Urology
1762
no comments
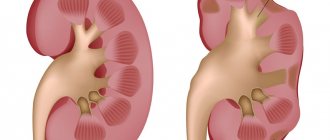
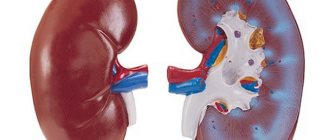
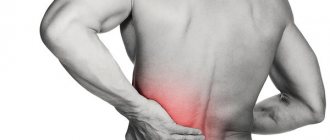
Renal colic is considered one of the most painful and dangerous pathologies: symptoms in men can manifest themselves in the form of severe spasm-like pain that radiates to the right or left lower back.
The onset of renal colic is always sudden. Severe pain is caused by the fact that urine cannot fully leave the kidney. A large amount of it greatly irritates the smooth muscles of the kidney; it can be injured by stones or sand. This leads to spasm and causes severe pain.
Provoking factors and causes of renal colic in men
The factor or cause of symptoms may be:
- the development of urolithiasis, which is one of the most common causes of colic. This pathology can occur in men of any age category, but the most common are deposits in the kidneys and ureters in men aged twenty to forty years. In the bladder, deposits may occur in a child or an elderly person;
- presence of oxaluria . Stone formations are characterized by increased hardness and sharp edges and spikes, which easily injure the urinary tract;
- with phosphaturia and uraturia, the occurrence of colic is rare, but in such cases, stones clog the urinary tract, which leads to fairly severe dull, constant pain;
- the occurrence of cystinuria , which manifests itself in a congenital disorder of the kidney’s secretion of the required set of amino acids. With this disease, kidney stones have a smooth, soft and round structure.
In the presence of formations of sand or stone deposits, the following appears:
- injury to the renal canals with the formation of blood clots that seal the ureteral system;
- tumor renal lesion that spreads to the ureter. A tumor may also develop in the bladder or in parts of the rectum;
- nephroptosis appears;
- congenital anomaly of one of the organs of the urinary system;
- pathological narrowing of the lumen in one of the canals of the urinary system.
Causes
Colic is not an independent disease; doctors consider them more as symptoms confirming the occurrence of a pathological malfunction of the renal organs.
The most common reason why men begin to experience painful colic in the kidneys is ICD.
Urolithiasis is characterized by the formation of stones in the kidneys that differ in size, composition, and shape.
If conglomerates with sharp protrusions have appeared in the kidneys, which is typical of oxalates, then renal colic will occur quite often, especially if the stones rush along with the urine to the exit through the urinary tract.
Violation of the outflow of urine can also provoke intense renal colic.
In fact, such pathological processes occur against the background of the presence of stones that block the urinary tract due to their large size.
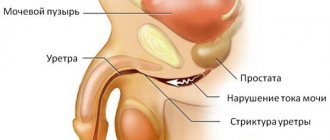
However, they are not the only provocateurs of failure of the urinary process. Malfunction of the urinary process can be observed in men if they have prostate adenoma or congenital strictures (they are more common in newborn boys).
Injuries received as a result of a blow or fall can provoke a failure of urination, as well as subsequent renal colic.
Hematomas, minor internal bleeding appear in the organs of the urinary system, and blood clots form. They are the ones who clog the ureter.
Malignant neoplasms that affect the kidneys can also cause renal colic.
Over time, the tumor grows, gradually squeezing surrounding organs. For this reason, the lumen of the urinary ducts may initially decrease, significantly slowing down the outflow of urine.
Subsequently, when the lumen completely disappears, the outflow of urine becomes completely impossible.
In any case, with a tumor lesion, a man will feel renal colic, accompanied by varying intensities.
Kinking of the ureter can provoke the disappearance of the lumen of the urinary tract. This condition is typical in cases where a man’s kidney is overly mobile, and doctors diagnose nephroptosis or a wandering kidney.
How does renal colic manifest in men?
