Nagging pain in the testicles in men occurs with various diseases occurring in this area. Such a symptom is indicated by pathologies that have a chronic course.
In addition to physical discomfort, aching pain also brings psychological discomfort, which will result in psychogenic secondary erectile dysfunction.
Symptoms of pain in the right testicle
Associated symptoms for pain in the right testicle:
- Discomfort when touching one or both testicles.
- Testicular enlargement.
- Changes in the structure and shape of the testicle.
- Pain in the scrotum.
- Nausea or vomiting, temperature reaction of the body.
- Formation of a bulge on the testicle.
A nagging pain in the right testicle is a rather serious sign that requires consultation with a doctor. Particularly alarming when nagging pain in the testicle appears are symptoms such as fever, nausea, and increased pain on palpation of the testicles. A nagging pain in the right testicle can be disturbing with a hernia of the inguinal region, with testicular torsion, as well as with diseases such as prostatitis, orchitis, epididymitis, ureaplasmosis. To differentiate symptoms, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. Often, pain in the right testicle is provoked by minor injuries received repeatedly, for example, while playing sports or riding a bicycle. A nagging pain in the right testicle can also occur with prolonged sexual abstinence.
Aching pain in the right testicle feels quite similar to nagging pain and in most cases is provoked by the same factors. Quite often, discomfort and pain occur due to injury to the scrotum, which in turn can lead to the formation of dropsy. The cause of aching pain can be epididymitis, accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process in the epididymis. Most often, this disorder occurs under the influence of bacterial infections. Testicular torsion can cause aching pain. The exact reasons for this phenomenon have not been fully explored. Painful sensations of aching nature can also occur with inflammation of the testicle. The development of chronic prostatitis, as well as prolonged abstinence from sexual intercourse, can provoke aching pain in the testicles.
Severe pain in the right testicle can occur with a disorder such as testicular torsion. In this case, emergency medical attention is required, since due to poor circulation due to torsion, testicular death may occur. Severe pain in the right testicle is characteristic of a disease such as epididymitis. Associated symptoms may include problems with urination and a rise in body temperature. It should be noted that severe pain that occurs during the development of the inflammatory process in the testicles can radiate to the groin, lumbar region, buttocks, and spread to the inner surface of the thighs.
Sharp pain in the right testicle can occur with trauma to the scrotum, testicular torsion, or infectious and inflammatory diseases affecting the organs of the genitourinary system. When the groin area is injured, sharp pain in the right testicle can be so intense that it can lead to shock and loss of consciousness. In this case, the patient needs emergency medical care. Inflammatory diseases that cause severe pain in the right testicle require timely and immediate treatment from an experienced specialist.
>>
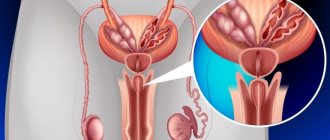
Why does the right testicle hurt and what diseases can provoke it? This is what will be discussed in this topic. The testicles are responsible for the production of testosterone and sperm. The appendages, located in the form of ridges near them, are responsible for the process of sperm maturation and their release into the vas deferens. As you can see, these functions are very important for men.
If your right testicle hurts, you should pay attention to it. Pain may signal the onset of a disease. If it is localized on the right, we can assume that the problem arose in the right egg. Moreover, pain appears in both adult men and children.
Inflammatory processes can lead to the development of male infertility. Therefore, if acute, nagging pain appears in the right testicle, it is necessary to undergo an examination.
The main causes of pain in the right testicle:
- dropsy;
- torsion of the spermatic cord;
- orchitis;
- injuries;
- epididymitis (inflammation of the appendage);
- varicocele on the right;
- inguinal hernia;
- sexual arousal that did not end with the act of ejaculation.
>>
>>
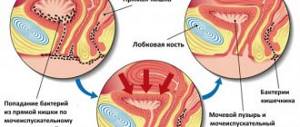
Emergency care algorithm for symptoms of renal colic
If a person has renal colic, emergency care (algorithm) can alleviate the patient’s condition and prevent various complications. Colic is not an independent disease. This is a clinical syndrome that can occur against the background of certain diseases of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system. What are the causes, signs and treatment of renal colic?
Characteristics of the disease
Colic is a severe, paroxysmal pain. The prevalence of this condition among the population reaches 10%. Pain syndrome can occur in people of any age and gender. The development of this symptom may be based on the following processes:
- blockage of the ureter;
- the formation of a blood clot that interferes with the passage of urine;
- deposition of uric acid salts;
- blockage of the urinary tract with necrotic masses;
- muscle spasm of the ureter;
- spasm of the pelvis;
- accumulation of mucus or pus;
- renal ischemia.
Depending on the level of the lesion, pain may be felt in the lower back, lower abdomen, or along the ureters. Most often, colic is felt on one side. Pain is the result of stretching of the renal pelvis and kidney capsule. This type of pain is one of the most intense in medical practice. This condition requires urgent attention.
Etiological factors
Colic occurs with the following diseases and pathological conditions:
- urolithiasis;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- hydronephrosis;
- narrowing of the ureter;
- acute pyelonephritis;
- torsion of the ureter;
- prolapse of the kidneys;
- dystopia;
- prostate cancer;
- benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The cause may be post-traumatic hematomas. The most common cause is the presence of stones in the kidneys or ureter. In the presence of a kidney stone, colic develops in every second patient. In case of blockage of the ureter - in almost all patients. Severe colic-type pain syndrome can occur with inflammatory diseases (urethritis, prostatitis). Less commonly, the cause lies in vascular pathology (vein thrombosis in the kidney area, embolism). In some patients, colic is caused by congenital organ abnormalities (achalasia, spongy kidney).
