Malfunctions of the kidneys lead to disruptions in the functioning of other organs important for human life and health. Fluid retained in the body affects the development of heart disease, causes pulmonary edema, and increases blood pressure.
Dialysis is a medical procedure whose purpose is to cleanse the blood. Hemodialysis is often the only option for chronic kidney disease. Thanks to the cleansing procedure, toxins are removed, blood pressure is stabilized, and the patient’s condition improves.
Indications for hemodialysis
Kidney dialysis is prescribed to clear the serum of increased accumulations of the following substances:
Poisons (pale toadstool, strontium, arsenic); Urea (protein breakdown product); Alcohol (ethyl and methyl); Electrolytes (calcium, potassium and sodium); Creatinine (a product of energy metabolism in muscles); Excess water.
Assessing the likely need for hemodialysis
Indications for dialysis:
Chronic renal failure – for detoxification and renal replacement therapy; Acute kidney failure - to remove waste products and excess fluid; Poisoning by poisons – neutralization of toxins, prevention of deficiency; Drug intoxication – removal of excess chemicals; Alcohol abuse - detoxification of formic acid and alcohol metabolites; Hyperhydration – removal of excess water; Violation of electrolyte metabolism, peritonitis - elimination of increased concentrations of electrolytes; Drug poisoning - elimination of opium from serum.
Kidneys in acute renal failure
Not every person with the types of pathology described above is recommended to undergo hemodialysis.
The use of an “artificial kidney” is rational for the following blood parameters:
The cleansing capacity of the kidneys is no more than 200 ml; The volume of daily urine is less than 0.5 liters; Plasma urea concentration is more than 35 mmol/l; Creatinine content – more than 1 mmol/l; Blood potassium – more than 6 mmol/l; Standard bicarbonate – below 20 mmol/l; A gradual increase in edema of the lungs, heart, and brain with the impossibility of eliminating it with medications.
Kidney hemodialysis
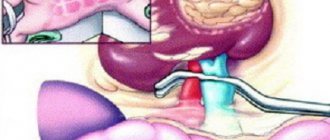
Hemodialysis is the process of purifying the blood using a special device, the so-called “artificial kidney”. In general, it is a selective semi-permeable membrane. The design of the device may be different, but the principle of operation remains the same: removal of substances from the blood by diffusion and convection methods.
- Diffusion is carried out in this way: on one side of the semi-permeable membrane there is the patient’s blood, on the other - the dialysate solution. Depending on the characteristics of the membrane, substances with a certain molecular weight can diffuse from the blood into the solution - from metal ions to large protein molecules.
Electrolytes or organic substances can also enter the blood from the dialysate solution, so the dialysate solution has the necessary concentration of electrolytes to restore their balance in the patient’s blood. The solution is thoroughly cleaned before use to prevent the introduction of toxins or bacteria.
- However, the diffusion method cannot remove hydrophobic hazardous substances from the blood. Convection is used for this. It is carried out through the same membrane due to the difference in pressure between the patient’s blood and the dialysate.
- Ultrafiltration is carried out due to blood pressure on the membrane created using a roller pump. In modern devices this process is controlled by a computer. This procedure removes excess fluid.
Hemodialysis allows you to cleanse the blood of the following substances:
- urea – a product of protein breakdown;
- creatinine – a product of energy metabolism;
- toxic substances such as strontium, arsenic, mushroom poison;
- various medications: barbiturates, tranquilizers, iodine and bromine compounds, salicylates, and so on;
- methyl and ethyl alcohol - therefore hemodialysis is also prescribed for acute poisoning;
- excess electrolytes - sodium, potassium, calcium;
- excess water.
The video shows the essence of the hemodialysis procedure:
Kinds and Types of Kidney Dialysis
There are 2 types of kidney dialysis:
Hemodialysis; Peritoneal dialysis.
Peritoneal dialysis
Hemodialysis is a procedure for cleaning the bloodstream using a special dialyzer that cleanses the blood of toxins and waste. To connect the device to the bloodstream, a venovenous or arteriovenous fistula is formed. To create it, the surgeon sews together a vein and an artery in the lower part of the right forearm. Blood is drawn through this anastomosis. Then it is passed through a system of tubes, lines and filters. After cleansing, the liquid returns to the blood.
Most modern hemodialysis centers are equipped with the following equipment:
"Fresenius 4008S"; "Dialog+"; "Fresenius 4008B".
Indications for emergency bloodstream cleaning
Such equipment has an “online” hemofiltration mode. The use of this equipment allows you to carefully monitor blood counts and carry out ultrafiltration.
Peritoneal dialysis involves internal blood purification. The dialyzer used in this method is the peritoneal membrane.
