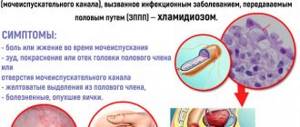
STD
Development of urethritis
This is the most advanced form of the disease. The condition is accompanied by a constant inflammatory process affecting the urethra. In men, the symptoms are pronounced, and all due to anatomical features.
Chronic urethritis appears several months after the onset of acute symptoms. Stages of remission and relapses may occur. Without treatment, the quality of life of the sick person will be reduced.
- Causes of development Symptoms of the disease
- Possible consequences and complications
- Treatment with metronidazole
Causes and nature of the disease
There can be many causes of urethritis. To properly treat it and avoid relapses, it is necessary to exclude all causes:
- partner's illness;
- violation of proper nutrition;
- changes in the microflora of the genital organs;
- urolithiasis disease;
- irritation of the urethra as a result of medical procedures, taking medications, or getting hygiene products into it.
Urethritis can be caused by:
- Chlamydia;
- Mycoplasmas;
- Gonococci;
- Gardnerella;
- Trichomonas;
- Ureplasma.
The course of urethritis in women differs from that in men. As a rule, in men it occurs in a more complex form.
Prevention
In case of chronic urethritis, it is necessary to adhere to certain rules of prevention in order to prevent relapse of the disease.
- Have an orderly sex life.
- When having sexual intercourse, always use a condom or other method of contraception.
- Strictly observe genital hygiene.
- Avoid hypothermia of the body.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day.
- Eat properly and balanced.
- See your doctor once every six months.
Chronic urethritis is an unpleasant disease of the urinary system that brings discomfort to a person. When the first symptoms of this disease appear, you must immediately seek help from a urologist, otherwise the consequences can be disastrous.
Timely therapy and compliance with preventive measures will help cope with exacerbation of the disease and minimize its impact on a person’s quality of life.
Disease in women: course and exacerbation
Urethritis can be confused with cystitis - inflammation of the bladder. An important difference here is that with urethritis, the urethra itself hurts, while with cystitis, pain appears during urination and is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. Both diseases can occur together.
The nature of the course of chronic urethritis in women can be divided into several stages:
- Symptoms of the disease appear only occasionally; they can be relieved by taking antibiotics for a short time. They disappear quickly and do not cause much inconvenience.
- Attacks of pain become more frequent; taking mild antibiotics does not help.
- Taking painkillers and antibiotics does not relieve symptoms or help get rid of pain, which becomes very severe. With such symptoms, a woman cannot even think about sex, fearing new pain.
The disease can be primary, that is, inflammation occurs directly in the urethra, or secondary, when inflammation spreads to the urethra from other inflamed organs.
Diagnostics
To identify chronic urethritis, the following diagnostic techniques are used:
Patient interview. The doctor analyzes the existing symptoms, collects information about previous diseases and provoking factors.- Culture of a smear from the urethra. Used to identify the causative agent of infection and select the most effective drugs.
- PCR. Through this test, bacteria and viruses can be quickly and accurately detected in the resulting sample.
- General urine analysis. Used to identify changes characteristic of long-term inflammation.
- Microscopic examination of a smear. Allows you to detect pathological processes occurring at the cellular level.
- Urethroscopy. It is an examination of the walls of the urethra using endoscopic equipment.
- Ultrasound diagnostics. Used to detect diseases of the pelvic organs.
- Urethrography is an X-ray examination of the organs of the excretory system using a contrast agent. Not performed during an exacerbation period.
Types of urethritis
Chronic urethritis has its own types. In this case we can distinguish:
- Gonorrheal . Characteristic of inflammation that occurs directly in the urethra. You can become infected through sexual intercourse, shared personal hygiene items, or contact with underwear.
- Non-gonorrheal.
In turn, nongonorrheal urethritis is divided into the following types:
- Herpes . It can occur during sexual contact; in most cases, the disease proceeds unnoticed.
- Candidiasis . Appears as a result of insufficient personal hygiene, during sexual intercourse, in public places (bathhouse, swimming pool).
- Chlamydia . The most common type of disease that occurs as a result of sexual intercourse.
- Trichomonas . Transmitted through blood, seminal fluid, during childbirth from mother to child.
Non-gonorrheal urethritis can be contracted through non-traditional types of sex. Also, chronic inflammation can be acquired not only as a result of the presence of infection, but also be non-infectious. This type is typical as a result of irritation of the urethra during medical procedures, the use of medications and allergic effects.
Acute urethritis will quickly develop into chronic urethritis not only with incomplete treatment, but also with urolithiasis, poor immunity and when a catheter is installed.