In women, colic can develop against the background of gynecological diseases (salpingoophoritis, uterine fibroids). These diseases often lead to adhesive disease, which is a trigger for increased pressure in the kidneys. Predisposing factors for the development of renal colic include family history (cases of colic in close relatives), previous history of urolithiasis, poor nutrition (excess in the diet of meat products and canned food), insufficient fluid intake, heavy physical labor, hypothermia, the presence of foci of chronic infection, the presence of systemic connective tissue diseases and urethritis.
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
Signs of the disease
Colic appears suddenly against the background of complete well-being. In this situation, no trigger factor (physical activity, stress) can be traced. Pain syndrome can overtake a person at work, school or at home. The main symptom of colic is pain. It has the following features:
- high intensity;
- acute;
- cramping;
- appears unexpectedly;
- does not depend on human movements;
- localized in the lower back, on the side of the kidney or in the groin area;
- gives to the genitals, groin area, anus;
- often combined with nausea and vomiting;
- often manifested by a change in the nature of urine (blood appears in it).
Nausea and vomiting are observed with colic, which is caused by a violation of the outflow of urine in the kidneys or ureters. Vomiting does not improve the condition of a sick person. With obstruction of the lower ureter, dysuric phenomena (frequent and painful urination) may occur. In some cases, ischuria occurs. Fever, chills and general malaise indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. Stagnation of urine is a favorable factor for the activation of microorganisms, which leads to inflammation.
The duration of colic varies. It can last from 3 hours to a day or more. The pain may wax and wane. All this significantly worsens the patient's condition. He can't find a place for himself. There is pronounced excitability. In severe cases, colic can cause loss of consciousness. Against the background of colic, the patient may be bothered by the following complaints:
- pain in the urethra;
- dry mouth;
- decreased diuresis;
- anuria;
- increased blood pressure;
- increase in heart rate.
Severe pain can lead to shock. In this case, pale skin, cold sweat, bradycardia, and a drop in blood pressure are observed.
Patient examination plan
Cramping pain can be observed not only with diseases of the genitourinary system. To establish the underlying disease, a series of studies should be carried out. Diagnostics includes taking an anamnesis, palpation of the abdomen, determining the symptom of a concussion in the lumbar region, ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, blood and urine tests, and urography. Diagnosis begins with interviewing the patient. During it, the characteristics of the pain syndrome and accompanying complaints are determined. It is important to indicate to the patient that there is a problem with urination and a change in the color of the urine.
With kidney damage, a positive Pasternatsky sign is very often detected. The most informative is a general urine test. The presence of a large number of leukocytes indicates the presence of pyelonephritis. Leukocytosis in combination with hematuria may indicate urolithiasis or glomerulonephritis. With urolithiasis, fresh red blood cells are found. To exclude glomerulonephritis, an ultrasound scan is required. Differential diagnosis of renal colic is carried out with pain in other acute diseases (appendicitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer).
First aid
With renal colic, first aid is of great importance, since the timeliness of medical care and hospitalization of the sick person depends on his further condition. The main goal of emergency care for colic is to eliminate pain. There are often cases when first aid for renal colic is provided at home. Colic can occur unexpectedly at home, on the street or at work. Every person should know what to do in this situation. Emergency care for renal colic includes the following measures:
- calling a doctor or ambulance;
- ensuring peace for the victim;
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- warming the patient (using a heating pad);
- determination of body temperature and general condition of the victim;
- determination of pain localization.
If possible, urine should be collected. First, it is necessary to eliminate the pain using thermal procedures. To do this, you can place a heating pad on the area where the pain is felt. An alternative method is to sit the victim in a bath of hot water. Heat will reduce pain and alleviate the patient's condition. The use of heat is justified only in the absence of an acute inflammatory process. Hot baths are contraindicated for people who have had a stroke or heart attack. At high body temperature and other signs of intoxication, heating is not used. If thermal procedures do not help, pain relievers (antispasmodics or analgesics) are used.
If skills allow, it is better to administer the medicine intramuscularly. The following medications can be used to relieve colic:
- No-shpa;
- Papaverine;
- Drotaverine;
- Baralgin;
- Pentalgin;
- Platyfillin;
- Diclofenac;
- Ibuprofen.
If colic does not disappear, medical workers may carry out novocaine blockades. In a hospital setting, catheterization or stenting can be performed. Diuretics are not used to relieve renal colic, since stimulating urination can lead to the advancement of the stone, which can cause increased pain. Emergency care for renal colic should be carried out as early as possible. To avoid complications and painful shock, this must be done within 2-3 hours from the onset of colic. After relief of colic, a thorough examination is carried out. Further treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of colic.
Therapeutic measures
Once the underlying disease is established, treatment is carried out. For nephrolithiasis (kidney stones), treatment can be conservative or surgical. Small stones less than 3 mm in size can be removed independently. In this case, the patient is prescribed a strict diet, depending on the type of stones, and drinking plenty of fluids. Medicines are used to dissolve the stones. To eliminate the inflammatory process, antibiotics and nitrofurans are used. For frequent colic due to kidney stones, lithotripsy and lithoextraction can be performed. If after this the stones do not disappear, a radical operation is performed. If renal tuberculosis is detected, long-term therapy with anti-tuberculosis drugs is carried out. Colic due to acute pyelonephritis requires antibiotics. Thus, if a person has developed renal colic, the symptoms will be very pronounced. First aid consists of eliminating pain and calling an ambulance.