The essence of the method is to introduce fluid into the abdominal cavity, into which toxins enter from the body. When passing through a natural membrane, it is cleared of toxic substances. The level of fluid inside the abdomen is controlled through a system of catheters installed surgically under anesthesia. These lines drain the filtered liquid.
Depending on the functions of the device, the following types of hemodialysis are distinguished:
Traditional; Highly efficient; High-flux (using high-permeability membranes).
The traditional "artificial kidney" is equipped with cellulose membranes with an area of 0.8-1.5 square meters. This matrix ensures filtration of even small molecules, but at a low blood speed, so the duration of the manipulation is at least 4 hours.
Operation of the artificial kidney device
Highly efficient dialysis is carried out on a machine containing dialyzers with a surface area of 1.5-2 square meters. In such designs, blood moves in a forward direction at a speed of 300-500 ml per minute. The reverse flow is slightly faster (600-800 ml/min). The use of such equipment allows you to reduce the filtration time to 3 hours, but the degree of purification is less than with the classic analogue.
High-flow kidney dialysis is performed using machines containing large molecule membranes. Through such systems, blood moves at high speed, but it is not cleared even of medium molecules. Such equipment allows you to avoid complications that arise during highly effective and traditional types of dialysis:
Anemia; Tunnel syndrome; Amyloidosis.
The disadvantage of the procedure is the presence of a highly permeable membrane with large pores, so the cleaning solution must be sterile.
Kinds
Hemodialysis for kidney disease can be performed not only in the clinic, but even at home. But, however, this practice is widespread mainly abroad. In Russia, patients can come from another region to undergo blood purification, so the classification of methods is rather arbitrary. Hemodialysis at home:
- There are special portable devices designed for “home” use. The most modern of them are worn on a belt and weigh from 4 to 7 kg. Hemodialysis is carried out every day or night, the procedure lasts 2–4 hours. In European countries and the USA, this option is considered a very effective alternative to outpatient treatment and is very common;
- The advantages of this method include safety, since only one person uses the device, ease of use, convenience, since cleaning is carried out at the appropriate time and there is no need to wait in line;
- The disadvantages of the solution include the cost of a hemodialyzer - about 15-20 thousand dollars, the need for training and supervision of a medical worker for the first time.
Video of home hemodialysis: Outpatient hemodialysis:
- in special outpatient centers provides hemodialysis for chronic or acute renal failure. Procedures are carried out on a first-come, first-served basis, usually 3 per week, lasting 4 hours. More specialized devices are used for this;
- The main advantage of the method is the supervision of a doctor, the ability to monitor the result by taking tests, and the ability to adjust the treatment. The device provides for setting the circulation speed, monitoring volume, pressure, hemoglobin and hematocrit levels;
- The downside is the need to wait in line and get to the outpatient center.
Hemodialysis during inpatient treatment:
- Hospitals have 24-hour departments equipped with the required equipment. The procedure is no different from an outpatient procedure;
- plus – constant supervision by a doctor;
- minus – the need to be in a hospital. In addition, there is, albeit a small, possibility of becoming infected with hepatitis B.
Another classification of the procedure is used, related to the functionality of the device itself.
- Conventional hemodialysis involves passing blood through a cellulose membrane with an area of up to 12.5 square meters. m. The material has low permeability, so small molecules pass through the filter. The speed is low - 200–300 ml/min, the vigilance of the procedure is 4–5 hours.
- Highly efficient - the membrane is a more modern material with an area of up to 2.2 square meters. m., which allows you to increase the blood flow rate to 350–500 ml/mi. At the same time, dialysate also passes through the membrane at a rate of 600–800 mg/min. The procedure in this case lasts 3–4 hours, and the cleaning result is better.
- High-precision hemodialysis - it is based on a highly permeable membrane that allows large organic molecules to pass through. Thus, it became possible to increase the lists of toxic substances that need to be removed from the blood. However, more substances enter the blood from the dialysate, so the quality of the solution must be monitored.
According to medical statistics, the number of people regularly undergoing hemodialysis increases by 9% every year.
However, these data should be considered very approximate, since this type of evidence-based research has not been carried out in the Russian Federation, and information was obtained only about registered patients. In this regard, the increase in outpatient and inpatient departments with an “artificial kidney” device - or program hemodialysis - is becoming more relevant.
How it is carried out: the essence of the procedure
The essence of hemodialysis is to cleanse the blood of toxic compounds and increased concentrations of certain biochemical substances.
The choice of the type of dialysis and the method of connecting the equipment is chosen by the doctor depending on the laboratory parameters and clinical symptoms of the patient.
Some private centers offer peritoneal dialysis services at home. There are special mobile teams equipped with anesthesia equipment that allows you to skillfully insert a catheter into the abdominal cavity.
The peritoneal dialysis procedure can be quickly mastered, which makes it possible for it to be widely used at home in patients who cannot be taken to the hospital for objective reasons.
