Characteristics of bacterial urethritis
Urethritis is almost always caused by infection. Only in some cases the disease is non-infectious, for example allergic. Urethritis caused by bacteria is divided into the following forms:
- Primary bacterial urethritis is diagnosed in a person who has no health complaints and does not have any infectious disease. The reason for going to the doctor is this pathology.
- Secondary occurs when there is already an inflammatory process of a general or local nature (angina, pneumonia, prostatitis, orchitis, cervicitis). Patients do not notice alarming symptoms for a long time, attributing them to the existing disease.
Both forms can manifest in acute or chronic stages. Accordingly, signs of the disease are detected almost immediately after the attack of pathogenic agents or after a certain period of time (30-45 days).
Distinctive symptoms
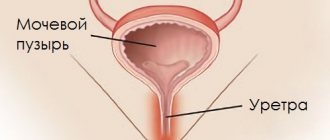
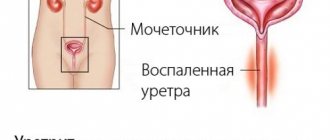
Bacterial (microbial) urethritis is a local focal inflammatory process. There are no standard symptoms such as high body temperature or intoxication. After 7-10 days from the time of stay in the provoking situation, the main signs of the disease appear:
- pain in the lower abdomen (above the pubis);
- urination causes sharp pain;
- concerned about unusual discharge (seropurulent, mucous-foamy) with a specific odor;
- the genitals become red and swollen.
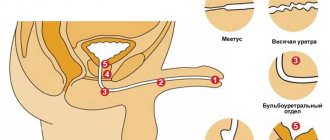
Microbial urethritis affects both sexes equally, but the male and female forms of the disease have differences. Painful manifestations in men are more pronounced than in women. This is due to the difference in the anatomy of the organs of the excretory system. In the weaker sex, the urethra is hidden, the urinary canal is much shorter than in men, all signs are blurred and not expressive. Therefore, bacterial urethritis in women is not immediately detected, treatment is delayed, and the inflammation usually transforms into the chronic stage.
In men, the urethra is located inside the penis, the length of the urethra is 17-22 cm. The disease leads to swelling and redness of the genital organ. Often there is a decrease in the lumen of the canal, which creates a problem when urinating, making the process difficult and painful.
It is important to know! Men, due to the clarity of the manifestations, immediately note the alarm signals of the body. In women, the disease often becomes chronic, since similar symptoms are characteristic of menstrual cycles and menopause, and against this background, urethritis can be missed.
Etiology of the disease
The human body is constantly inhabited by many bacteria that participate in vital metabolic reactions, such as digestion. But among the beneficial microflora there is the so-called opportunistic microflora. It includes staphylococci, Escherichia coli, streptococci (nonspecific flora). Representatives of this “community” live quietly in the body without causing harm. To “trigger” a disease, the active reproduction of pathogens must be provoked by something; certain conditions are needed when they “begin to act.”
But there are a number of specific microorganisms that, once inside a person, immediately provoke the onset of a pathological process. Such infectious agents include chlamydia, trichomonas, and ureoplasma.
Bacterial urethritis is named after the pathogen that caused it:
- Specific - develops in the presence of gonococci, chlamydia, trichomonas, candida, gardnerella.
- Nonspecific - the disease is caused by staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, E. coli (representatives of nonspecific opportunistic flora).
- Mixed.
You should not be exposed to factors that can provoke urethritis. They trigger mechanisms that activate the activity of pathogenic microflora, and processes that lead to pathology are triggered. List of negative prerequisites:
- unsafe sex;
- traumatic injuries to the urethra;
- insertion of a catheter into the bladder;
- mechanical damage to the walls of the urethral canal due to urolithiasis;
- narrowing of the walls of the urethral canal;
- weakening of the body's protective functions.
Bacterial urethritis is initially provoked by specific pathogenic microbes, which leads to weakened immunity. This activates opportunistic flora. The result is nonspecific bacterial urethritis. Men often have problems going to the doctor: they are embarrassed, afraid of publicity, and do not like to be treated. But the later treatment is started, the more difficult it becomes.
Result of inaction
When the body gives alarming signals, you should consult a doctor and, if necessary, begin treatment. If you postpone therapeutic measures, the unpleasant irritating signs gradually go away, and the illusion of recovery is created. But when exposed to any unfavorable factor (hypothermia, drinking strong drinks, multiple sexual contacts), the disease returns. In women, recurrent symptoms of urethritis include cystitis, bartholinitis, vaginitis; sites of inflammation appear in the bladder, in the vagina and its vestibule.
Attention! Infection spreading along the ascending tract and certain types of bacteria cause infertility in young women, as the organs of the reproductive system are affected.
In men, pathological phenomena can affect the back of the urethra. The seminal vesicles and prostate gland are also affected. Orchitis and prostatitis are diagnosed. In parallel, an infection that exists for a long time in the walls of the urethra leads to its narrowing and adhesions appear.
