Symptoms of herpes zoster pancreatitis are expressed, first of all, by the formation of girdling pain in the area of the pancreas, which causes a lot of discomfort to the patient and is the primary reason for further visiting a gastroenterologist for consultation and prescription of effective therapy. In most cases, the pain during a pancreatic attack becomes so intense that the person simply cannot make any movements. The method of therapeutic treatment of such symptoms completely depends on the degree of damage to the parenchymal organ, as well as on the severity of the disease itself. In this article, we will consider in more detail the symptomatic signs of pancreatic lesions of the pancreas, the main diagnostic methods and methods of treating such a complex disease.
Causes of acute pancreatitis
There are many reasons that contribute to the formation of acute pancreatitis, which is a disorder and inflammation of the digestive system. The causes of inflammation of the pancreas can be considered:
- Gallstone disease (one of the main factors).
- Diseases of the stomach, duodenum.
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes), arterial hypertension, pregnancy.
- Various types of poisoning.
- Binge eating.
- Tendency to allergies.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Taking certain medications.
- Infectious, parasitic diseases.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
There are many causes of pancreatitis
These problems must act in combination with each other, which will cause not only acute pancreatitis and complications, but also other ailments. As a result, you will have to attempt long and complex treatment.
What could have caused the attack?
Knowing what can provoke pancreatitis, you can better understand whether this phenomenon is encountered. Pancreatitis is not uncommon in women. Almost all cases of its occurrence are associated with the main factors:
- poor nutrition or alcohol abuse, especially during feast celebrations;
- stones present in the gall bladder;
- spasms of the ducts due to nervousness.
The older a woman is, the more likely she is to develop inflammation in the pancreas. After 30 years, women have a high risk of acute pancreatitis. A third of patients find it necessary to operate the organ.
Timely treatment of the pancreas, adherence to a diet, and in case of acute attacks - fasting, all this saves from fibrosis of the pancreatic body. With prolonged inflammation, the cells of the pancreas are replaced by connective tissue, like scars arising after a burn, the gland loses the ability to function and stops working.
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis.
During the developmental stage, the symptoms of the disease resemble acute poisoning. The enzymes that iron produces are retained in its ducts and trigger the process of self-destruction, then enter the bloodstream, provoking symptoms of intoxication. One of the most pronounced signs is intense, acute pain. Symptoms also include:
- elevated temperature;
- hypotension or hypertension;
- change in the shade of the skin of the face (grayish-white);
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- dry mouth;
- shortness of breath;
- flatulence.
Diarrhea or constipation may be symptoms
If these signs of pancreatitis occur, a person’s well-being immediately worsens; in such circumstances, they immediately seek help from specialists. It is impossible to proceed to independent treatment, since without the help of qualified doctors the patient will face a painful death. Some medications can aggravate the situation and complicate the treatment process, so they are prescribed only by the attending physician, the same applies to traditional methods of treatment.
Mechanism of pain
Inflammatory processes, changes in the structure of the membrane, blockage of the ducts affect the appearance of pain. The occurrence of tumors and scars interferes with the outflow of pancreatic juice from the pancreas. This, in turn, increases the pressure in the ducts and leads to disruption of the blood supply to the tissues. Inflammation causes enlargement of nerve endings and damage to the nerve sheaths, which is accompanied by pain. If pancreatic pain occurs, you should consult a gastroenterologist. It is he who will help determine the causes of the disease and make a diagnosis. Further treatment will take place under his supervision. In complex cases, the treatment process is led by a surgeon.
Treatment
Patients diagnosed with acute pancreatitis are prescribed mandatory inpatient treatment. In hospital settings, intravenous injections of sodium chloride (saline) are performed, and diuretics (diuretics) are used to relieve swelling in the pancreas. Painkillers are prescribed for acute pain. To support a weakened body, vitamin therapy is recommended, especially vitamins C and B.