Innovative developments have made it possible to create equipment that allows a person to purify their blood while they sleep.
Advantages of home peritoneal dialysis:
Preserves renal function; Helps to conduct natural life activities; Reduces the likelihood of heart failure; Reduces the need for careful selection of diet; Best for classic diabetics; Increases the chances of a successful kidney transplant.
The principle of hemodialysis due to diffusion. Red - blood flow, blue - toxins, yellow - membrane
The essence of hemodialysis is the passage of blood through a system of main tubes, followed by filtration of the liquid through membrane systems. A dialyzer is an artificial filter with specific pore sizes.
The “artificial kidney” is carried out 3 times a week with a duration of 4-5 hours. The manipulation is carried out in a hospital setting under the close supervision of a doctor.
Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis can save the lives of patients who suffer from kidney failure.
Before the introduction of dialysis, patients with kidney diseases simply died, since there was no alternative to the method.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the procedure?
Like any other treatment method, kidney dialysis has certain pros and cons. They allow us to conclude that it is necessary to use this remedy and, if possible, select alternative treatment options. During planned hospitalization, the patient must be introduced to all the conditions and asked to weigh the pros and cons.
As my practice shows, in some cases, the kidney dialysis procedure is the only technique that can save the patient from immediate death. In conditions of burn or septic shock, when hours or even minutes count, doctors discard all the disadvantages of this method. In difficult situations, there is no alternative technique that could give a similar result in an extremely short period of time.
Table: advantages and disadvantages of kidney dialysis
| Positive points | Negative points |
| Rapid removal of toxic substances and foreign microorganisms from the human body | Frequent use required to obtain lasting results |
| Constant monitoring of health status and monitoring of disease dynamics | High probability of developing adverse reactions in the body |
| Staying in a hospital setting under the supervision of qualified medical personnel | Inability to go on a trip or business trip |
| Possibility of combination with other treatment methods (use of pharmaceuticals, physiotherapy, surgery) | Constant absences from work (the procedure can take a whole day) |
| Allows you to prepare the body for organ transplantation (during transplantation of a donor kidney) | Presence of a catheter in the vessel (high risk of infection) |
| You can bring the patient out of shock, quickly raise and stabilize blood pressure at the required level | |
| Can replace kidney function by 70–90% |
Conditions
The conditions and mode of kidney dialysis are selected individually. According to the classical scheme, the procedure is carried out three times a week with a duration of about 5 hours.
There is a large list of different membranes for the procedure, which are selected depending on the laboratory results of the patient’s serum and urine.
The choice of the “artificial kidney” mode depends on the functionality of the kidney tissue after purification. If residual function remains, the frequency of hemodialysis can be increased to 2 times a week.
For most patients, dialysis is performed on an outpatient basis, but modern technological equipment allows the procedure to be performed at home.
Portable blood purification devices can even be taken on tourist trips.
Important features of dialysis:
Before cleansing, access to the bloodstream should be ensured; A fistula provides a connection between a vein and an artery, but must be placed by a qualified physician; To fix the vein to the artery, a graft based on synthetic tissue can be used; For temporary access, you can use a catheter that is placed in the thigh, neck, or chest. For hemodialysis, a needle is inserted into the tube, to which the dialyzer is connected.
Diet
For hemodialysis and severe renal failure, diet No. 7 G (“renal”) is used. There are a large number of dietary therapy options used for impaired renal function.
The essence of using diet No. 7
Diet No. 7 is used to provide the body with a balanced vitamin-mineral, protein and carbohydrate composition.
With the help of this diet, complications that arise after blood cleansing are reduced.
The essence of diet No. 7 G:
Protein restriction; Reducing sodium content; Moderate water consumption.
All dishes included in the composition are prepared without the use of salt. To replenish the amount of necessary amino acids, you should consume fish, meat, and seafood. In case of kidney failure, high protein intake is dangerous. Culinary processing of food should be done in boiled form. To add flavor to dishes, you can add spices, sauces, and citric acid.
Approximate composition of diet No. 7G:
100 grams of fat (30% vegetable); 400 grams of carbohydrates (mostly from sugar); 60 grams of protein (75% animal); 2 grams of potassium; 0.7 liters of water.
The calorie content of diet therapy for renal pathology is about 2.8 kcal.