The symptoms of renal colic can be different, because it depends on the cause of its occurrence, in addition, the symptoms often depend on the location of the problematic source.
Symptoms in men with renal colic:
- pain that passes through the channel, while radiating to various parts of the body, for example, to the groin or lower back;
- the appearance of blood clots or color changes in the urine;
- dyspeptic type of disorders, including vomiting and increased gas formation;
- the occurrence of frequent and painful urination;
- the amount of urine excreted decreases;
- weakness appears throughout the body, with loss of appetite and headache. These symptoms often signal the development of pyelonephritis.
If you have these symptoms, which are characteristic of colic, you need to start providing medical care.
Complications of the disease
If symptoms of renal colic appear, you should seek medical help, as this disease can cause the following complications:
- urosepsis;
- renal failure;
- obstructive pyelonephritis;
- formation of ureteral stricture;
- bacteremic shock.
Diagnosis of the disease in men
If symptoms occur, a man should promptly consult a doctor who will diagnose the identified pathologies and find out the reasons for their occurrence.
Diagnostic procedures:
- interviewing the patient to clarify all provoking factors and circumstances;
- examining the patient and palpating the abdomen and lower back;
- laboratory tests of general blood and urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary system;
- if necessary, excretory urography or computed tomography examination is used.
When the cause is identified, the necessary therapy is prescribed; if the causes of renal colic have not been identified, then a re-examination is carried out, during which the patient is under constant observation.
First aid
If a spasm occurs in the lumbar region, you must call an ambulance. Pain in the lumbar region can indicate many diseases, so it is important to undergo studies that allow you to determine the cause of the discomfort and prescribe appropriate treatment. Delay may lead to complications.
Medical assistance is needed when:
- hyperthermia reaches critical levels of 38-39 0 C;
- the number of urges to empty the bladder increases, discomfort and burning occur;
- a white precipitate or flakes, impurities and blood clots are found in the blood;
- symptoms of intoxication develop;
- the body swells.
Features of therapy
Therapy is prescribed by a specialist depending on the disease. In addition, treatment should be aimed at relieving pain and ensuring the normal functioning of the urinary system.
Therapy methods:
- surgical intervention is used only in severe cases or when a serious complication occurs;
- medication treatment is carried out for pain relief, using antispasmodic and analgesic drugs, for example, noshpa, promedol, spazgan, analgin;
- if the attack is prolonged, then a novocaine-type blockade of the spermatic cord area is performed;
- the acute stage requires the use of a certain set of drugs that will facilitate the passage of stones. For example, cystenal, piston, avisan.
One of the features of therapy is diet therapy:
- oxaluria is treated by reducing the consumption of sour vegetables, for example, sorrel;
- uraturia requires limiting the consumption of various meat broths and semi-finished products;
- phosphaturia is treated by reducing the consumption of dairy products, fruits and vegetables;
- For some diseases, treatment is carried out with mineral water, the use of which is regulated by a doctor, since excess consumption often aggravates the course of the disease.
Even with the initial manifestation of renal colic, treatment in sanatorium-resort places is recommended, and the place must be prescribed by a doctor, since different types of diseases require treatment with different substances.
Treatment with physiotherapy and herbal medicine is also recommended. If chronic inflammation of the urinary canal has been detected, then treatment is carried out with a number of antimicrobial drugs, for example, etazol or biseptol.
Pathology therapy
With renal colic, symptoms in men and treatment depend on the stage of the disease, the size of the stones that caused the pain, the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases. The goal of treatment therapy lies in 2 factors:
- clear the urinary tract;
- relieve pain.
Treatment consists of taking:
- antispasmodics;
- painkillers;
- diuretics (water medications);
- means that crush stones.
At high temperatures, antipyretics are prescribed in appropriate dosages.
If necessary, a procedure using ultrasound is prescribed to crush large stones.
