Author of the article
Arthur Viniaminovich Artemyev
Urologist, gynecologist, practicing specialist
Articles written
64
Contact the author
Today, diseases of the genitourinary system are one of the most common pathologies. Hematuria in men is no exception, the causes of which can be very diverse.
How does hematuria form and what does it mean?
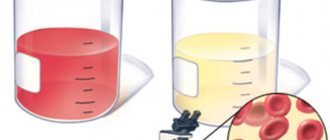
Hematuria is the presence of blood clots in the urine.
Normally, urine is straw-yellow in color and transparent. There are microhematuria and macrohematuria. Microhematuria is the appearance of red blood cells in the urine as a result of microscopy. It is almost impossible to notice blood in the urine with the naked eye. Microhematuria can be caused by excessive physical activity. It is not a pathological condition, because after rest it disappears. Macrohematuria is the presence of blood clots in the urine, visible without a microscope.
The development of hematuria is facilitated by various injuries, infectious and inflammatory processes and other pathological conditions. This leads to thinning of the walls of capillary vessels, which burst. The result is the release of blood in urine.
Causes of blood in urine in men
Depending on the location of the pathological process, various causes of hematuria are distinguished:
- Damage to the upper parts of the urinary system (kidneys) leads to the development of hematuria in the following pathological conditions:
- blunt trauma, knife/penetrating wounds;
- urolithiasis (the movement of kidney stones through the structures of the urolithiasis leads to their violation of their integrity and the release of blood);
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the kidneys (acute/chronic glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis);
- abnormalities of kidney development (cysts);
- pathologies of the blood system (sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, von Willebrandt disease, leukemia, leukemoid reactions);
- renal vein thrombosis;
- renal embolism;
- kidney tumors (benign and malignant);
- foreign bodies;
- sepsis.
- The occurrence of morphological-destructive changes in the ureter also leads to the appearance of blood in the urine during injuries of the lumbosacral region, ascending genitourinary infections, in the presence of stones and tumors in the ureters.
- Inflammation of the bladder, hemorrhagic cystitis, infectious and parasitic diseases caused by fluke worms (schistosomiasis), injuries, tumors contribute to the development of hematuria. Treatment of oncological diseases with drugs with high chemical activity (cyclophosphamide) and chemotherapy can also lead to the appearance of blood in the act of urination.
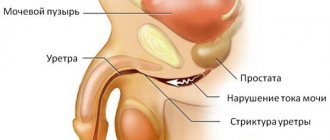
- Foreign bodies, benign and malignant neoplasms, inflammatory processes in the urethra injure the vascular walls, causing bleeding.
- Inflammation of the prostate gland, prostate adenoma, malignant tumors and sexually transmitted infections are a common cause of hematuria.
Hematuria can occur during medical procedures, namely catheterization of the bladder and when collecting material from the urethra. It can also be accompanied by pain when urinating, pain in the lower back, increased body temperature and chills.
Diagnostic methods
When the first symptoms appear, you should seek help from a urologist. After collecting complaints and identifying possible causes, laboratory research methods will be prescribed. These include:
- A general blood test will change with infectious and inflammatory processes in the urinary system. The level of leukocytes and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increase. With pathologies of the blood system, the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells may decrease.
- In a general urine test, in the presence of inflammation (glomerulonephritis/pyelonephritis), urolithiasis and tumors, urine color and density change, and the number of red and white blood cells in the field of view increases. Normally, there are 1-2 red blood cells per subsection, and 3-6 leukocytes per subsection.
- In a urine test according to Nechiporenko, you can determine signs of inflammation (increased number of leukocytes and cylinders), as well as a high level of red blood cells, which changes the color of urine.
- In tank culture, the causative agent of the disease and the sensitivity of antibiotics to the pathogen are determined in order to prescribe effective treatment.
In addition to laboratory research methods, instrumental ones are used. These include ultrasound of the pelvic organs, renal angiography, computed tomography.
Using ultrasound, it is possible to detect tumor formations in the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and changes in the structure of the organs of the urinary system.
Computed tomography provides clear localization of the affected area.