And a little about secrets...
Have you ever suffered from problems due to PROSTATITIS? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, victory was not on your side. And of course you know firsthand what it is:
- Increased irritability
- Impaired urination
- Erection problems
Now answer the question: are you satisfied with this? Can problems be tolerated? How much money have you already wasted on ineffective treatment? That's right - it's time to end this! Do you agree? That is why we decided to publish a link with a comment from the Chief Urologist of the country, in which he recommends paying attention to one very effective remedy for PROSTATITIS. Read the article...
Content:
A third of the male population has at least once in their lives encountered such a problem as pain in the right testicle. This pathology can develop not only in adulthood, but also in adolescence and is accompanied by increased sweating, weakness, and vomiting. There are a huge number of reasons why the right testicle hurts.
If the right testicle hurts, then there are various reasons that cause this symptom in men. Factors of painful sensation are divided into physiological and pathological types. Usually doctors have to deal with physiological causes. Most often they occur in men with increased libido levels. Their testicles may hurt if they have not had sexual intercourse for a long time. Since during sexual arousal, the blood vessels that supply the testicles begin to work more intensely, the flow of blood to the genitals increases, and an unpleasant pulling sensation appears. This condition is not dangerous for men. However, in the absence of sexual contact, discomfort increases several times, leading to pain.
In addition, if a man’s right testicle hurts, then pathological causes may be the culprits. Moreover, this discomfort serves as a secondary symptom, which is formed under the influence of the following diseases:
Inflammation of the testicles, as an independent disease in men, is quite rare and is a rather serious pathology with many unpleasant symptoms. Usually the inflammatory process causes pain on the right after infections such as chickenpox, measles, mumps. There are cases of inflammation in the absence of regular sexual intercourse due to impaired outflow of seminal secretions. Hepatitis mellitus and HIV infection increase the risk of this pathology. In addition to pain in the testicle, a man experiences elevated temperature, swelling and redness of the organ, nausea, headache, apathy, and sleep disturbance.
Tumor processes affecting the male genital organs are distinguished by their aggressiveness. Usually occurs in men under 45 years of age. There is a connection with the failure of the testicle to descend in infancy, which is explained by increased body temperature from the abdominal region, where the egg was located until it descended into the scrotum. At the beginning of the disease, the lymph nodes are affected, the testicle swells, the person experiences pain, fever, loss of appetite, difficulty breathing, and weakness.
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader got rid of PROSTATITIS using an effective method. He tested it on himself - the result was 100% - complete relief from prostatitis. This is a natural remedy based on honey. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast.
EFFECTIVE METHOD
.
Cystitis
Cystitis often causes pain on the right side. The inflammatory process in the genitals spreads from the bladder, which is affected due to impaired outflow of urine as a result of narrowing of the foreskin, bladder stones, and tumors. Prostatitis and sexually transmitted diseases predispose to the transition of inflammation to the genitals.
Urolithiasis often causes discomfort in the genitals. When stones move, sharp pain develops, which is characterized by renal colic. The patient experiences an increase in temperature, the change in body does not improve the general condition, the pain extends to the groin area and lower back. With this disease, the male sphere is not affected; the pain syndrome is radiated from the ureters.
Inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernia
An inguinal hernia that develops due to heavy lifting, jumping from heights, prolonged standing, and obesity. This pathology develops in older men as a result of age-related changes in the abdominal muscles. An inguinal hernia is characterized by the release of a section of intestine into the scrotum, thereby developing swelling and bloating, which decreases in a supine position. The man experiences pain in the right region, a feeling of heaviness, a burning sensation, and problems with urination.
Testicular torsion occurs as a result of twisting of the spermatic cord due to the rotation of the folds between the testes and the epididymis, which leads to pinching and the development of tissue necrosis. It usually occurs in children, but there are cases of occurrence in adult men after injury. Torsion also occurs due to increased mobility of the organ as a result of an inguinal hernia and an elongated spermatic cord. In young children, this pathology is most often associated with prematurity, immaturity of the reproductive system, and abnormal growth of male organs. Provoking factors include active games, wearing tight underwear, and increased intra-abdominal pressure. If a 180-degree torsion occurs, then blood circulation is sharply disrupted, which results in thrombosis of the genital veins and tissue necrosis. This disease requires immediate medical attention, otherwise the organ will need to be removed.
Varicocele
Varicocele appears due to increased pressure in the blood vessels, leading to expansion of the venous cord. Under the influence of increased venous pressure, the blood vessels stretch, and the testicle seems to sink into the venous network. The scrotum loses thermoregulation, as a result of which the testicle loses its cooling function, which is important for the synthesis of sperm. The consequence of this is the suppression of normal spermatogenesis and the development of infertility. Usually the left side is affected, but there are also cases of damage to the right testicle.
A spermatocele, which is formed as a result of disturbances in the outflow of secretions, is defined by a round, smooth neoplasm to the touch. A spermatocele has contents consisting of sperm, seminal fluid, leukocytes, and fat bodies. Most often develops during active hormonal changes. This disease has a congenital and acquired form. Congenital pathology does not contain sperm. Acquired pathology occurs as a result of trauma and previous diseases of the genital area. With spermatocele, the scrotum becomes enlarged and the leg hurts when walking. As the cyst grows, discomfort appears while sitting or during sexual intercourse.