If the stone is very large, then surgery is required. Therefore, patients are prescribed a number of diagnostic procedures to help determine the size of the stones. Diuretics are prescribed only when the stones are small.
Among the common antispasmodics that help relieve spasms are No-shpa, Papaverine. You can relieve pain and fever by taking Diclofenac. Complex therapy may also include the following drugs:
- Platyfillin;
- Analgin;
- Baralgin;
- Promedol;
- Atropine;
- Cystenal;
- Olimethine;
- Avisan;
- Ortofen;
- Trigan.
In case of infectious processes, antibacterial agents (antibiotics) are prescribed. Diet plays an important role in treatment.
You should limit your consumption:
- sorrel;
- salad;
- spinach;
- meat and rich broths;
- offal;
- fruits and vegetables;
- milk;
- cocoa, chocolate, strong coffee;
- smoked meats and canned goods.
The use of mineral waters to improve your condition is only possible after consulting a doctor.
For chronic processes, herbal remedies and physiotherapeutic manipulations are prescribed.
Antimicrobial medications are required for prostate adenoma and other urological diseases that cause renal colic.
First aid for renal colic
During an attack of renal colic, there is a certain algorithm of actions that is aimed at relieving the spasm:
- the patient is provided with complete rest, and he should not make sudden movements;
- the patient is given antispasmodics, for example, noshpa or tempalgin;
- for severe pain, you can give two or three tablets at once or inject two milliliters of noshpa intramuscularly;
- In case of persistent pain, an ambulance must be called and the patient must be hospitalized.
How to give first aid
Since the pain is very severe, the patient must be given assistance before the doctors arrive. To stop an attack, a person can sit in a warm bath. If this is not possible, you need to fill a heating pad with hot water and apply it to the sore area. At home, you can take No-shpa, Baralgin or give an injection of Platiphylline. It is necessary to provide the person with complete peace. In acute form of pyelonephritis, you should not take a hot bath. After hospitalization, the man needs to have his kidneys, prostate, and abdominal cavity examined to clarify the diagnosis.
source: vpochke.ru
The pain syndrome of a number of urological diseases has a general name - renal colic: the symptoms in men and the treatment of this disease have their own characteristics.
Cramping pain appears due to difficulty, for some reason, in removing urine from the body. They appear unexpectedly, at any time of the day, regardless of a person’s state of activity or rest, and cause him great suffering. Sometimes their appearance is provoked by previous heavy drinking.
Intense, sharp, difficult-to-bear pain can appear in the lumbar region, on both sides or only on one, moving or simultaneously involving the lower abdomen, groin and genitals of a man in painful areas. The patient tries to find a forced body position in which attacks of colic are more easily tolerated.
When is hospitalization necessary for renal colic?
Hospitalization occurs when:
- inability to relieve pain attacks with antispasmodics;
- the occurrence of pain simultaneously in two kidneys;
- difficulty urinating;
- the presence of inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract;
- the appearance of high fever and vomiting.
It is important to remember that painful symptoms in the kidney area can also appear in a healthy person, and the pain will not be renal colic, since this symptom can be caused by another acute disease.
First aid and hospitalization
First aid for a patient who has developed colic is quite simple. To relieve an attack, you can use a hot bath. The patient should stay in it for about fifteen minutes. If this cannot be achieved, you can use a heating pad. It should be applied to the lower back. It must be borne in mind that such treatment methods cannot be used by those who have developed pyelonephritis.
The effectiveness of these methods will increase if you additionally take analgesics or antispasmodics. They have a beneficial effect on the elimination of spasms. The following drugs can be used:
- "Atropine";
- "Missed";
- "No-shpa";
- "Platifillin."
If these remedies do not help, the doctor who comes to the call may use a narcotic pain reliever. In some cases, hospitalization of the patient may be necessary. Such a need arises if:
- the patient's only kidney is affected;
- the patient feels pain in two kidneys at once;
- the patient is elderly;
- the patient experiences complications, such as: fever, chills, anuria;
- Over time, the patient's condition does not improve.
