06.08.2017
Hematuria or bloody urine in men manifests itself in two forms: macro- and microhematuria.
The first condition is blood and blood clots in the urine of men, which are visible to the naked eye. The second is when blood in the urine of men is detected only on the basis of laboratory analysis. In any case, hematuria in men is a reason to undergo an examination of the body to find the cause of the pathology.
The provoking factors are varied and only a doctor can find out why bleeding appears in a particular case.
Even if the condition is not accompanied by pain, it is imperative to undergo urological control of men's health.
Why is there blood in the urine?
As mentioned above, the reasons for the appearance of blood in the urine of men are varied, but among them there are several main ones.
The first reason why bloody clots appear in the urine is stones in the bladder and ureters. Stones injure the mucous membranes of organs, injuring and provoking bleeding; as a result, red blood cells are found in the urine of men. You can recognize this cause by pain on the left or right side.
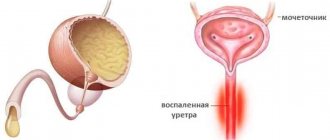
The second factor that provokes urination with blood in men is infections affecting the urinary tract. In a healthy body, urine is sterile. If a person has pyelonephritis or cystitis of a bacterial nature, inflammation of the urinary system is quite possible.
A benign tumor is another factor that determines the presence of drops of blood in urine. A tumor in an adult man can affect the bladder, prostate and kidneys. Elderly patients are at risk. More often, the cause lies in inflammation of the prostate; this disease occurs at any age.
Oncological disease of the urinary system is the next factor that causes gross hematuria in men. Usually bleeding occurs after the tumor affects the blood vessels. With cancer, blood appears in the urine for a long time in men without pain.
There are other reasons why increased red blood cells are found in the urine; an increase in red blood cells in the urine appears due to the following conditions:
- acute or chronic inflammatory process, which is accompanied by stagnation of blood, impaired circulation of blood flow in the tissues;
- injuries during sports and sexual activities. In such situations, men bleed more often than women;
- taking blood thinning medications. This pathology is very rare, but you need to know about it;
- hemophilia;
- glomerulonephritis;
- sickle cell anemia.
If the reasons mentioned above provoke blood when urinating in men, this is a serious reason to consult a doctor. Herbs and poultices will not be able to remove blood from urination in men, but it is easy to get complications.
The most common reason for urine turning red is not urology, but the consumption of beets, peppers, and rhubarb. It could also be exposure to food colorings that are added to most store-bought foods.
How to treat?
Treatment of hematuria must begin immediately after an accurate diagnosis has been established.
Therapy may include medication or the use of traditional medicine recipes.
Medicines
Drug therapy is prescribed taking into account the cause of hematuria.
Typically, patients are prescribed the following medications:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antimicrobial;
- diuretics.
What treatment is prescribed for hematuria is described in the video:
Folk remedies
The most popular recipes against hematuria:
- Barberry . You should take the bark or root of this plant (1 tablespoon), add 1 glass of water, and boil the medicine for 20 minutes. Take the prepared decoction 3 tablespoons 2-3 times a day.
- Blackberry . You will need blackberry root - 20 grams. Pour in 100 ml of red wine and boil for 15 minutes. Drink the medicine 2 tablespoons 3 times a day.
- Bearberry . To prepare this medicine, you need to grind dried bearberry leaves to a powder consistency, combine with powdered sugar in a 1:1 ratio, and mix. Take 1 teaspoon 5 times a day.
Diagnosis of hematuria
If urine with blood appears in men, a doctor will help determine the cause. He needs to provide information about everything that could have caused the problem. The time of appearance of blood is of great importance - after sex or before, whether it is related to the time of heavy lifting, stress, how often the man had to urinate with blood, etc. After collecting an anamnesis, if necessary, a diagnosis is prescribed.
Detecting bacteria in a urine test will reveal signs of cystitis. If no bacteria are found in a man’s urine, GDP is prescribed, based on the results of which further diagnostics are planned. Retrograde ureteropyelography will show if kidney pathology has appeared. Cystoscopy is prescribed if a tumor is suspected. Ultrasound reveals the condition of the genitourinary organs. Sometimes a CT scan is performed if indicated. This list contains the main diagnostic measures, but not all of them will be needed.
Often, if there are blood clots during urination in men, a test is prescribed. You need to sequentially collect urine in 3 containers, and then submit them to the laboratory. This will not only determine the increased content of red blood cells in the urine, but will also reveal where the cause is localized. For example, the presence of blood in the urine from the first container indicates damage to the urethra. If red blood cells are elevated in containers 2 and 3, then the cause is localized in the neck of the bladder. If red blood cells in the urine are elevated in all three containers, it means there may be a tumor in the body.