The natural environment of the testicles consists of a small amount of fluid. When it accumulates in a larger volume, a disease is formed that can affect both one or both testicles. When one organ is damaged, the second appears completely healthy. The diseased testicle becomes enlarged, dense, and takes on a pear-shaped shape. The cause of hydrocele is often a bacterial infection, which is caused by ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, and chlamydia. Also contributes to the development of the disease injury. If children have a congenital pathology leading to hydrocele, then the testicle increases in size during the day, and by the morning it takes on its normal shape.
Hydrocele
Physiological causes of pain
Discomfort and pain in the testicles in men are not always associated with the development of pathological processes. This is often due to the simple physiology of a man. This happens if after sexual arousal there is no release of sperm and explains why the balls hurt after a boner . This happens more often in adolescence, when young men are very active sexually, but still do not understand why men’s balls hurt and do not know how to relieve sexual tension.
But sometimes the question of why the balls hurt after a long period of abstinence worries adults too. If a man becomes aroused, his genitals swell due to a rush of blood. If for some reason he cannot get sexual release, pain appears in the testicles. If a problem arises that the testicles hurt from abstinence , the question of “what to do” can be solved in several ways:
- Sex. You can solve the question: what to do if your balls hurt from excitement by having sex, during which the excess tension from the testicles will subside and the pain will disappear.
- Self-satisfaction. Another answer to the question: if your balls hurt from abstinence, what should you do?
- Distraction from thoughts about sex. If your balls hurt from abstinence, but doctors forbid you to have sex, you need to wait a few hours until the excitement subsides (usually the pain does not last more than 4 hours).
Symptoms
Most often, concomitant symptoms are observed simultaneously with the discomfort, allowing one to understand why the right testicle hurts and manifesting itself in:
- discomfort in the testicles when touched;
- enlarged testicles;
- violation of the structure of the organ;
- nausea;
- increased body temperature;
- presence of bulge.
In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the pain, since this is important for finding out the cause of the discomfort and understanding what to do if a man has pain in his right testicle.
Nagging pain
Mechanical damage
If acute pain in a healthy testicle occurs suddenly and for no apparent reason, then there is a high probability of torsion of the spermatic cord. Most often, the pathology occurs in adolescents aged 12-16 years; adult men account for about 35% of cases. Torsion can be caused by wearing tight clothing, sudden movements, overexertion of the abdominal muscles, and even a persistent cough.
- stitching pain in the scrotum;
- nausea and vomiting (typical for children);
- acute urinary retention;
- increased body temperature;
- the testicle increases in volume and hardens;
- the scrotum becomes bluish and swells.
This condition requires immediate medical attention. In the first hours after the pathology is detected, the testicle can be returned to its normal position using the detorsion method (manually without surgery), but only in children and adolescents. When the manipulation is successfully performed, the pain subsides and the testicle becomes mobile. Adults are usually prescribed emergency surgery. If the intervention is performed within the first 6 hours, complications are rare. The testis is removed in cases where its blood supply is not restored within 15 minutes.
Any blow or compression of the testicles also leads to acute pain. Most often, athletes suffer from groin injuries sustained during training. With a strong blow, the scrotum swells, subcutaneous hemorrhages are noticeable, the testicle enlarges and remains painful for another 2-3 weeks. Injuries are dangerous due to torsion of the cord, rupture of the testicular membranes, and damage to the bladder. If the scrotum turns blue and swells, it is necessary to go to a medical facility or call a doctor, until whose arrival it is important for the victim to remain calm.
Pulling pain
When a man experiences nagging pain, this is a rather serious symptom that requires an immediate visit to a specialist. It is necessary to be wary of increased body temperature, nausea, and increased pain on palpation. A nagging pain disturbs a man in the presence of prostatitis, ureaplasmosis, inguinal hernia, or testicular torsion. Only a doctor can differentiate the pathology during an examination. Also, similar discomfort occurs due to prolonged sexual abstinence, wearing tight underwear, and minor injuries. Nagging pain is the body’s reaction to overheating or hypothermia. Frequently repeated physiological factors can trigger the occurrence of pathologies.
Important! If the discomfort is caused by physiological factors, then it goes away 2 hours after the cause is eliminated; its prolonged manifestation requires consultation with a specialist.
Aching pain is similar in its sensations to nagging discomfort; it is provoked by the same reasons. It often hurts in this way as a result of injuries to the genital organs, which can cause dropsy. Also, aching pain is considered a symptom of inflammation of the testicle, its appendages and various bacterial infections. Similar sensations occur with testicular torsion, chronic prostatitis, prolonged sexual abstinence, frequent cycling or horseback riding.
Testicular torsion
How to treat a symptom
Which doctor to contact for aching pain depends on the root cause of the symptom. First of all, you need to visit a urologist, who, if necessary, will refer you to another specialist.
Treatment of discomfort is determined taking into account the primary disease. There is no need to endure pain, because only with the timely initiation of appropriate therapy can one hope for a favorable prognosis and a speedy recovery.
If inflammation is diagnosed, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. The type of drug is determined after identifying the pathogen and based on the results of a study on its sensitivity to drugs. The symptoms of inflammation can be eliminated with anti-inflammatory drugs.
One of the most dangerous diseases of the male genital organs is cancer. To prevent the spread of tumor cells to other organs, surgery is performed, during which the tumor along with the testicle is removed. If the spread of metastases cannot be avoided, chemotherapy or radiation treatment is performed.
If varicose veins (varicocele) are diagnosed, appropriate surgery is performed. Torsion is also treated with surgery.
Severe pain
When a man is experiencing severe pain, he may need immediate medical attention. Often this type of pain indicates testicular torsion, which impairs blood circulation, leading to the death of the organ. In addition, such sensations are characteristic of inflammatory diseases, which, along with pain, are accompanied by impaired urination and increased body temperature. In addition, inflammatory processes are characterized by pain radiating to the lumbar region, hip, and groin.