Factors in the development of the disease
Diagnostics
To accurately determine the cause of hematuria and prescribe further treatment, a diagnosis is carried out, which includes the following measures:
- general urinalysis: the density of urine, its color and transparency are determined,
- general blood test: will exclude anemia and identify inflammatory processes,
- assessment of daily urine volume,
- blood test for biochemistry: determination of the level of urea, creatine, potassium and sodium,
- urine analysis using the Nechiporenko method,
- X-ray examination for urolithiasis to determine the location of stones,
- Ultrasound of the urinary system,
- Ultrasound with the Doppler effect: allows you to assess the condition of the kidney vessels, the speed of blood flow in them and exclude relevant pathologies,
- bacteriological analysis: prescribed to exclude the infectious origin of hematuria.
It is this comprehensive approach that will allow timely identification of the cause of blood discharge in the urine, prescribing the necessary treatment and preventing further development of pathological processes.
Blood in the urine in men is a fairly common ailment caused by a malfunction of the urinary system. It can occur in every person (adults, children, elderly people).
How is the treatment carried out?
After visiting a specialist and establishing the cause of blood in the urine, adequate effective treatment will be prescribed. Taking medications aimed at eliminating the symptoms of hematuria will not lead to a successful cure. First, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the development of the pathology.
It is prohibited to treat hematuria on your own. This can lead to serious complications, decreased sensitivity to antibiotics and worsening symptoms.
Depending on the cause of hematuria, the following treatment options exist:
- In the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process in the organs of the urinary system, antibacterial therapy is recommended. The most effective are broad-spectrum antibiotics (Augmentin, Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin).
- In the presence of pathologies in the blood system and blood loss (≥500 ml), blood transfusion is recommended.
- In the presence of kidney stones, thrombosis of the renal vessels, neoplasms in the organs of the urinary system, or injuries, surgical treatment is recommended.
Methods for detecting hematuria
How is hematuria diagnosed?
1. First of all, the doctor will collect an anamnesis, asking the patient in detail about his well-being and studying the medical history, firstly, of the sick person himself, and secondly, of his blood relatives.
2. A rectal examination will then be performed to look for tenderness or lumps in the urinary organs.
3. To complete the picture, the patient will be asked to take a blood and urine test.
4. If necessary, they will resort to an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder.
5. In some cases, cystoscopy is prescribed: under local anesthesia, a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the patient’s urethra and the bladder mucosa is examined for damage and tumors.
Based on medical examination data, treatment is prescribed.
But you definitely shouldn’t resort to folk remedies without consulting a specialist.
Causes of hematuria in men
Determining the root cause of the appearance of blood in men’s urine is the main point for prescribing a course of treatment and preventing complications.
Inflammation
Changes in the composition of urine and the appearance of blood impurities in it are often the result of inflammatory processes in the male urinary system. Inflammation can occur due to autoimmune diseases - systemic lupus erythematosus and glomerulonephritis.
As a result of an immune attack on kidney cells, the structure, metabolic processes, condition of blood vessels and blood circulation are disrupted. In addition to blood in urine, symptoms manifest themselves in:
- high blood pressure (hardly reduced even with medication);
- severe swelling of the face and body;
- feeling of “hot” joints.
Another cause of inflammation of the male excretory system is congestive diseases of the kidneys, bladder, and prostate gland.
Stagnation of urine, hypothermia, decreased immune forces of the body are the main factors of inflammatory non-infectious diseases.
- regularly appearing blood in the urine of a man with pain of varying intensity;
- pain, burning in the urethral area that occurs during urination and persists after;
- feeling of constant fullness of the bladder;
- nagging pain in the groin area, lumbar region.
Infections
Diseases arising from the ingress of microbes are the cause of hematuria in men in 70%. Pathologies of infectious nature:
- Pyelonephritis. Blood stains the urine dark red or tea-colored, hematuria is accompanied by lumbar pain.
- Kidney tuberculosis. Hematuria occurs due to ulceration of blood vessels. A man bleeds during urination, the process is not accompanied by pain. The shade is dark red.
- Cystitis. Blood impurities are insignificant, pure red.
- Urethritis. Inflammation of the urethra in a man is characterized by small inclusions of a brownish color. Hematuria is accompanied by a strong, persistent burning sensation.
- Infectious prostatitis. Urine contains blood inclusions of medium volume and may turn pure red.