Diet for kidney pathologies
Basic principles of nutrition during kidney dialysis:
You can take 200 grams daily. of bread; Vegetarian soups are allowed: cabbage soup, beetroot soup, borscht, vegetables, fresh cabbage; Of the meat ingredients, 100 grams of lean veal, turkey, fish, rabbit and chicken are allowed; Consumption of dairy products should not exceed 140 grams daily; You can eat 2 eggs a day; Among cereals, preference is given to rice, sago, casseroles and pilaf; Consumption of vegetables up to 400 grams per day: carrots, potatoes, tomatoes, dill, onions, cucumbers, lettuce, beets; Sweet foods and fruits should be taken boiled, baked or raw. Jelly, jellies, mousses, grapes, figs, peaches are allowed for consumption; You can drink coffee, weak tea, fruit drinks; Refractory fats: 35 grams of vegetable oil and 40 grams of butter. Chronic renal failure
— Are hemodialysis and plasmapheresis required? Clinical picture of the disease, nutrition and prognosis, read more.
And in this article everything about acute renal failure - classification, stages of the disease, possible prevention.
Cost of the procedure
The price of hemodialysis is influenced by a number of important factors:
Number of weekly procedures; According to the law, for most patients with renal pathology, dialysis should be provided free of charge (according to government programs); Paid hemodialysis is performed for patients who come to the city for a specific need; Patients who are not assigned to a specific hemodialysis center.
On average, the cost of paid dialysis in Russia ranges from 4.5 to 6 thousand rubles, but some adjustment is possible on an individual basis according to indications.
Video on the topic
When the functioning of internal organs in the human body is disrupted, medical intervention is required. Kidney dialysis is prescribed when the kidneys stop functioning normally and removing toxic substances and toxins from the body. When is this procedure prescribed and what are the indications for it, how long does the method last, and what recommendations should the patient follow in order to improve the condition?
Side effects
Filtering the blood from unnecessary substances through dialysis is stressful for the body. Therefore, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems are possible. The risk of their formation is small, but it is not always possible to completely avoid it. The following side effects are observed:
- pressure changes in blood capillaries;
- numbness of the limbs;
- inflammatory process in the membrane of the heart muscle;
- anemia;
- changes in hearing, vision;
- pain in the back, chest;
- damage to bone tissue;
- nausea, vomiting;
- slowing, increased heart rate.
There have been cases when patients during dialysis experienced an allergic reaction to a constituent substance of the dialysate solution. Neurological signs or mental disorders can develop with prolonged use of the procedure. The patient begins to feel oppressed by constant manipulation and attachment to equipment. There is an imbalance of substances that occurs after frequent diffuse transfusions.
General information
Kidney dialysis is a method by which a person with problems with the normal functioning of the kidneys uses a machine that performs the functions of removing fluid and waste products from the body and blood. The hemodialysis procedure is prescribed and performed only after a thorough diagnostic examination and an accurate diagnosis. Dialysis does not heal the kidneys or eliminate inflammation. It performs the function of the kidney and helps get rid of unnecessary waste products that are carried by the blood throughout the body.
Return to contents
Indications for use
In acute renal failure, dialysis is prescribed.
With timely detection of the pathology of renal failure and adequate treatment, organ functions are restored. Blood flow in the organ is normalized and it is able to filter and pass fluid and blood through itself. In this case, hemodialysis is not performed and is cancelled. Such situations occur when renal function is damaged by exposure to large doses of toxic substances, after an infectious disease or bacteriological complication, in which renal failure develops.
In more complex situations, the kidneys reduce their efficiency, resulting in the development of chronic renal failure. This leads to the accumulation of many toxic and poisonous substances in the blood, which lead to intoxication of the body and the patient becomes ill. In this case, it is impossible to restore the functioning of the organ. Renal hemodialysis is prescribed in the following cases:
for acute and chronic renal failure; for poisoning with alcohol and other toxic substances; for poisoning with pesticides and pesticides; for mushroom poisoning; for poisoning with heavy medications; for imbalance of electrolytes in the body. Return to contents
Who is contraindicated for hemodialysis?
The issue of contraindications to performing blood purification with the “artificial kidney” system was raised above. Let us take a closer look at which patients should not undergo hemodialysis.
- People with an active infectious disease, since during dialysis the blood flow circulates intensively, rapidly spreading the infectious agent throughout the body.
- Those who have suffered a stroke and have mental disorders (epilepsy, schizophrenia, etc.).
- Patients with acute tuberculosis.
- Cancer patients.
- Patients who have recently experienced a heart attack, as well as people with chronic heart failure.
- In severe forms of hypertension.
- Elderly people (80 and older).
- Patients with pathologies of the circulatory system (leukemia, anemia, etc.).
But if there is a mortal danger, hemodialysis must be carried out, despite all contraindications.
Types of kidney dialysis
With severe kidney pathologies, people live as long as possible to resort to dialysis. This procedure is not cheap, but in modern medical institutions it is possible to perform hemodialysis for ordinary people. There are types of dialysis such as peritoneal and hemodialysis. Which method is more preferable is determined by the attending physician, since both peritoneal and hemodialysis have their advantages and contraindications. Let's take a closer look at the characteristics of the types of kidney dialysis.