Sharp pain is observed with injury to the scrotum, testicular torsion, and infectious processes that affect the genitourinary system. There are cases that such a manifestation is accompanied by loss of consciousness. Inflammatory processes that cause severe pain in the right region require immediate treatment from a specialist.
Adolescent children often suffer from pain in the right testicle
Often teenage children suffer from this symptom, which is caused by inflammation of the gonads. This pathology has an acute and chronic course. The first occurs against the background of an increase in body temperature above 39 degrees, sharp pain that radiates to the groin area, lower abdomen, and lower back. In adolescents, the testicle becomes enlarged, the scrotum becomes tense, and signs of intoxication appear, such as headache, nausea, and weakness. This disease requires prompt treatment, otherwise there is a risk of infertility in the future as a result of reduced production of male hormones.
In an infant, this symptomatology occurs with testicular torsion, characterized by swelling and severe pain. Typically, this phenomenon develops due to the immaturity of the spermatic cord or in the presence of severe tension in the muscles that lift the gonads. If a testicle hurts, then babies become more restless, refuse to breastfeed, and cry. Older babies complain of sharp pain in the lower abdomen. Upon examination, a mass may be detected in the lower part of the scrotum, characterized by extreme pain. The testicle is located above its natural state; if an attempt is made to change the position of the testicle, the pain syndrome increases.
Men often experience injuries to the genital organs, leading to the development of pain:
Testicular bruise
Puncture injuries require emergency surgical intervention. Pain syndrome often causes fainting.
To ensure that the pain that occurs in the right testicle does not bother a man, you need to adhere to the following simple recommendations:
- First of all, warmth in the lumbar region is important. Since half of the men who went to the doctor have problems with the genitourinary area due to hypothermia;
- medical examinations should be carried out. They are especially necessary if a man sometimes has pain in his right testicle;
- it is important to have a permanent sexual partner, since a similar problem often arises in the presence of sexually transmitted diseases;
- To avoid physiological pain, you should have sex regularly. Since a long absence of sex negatively affects the sexual sphere of men, leading to stagnation;
- You need to monitor the regularity of visiting the toilet. It is important to empty your bladder at least once every 3 hours.
Pain arising in the right testicle is considered a rather serious sign that requires immediate consultation with a specialist. Ignoring this symptom can cause serious consequences for the male reproductive system.
Do you have serious problems with potency?
Have you tried a lot of remedies and nothing has helped? These symptoms are familiar to you firsthand:
- sluggish erection;
- lack of desire;
- sexual dysfunction.
The only way is surgery? Wait, and do not act with radical methods. It is POSSIBLE to increase potency! Follow the link and find out how experts recommend treating...
How does a doctor make a diagnosis?
First of all, the doctor collects information about how long ago the discomfort occurred, its nature, intensity of manifestation and accompanying symptoms. Next, the painful area and the following areas are palpated: penis, groin, abdominal cavity.
Laboratory diagnostic measures include:
- Analysis of urine;
- blood analysis;
- urethral smear for examination.
Instrumental studies are also carried out, including ultrasound diagnostics, which makes it possible to determine the level of blood flow in the testicles.
Such a study is also carried out to examine the condition of other areas, for example, the abdominal organs. In the testicles, an ultrasound will show abscesses, varicoceles, and tumor-like neoplasms.
If there is a nagging pain syndrome in the scrotum, a nuclear scan is prescribed using radioactive dye, which is injected using a venous catheter. This event helps identify testicular torsion.
Read also
What to do when your right testicle hurts? Most men have had to deal with a similar problem at least once. Unpleasant sensations in the scrotum area appear regardless of age and have a different nature of pain, ranging from aching or pulling to sharp or cutting. Often the causes of such discomfort do not pose a serious threat to a man’s health, but in any case they negatively affect the overall emotional state. This is because they are frightening and often cause real panic, especially if accompanied by other symptoms.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men
Soreness does not always correspond to the severity of the patient’s condition, therefore, even with uncomplicated prostatitis or another disease, a man may experience pronounced sensations of discomfort, and this is due to the peculiarities of the state of the autonomic and central nervous system at the moment. Only after detailed diagnostic studies can the extent of damage to the prostate or other organ be determined and adequate analgesic and etiotropic treatment prescribed.
Important!
You should not take large amounts of painkillers for prostatitis, since many of them have an adverse effect on the liver and kidneys: taking medications should be agreed with your doctor.
What kind of pain in the pelvic organs a patient may experience depends on many parameters:
- Localization of the source of inflammation in a specific area of the organ: on the periphery or in the center, on the side, front or back wall.
- Involvement of the organ capsule (prostate, kidneys, testicles).
- Damage area.
- Age.
- Type of nervous system.
- Presence of concomitant pathology.
What pain symptoms a man feels is largely determined by the involvement of certain nerve fibers, which are a continuation of the various nerve plexuses of the pelvis. Therefore, pain can be different:
- give to the groin, sacrum, lower back, scrotum, rectum and anus, stomach, leg;
- without irradiation;
- sharp or dull;
- constant or periodic;
- weak or strong.
The localization of pain, its severity and irradiation may not coincide with the identified disease.
Why do discomfort occur in the right testicle?
Let's try to find out the main causes of pain in the right testicle.