In all the cases described above, the patient must be hospitalized. Otherwise, he may experience serious complications that pose a danger to his life. After delivery to the hospital, a diagnosis will be carried out.
Diet for men with renal colic
When renal colic occurs in a man, a diet is prescribed, which has several specific principles:
- food should be taken every four hours in small portions. This is necessary so that the digestive system does not become overloaded;
- the consumption of carbohydrates and fatty foods is reduced to a minimum;
- all meat and fish products must be boiled, since fried and smoked foods are excluded from the diet;
- Confectionery products, as well as rich and flour products should be excluded from the diet;
- fluid consumption, in particular water, increases to three liters per day;
- the basis of nutrition is porridge and vegetable broths;
- in the first twelve hours after the onset of renal colic, therapeutic fasting is recommended.
List of products prohibited for consumption:
- salty, spicy, pickled dish;
- smoked meat or fish;
- various canned foods;
- any fat looking;
- beans and beans, as well as dishes made from them;
- chocolate, desserts;
- spices and hot spices;
- any drinks containing alcohol.
Manifestation
Renal colic is not a disease, but a symptom that indicates other diseases. It is characterized by the appearance of sharp, acute and unbearable pain in the lumbar region. When the pathological process is localized in the left kidney, the pain syndrome covers the left side and side. When the right organ is affected, a feeling of pain and discomfort spreads along the right side of the lumbar region.
Pain in the right side is often a sign of liver pathologies or inflammation of the blind appendix of the intestine.
A feature of colic is the irradiation of an unpleasant symptom. In men, the feeling of pain can spread to the groin area and cover the external genitalia. If the pain syndrome spreads throughout the abdominal cavity and extends to the navel, the cause may be a blockage of the ureter at the site of its exit from the renal pelvis.
The severity of the symptom in men increases during emptying of the bladder - a feeling of discomfort and burning in the urethra occurs. Blood may be excreted in the urine. This sign indicates the movement of stones through the urinary organs, resulting in injury to their walls. There is also a decrease in the amount of urine discharge, while the urge to urinate may increase. The patient may have a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. During general clinical studies, an increase in the level of protein and mucus in urine is determined.
Interesting! During physical activity, prolonged walking, and significant fluid intake, the pain syndrome may intensify.
Other symptoms of renal colic in men may also be present. There are frequent disorders of the digestive tract, which manifest themselves in the form of nausea, flatulence, severe vomiting and diarrhea. Symptoms of intoxication lead to loss of appetite and a feeling of weakness.
Headaches are common. With severe intoxication, body temperature rises, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys. If the outflow of urine is disrupted, an increase in intrarenal pressure is observed, against the background of which blood pressure levels rise. Impaired diuresis causes swelling of the limbs, and later the face and body swell.
Traditional methods of treatment for renal colic in men
Traditional treatment can be of three types:
- treatment with medicinal herbs and plants that help relieve pain and remove stones and sand;
- treatment with popular recipes;
- diet treatment.
The diet uses the same procedure as with conventional medical treatment, that is, all foods that could become one of the causes of renal colic are excluded. There is also a transition to a vegetarian type of cuisine and an increase in water consumption.
Medicinal herbs used for renal colic:
- marshmallow seeds;
- blackberry and henna roots;
- hawthorn;
- wormwood leaves;
- artichoke root;
- radish seeds;
- asparagus roots.
The most popular recipes are:
- seven cakes made from peppercorns, which should be consumed one cake per day;
- using a warm bath for twenty minutes with the addition of several glasses of horsetail decoction;
- mandatory consumption of boiled wheat;
- eating up to two and a half kilograms of watermelons per day with a combination of taking a warm bath;
- carrot seeds are poured with boiling water, after which the infusion is wrapped and infused for twelve hours, after which it is filtered and taken half a glass before meals every day. The ratio of the decoction is a tablespoon of seeds per glass of boiling water.