One of the main keys to successful treatment of pancreatitis is fasting. As a rule, fasting is prescribed for a period of 5 days along with warm drinks, water with gas is completely excluded. After a fasting diet, yogurt is allowed to be consumed, then a small amount of cottage cheese is included in the diet. After several days, the patient is prescribed a special diet, which is based on the exclusion of foods that cause flatulence and contain coarse fibers. Boiled or steamed food is allowed.
The best way to prevent the occurrence of the terrible disease pancreatitis is its prevention. Prevention of pancreatitis consists of proper nutrition, reducing or eliminating from your lifestyle the causes that contribute to disorders of the digestive system, as well as timely contacting a specialist in case of any ailments, inconvenience and painful sensations. You need to stop using tobacco products, excessive exercise and drinking coffee. It is also not recommended to consume foods high in sugar, fat, acid, and coarse fiber. The best option is considered to be separate meals with fasting days included in it.
Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor, and you must also follow a diet.
If you suspect the development of pancreatitis, mineral water, low-fat dairy products, and seafood will be of irreplaceable benefit.
Complications of pancreatitis are serious diseases of various body systems, but primarily the cardiovascular, excretory and digestive systems suffer, so the main complications include:
- peritonitis;
- heart failure;
- renal failure.
These complications belong to the group of early ones, that is, they occur in the first stages of the development of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Next we will get acquainted with each of these ailments in more detail.
Pain relief in hospital
Pancreatitis will not go away without treatment. And, as a rule, it takes place in a stationary mode. The hospital prescribes:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- sandostatin, which reduces tumors;
- enzyme preparations (Creon, Pancreatin, Festal, etc.);
- a solar plexus block is used;
- surgery as a last resort.
Diagnosis of pancreatitis
Contrary to popular belief, acute pancreatitis cannot be diagnosed by relying solely on clinical symptoms. The most common complaints that patients with acute pancreatitis present with are nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, high fever, weakness, acute or nagging pain in the abdomen, since these symptoms are characteristic of almost all diseases of the digestive system, then additional tests are necessary to make a final diagnosis. research. All diagnostic measures carried out by the attending physician to establish an accurate diagnosis can be divided into two groups:
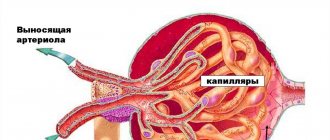
- Instrumental research. The use of instrumental methods is necessary for visual examination of the pancreas for the presence of inflammation and other pathological changes. The most popular instrumental method for diagnosing pancreatitis is ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. Ultrasound provides comprehensive information about the condition of the tissues and ducts of the gland, the presence of purulent or necrotic lesions, stones, and fluid in the abdominal cavity. Only in some cases additional instrumental studies such as X-ray, CT or endoscopy are required. In severe cases, it is necessary to use laparoscopy - an operation that makes it possible to examine the pancreatic gland without using any instruments and immediately perform surgery to improve the patient's condition.
- Laboratory research. Laboratory methods involve conducting studies of human biological fluids, the composition of which is influenced by the pancreas. A clinical analysis of blood and urine provides significantly less information about inflammation of the gland, but these tests are necessary to assess the general condition of the body.
Research needs to be done
Since pancreatic secretion products have a significant impact on the biochemical composition of the blood, the most revealing test for acute pancreatitis is a biochemical blood test. Damage to the pancreas is indicated by an increase in the level of alpha-amylase, lipase, glucose and a sharp decrease in the amount of protein, for example, albumin, in a blood test for biochemistry. It is worth noting that in the presence of complications of acute pancreatitis, the patient is immediately hospitalized, and further diagnosis and treatment is carried out only in a hospital under the constant supervision of medical personnel.
Eliminating pain after drinking alcohol
After penetration into the gastrointestinal tract, ethyl alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream and enters hepatocytes in the liver cells for further processing. Ethanol breaks down into the toxic compound acetaldehyde, and then into acetic acid. These organic substances accumulate in the nephrons, irritating them, destroying cells and tissues.
