to remove sour juices, spicy foods, and citrus fruits from the patient’s daily menu.
For kidney diseases, treatment usually takes quite a long time. Only a qualified doctor will select effective methods of therapy. Self-medication in this situation is unacceptable, so if during the examination you are found to have pathological casts, immediately go to a urologist or nephrologist.
Symptoms of cylindruria
There are no clinical symptoms indicating cylindruria. Cylindruria (all its manifestations) are associated with the underlying disease that caused this condition. For correct diagnosis, it is necessary to carefully monitor all changes in the analysis parameters.
When collecting anamnesis, it is necessary to pay special attention to such clinical symptoms as edema, fever, previous infectious diseases, and arterial hypertension. You should also find out whether family members suffered from diseases of the urinary system (urolithiasis, kidney failure, etc.).