Diagnostics
The man who immediately seeks help from a doctor does the right thing. It is better to prevent the development of renal pathology than to subsequently strive to eliminate it with therapeutic measures.
When contacting a medical institution, the urologist collects anamnesis, clarifying the hereditary factor, obtaining data regarding the symptoms that appear.
Also, during the first visit, the doctor must examine the man and perform palpation. Even such a simple diagnostic method makes it possible to identify the location of pain and detect the fact of displacement of the renal organ.
During palpation, the doctor may detect a change in the size of the kidney. However, it is impossible to establish a final diagnosis only based on the results of palpation and anamnesis.
For this reason, the man is sent for additional diagnostic measures.
During a laboratory urine test, traces of salt deposits, blood clots, and epithelium may be detected.
If the results of a laboratory test confirm the fact of urolithiasis, it is necessary to take into account what substances have filled the organ.
This will allow the urologist to classify which specific stones damage the kidney and provoke renal colic. Based on such data, successful treatment can be prescribed.
In addition to laboratory tests, the man undergoes ultrasound diagnostics, during which it is possible to identify problems not only with the kidneys, but also with other organs of the urinary system, as well as the intestines.
Urography is indicated, since this type of diagnosis indicates some internal changes in the renal organs, their pathological displacement relative to their natural location.
Radiography can detect not only kidney damage, but also intestinal pneumatosis.
Men are offered to undergo chromocystoscopy if they have symptoms of swelling or if the urologist suspects hemorrhage in the kidney.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may also be performed to identify pathological changes.
How to help a person with renal colic?
Helping a person with renal colic necessarily includes:
- first emergency aid;
- if necessary, call an ambulance, which will carry out hospitalization;
- providing rest to the patient until the pain stops or the ambulance arrives.
To relieve pain, the following procedure is performed:
- antispasmodics are used;
- the patient takes the most comfortable position for him;
- An attempt is made to restore the urinary process, which will reduce pain.
Renal colic is an unpleasant and painful disease that requires immediate medical attention to the patient. The provision of assistance may vary, but it is worth remembering that if the pain syndrome continues, hospitalization is required.
Renal colic: symptoms and treatment, how to relieve pain
The risk of pain depends on age. The pathology occurs least often in children and adolescents, somewhat more often in the elderly. A surge in symptoms is observed at the age of 25–50 years.
Causes
In the vast majority of episodes, the cause of renal colic is urolithiasis (urolithiasis). When stones are found in the ureter, the symptom occurs in 97-98% of patients, in the kidney - in 50-60%. In this case, the lesion can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Other causes of renal colic:
- pyelonephritis;
- neoplasm in the kidney;
- nephrotuberculosis;
- organ damage (compression causes ureahematoma or blood clots);
- gynecological diseases;
- pathologies of the retroperitoneal space.
In addition, an attack of renal colic can be triggered by pinching of the ureter from the outside due to extensive injuries or tumors of the pelvic organs.
It should be noted that such a rarely diagnosed ailment as a wandering kidney. With this disease, a painful symptom occurs as a result of kinking of the urinary tract and makes itself felt after walking, shaking from driving, jumping, and physical activity.
Predisposing factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- employment in hazardous industries (hot workshops, shaking);
- professional sports;
- frequent hypothermia;
- abnormal structure of the urinary tract;
- prolonged dehydration of the body.
The risk group includes people who are fond of salty foods and adhere to a protein diet with a predominance of fatty varieties of red meat.
Symptoms
The classic attack of renal colic begins suddenly. Its appearance is difficult to associate with nervous tension, vigorous activity or other unfavorable factors.
The main symptom of renal colic is a sharp pain lasting from several minutes to a day, and with persistent obstruction of the stone, it lasts for a week.