Why dysbiosis develops in adults and children
Normally, each person has his own set of bacteria, which is called “microflora”.
Bacteria are present everywhere: in the oropharynx, nose, vagina, intestines, lungs, urethra. Under the influence of a predisposing factor, against the background of inadequate functioning of the immune system, pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply and prevent beneficial microbes from doing their job. • prolonged stress, • poor nutrition, change of usual food and water, • alcoholism and other chronic intoxications, • poor environmental conditions, • all types of immunopathies, including those associated with HIV (AIDS), • hormonal surges (pregnancy, menopause ), • taking certain medications: oral contraceptives, hormones, antibiotics, • conditions after surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, etc.
Sometimes factors “harm” the body in combination, and then the chances that the immune system will fail and the balance of microorganisms will be disrupted increase.
Pathology detection methods
At the first manifestation of painful symptoms, you should immediately go to the doctor. If urethritis was preceded by a venereological disease, then consultation with a venereologist is required.
For a correct diagnosis, especially if the disease is asymptomatic or has mild symptoms, in addition to a medical examination, tests and studies are prescribed.
- Laboratory examination of urine. An increase in the white blood cell count confirms the presence of inflammation. For research, take a morning portion of urine.
- To detect bacterial urethritis, blood is always taken for testing.
- A smear from the urethra is required. It is examined under a microscope for the presence of bacteria. Before the procedure, you should avoid sex and taking antibiotics. A couple of hours before taking biomaterial, you should not go to the toilet.
- Sometimes patients are referred for an ultrasound.
Additional methods for identifying urethritis caused by bacteria include the following:
- three-glass sample;
- urine analysis according to Nichiporenko;
- urethroscopy;
- tank. urine culture;
An increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood and urine, the presence of protein in the urine - all these indicators indicate urethritis of bacterial origin. Urine culture allows not only to identify representatives of pathogenic flora, but also to select an effective drug for treatment.
Forms of the disease
Pathology leads to inflammation of the urethra. Bacteria enter through the ascending route. The disease is divided into 2 types: specific and nonspecific. The first form is characterized by the fact that the causative agents of the inflammatory process are pathogens that are transmitted primarily through sexual contact. These include gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasma, etc.
The occurrence of nonspecific urethritis in men is caused by the penetration of opportunistic microflora, which include streptococci, staphylococci, fungi, etc. The disease is divided into primary and secondary types, which is caused by the penetration of bacteria: the primary inflammatory process occurs due to the entry of bacteria during sexual contact, and the secondary develops when pathogens penetrate from infectious foci - prostate, bladder, etc.
The nature of the course determines the presence of acute and chronic types of disease:
- The first is characterized by vivid symptoms and develops quickly.
- The chronic form can last a long time with periods of remissions and relapses.
Types of treatment for bacterial urethritis
Medicine today has effective methods of combating microbial diseases. The method of treatment is selected by the attending physician, taking into account the type of pathogen, the severity of the symptoms of the disease, and the development of complications. If, along with urethritis, there are also inflammatory processes, everything needs to be treated as a whole.
Main therapeutic areas
For nonspecific urethritis with a chronic status, antibiotics are combined with the administration of the drugs Collargol and Silver Nitrate. The patient is prescribed immunostimulants. A successful outcome in secondary urethritis is associated with the effectiveness of therapy for the primary infection on the basis of which it developed.
For patients with bacterial urethritis, the following is recommended:
- At the peak of the disease, bed rest is prescribed. The speed of recovery will depend on how diligently you follow this recommendation.
- You need to drink a lot of fluid, you should drink at least 2.5-3 liters per day. This can be not only water, but also compotes, fruit drinks, and medicinal decoctions. When there is a lack of fluid in the body, a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria is created.
- In nutrition, you must adhere to the rules: do without spices, herbs, fatty, smoked foods and consume a minimum of salt.
- During treatment, it is advisable to abstain from sex. Or condoms should be used if necessary.
Conservative treatment methods are based on taking antibiotics and antimicrobial medications. Features of the therapeutic course depend on the clinical picture of the disease.
It is important to know! If the cause of the pathology is representatives of a specific flora, then treatment is prescribed for both sexual partners.
Symptomatic therapy is aimed at reducing the manifestations of the disease and improving the patient’s well-being. Patients are recommended to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, UHF, magnetic therapy), but only in the absence of pain symptoms.
Folk recipes
Traditional recipes are not an alternative to conservative therapy. They are only a complementary component to antibiotic agents and give good dynamics. Herbs are usually inexpensive and can be purchased at any pharmacy. It is important to choose the right herbal mixture to eliminate inflammation due to bacterial urethritis.