The first of them is orchitis. A disease characterized by the onset of an inflammatory process. Mostly orchitis is a complication that occurs with mumps, influenza or gonorrhea. Also, the triggering of inflammation can be caused by various injuries, physical stress, a low level of the body’s defense against infections and viruses, and hypothermia. Orchitis can be acute or chronic. In the first case, the duration of the disease lasts from 2 to 4 weeks, in the second, symptoms may not disappear for more than a month. Often with orchitis, there is an enlargement of the scrotum and the appearance of red spots.
The second possible reason is epidymitis. Doctors use this term to refer to inflammation of an organ appendage. The disease can occur due to infection that lives in the urinary canal, or as a result of urethritis, prostatitis, mumps or tuberculosis. A recognizable feature of epidymitis is the pain that radiates to the side.
A minor injury can cause pain. It is possible to receive such an injury as a result of a fall, impact, or while riding a bicycle. In this case, the scrotum often swells and changes color. If the damage is minor, the hematoma will disappear after 2-3 weeks, but if the injury was severe, it can cause complications, for example, displacement of the testicle closer to the inguinal canal.
Perhaps the most common cause of pain among young men is unsatisfied arousal of the genital organ. During arousal, copious amounts of blood flow to the genitals. If ejaculation does not occur after arousal, the testicles swell and then begin to hurt.
Another answer to the question of why the testicle hurts is hydrocele - dropsy. With this disease, a serous liquid mass accumulates, as a result of which the egg increases in size. When palpated, you can feel a compaction. If it is significant in size, this will soon lead to discomfort during sexual intercourse or urination.
Among the causes is spermatocele, a cyst in the scrotum. If the cystic formation is large, then it causes discomfort when walking, sexual intercourse or other movements. In this case, the pain may radiate to the right side and leg.
Less commonly, the cause of pain is testicular torsion. This pathology occurs in cases where nearby tissues are poorly connected to the scrotum. This causes a disruption in the blood supply to the testicle, which can lead to a decrease in its size if you do not immediately seek help from a doctor. If more than a day has passed since the torsion, the testicle will have to be removed.
These are not all the reasons that can explain the occurrence of pain in the testicle. To accurately determine the cause and choose the right treatment, you need to consult a doctor.
Why do my kidneys hurt after antibiotics?
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
Many diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria are treated with antibiotics. Taking them ensures a speedy and complete recovery in most cases. But antibiotics themselves often pose no less danger to the body than the disease for which they were used.
The negative impact of antibiotics is reflected primarily in the functioning of the kidneys.
Why are antibiotics dangerous for the kidneys?
Antibacterial drugs inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacterial cells by consistently destroying their DNA. They have a negative effect on pathogenic microflora, destroying it and thereby bringing recovery closer.
Unfortunately, beneficial bacteria, including those responsible for normal kidney function, are often influenced by the substances contained in medications.
The lack of such microorganisms causes various disorders in this organ, which explains pain in the kidneys after taking antibiotics.
Top 9 medications to take with caution
Any drugs, especially those used to treat the disease independently, should be used only after preliminary and extremely careful study of the instructions. If possible, you should avoid uncontrolled use during illness:
- Diuretics, ACE inhibitors and vasodilators that have a depressant effect on the kidneys.
- Sulfonamides, aminoglycoside antibiotics (if the body is predisposed, the renal tubules are affected during treatment).
- Beta-lactam drugs (long-term treatment provokes the development of interstitial nephritis).
- Penicillamine (causes the development of glomerulonephritis).
- Antibacterial drugs of the cephalosporin group (increase the risk of developing renal failure).
- Demeclocycline and amphotericin B (during long-term treatment of diseases, they cause constriction of the renal vessels, which causes pain).
- Cephalothin, furosemide and polymyxin when taken simultaneously with aminoglycosides (functional changes occur in the functioning of many organs, including the kidneys).
- Rifadin, rimaktan and makoksa (leads to the formation of dysfunction due to disruption of the kidney structure).
- Ifosfamide, choloxane and cyclophosphamide (drugs promote the formation of kidney stones and can cause hyperuremia).
Naturally, the negative consequences of using these drugs do not appear in every patient. Only those who neglect to visit a doctor suffer pain and treat themselves, without thinking that the kidneys only hurt when their function is seriously impaired, one of which is kidney failure.
For example, safe aminoglycosides, if the dose is exceeded, negatively affect the proximal renal tubules. This effect occurs in at least 10-12% of patients. This is how many people complain that their kidneys hurt after taking antibiotics.
The penicillin group of antibiotics has a slight effect on the kidneys. These drugs can be prescribed in large quantities and used for long-term treatment.
Mechanism of kidney damage by antibiotics
If it was antibiotics that affected the functioning of the kidneys, then characteristic signs of this are a change in the volume of urine up or down, a constant lack of fluid and an increase in the amount of urea entering the blood. The appearance of these symptoms suggests that kidney function is impaired. In some cases, obvious signs of the disease are observed, such as:
- suppression of the immune system;
- deterioration of vascular function;
- insomnia;
- dizziness;
- general weakness of the body;
- increase in the proportion of protein in the urine (over 12 g/l).
Significant dysfunction of major organs during antibiotic treatment is indicated by yellowing of the skin, change in the color of urine, loss of appetite and the appearance of fever.
As a result of taking drugs to combat pathogenic bacteria, mechanical or toxic damage occurs, which causes kidney pain. In some cases, both options are possible. A negative reaction of the body develops as a result of initial contact with the allergen contained in the medicine, as well as the transformation of immune complexes.
With repeated use of an antibiotic, an immune response occurs, manifested in the formation of an antigen-antibody complex, activation of macrophages and increased synthesis of antibodies. If the immune reaction predominates, damage to the glomeruli is observed, and glomerulonephritis develops.