When a calculus is located in the pelvis of the organ, the unpleasant sensation is localized in the upper third of the lumbar region. In this case, the pain radiates to the stomach and anal area, provoking the urge to defecate. If the blockage occurs in the ureter, discomfort is felt in the lower back and side on the affected side, with irradiation directed down the course of the ureter, to the genitals and groin area.
Often an attack of colic is accompanied by frequent trips to the toilet and pain in the urethra or complete anuria. Other accompanying symptoms may appear:
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness, general intoxication of the body;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- violation of intestinal motor function;
- increased blood pressure;
- decrease in heart rate.
A few hours before the onset of acute renal colic, turbidity and blood appear in the urine. After the attack subsides, the painful syndrome persists for some time, but other manifestations quickly disappear and the patient feels much better.
In men
Symptoms of renal colic in men may resemble other common diseases. For example, with a right-sided lesion, the pain is localized under the lower ribs in the area of the liver or spreads along the right side of the abdomen, creating the appearance of inflammation of the appendix.
When a stone is found inside the bladder, discomfort radiates to the head of the penis and is accompanied by frequent and painful urination.
Among women
Symptoms of renal colic in women often resemble the picture of gynecological diseases: pain is localized in the lower third of the abdomen, radiates to the groin and pubis, lower back ache, and health deteriorates.
Therefore, for representatives of the fair sex, a differentiated analysis of symptoms is necessary to separate colic from diseases such as rupture of the fallopian tube, torsion of the cyst leg, adnexitis or ovarian apoplexy.
Renal colic in women in the third trimester of pregnancy is manifested by severe pain in the lumbosacral region. Symptoms are complemented by unrelief vomiting, dizziness, and possible loss of consciousness.
In children
In babies, an attack of colic does not occur as often as in adults and, as a rule, manifests itself atypically. This is associated with many medical errors when making a diagnosis. What's the problem?
The fact is that in a young child the pain is localized not in the lower back and abdomen, but clearly in the navel area. In this case, additional symptoms are observed:
- vomit;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- bloating;
- constipation.
Pain with renal colic lasts no more than 25–30 minutes, sometimes accompanied by a temperature of 37.0–37.2 °C. Children behave very restlessly at this time: they scream, cry, rush around the room, and do not allow anyone to touch their stomach.
First aid
An attack of colic requires urgent hospitalization. Before the ambulance arrives, the patient must be put to bed and calmed down, and then, if the nature of the discomfort is beyond doubt, emergency medical measures must be taken.
Emergency care for renal colic includes:
- taking painkillers. It could be Baralgin, No-shpa or Analgin;
- heat on the sore spot - apply a heating pad strictly to the lower back (not on the stomach or between the legs) or take a hot bath. The procedure will help get rid of spasms and ease the attack.
If the pills do not help and the person continues to suffer, the painful symptom can be relieved with injections. Adults and adolescents over 15 years of age are administered Revalgin. Drotaverine (Noshpa) and Ketorolac provide a good analgesic effect.
All medications taken and administered must be written down and then reported to the doctor. Properly performed first aid for renal colic can shorten the hospital period, and in some cases, do without it.
Complications
The risk of complications depends on the underlying disease, the initial condition of the patient and the adequacy of the measures taken. If renal colic is not treated correctly, acute pyelonephritis, ureteral stenosis, urosepsis and endotoxic shock may be added to urolithiasis.
Prevention
Prevention of renal colic is based on the prevention of urolithiasis. The following measures will help you avoid this dangerous disease:
- a balanced diet with a predominance of vitamins A and D;
- systematic intake of mineral complexes with calcium;
- limiting salty and spicy foods;
- drinking at least two liters of plain water per day;
- timely treatment of nephrological pathologies.
It is necessary to avoid hypothermia and any injury to the lower back. If urolithiasis has already been diagnosed, the patient should follow the prescribed diet and all the doctor’s recommendations.