Urolithiasis disease
Hematuria in men with urolithiasis is the most common symptom (manifests in 90% of cases). As sand and stones move, they injure the vessels of the excretory system, causing blood to appear in the urine.
The removal of sand from the kidneys is not always intensive. In this case, the main sign of the disease in a man will be a slight nagging pain in the lower back and reddish-brown spots in the urine.
Intense release of stones and their passage through the organs of the excretory system is characterized by acute pain (renal colic), concentrated in the lower back and spreading to the pubic area, groin, and penis. In the urine, inclusions of blood of a rich red color appear, or the entire urine acquires a bright scarlet hue.
Adenoma
Benign proliferation of prostate tissue can also manifest as hematuria. Venous stagnation, compression of blood vessels, circulatory disorders due to an enlarged gland are the main reasons for the appearance of blood in the urine in men.
The expanding prostate primarily affects the process of urine expulsion. If hematuria is accompanied by a sluggish stream, the time of urination increases, this means that the man has blood due to an enlarged gland.
Hematuria manifests itself in different ways, depending on the stage of prostate adenoma:
- Initial. Blood is not detected visually, but can be detected in a laboratory.
- Average. There are minor blood impurities (dark red or brown).
- Launched. The process of urine excretion is very difficult (urine is excreted drop by drop), and blood inclusions have a brownish tint.
Malignant neoplasms
Oncological diseases of the urinary system at the initial stage are often practically asymptomatic. However, even a small tumor is accompanied by subtle signs that can be noticed:
- Kidney damage. Subtle, irregular lumbar pain appears.
- Bladder cancer. A man experiences slight discomfort after urinating.
- Malignant lesion of the prostate. Subtle difficulty urinating.
At the initial stage, the disease is accompanied by microhematuria, which is not visually detectable.
As the formation grows, the veins, vessels, and lymph nodes of the system are affected, which is why blood appears in a man’s urine:
- With malignant kidney tumors, the urine turns brown.
- Bladder cancer is characterized by a red tint to the urine.
- Prostate oncology. When a tumor lesion grows into the rectum, blood appears in urine and feces. Shade – burgundy-red.
Physical exercise
If urine with blood appears after intense strength training or a long static sitting position (driving, at the computer), there is no need to panic. During sports, blood flow in the kidneys accelerates, causing microscopic vascular damage. This causes the appearance of bloody elements in urine.
Should I go to the doctor if there is no pain?
Blood clots in the urine in men are a reason to immediately consult a urologist, even if there is no discomfort or pain. The appearance of bloody spots in a man’s urine without pain is a possible sign of cancer. To exclude such a diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a detailed examination.
Dark, red urine in a man without any pain may indicate serious kidney injury. Damage to an organ is not always accompanied by pain. The only symptom may be a change in urine color.
Prevention
To prevent hematuria, following simple recommendations is indicated:
- it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle: monitor your diet, drinking regime, introduce moderate physical activity, give up bad habits
- avoid hypothermia
- focus efforts on strengthening the immune system
- refrain from casual, unprotected sexual intercourse, use barrier contraception
- observe personal hygiene rules: shower twice a day, use high-quality toilet paper
- promptly treat emerging dysfunctions of the urinary and cardiovascular systems, refrain from self-medication
- undergo regular examinations with a urologist
- limit excessive psycho-emotional stress
- give preference to high-quality, comfortable underwear made from natural materials;
- normalize weight
- observe the work and rest schedule
- men are also recommended to visit the restroom in a timely manner: empty the bladder upon request
To prevent kidney disease, it is recommended to limit the consumption of salt, sugar, smoked foods, fatty, sour, and spicy foods.
The presence of a few drops or a large volume of blood in the urine is an alarming sign that should not be ignored. At the first signs, it is recommended to consult a doctor and undergo diagnostics. Microhematuria (small amounts of blood) may require additional tests because it is not always immediately detectable.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostic measures for hematuria:
- general clinical tests: OAM determines red blood cells in the urine, OAC reveals changes in the blood that indicate the root cause of hematuria;
- studying urine using the Nechiporenko method is one of the most sensitive tests, which is guaranteed to detect microscopic traces of blood in the urine of men;
- three-glass test (detects the type of hematuria);
- urine culture for flora - if hematuria is suspected to be of a bacterial nature;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- hematuria with cystitis of unknown nature requires cystoscopy.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor interviews and examines the patient. A comprehensive examination is prescribed, aimed at checking the condition of the urinary system and the body as a whole. Detection of increased levels of red blood cells is carried out using the following methods:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. Screening allows you to assess the condition of organs and their functioning. Sometimes tissue is collected using a needle for more detailed study in the laboratory.