Detection of red blood cells in the urine of men requires urgent consultation with a doctor, since it can signal chronic pathologies that require lifestyle adjustments and competent therapy.
Unlike women, urine with blood in men is determined by anatomy, and therefore has peculiarities. In women, blood during urination can be a signal of cystitis, and blood in the urine of a man without pain is more often caused by other ailments. Conventionally, all pathologies when blood is detected from the urethra in men are divided into several groups, based on the causes of the problem. Listed below are the main reasons that can cause a high red blood cell count.
Symptoms of diseases
The presence of blood in the urine in the vast majority of cases is only one of the signs of an extensive symptom complex that combines various pathological manifestations depending on the nature and characteristics of the existing disease. Below are the most common symptoms that can be combined with such a negative phenomenon as hematuria:
- Various pathologies and diseases of the prostate gland, for example, are often accompanied by the release of not only hemolymph, but also particles of purulent masses in the urine. Additional symptoms are also observed, including decreased libido, pain in the pelvic organs, and disruption of urination processes in general.
- Kidney diseases cause symptoms such as pain in the lumbar area, unpleasant smell of urine, cloudiness, severe burning sensation when urinating. Inflammatory processes may be accompanied by an increase in general body temperature, the appearance of reddish or bloody streaks and clots in the urine.
- The appearance of red urine, not accompanied by pain, often means that the tissue of the urethra is damaged. Most often, such urine occurs after sexual intercourse.
- Oncological diseases associated with the growth of malignant tumors are accompanied by acute painful sensations and a rapid deterioration in general well-being. Most often in such cases, it happens that the urine comes with large bloody clots.
- The most rarely detected pathology, the development of which is characterized by the appearance of blood streaks, ichor, and particles of purulent masses in urine, is cystitis - a disease of an infectious-inflammatory nature that affects the mucous tissues of the excretory system. Against the background of this disease, it can be painful for a man to urinate, and very little biological fluid is released at a time.
Blood in urine due to surgical pathology
If a person has surgical pathologies, it is quite possible to see blood at the end of urination. Main pathologies:
- tumor of the bladder and ureters, kidneys. The neoplasm can be benign or malignant;
- urolithiasis - often because of it, red blood cells in the urine increase. Especially when the pebbles are sharp and small and can damage the tissue around them;
- Prostatitis is a disease that affects older and younger men. If a symptom such as microhematuria has already appeared, this is dangerous. Bleeding is difficult to stop. More often, bleeding due to prostatitis is detected in elderly patients;
- vascular abnormalities;
- damage to the urinary tract, including during a medical examination.
If a man’s blood pressure drops due to hematuria, this may indicate an urgent need for surgical intervention.
Treatment methods
The appearance of blood in the urine is a mandatory reason for carrying out diagnostic measures with the subsequent prescription of therapeutic procedures and measures. Treatment tactics are developed based on the research results. Depending on the previous diagnosis, the treatment methods used for the appearance of hematuria can vary significantly:
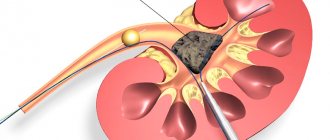
- The most common cause of the appearance of blood clots and hemolymph streaks in urine is the formation of stones. To remove stones from the kidneys, urinary ducts, and directly from the bladder, various methods are used, the choice of which depends on the size and shape of the tumors. Large stones are removed through surgery, while smaller ones are eliminated using physiotherapeutic procedures and medications.
- If blood in the urine is not a consequence of any disease, medications such as Dicynon and Vikasol are used to eliminate hematuria.
- Against the background of infectious and inflammatory diseases, medications that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects are used.
- Surgical intervention may also be required if the patient receives severe injuries and bruises of the organs of the excretory system, or with the formation of malignant and benign tumors.
- If a large amount of blood is excreted in urine, there is a possibility that the patient will develop anemia. Treatment of this pathology requires the use of iron-containing drugs and correction of the diet.
- Patients suffering from urolithiasis, infectious and inflammatory diseases are required to follow a gentle diet, the main goals of which are: cleansing the body of toxic substances and breakdown products, preventing deficiency of important microelements, and normalizing the outflow of urine.