When your kidneys hurt after drinking alcohol, then most likely a pathological process is developing in the body, signaling in a similar way. This is how the following diseases manifest themselves:
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- renal failure;
- urolithiasis disease;
- renal dystrophy;
- nephrosclerosis;
- nephritis;
- formed malignant tumors in the kidneys or adrenal glands.
Ethyl alcohol has a pronounced diuretic activity, so under the influence of alcoholic drinks, a kidney stone or sand can move and begin to come off. This often causes painful renal colic. Regular consumption of ethyl alcohol reduces the body's resistance to bacterial pathogens and worsens the condition of large and small vessels that supply blood to the kidneys. It is not surprising that they become the object of infection and development:
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis.
The kidney partially loses its ability to filter, concentrate and excrete urine. Lack of fluid reduces the functional activity of paired organs. If in the morning after a fun feast your right or left kidney hurts, then in addition to taking an antispasmodic or analgesic, you need to take the following actions:
- use adsorbents to bind the alcohol remaining in the blood and stomach - Polysorb, Polyphepan, Smecta, activated carbon;
- take a couple of capsules of any hepatoprotector to reduce the load on the liver - Essentiale Forte, Essliver Forte, Karsil, Liv-52.
Drinking alcohol provokes severe intoxication of the body and contributes to the development of water-salt imbalance. To replenish fluid reserves and microelements necessary for all vital systems, you need to drink a rehydration solution - Regidron, Gidrovit, Trisol.
To eliminate kidney pain, in some cases, nephrologists resort to antibiotic therapy
Primary peritonitis is a complication of acute pancreatitis
Primary peritonitis is an inflammatory process that occurs as a result of inflammation of the peritoneum. Based on the nature of the clinical picture, the use of therapeutic measures and prognosis, two groups are distinguished:
- peritonitis, which is not a consequence of other diseases;
- peritonitis that occurred with ascites.
Depending on the form in which peritonitis occurs, it is divided into simple and toxic. The clinical picture of simple peritonitis is characterized by a gradual onset. The child begins to complain of painful sensations in the abdominal area, which are of a different nature. Gradually, the patient’s condition deteriorates, the general body temperature rises, the pain becomes more localized, vomiting and lack of feces appear. The pulse remains satisfactory, and blood pressure is slightly deviated from normal values.
Acute abdominal pain
In the toxic form, unlike the simple form, the disease begins at lightning speed. The spread of this type of peritonitis is associated mainly with spread through the genitals in girls. This phenomenon is associated with the absence of the vagina’s own microflora and its insufficient acidity. Acute pain immediately appears in the abdominal area, fever and repeated vomiting occur. The general condition worsens, the face becomes pointed, the skin turns pale, and the tongue becomes coated with a whitish coating.
Several hours after the development of peritonitis, the patient experiences confusion and convulsive contractions of muscle fibers. Objective signs are characterized by severe and sharp pain in the abdominal area, tachycardia, hypotension and symptoms of general intoxication of the body. The clinical picture of peritonitis, which arose against the background of ascites in chronic diseases of the liver and kidneys, and completely depends on the underlying disease. Children with this form of peritonitis are very irritable and have difficulty making contact, since with this form of peritonitis the pain is different in its intensity.
The first symptomatic sign is a sharp pain in the lower right abdomen or near the navel. The general condition of the patient rapidly deteriorates with an intoxication component, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. The abdomen is tense and very painful.
Pain near the navel accompanied by nausea
Therapeutic measures have several distinctive features that must be considered in more detail. If the disease lasts more than a day, the presence of symptoms of intoxication, and characteristic clinical manifestations, the patient is given therapeutic measures to restore basic vital functions: improving pulse and blood pressure. Invasive therapy in the preoperative period is carried out under the control of standard laboratory tests. The prognosis for recovery is favorable with timely surgical intervention.
Why does my kidney hurt?