- Biochemical analysis of blood and urine. The presence of an inflammatory process and infections is checked. If necessary, testing for cancer markers is done.
If the bleeding is heavy, then the specialist makes a three-glass sample to determine the nature of the bleeding and its intensity.
Complications of blood in urine
Excretion of blood in the urine in men is a condition that requires mandatory diagnosis, since in most cases it indicates the presence of serious problems. Diseases that cause hematuria can be successfully treated at the initial stage, but as they progress, they cause severe complications:
- Minor pain intensifies, pathological processes affect an increasingly larger area, spreading to nearby organs.
- In a man, in addition to malfunctions in the excretory system, sexual function is disrupted, libido decreases until it disappears completely.
- The presence of hematuria indicates the possibility of malignancy (transition to cancer) of benign formations.
- The risk of acute renal failure, pathological changes in all organs of the urinary system, and blood poisoning (sepsis) increases.
How to treat
When blood is detected in a man’s urine, the therapeutic course is aimed at eliminating the root cause and accompanying symptoms.
Infectious and inflammatory processes are controlled by antibacterial therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs. This allows you to destroy the cause of inflammation - the infectious pathogen.
A malignant neoplasm (depending on its shape and type) is eliminated surgically. Complex treatment includes hormonal, chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Urolithiasis requires the mandatory introduction of a special treatment table and correction of the drinking regime. This allows you to normalize metabolic processes, reduce the load on the excretory system, and prevent the formation of new stones. For particularly large stones, procedures are prescribed that crush them into smallest elements.
Additionally, for any disease, antispasmodic, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and immunomodulators are prescribed.
The appearance of blood in a man’s urine is a signal of pathological processes. They are not always dangerous, but require mandatory diagnosis and monitoring by a urologist. Timely medical care will prevent the progression of the disease, complications and serious consequences.
What it is?
Hematuria is a condition in which red blood cells (erythrocytes) are found in the urine. In case of serious problems, the urine takes on a pronounced pink or red-brown color, but in the initial stages of the disease, the urine may look quite normal. The disease manifests itself not only in the male half of the population; hematuria in children and hematuria during pregnancy are also known in medical practice.
The mechanism of development of hematuria is quite well studied. The development of the disease is based on three processes:
- increased permeability of the glomerular capillary membrane,
- destruction of small capillaries of the glomeruli of the kidneys,
- violation of the integrity of the walls of blood vessels in which secondary urine is formed.
In order to accurately establish the cause of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and collect a complete medical history.
Brief description of the mechanism
Modern means of self-defense are an impressive list of items that differ in their operating principles. The most popular are those that do not require a license or permission to purchase and use. In the online store Tesakov.com, you can buy self-defense products without a license.
The formation of primary urine occurs in multiple glomeruli of the kidneys, each of which is a network of capillaries enclosed in a capsule (Shumlyansky-Bowman capsule). The capillary wall consists of three shells:
- internal, consisting of a single layer of endothelial cells;
- outer - one layer of large epithelial cells from the side of the glomerular capsule;
- middle (basal membrane), which is a structure of three layers formed by special thread-like collagen-like proteins, glycoproteins and lipoproteins, between which there are filtration pores.
The basement membrane is a kind of filter. Through its pores, water molecules, low-molecular proteins, waste products, etc. freely pass from the blood into the Shumlyansky capsule, which constitutes primary urine. However, the pore size is significantly smaller than the volume of blood cells, due to which only a few red blood cells are able to pass through the basement membrane into the urine. From the capsule, primary urine enters the tubules, where water, macro- and microelements, chlorine, proteins, etc. are reabsorbed into the blood, that is, secondary urine is formed, entering the ureters, bladder and then into the urethra ( urethra).
So, hematuria can occur as a result of destruction of glomerular capillaries or increased permeability of their basement membrane, as well as destruction of the vascular wall throughout the formation of secondary urine and its excretion.