With chronic damage to the organ, decay processes begin, growth of connective tissue, swelling of the glomeruli, and damage to blood vessels are observed. Eventually, kidney failure occurs.
What should you do if you experience kidney pain after taking antibiotics?
Before starting treatment for a disease, its cause is determined. To do this, the patient must describe to the doctor the nature of the pain, list the names of the antibiotics used and indicate the disease that was the reason for prescribing the medications. Unfortunately, stopping a specific drug does not guarantee immediate restoration of kidney function, so the patient will be asked to donate blood and urine for laboratory tests.
Abruptly stopping medication before a positive therapeutic effect occurs is undesirable, as it can complicate the course of the disease and damage the structure of the kidneys. Before stopping treatment for the disease, it is recommended to be examined by a urologist. Painful sensations should not be ignored.
What to do if your kidneys hurt after antibiotics?
The intensity and duration of a painful attack depends on the drug that caused it and the body's tendency to have an allergic reaction to a particular drug.
Patients often describe a sharp change in the nature of the pain. So, for a few minutes there is acute pain, and after some time it is mild. Some patients have pulling, cutting, stabbing and aching in the right back part of the back. The localization of pain after taking antibiotics may change, which makes it difficult to independently determine its cause.
If unpleasant symptoms that follow after taking medications bother you more often than usual, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
You should not give up the drug on your own, as has been repeatedly stated above.
There is always a risk of complications during and after taking medications. But this does not mean that it is necessary to completely abandon antibiotics. Most of them not only bring significant benefits, allowing you to get rid of serious diseases, but also, if taken in doses prescribed by a doctor, are safe for health.
If the patient has healthy kidneys, then taking the drugs in the correct dosage is not dangerous for the body. It is important to understand that pain is not always a consequence of taking medications. So, kidney failure can develop on its own, without the participation of antibiotics.
How to restore kidney function?
The choice of method for restoring the kidneys after an illness depends on the cause of the problem. Restoration measures include:
- diet;
- use of probiotics (Linex, yogurt);
- refusal of physical and psychological stress;
- rest;
- adherence to daily routine;
- taking vitamins;
- hardening;
- measures aimed at strengthening immunity.
It is worth noting once again that it is prohibited to refuse to take antibiotics on your own. If there is minimal harm to the body, the doctor may insist on continuing use. Otherwise, treatment of the disease may not bring results.
Kidney pain after antibiotic therapy
Pain in the kidneys after taking antibiotics disappears immediately after the end of the course of treatment.
If antibacterial therapy cannot be completed as soon as possible, then patients are prescribed painkillers and drugs to maintain this organ in working condition. Kidney failure, regardless of the cause of its occurrence, can result in the death of the patient. Less dangerous complications that develop after taking synthetic drugs are eliminated within six months. The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
Every person should know that antibiotics should not be abused.
If the doctor has not prescribed a specific medicine, then you cannot buy it on the advice of friends and take it more often than written in the instructions. This can negatively affect the health of the body in general and the functioning of the kidneys in particular.
What does the nature of the pain indicate?
You can try to determine the cause of the discomfort, taking into account the nature of the pain. For example, nagging or aching pain in the right testicle is a serious reason for urgent medical attention. This is especially true in cases where pain is accompanied by fever and a feeling of nausea. Drawing and aching pain may indicate a hernia in the groin area, testicular torsion, or infectious diseases, such as orchitis, prostatitis, epididymitis. Often discomfort occurs due to injury to the scrotum. Prolonged sexual abstinence can cause nagging or aching pain in the right testicle.
Severe, sudden pain accompanied by problems with urination usually indicates testicular torsion or epididymitis. Often this pain radiates to the right side.
Sharp pain mainly appears due to injury to the groin area. In this case, it is necessary to provide emergency assistance, since the intensity of the pain may be so great that it will lead to a state of shock.
Symptoms of diseases and their diagnosis
The pain can be aching, cutting, dull. Painful sensations often intensify with movement and palpation. Pain may occur in the right testicle or the left testicle, or both. It is possible to increase the local temperature of the diseased organ, while the temperature of the whole body will be normal. Sometimes the testicle becomes enlarged and the scrotum hardens. In some cases, patients complain of nausea, vomiting, and weakness. The presence of a serious disease is indicated by enlarged veins in the scrotum.
On palpation, tuberosity of the testicle is noted. As diagnostic measures, the doctor may prescribe:
Spermogram is an important element in diagnosing the disease.
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- spermogram;
- ultrasound examination;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- testicular biopsy.
To eliminate pain in the lower back and testicles, you need to clearly know the cause. the one who called them. An important point is to first seek advice from an andrologist or urologist. Specialists prescribe the necessary examination and, based on its results, select treatment methods.
To prevent the occurrence of pain, it is recommended to lead a healthy, active lifestyle, adhere to a balanced diet, and use contraceptives during sexual intercourse.
Features of manifestation
Pain with this disease has its own characteristics. Basically, it is dull or aching in nature, sometimes it affects other organs that are located nearby. Its manifestation depends on the stage of development of the disease. In the acute form, there is mainly sharp pain. It comes and goes quickly. If we talk about the chronic form of the disease, the pain is not severe. At the same time, it appears with a certain frequency.
This is all explained by an increase in the size of the prostate gland. It compresses the ureter, which leads to disruption of their function. The patient has a feeling that the bladder is not emptying completely.