There are many causes of kidney disease. These include inflammatory and tumor diseases, injuries to this area, and developmental anomalies of the urinary system, which “raise their heads” under the influence of provoking factors. Let's look at everything in order.
Glomerulonephritis
Hydronephrosis
This is the name of a condition in which the renal pelvis expands under the influence of urine accumulating in it. It can be caused by urolithiasis, tumors compressing the ureters, or developmental anomalies of the latter.
With hydronephrosis, pain is felt in the last stages of the disease
It manifests itself in the form of pain, which can be localized in the lower back, but can also be felt in the abdomen. There may be other symptoms: decreased urine volume, nausea, fatigue.
Renal tuberculosis
With this disease, pain in the lower back will have a stabbing, cutting character; the person will also be bothered by severe weakness and fatigue. There is also a change in the nature of the urine: it becomes cloudy, bloody, and pus may be clearly visible.
Kidney prolapse
It does not manifest itself for a long time, but in the last stages of the disease pain appears in the kidney, which intensifies in an upright position and reaches its peak in the evening. Over time, it becomes unbearable, leading to personality disorders. A person loses weight and practically stops feeling hungry; Nausea and heartburn are periodically observed.
Warning! The risk of kidney prolapse increases with sudden weight loss, intense physical activity, and injuries to the lumbar region.
The main complication of chronic pancreatitis is heart failure
Heart failure is a disease of the cardiovascular system in which the heart does not have time to pump fluid, resulting in swelling, congestion, shortness of breath and fatigue. Heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias are a serious health problem that has various significant aspects today.
According to statistics, in the USA there are 3% of such patients, and in Russia 4.5%, of which 2% of patients are seriously ill, who are in clinics under the constant supervision of doctors. 2% of the population, despite the fact that Russia has an adult population of more than 100 million, is 2.5 million people. Over the past 25-30 years, methods of treating and diagnosing patients with heart failure have changed dramatically.
Back in 1993, patients with heart failure were considered the same as cancer patients. Both of them were given only three to three and a half years to live. At the moment, medicine has given patients 9 years of life; 7.5 years of them are cardiovascular diseases, 6 years of them are heart failure, 4 months are oncology. There are four main clinical symptoms of heart failure:
- Congestion and/or swelling.
- Left ventricular dysfunction.
- Decreased tolerance.
- Ventricular arrhythmia.
The disease is characterized by the fact that the heart does not have time to pump blood
If we consider the nature of sudden death, then the hospital attributes about 20% of sudden deaths, that is, one in five; in the remaining four cases, a cause is found (exacerbation or compensation, or some other). Outpatient sudden mortality is 72%, because the outpatient stay of the patient does not provide for daily observation by a doctor.
Sudden mortality from heart failure depends greatly on how it is observed. In an inpatient setting, sudden mortality is a death that occurs after no deterioration in the patient’s condition an hour before death, and in an outpatient setting, if the patient’s condition has not deteriorated a day before death. Causes of death in patients with coronary heart disease:
- in the first place is a heart attack;
- in second place is stroke;
- in third place is sudden death, which most likely occurred from hidden coronary insufficiency;
- in fourth place, only 8%, is heart failure.
This was the case before. Now all these patients develop heart failure. They no longer die from a heart attack, from a stroke, they die primarily from heart failure. That is, the cause of death changes significantly over time. Sudden death can occur as a result of acute coronary syndrome, thromboembolism, arrhythmia, or hidden worsening of heart failure.
Heart failure can lead to death
Psychologically, for people, sudden death is attributed to heart rhythm disturbances and ventricular fibrillation, although there are many reasons. The incidence of sudden death varies greatly depending on the condition. Of the general population of the entire globe, people who are not sick with anything most often die from sudden death. The incidence of sudden death in different risk groups compared to the annual total is 35% (with left ventricular dysfunction, heart failure, with fraction, etc.). The incidence of coronary complications in patients (according to autopsy data) is about 55% with sudden death. That is, about half of the patients are not from heart rhythm disturbances.