There are plants, decoctions and infusions of which have analgesic and diuretic effects, cope well with spasms and are antiseptics. For example, cranberry juice with lingonberries helps remove pathogenic flora from the urinary system. It contains a huge amount of vitamins, the drink has a pleasant taste. Bearberry leaves, a decoction of yarrow herb, parsley, an infusion of elderflower flowers, calendula flowers, knotweed, berries and rosehip roots have proven themselves well. Medicinal products are drunk before meals, one-third of a glass.
Patients are also recommended to make local warm chamomile baths at home with the addition of a string. They reduce inflammation and soothe.
Therapy
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause of dysbiosis, that is, treating the underlying disease and correcting pathological symptoms.
The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Prebiotics. Necessary for the rapid relief of intestinal manifestations and symptoms of dysbiosis in general. However, drinking them uncontrollably is not the best option. The symptoms will return and will only get worse. It is impossible to do without complex treatment.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Necessary to relieve inflammation in colitis and peptic ulcers.
- Antacid drugs.
- Hepatoprotectors, if the cause lies in liver diseases.
It is important to adjust your diet. As much as possible fermented milk products, especially kefir, vegetables and fruits rich in fiber. This way you can normalize the state of the flora quickly enough and cope with the problem.
Read on the topic: How to cleanse the body of toxins and toxins naturally
Prevention recommendations
In the fight against any disease, prevention should come first. It includes measures not only to prevent primary inflammation, but also to prevent relapses. Here are the basic rules to help you avoid getting bacterial urethritis:
- Sex should be safe.
- Toilet of the genitals should be done carefully, preferably using natural detergents.
- Do not be exposed to hypothermia, do not sit on a cold surface.
- Choose underwear from cotton materials.
- It is not recommended to wear trousers or jeans that are too tight and compress the pelvic area.
- If medical instrumental examinations of the pelvic organs are coming, it is advisable to take a preventive course of antimicrobial drugs.
Don't neglect your health. You shouldn’t self-medicate, and especially don’t do nothing. If manifestations of urethritis occur, you should immediately go to the doctor for qualified help and begin treating the pathology. If left to its own devices, a disease tends to produce complications that can ruin the established order of life.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is quite nonspecific, since we can talk about many other diseases in addition to dysbiosis. Among the characteristic manifestations are:
- Pale skin tone caused by mild anemia.
- Paleness of the gums, caused by the same thing.
- Frequent diarrhea. In this case, the stool has a heavy, putrid “aroma”.
- Brittle nails caused by poisoning of the body with waste products of putrefactive bacteria.
- Flatulence. An increase in the production of intestinal gases is also a consequence of a shift in the microflora in the intestine towards increased proliferation of putrefactive bacteria.
- Cracking of the skin in the corners of the mouth, so-called jams.
- Discomfortable sensations in the abdomen, in the epigastric region and iliac regions in particular.
- Rumbling in the abdomen.
- Dryness of the dermal layer. Caused by insufficient sebum production. The dermis becomes flabby and insufficiently elastic, often cracking.
- Pain in the projection of intestinal structures. Observed in the iliac regions, epigastrium, lower abdomen in the projection of the rectum.
The non-specificity of the clinical picture is explained by a variety of intestinal diseases, the consequence of which is dysbiosis - Nausea and vomiting. They occur somewhat less frequently and only in severe forms of dysbiosis.
- Belching with a sour taste. A nonspecific sign indicating possible gastritis.
- Allergic reactions to foods and substances that have been familiar to the body for a long time, to which there was no allergy before.
- Headaches, dizziness.
If a woman complains of itching, burning, or discharge, she should first be examined for dysbacteriosis, and then for other infections. Dysbacteriosis can be determined by standard elementary bacterial culture. So, if there is dysbiosis, then antibiotics are contraindicated!
Causes of infection
Causes of bacterial urethritis:
diseases of the urinary system - cystitis, pyelonephritis, etc.;- the presence of sexually transmitted infections;
- inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs;
- unprotected sex with different partners;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- untimely treatment of prostatitis and hydrocele.
Fighting the disease
Treatment of genital dysbiosis should be based on identifying the main imbalances of the microflora. So, if a large number of fungi are detected in a smear, treatment should begin with adequate antifungal therapy, and if trichomonas are detected, dysbiosis should be treated with the drugs that best destroy these protozoa.
https://youtu.be/Dwa2Szzee3U
In order for the treatment of banal microflora, which has turned into pathogenic, to bring the most pronounced and lasting results, it is necessary to inoculate the contents of the urethra in order to isolate the most active representatives of the microbiocenosis and determine their sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. Without this, treatment is often ineffective, since microorganisms often show resistance to the most common antibiotics.
The reason for this is that a person could take these medications in order to treat other somatic diseases; often the course is not completed, but until the symptoms are eliminated, as a result of which the bacteria adapt to the antibacterial components entering the body, and their new generations acquire innate stability.
It is not necessary that dysbiosis can be eliminated only by the newest generations of antibiotics. Often, bacteriological culture reveals sensitivity to the simplest and even outdated drug.