Return to contents
Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis is carried out using a special machine called a dialyzer, which filters the blood. Circulating blood enters a device in which excess salts, toxins and waste are separated from it, and then in its pure form enters the main bloodstream. Hemodialysis lasts about 6 hours and, depending on the state of organ failure, is carried out at least 2 times a week. The number of times to use this type of dialysis is decided by the attending physician.
The hemodialysis procedure is performed at home, the person does not need to be in the hospital, in addition, you can control the duration of the procedure yourself, while getting a better effect. It is convenient and costs less; the patient does not have to constantly travel to the hospital. For the first time, a tube is inserted into a person through a vein through which blood will circulate. This method is used when the duration of hemodialysis is short. With the development of kidney failure, when the need for dialysis increases, a special fistula is made through surgery, which helps to gain painless access to the vein.
Return to contents
Peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis involves a surgical intervention in which a section of the abdominal cavity is dissected and the person is connected to a machine that will filter the blood. With peritoneal dialysis, there is no danger that bleeding will begin to develop, since the blood vessels are not damaged, and the additional load on the heart does not increase, as happens with hemodialysis.
More than 1.5 liters of special liquid is poured into the abdominal cavity using a catheter. Further, after some time it is removed from the body along with toxins and harmful impurities. There are 2 methods of peritoneal dialysis - continuous outpatient and automatic, which have differences in implementation. With continuous peritoneal dialysis, the solution is introduced into the human body for 6-10 hours, then it is removed, and then the abdominal cavity is filled again. This is done 3 to 6 times a day. Automatic peritoneal dialysis involves changing the solution only at night, while the person experiences minimal discomfort.
Return to contents
Methodology and necessary conditions
The duration of dialysis is prescribed by the attending physician.
If kidney dialysis is performed using an artificial machine, then this procedure is carried out only in a hospital. The amount and duration of dialysis is prescribed by the attending physician, depending on the patient’s health condition. If the patient has developed chronic kidney failure, then the procedure is performed at least 3 times a week. The device that performs the function of the kidney is: a system for pumping blood; a device that injects a special solution into the body (the liquid may have a different composition, depending on the person’s health status); a system of membranes that filter blood. When the blood is purified, it enters the human body again.
Return to contents
Complications, side effects
Complications in the operation of the equipment are rare. A malfunction can lead to an air embolism, which can lead to the end of life. The main reason for the complication is the individual condition of the patient, including problems with the underlying disease (for example, anemia). Most often, the patient experiences nausea, vomiting, possible muscle cramps, increased or decreased blood pressure.
Vascular access is also a cause of the problem. A vascular catheter causes the formation of blood clots, and a fistula vascular connection is dangerous due to infections. As internal pressure decreases, consciousness disorders, dizziness, heart rhythm disturbances and epileptic attacks are possible. Allergic consequences are rare, but potassium levels in the blood often increase.
If the slightest side effect occurs, you must immediately tell a specialist; the procedure must be interrupted, adjusted and the solution replaced.
Preventive recommendations
You can avoid the cause of unpleasant side effects by following the recommendations:
- diet;
- pregnancy planning;
- hygiene rules;
- sufficient amount of liquid;
- medicines;
- monitor your condition at home and report any deterioration;
- regular check-ups with a doctor.
Diet for dialysis
In order for dialysis to be effective and a person to feel normal, you need to maintain a drinking regime and follow a diet. The amount of liquid drunk per day is regulated by the attending physician, since the condition of the genitourinary system must be strictly taken into account. The diet involves reducing the amount of salt consumed. The menu should be rich in proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Fatty meats and broths based on them, sweets and sweet pastries, sweet soda, black tea, pasta, white bread, spicy and fatty sauces and seasonings, and mayonnaise are excluded from the diet. The menu should be dominated by vegetarian food with an abundance of fruits and vegetables, which are prepared using a minimum amount of fat. It is useful to eat vegetable soup, use honey and dried fruits instead of sweets, replace white bread with whole grain bread, and ordinary clean water is suitable for drinks.
Return to contents
Complications and their prevention
More often, complications of this procedure appear after the first procedures, then the body gets used to it and the person does not experience such discomfort. Dialysis causes complications such as nausea and vomiting, blood pressure decreases, red blood cells decrease due to cleansing procedures, and the patient suffers from anemia, which manifests itself as dizziness, weakness, loss of consciousness, headaches, and arrhythmia.
Scheme of the peritoneal dialysis method.
The peritoneal method of dialysis causes a complication in the form of peritonitis, when inflammation of the abdominal cavity occurs with the addition of a bacterial infection. This provokes disturbances in the functioning of the excretory system, which worsens the situation and the patient’s well-being. Complications are caused by the development of a hernia on the peritoneal organs. To avoid serious complications, you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and instructions, and if your health changes, immediately notify you.