Renal colic is a rather serious symptom that requires qualified medical assistance. You can, of course, try to alleviate the painful condition on your own, but only if the diagnosis is beyond doubt. In all other cases, it is better to immediately contact a specialist.
Source: https://nefrologiya.pro/pochki/kolika/pochechnaya-kolika/
Treatment methods
To alleviate the condition of a patient experiencing renal colic, you can resort to the following measures:
- Taking an antispasmodic. To slightly reduce discomfort, it is necessary to relieve renal spasm. For this, the patient is given No-Shpu, Drotaverine, Spazmalgon. If possible, it is better to give an intramuscular injection of an antispasmodic.
- Thermal procedures. If we are talking about real renal colic, then heat will bring significant relief. To do this, you can apply a heating pad to your lower back or take a bath.
- Preparing the container. It is better to empty the bladder into a specially prepared container so as not to miss the release of the stone. It is not the liquid that is valuable, but the stone that comes out. Subsequently, it is submitted for testing of its chemical composition. This will allow you to determine exactly what disorders are occurring in the body and select the optimal treatment methods.
To reduce the pain of renal colic, you can take a hot bath
You can practice thermal procedures only if you are 100% sure of renal colic. If there is even the slightest doubt about the diagnosis, it is better not to resort to this method. Using heat for appendicitis or peritonitis can lead to serious consequences.
To relieve acute symptoms and restore urodynamics, a patient in a hospital setting may be prescribed the following medications:
- Antispasmodics and analgesics. Such drugs can reduce pain and stop spasms. The following remedies are most often recommended: Baralgin;
- Platifilin;
- No-Shpu;
- Papaverine;
- Atropine;
- Promedol.
- Nitroxoline;
- Trental;
- Diclofenac;
- Furosemide;
- Glucagon;
Compliance with nutritional rules
For urolithiasis and renal colic, as well as for other problems with the urinary system, accompanied by pain, no treatment methods will be effective unless you follow a certain diet.
It is prohibited to use:
- strong brewed tea and coffee;
- smoked meats, sausages, preserves;
- cocoa and chocolate;
- pickles;
- legumes;
- offal.
Can be used:
- fruits;
- cereal porridge;
- boiled or steamed vegetables;
- vegetable broth soups;
- fresh vegetable salads.
If renal colic occurs due to the presence of stones, then with urates you should not eat offal and sour fruits, with phosphates you should not eat dairy products, and with oxalates I require a ban on milk, spinach and lettuce.
Outpatient treatment
After relief of the acute condition, the doctor recommends taking medications to dissolve and remove stones:
- madder - helps with phosphates, it is not recommended to use it with cystone (since it also contains this active substance);
- asparkam – helps with oxalates (should be taken with caution in case of cardiac pathology);
- blemaren – for urates and oxalates;
- allopurinol and purinol (reduces the amount of uric acid, helps with urate);
- cystone - does not affect the acid composition of urine, and helps with all types of formations.
Dissolution of stones in men and women is a long process, so medications should be taken for several months to obtain a positive effect.
Lithotripsy
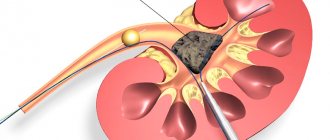
Specialists and scientists are constantly looking for new methods in the treatment of renal colic. One of the modern ways to get rid of kidney stones is lithotripsy. This technique allows you to destroy a calculus using ultrasound or laser without disturbing the integrity of the patient’s skin. Under the influence of a directed wave, the stone is destroyed, until dust is formed, after which it is freely excreted in the urine.
The technique has certain advantages, since it is highly effective, does not require long-term recovery (after a few days the patient begins daily activities), and allows one to avoid surgical intervention.
Lithotripsy is performed in two ways - remote and contact. With remote exposure, crushing is carried out using wave focusing, without introducing special devices into the body cavity. But this can cause damage to neighboring organs and tissues, and it is not always possible to get rid of the stone in one session.