If hematuria develops, it is strictly not recommended to use various methods of alternative therapy without prior agreement with the attending physician. Homemade folk remedies, despite their relative safety and undoubted benefits, may well cause harm to the body if used incorrectly.
Unfortunately, there are currently no truly highly effective methods for preventing the appearance of blood in the urine. However, a number of measures can be identified that will help somewhat reduce the likelihood of developing a dangerous and unpleasant symptom.
First of all, it is necessary to give up bad habits, because they often contribute to the destruction of the tissues of small vessels, including those penetrating the tissues of the bladder. Equally important is giving up a sedentary lifestyle, this is especially true for older men. Lack of physical activity leads to the development of stagnant phenomena and dysfunction of the internal organs of the small pelvis.
It is important to remember that measures taken in a timely manner will minimize the possible risks of developing severe complications of hematuria. Even against the background of a one-time appearance of blood in the hemolymph, you should immediately contact a specialist to make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Therapeutic pathologies that cause blood in the urine
Along with surgical pathologies, therapeutic pathologies often occur with pain. This alone may tell a person that he needs to go to the doctor. If, after urinating, there is blood on your underwear, you need to go to the clinic as soon as possible. The following therapeutic pathologies are known that cause microhematuria:
- glomerulonephritis. In the early stages of this pathology, the norm of red blood cells in the urine is greatly exceeded. The analysis detects protein. The stronger the inflammation, the more red blood cells will be in the urine;
- infections of the genitourinary organs (pyelonephritis, urethritis, cystitis);
- pathologies of blood vessels in the kidneys (acquired, congenital);
- hemolytic diseases, causing the penetration of red blood cells through blood vessels without damaging them.
Any reasons that provoke the release of blood from the urethra require clarification of the diagnosis, which means it’s time to contact a doctor.
What is not recommended to do is to treat yourself without knowing exactly why.
What to do and who to contact?
Self-treatment is absolutely unacceptable; it is necessary to contact a therapist, who will refer the patient for tests to determine the source of the problem. A urine and blood test, an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder will be required.
Based on the results obtained, the therapist will make a preliminary conclusion and give a referral for consultation with a specialist:
- A urologist - if there is a suspicion of cystitis, urethritis, urolithiasis or prostate diseases.
- Nephrologist - if preliminary observations diagnose pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis and other renal pathologies.
- Oncologist - if there is a suspicion of tumor diseases.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of diseases, you must adhere to the following rules:
- follow a proper diet (exclude large amounts of fatty, fried and overly salty foods);
- exercise regularly (physical activity should be dosed);
- do not self-medicate when the first signs of dysfunction of any organ appear.
The presence of hematuria always indicates the presence of some pathological process in the body. If this symptom is detected, a man, instead of self-medication, should immediately contact a competent specialist (nephrologist or urologist) for diagnosis and treatment.
The most common cause of hematuria is a simple bacterial infection of the urinary tract due to poor personal hygiene. Basic recommendations to prevent damage to the mucous membrane by microbial agents:
- you should wear loose underwear made of natural fabrics, with high-quality dyes;
- use public toilets and baths with caution to prevent sexually transmitted infections from entering the mucous membranes;
- it is necessary to avoid hypothermia of the body in the cold season;
- For women, it is important to timely change personal hygiene products during menstruation;
- it is necessary to monitor the child’s personal hygiene in the morning and evening, to carry out timely changes of linen and diapers;
- compliance with the physical activity regime;
- regularly do a complete examination of the body.
Cause: Bladder cancer
If there is blood in the urine, the causes may lie in malignant diseases. One of them is bladder cancer. This is a neoplasm that is formed from epithelial tissue. Men get sick more often than women. Cancer can be caused by the following reasons:
- exposure to carcinogenic substances,
- smoking,
- harmful production factors,
- schistosomiasis.
The disease occurs in 4 stages. In the first stage, only the mucous layer grows into the tumor. Stage two cancer is characterized by damage to all membranes, including the muscle membrane. In the third degree, the surrounding soft tissues are involved in the process. Stage IV cancer is characterized by the presence of distant metastases. This affects other organs.
Bladder cancer manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- intense aching pain in the lower abdomen,
- difficulty in urine flow,
- skin itching,
- weight loss,
- false urge to go to the toilet,
- the presence of fresh blood in the urine.
If hematuria is combined with pain during voiding, then other diseases must be excluded. Urine takes on a reddish tint. Microhematuria is most often observed. In this case, red blood cells are detected only during laboratory testing. This disease is often detected in older people. Urinary problems in women and men with cancer may manifest as urinary incontinence.