Causes
The disease can be provoked by various factors, ranging from improperly selected personal hygiene products to fungal and sexually transmitted infections. Depending on the pathogen, there are several types of urethritis :
- gonococcal;
- herpetic;
- trichomonas;
- fungal (candida);
- parasitic (chlamydial).
The most common types of pathogenic microorganisms are protozoa mycoplasma and ureplasma. In rare cases, urethritis develops due to circulatory problems in the pelvic organs or trauma to the penis.
Regarding the chronic form of urethritis, it occurs after the end of the acute form. The mechanism for the development of pathology is usually the following: the patient begins to feel the characteristic signs of the disease, understands that he may have become infected with something, acquires a set of standard medications (available antibiotics, ointments, etc.), uses the medications until the symptoms are relieved. The painful sensations disappear for a while, but the infection and its causative agent have not gone away. The latent period of urethritis begins, at this moment the patient only sometimes feels a slight tingling sensation during urination; with a sudden movement, an unpleasant pulling sensation may appear in the groin area.
Chronic urethritis goes from latent to subacute form as soon as accompanying factors : the addition of a secondary infection, seasonal decrease in immunity, stress, hypothermia. In this case, all the symptoms return with renewed vigor, but curing the disease becomes more difficult.
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of chronic urethritis include:
- pain, itching and burning when emptying the bladder;
- redness of the genitals;
- the appearance of purulent discharge;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- blood when urinating;
- frequent desire to go to the toilet;
- In men, the lips of the penis may stick together in the morning.
It is important to understand that in advanced cases and the absence of treatment for the disease, inflammation can spread to other organs, and the urethra may also narrow, which increases pain.
Treatment methods
The main drugs for the treatment of chronic urethritis are antibiotics. But doctors prefer to start therapy with immunostimulants so that the body can fight this disease on its own. Such drugs improve the permeability of soft tissues, and antibiotics are faster transported to the inflamed area.
It is recommended to take Metronidazole or Trichopolum simultaneously with antibacterial agents.
As for drugs with antimicrobial action, they can be divided into the following groups:
- Tetracycline - prohibited for patients under 18 years of age and pregnant women;
- Azithromycin - has no age-related contraindications, but pathogenic microorganisms quickly adapt to the effects of this antibiotic;
- Penicillin – a large dose of the drug is required to achieve results, but its effect is long-term;
- Fluoroquinolone - affects pathogenic bacteria in all organs of the genitourinary system, but, due to its high toxicity, is not prescribed for the treatment of children and pregnant women.
In addition to antibiotics, it is recommended to additionally rinse the urethra with antiseptics, such as Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. They disinfect the mucous membrane of the urethra. If urethritis is caused by Candida bacteria, it is better to use Flucanazole as an antiseptic.
In combination with antibiotics and antiseptics, traditional medicine is also used - infusions of celandine, coriander, knotweed, tansy, immortelle and other medicinal plants that help suppress inflammation in the urethra.
Diagnosing the disease
To make a correct diagnosis, it is important to undergo all examinations prescribed by the doctor; this is also important to exclude cystitis, because both of these diseases can easily be confused with each other.
To restore the picture of the disease, the doctor prescribes the following examinations:
- visual inspection for redness of the genitals;
- palpation of the bladder area in men and women, prostate in men to exclude inflammation of these organs;
- culture of discharge from the urethra to determine the nature of the inflammation, its causative agent and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- urine analysis for the presence of an inflammatory process;
- blood test for sexually transmitted infections;
- urethroscopy to visualize the source of inflammation;
- ultrasound examination of adjacent organs to exclude their inflammation.
If treatment is not started, temporary relief may occur due to immunity, but the disease will return with renewed vigor as soon as the sick person gets a little cold, drinks too much alcohol, or has unprotected sexual contact with a new partner. When inflammation becomes chronic, complications, sexual dysfunction and infertility may begin.
How is the diagnosis made?
If the symptoms described above bother you for several days, you should consult a doctor. The treatment of such pathology is carried out by a urologist, and in his absence, by a nephrologist or therapist. The disease must be differentiated from the following diseases:
- urolithiasis disease;
- benign or malignant neoplasms;
- inflammation of the kidneys or bladder.
Before starting laboratory and instrumental studies, an examination is carried out. The doctor notes the condition of the skin and mucous membranes (with urethritis, their blanching is observed). When palpating the suprapubic and groin areas, severe pain is felt.