Therefore, a more accurate technique is contact lithotripsy. It is carried out by bringing the endoscope directly to the site of the stone through the bladder and ureter directly into the pelvis. Then, by aspiration, the remaining stones are removed from the kidney.
If renal colic occurs in women, treatment is the same as in men. But crushing stones and many drugs for dissolving them are contraindicated during pregnancy. Therefore, during this period, only careful observation and symptomatic therapy are recommended. As a last resort, for renal colic, antispasmodics are used during pregnancy.
It is not recommended to endure such an attack in this condition, since severe pain can lead to premature birth or miscarriage.
Prevention
Prevention of renal colic includes several simple rules:
- Water mode. A healthy person needs to drink at least 2–2.5 liters of water per day. In the summer heat, the amount of liquid increases to 3 liters.
- Proper nutrition. Eliminate unhealthy foods from your diet: fatty, fried, salty, smoked foods. Avoid products that promote stone formation (soda, coffee, alcohol, sorrel).
- Physical exercise. Try to lead an active lifestyle, play sports, walk in the fresh air. At the same time, remember that physical activity should be feasible.
- Dress appropriately for the weather. Avoid hypothermia or overheating. Such extreme conditions serve as a trigger for the development of kidney diseases.
- Timely visit to the doctor. Get regular medical checkups. Be careful about your health. Remember, any pathologies must be treated adequately and in a timely manner.
A painful condition called renal colic can occur as a result of various pathologies of the urinary system. But most often, according to statistics, the source of the problem is urolithiasis. It is impossible to predict in advance what renal colic will lead to. Therefore, it is imperative to consult a doctor. In this case, the patient's chances of healing are significantly increased.
A sudden and very severe attack of pain, manifested in men in the lumbar region and resulting from a sharp spasm of the smooth muscles of the upper urinary tract, is called renal colic.
This condition has various provoking factors; depending on the different causes of its occurrence, it requires specific treatment, although first aid measures during an attack are the same. Renal colic in men is a very painful process, but what is even more important is that it signals the occurrence of potentially dangerous pathological processes in the body.
Three main areas of treatment
The only measure that can help completely get rid of renal colic is curing urolithiasis. However, until this goal is achieved, something must be done directly about the attacks.
One of the first measures is to prescribe a diet that is beneficial for a particular patient:
- For colic caused by oxalate stones, patients are prescribed to limit the consumption of foods with a high content of oxalic acid, as well as to include foods rich in magnesium in the diet. You should limit foods rich in carbohydrates, calcium and ascorbic acid, and salt.
- For paroxysmal colic provoked by urates, a diet that increases the alkalinity of urine is recommended.
- If phosphates are the cause of renal colic, dietary nutrition should help increase the acidity of the urine and limit its alkalization.
- carrot juice (or 1 tsp grated carrots mixed with honey),
- onion juice (1 tsp per 1 tbsp honey),
- brewed herbs - chamomile, immortelle, collection of oak bark, calamus root and angelica or sage, chamomile and centaury.
It is important to remember that folk therapy, like traditional treatment, must be prescribed by the attending physician.
The third direction of treatment is emergency care for an acute attack, mainly including pain relief. Patients are prescribed the following tablets or injections:
- against spasms,
- for pain relief,
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
The patient must observe bed rest (at least semi-bed rest), adhere to the diet prescribed by the doctor, and in case of exacerbation of the syndrome, perform thermal procedures. A heating pad placed on the lower back helps, as does taking a hot bath. It is very important to urinate in a timely manner without holding back, even with very severe pain.
Every man who experiences an attack of renal colic should know that spasms cannot always be treated at home, so you should immediately call a doctor if:
- colic recurs with short breaks,
- fever and chills develop
- Nausea and vomiting occur
- When urinating, an abnormally small amount of urine is released,
- health condition worsens.
If such manifestations occur, you need to call an ambulance and go to a medical facility.