Return to contents
Complications
Dialysis is a procedure for extrarenal blood purification, as a rule, does not lead to the development of complications and can significantly prolong the life of a patient with renal failure. Thanks to the development of medicine, today it is possible to extend the life of a patient to 20. In young people, it is possible to extend the life of 22 or more years.
However, the procedure for extrarenal blood purification using an “artificial kidney” apparatus is stressful for the entire body, and therefore the following side effects may occur:
- headache;
- disorders of the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, flatulence, abdominal pain;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- loss of consciousness;
- an increase in body temperature is a complication that may indicate an infection;
- air embolism - blockage of the lumen of a vessel as a result of air entering during medical procedures, can lead to disruption of blood flow to the organ and its dysfunction; when reaching the heart muscle, death is inevitable;
- opening of external bleeding (from the nose) and internal (gastrointestinal tract);
- aluminum disease manifests itself with a pronounced clinical picture, which includes disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system (bone fragility, pain in muscles and joints), speech disorders; occurs due to high levels of aluminum in the dialysis solution;
- cyst formation;
- allergy to dialysate solution.
The main causes of death after dialysis: formation of blood clots in blood vessels; incorrectly selected dialysate solutions; untimely assistance in the event of an allergic reaction to medications; the addition of a secondary infection, which the body cannot cope with due to decreased immunity.
Dialysis is a procedure that is indispensable in the nephrotic industry and allows to prolong the life of patients with renal failure, which is the result of inflammatory pathologies of paired organs or intoxication of the body with toxic compounds, medications or food. Depending on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease, doctors recommend one type of dialysis - peritoneal or hemodialysis, each of which has a number of advantages and disadvantages, but is often the only method to cure and save the patient’s life.
How long do people live on dialysis?
Many people are interested in how long can you live on dialysis? About 10 years ago, patients who received dialysis lived from 3 to 7 years. And the cause of death was not always malfunction of the kidneys or imperfect equipment. More often, the patient encountered serious complications that disrupted the functioning of the entire body and he could no longer overcome such a heavy load. Modern medicine has improved the device, people experience minimal discomfort and pain during the procedure, and live accordingly longer. During kidney dialysis, the patient can sleep or carry out activities without paying attention or being distracted by discomfort.
Today it has been established that when using dialysis and strictly following the rules and instructions of the doctor, people live 22 years, and if their health is normal and no additional complications arise, then they can live 30-50 years. But we must remember that life expectancy and positive treatment results depend on the person himself.
Return to contents
Kidney dialysis: how long do they live and what does it do to the body?
Hardware dialysis is used when the patient’s kidney function is impaired and their failure at different stages.
Many patients are afraid of dialysis, explaining that this procedure has a high risk of mortality. Of course, this method can cause the formation of a blood clot in the catheter, an incorrectly prepared solution or a malfunction in the device, but much more often the cause of death is inaction in treatment, that is, when a person delays starting hemodialysis and dies from the main problem - renal failure. If we consider kidney dialysis and how long people live when performing this procedure, then we can say for sure that this method prolongs the patient’s life by at least another ten years. At the same time, there is still no precisely deduced life expectancy for a person undergoing kidney dialysis; how long patients live depends on the severity of their condition and the initial functions of the kidneys in the body.
Kidney dialysis has the following effects on the body:
- Cleanses the body of toxins and waste, preventing their accumulation.
- Clears the blood of excess salt and fluid.
- Controls the level of important microelements in the blood.
- Adjusts the patient's blood pressure.
- Eliminates anemia.
- Almost completely replaces the functions of the kidneys, that is, it performs their “work” in the body.
Thanks to the fact that modern medicine is constantly improving, today a person’s need for dialysis is not a death sentence at all, but only a necessary measure of life. And if ten years ago patients were tremblingly awaiting their next dialysis procedure, now during the procedure they can listen to music or watch a movie.
Moreover, with certain financial support, a person can install dialysis equipment at home and go to the doctor only for a follow-up examination. While patients wait for a kidney transplant, which can take years, they are forced to undergo regular dialysis. As practice shows, the average life expectancy for people with complete kidney failure during dialysis is 12-15 years.
If the patient’s condition is advanced, this period can be shortened to six years. This statistic is justified by the fact that when the kidneys fail, a person has practically no immunity, so any infectious disease, even not a dangerous one, can become a death sentence for a person. This is also confirmed by the fact that patients with renal failure usually die not from it, but from concomitant diseases.
At the beginning of dialysis, death has a greater chance of death, since this blood purification procedure itself is not suitable for everyone. That is why a person must understand that if the first dialysis was successful, then there is a high probability that he will live for at least another six years. In our country, people can live on dialysis for up to twenty years, although in the world patients can lead a full life for more than thirty years.
impotencija.net
More information about dialysis
The doctor must assess the patient's psychological stability.