Prostatitis reveals itself with sharp attacks of painful sensations. They can be dull and aching and affect organs located nearby. That's why the testicles may hurt. Prostatitis in the acute phase manifests itself in the form of severe pain that appears sharply and then disappears. The chronic form of prostatitis is not accompanied by severe pain, which appears only periodically.
Pain in the scrotum also radiates to the testicles when a man goes to the toilet with prostatitis. This appears due to the effect of prostatitis on the prostate gland in the form of an increase in its size, which causes compression of the ureters.
With prostatitis, the urination process becomes a little difficult, because emptying does not occur completely.
The testicles themselves hurt, the scrotum
Diseases can be different - from inflammation or injury of the testicle, to inflammation or cyst of the epididymis, etc. It is quite easy to identify this.
A simple examination of the scrotum (by the hands of an experienced urologist, andrologist, sexologist), first of all, can reveal the dependence of changes in the size, density and soreness of the contents of the scrotum on pain and condition. Or – the absence of such dependence.
Treatment by a urologist or andrologist is highly recommended. They start with an ultrasound of the scrotum, then according to the situation. There are many options - from varicocele to epididymitis and even torsion (urgent surgical treatment!).
Painful sensations: how to cope with them
How to understand that pain in the groin area is the result of the development of prostatitis?
The answer is simple: due to sharp and aching pain. In addition, a man may notice discomfort in the groin area. The acute form of prostatitis is characterized by very strong, cutting pain. They have interval frequency. If a patient comes to see a doctor with such complaints, the specialist makes a preliminary diagnosis – prostatitis. Very often, men experience pain when urinating. This occurs due to compression of the ureters and an enlarged prostate gland. This negatively affects the act of urination, resulting in a feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder. For this reason alone, men often go to the toilet.
A huge number of men want to find out what to do if severe pain occurs. In order to at least slightly reduce pain, you can perform a light massage of the scrotum, lie in a warm bath, and take certain painkillers prescribed by your doctor. However, it is worth remembering that the above methods are aimed only at reducing the threshold of pain sensitivity, but not the disease itself.
To dull severe pain, your doctor may prescribe painkillers and physical therapy. Traditional medicine also gives good results.
Men suffering from prostatitis have to endure terrible painful sensations that haunt them and prevent them from living a normal life. Pain prevents males from carrying out the usual daily procedure of urination and enjoying their sex life. In order to slightly reduce pain, analgesics are prescribed.
- Analgin - has an anti-inflammatory effect and also relieves pain;
- Diphenhydramine - considered a local anesthetic, relieves spasms and soothes;
- Novocaine is one of the best painkillers and effective remedies prescribed by doctors for prostatitis;
- Nimesil – has anti-inflammatory properties;
- Belladonna is considered an effective remedy that should be taken only under the strict supervision of a doctor;
Carrying out complex treatment of the disease in question, doctors prescribe physiotherapy along with medications. When chemicals interact with physical stimulation, they have a more effective effect on the treatment process. This complex also improves the general condition of the body.
Hirudotherapy
Physiotherapy treatment usually includes the following:
- Magnetic therapy – accelerates blood flow in affected tissues, reduces the degree of inflammation;
- Laser therapy – increases the body’s resistance, restores the acini of the prostate gland;
- Hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches) - has a positive effect on general blood flow, improves lymph outflow, increases the body's resistance, and has a positive effect on reducing the inflammatory process.
- Massage of the gland - increases blood supply, stimulates the outflow of accumulated secretions in the canal, and the removal of dead cells;
Folk remedies
For prostatitis, folk remedies are also used to improve general well-being and relieve pain:
- Pumpkin seeds. They can also be used as prophylaxis. You need to take them 1 tbsp. spoon one hour before meals, for two months 2-3 times a day.
- Burdock tincture. Finely chop the burdock root and boil for 10 minutes. Let the broth brew and strain. Take the tincture 2 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
From here we conclude that it will be possible to completely forget about pain and discomfort only after prostatitis is cured. For treatment, certain types of therapy are used to get rid of all the symptoms of this disease. Self-medication is completely contraindicated. And you don't need to count on a lucky break.
The testicles themselves hurt, the scrotum
Diseases can be different - from inflammation or injury of the testicle, to inflammation or cyst of the epididymis, etc. It is quite easy to identify this.
A simple examination of the scrotum (by the hands of an experienced urologist, andrologist, sexologist), first of all, can reveal the dependence of changes in the size, density and soreness of the contents of the scrotum on pain and condition. Or – the absence of such dependence.
Treatment by a urologist or andrologist is highly recommended. They start with an ultrasound of the scrotum, then according to the situation. There are many options - from varicocele to epididymitis and even torsion (urgent surgical treatment!).
Stones in the kidneys
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts. Small stones do not always make themselves felt by symptoms, but large ones can block the outflow of urine from the kidneys and thereby provoke acute pain in the lumbar region and sides, which can spread to the lower abdomen, groin area and the tip of the penis.
Other symptoms include:
- presence of blood in urine
- painful or difficult urination
- frequent urge to urinate
- nausea and vomiting
Treatment
Treatment is selected depending on the severity of symptoms and the size of the stones. For small stones, this is not always necessary, since they can leave the body on their own - along with urine. Drinking plenty of liquid will help speed up this process. If necessary, the doctor can prescribe painkillers and drugs to reduce the tone of the walls of the urethra.
For stones that are large, very painful, or that affect kidney function, your doctor may recommend removing them. This may be surgery or extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. The latter is the extracorporeal crushing of kidney stones using electromagnetic waves. Penetrating through soft tissue, shock waves crush the stone into small fragments, which then painlessly leave the body during urination.