Do not forget that if you suspect chronic urethritis, you must take a urine test. During my time working in a clinical laboratory, I often encountered patients bringing urine in inappropriate containers. Jars of food products, paints, and chemicals contain residues of organic and inorganic compounds on their walls. When washing such dishes with soap, alkali remains on the rims in the smallest cracks, which reacts with biological fluids. Therefore, the scanner in the laboratory gives an incorrect result and the patient has to give urine again. This difficulty leads to late diagnosis and can negatively affect treatment. That is why it is necessary to purchase special disposable containers for collecting urine at a pharmacy or store.
What methods are used to confirm the diagnosis:
- General urine analysis. In a healthy person, urine is straw-yellow in color and does not contain pathological impurities. During inflammation, these indicators change; the cellular composition is dominated by erythrocytes, leukocytes and protein.
Cloudy urine occurs due to a large amount of protein and leukocytes - For chronic urethritis, a three-glass test is performed: in the first, pronounced redness of the urine and the appearance of clots are observed, the second has a more pink tint, and the third can be completely normal.
- Bacteriological culture of urethral contents on nutrient media. In this case, a colony of microbes is formed in a Petri dish in 10–14 days, which has its own external individual characteristics. In this way, it is possible to identify the causative agents of chronic inflammation and select a specific drug that will help destroy them.
- Endoscopic examination of the urethra. A special device with a camera is inserted into the opening of the urethra, which transmits the image to the screen. This way you can see inflammatory swelling and redness of the soft tissues.
During endoscopic examination, you can see the swollen walls of the urethra
An integrated approach to the treatment of pathology
To fully select treatment, you should undergo examinations prescribed by your doctor and take tests. Only on the basis of these data will the doctor be able to select the correct treatment and prescribe drugs that suppress exactly the pathogen that caused chronic urethritis in a particular case.
Drug therapy
Treatment of urethritis requires an integrated approach. The patient is prescribed various drugs that are suitable for his specific case based on tests. Antimicrobial, antibacterial drugs and antibiotics are required.
Doctors often prescribe the antibiotic Amoxiclav. The doctor may prescribe lavage of the urethra to reduce inflammation, as well as baths using herbal ingredients that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
When treating urethritis in a woman, it may be necessary to administer antibacterial suppositories or specially impregnated tampons. To exclude allergic urethritis, your doctor may prescribe antihistamines, for example, Tavegil or Suprastin. To increase the body's resistance to infections and viruses, the patient is prescribed B vitamins, vitamin PP, as well as drugs that enhance immunity.
It is important to understand that the duration of treatment depends on the advanced stage of the disease; the longer the patient does not see a doctor, the more complex and lengthy the treatment will be.
To quickly restore the body during treatment, you must follow the following instructions:
- A diet that excludes salty, spicy and smoked foods is necessary, as these products can increase the acidity of urine, which will irritate the urethra.
- You should increase the amount of fluid you drink per day - this is necessary to cleanse the urethra.
Urethritis in advanced form can lead to inflammation of the bladder, which then spreads to the kidneys, causing pyelonephritis.
For a full recovery, it is necessary to completely restore the integrity of the urethral mucosa; if the disease is advanced, hospitalization and cauterization of the epithelium are possible.
After completing the course of treatment, the patient is required to undergo a re-examination to ensure complete recovery, and not that symptoms are temporarily suppressed and the disease enters a chronic stage. It is important to understand that to avoid complications, treatment should be selected by a highly specialized doctor, in this case a urologist.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are best used in combination with drug treatment, as they will help relieve unpleasant symptoms. For this you can use:
- Cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks , which have anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects.
- Blackcurrant - berries and leaves. The berries can be eaten fresh or made into a fruit drink; a decoction is made from the leaves. Pour boiling water over the currant leaves: for one tablespoon of leaves there is one glass of boiling water. The decoction should be divided into two doses per day.
For the treatment of urethritis, products and herbs that have anti-inflammatory, disinfectant and diuretic effects are suitable. The course for chronic forms, together with treatment selected by a doctor, is at least one month.
Treatment of chronic urethritis in men
The goal of treatment is to relieve the inflammatory process and eliminate the infection. Treatment largely depends on what caused the disease. In other words, an individual course of treatment is selected for each man.
The main method of treatment is taking antibiotics
Just like in women, treatment in this case is carried out with antibiotics. The best remedy in this group is Monural. The drug is prescribed both for the bacterial form and for other forms of the disease.
Additional treatment is carried out using the following drugs:
- painkillers;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - ointments, gels, tablets, etc.;
- when body temperature rises, antipyretics are prescribed;
- medications to improve kidney function.
Instructions for taking medications are issued by the doctor individually for each patient. For chronic urethritis, sitz baths with the addition of decoctions of medicinal herbs are very helpful.
Sitz baths are recommended
If the disease was detected in a timely manner, it is treated at home. In advanced cases, it will not be possible to do without hospitalization.