If a person requires an ongoing dialysis procedure, then the treatment requires the help of several specialists, namely a neurologist, a psychiatrist and attendants who will navigate the pathological manifestations of the patient’s condition. If dialysis cannot be avoided, then it is necessary to psychologically help the patient prepare for this procedure so that he understands what he has to go through, how long it will last and what life will be like after. Using this approach you can evaluate:
psychological stability of the patient; provide the person with the opportunity to take part in determining the method of therapy; carry out manipulations in advance that will provide access to the blood flow system, which will help the person begin to gradually adapt to the conditions.
When choosing a treatment method, the person’s health status, psychological mood and desire to fight for life are taken into account, since dialysis will introduce restrictions that can negatively affect a person’s mood. To prevent additional complications from occurring during this method, the patient is prescribed drug therapy, which includes the use of antibiotics, steroids, and multivitamins. How long the therapy lasts and other aspects are determined by the doctor.
Due to frequent blood transfusions, a person undergoing hemodialysis develops iron overload. In this case, you need to regularly monitor the tests and not prescribe ferrous sulfate. During hemodialysis, the formation of stones in the genitourinary system is possible, then the doctor regulates the dose of vitamin C, which provokes the formation of calcium inclusions. If complications develop, the patient remains in the hospital under constant medical supervision.
When following a dietary diet, it is advised to pay attention to following a diet in which protein foods are excluded, and the basis of the diet is carbohydrates and the right amount of healthy fats. During this diet, you do not have to limit the amount of liquid, but salt is removed or replaced with artificial analogues. The diet is dominated by fruits and vegetables, in order to improve the taste of unleavened dishes, the following seasonings are added to them: parsley, cumin, cinnamon, and vanillin for sweet baked goods. If you follow the rules of diet, people live long.
When kidney function is preserved by 10-15%, when blood filtration is reduced to a life-threatening level, kidney dialysis is prescribed, a procedure that removes waste from the body. Dialysis allows you to control blood pressure levels, remove waste and excess fluid, maintain a normal balance of electrolytes in the body and acid-base balance.
Indications for dialysis
Every year, thousands of patients with chronic and acute kidney disease are prescribed kidney dialysis. This procedure is prescribed by a doctor if the symptoms of chronic renal failure increase:
swelling, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, high blood pressure.
The decisive factor in the blood test is to increase the level of urea nitrogen and creatinine, as well as to compare the level of creatinine in the blood and urine. Regardless of the test results, the patient is prescribed dialysis:
with severe discomfort; in case of disruption of the heart, lungs, stomach; in the absence of taste sensations; with decreased sensitivity in the legs.
Kidney dialysis is prescribed before the patient experiences life-threatening complications. The stage of kidney failure at which dialysis becomes necessary occurs as a result of:
diabetes; high blood pressure; glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidney glomeruli); vasculitis (inflammation of the kidney vessels); polycystic kidney disease.
Kidney dialysis may also be required in acute renal failure that occurs suddenly during a complex operation, severe injury, or heart attack. Sometimes acute renal failure with adequate timely treatment can result in recovery. In such cases, dialysis is prescribed until kidney function is restored.
If renal failure is severe and chronic or has already reached the terminal stage, dialysis is prescribed for life.
Contraindications
Hemodialysis is prohibited for use in certain diseases and conditions. There are absolute and relative restrictions. The absolute ones include:
- leukemia;
- cancer;
- anemia;
- severe mental illnesses such as epilepsy, schizophrenia, acute psychosis;
- severe forms of central nervous system disorders;
- the presence of 2 or more pathologies: liver cirrhosis, atherosclerosis, heart failure;
- age over 80 years;
- diabetes mellitus if the patient is over 70 years old;
- alcoholism and drug addiction - in the absence of social rehabilitation of such patients, it is impossible to achieve any positive effect.
Relative restrictions include:
- active tuberculosis;
- illnesses fraught with massive bleeding - peptic ulcer, for example.
Types of dialysis
There are several types of procedures that differ from each other in the mechanism of purifying the blood from toxins and metabolic products. Kidney dialysis is divided into two main types:
hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis.
The removal of waste substances from the blood using a hemodialyzer (artificial kidney) is called hemodialysis. Access to blood vessels and connection of an artery to a vein is made through artificial vessels specially implanted under the skin as a result of surgery:
fistula, stent, catheter.
During hemodialysis, the patient's blood is purified through special filters and infused back into the patient. On average, the procedure is carried out three times a week, lasting three to four hours.
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is practiced in two varieties:
CAPD (continuous ambulatory PD); PCPP (continuous cyclic PP).
With continuous outpatient PD, the patient uses his own body tissue (intestinal wall) as a filter. The procedure is carried out independently without the help of devices four to five times a day. Between procedures, about two liters of dialysate solution are kept in the peritoneal area.
Constant cyclic PD is carried out using a device - a cycler, which automatically alternates between cleaning and rest cycles. The peritoneal dialysis procedure can be performed at home and takes about half an hour. The advantage of this type of dialysis is independence from the dialysis center, but the disadvantage is the likelihood of infection.
Diet for dialysis
With any type of dialysis, the patient must adhere to a salt-free diet, since salty foods cause thirst. The kidney dialysis diet also aims to limit the consumption of phosphorus-rich foods (cheese, milk, beans, nuts), as it helps remove calcium from the bones. At the stage of chronic renal failure at which dialysis is prescribed, patients adhere to diet No. 7G. Its main daily parameters are the average content:
protein from 60 to 70 g; energy value just over 2000 kcal; carbohydrates about 300g; animal fats about 70 g; liquids up to half a liter; salt 3-4 g; calcium up to 1g; potassium up to 3 g; phosphorus up to 1g.
On days of dialysis, appetite may decrease, which requires increasing food intake on days free from hemodialysis.
Diet 7G provides for daily consumption:
salt-free bread about 150 g; vegetable soups up to 250 g; lean meat and fish up to 100g; fermented milk drinks and milk up to 200g; sour cream up to 50g; cottage cheese up to 40g; one soft-boiled egg; potatoes up to 200 g, other vegetables up to 300 g; fruits and berries up to 300 g; sugar up to 20g; butter up to 20g; vegetable oil up to 25g.
Broths and sauces made from meat, fish and mushrooms, sausages, canned food, caviar, legumes, smoked meats, cheese, mushrooms, dried fruits, cocoa and chocolate, as well as vegetables and fruits rich in potassium and oxalic acid are strictly excluded from the diet.
How to prolong life after dialysis?
While on an “artificial kidney” device, a person is doomed to adhere to the regime indefinitely. It includes a diet, giving up bad habits, and strictly following the nephrologist’s prescriptions.
Nutritional guidelines for a patient with end-stage renal failure attending dialysis:
- The daily energy value is determined based on the principle - 35-40 kcal per kg of weight per day. This roughly corresponds to 2800-2900 kcal.
- The content of carbohydrates and fats in the menu in case of insufficiency of kidney function must meet the norms of human physiological needs - within the range of 100-110 g and 400-450 g per day, respectively. It is important not to exceed the volume of low-density lipids rich in cholesterol. Carbohydrates are limited with concomitant diabetes mellitus.
- The amount of protein in the diet should be no more than 1.0-1.2 g per kg of human body weight per day. This is explained by its loss during the dialysis procedure, decreased digestibility and increased destruction. Such a dose of the nutrient will not cause an increase in nitrogen compounds in the blood and will not provoke uremia. Animal protein is recommended for people with chronic kidney failure. These are rabbit, veal, chicken, lean fish, dairy products, eggs.
- During dialysis, it is mandatory to include vegetable oils and fish oils in the diet. They are sources of healthy polyunsaturated fatty acids.
- Limiting table salt is the main goal of the diet for kidney disease. In the absence of complications, it is allowed to add 2–3 g/day to prepared foods. And in the presence of hypertension and edema, sodium is completely excluded.
- It is important to monitor the intake of potassium, magnesium, phosphorus and calcium using laboratory diagnostics. Based on this, it is necessary to regulate the intake of products containing these microelements.
The volume of liquid that a person with end-stage renal failure is allowed to drink per day is on average 800–1000 ml.
Hemodialysis is a procedure that is quite traumatic for the body. It may cause the patient the following side effects:
- loss of essential mineral salts, electrolyte disturbances;
- muscle pain, cramps, spasms caused by a lack of sodium, magnesium, chlorides, potassium and other elements in the blood;
- heart rhythm pathology, atrial fibrillation, extrasystole, right or left bundle branch block;
- hypotension;
- anemia caused by the destruction of red blood cells during the procedure;
- bone pain.
Cost of the procedure
The cost of kidney dialysis in Moscow ranges from 4.5 to 6 thousand rubles per session. In the regions, prices for paid hemodialysis may differ significantly from Moscow. In the Siberian Federal District, the cost of the procedure ranges from 3.5 thousand in Tyva to almost 7 thousand rubles in the Omsk region. On average, a year of dialysis costs about $20,000.
For citizens who have a compulsory insurance policy, the hemodialysis procedure is paid for by the state. When traveling to other regions of Russia, hemodialysis services provided at the place of temporary stay must be paid for under the compulsory medical insurance policy in the manner of mutual settlements between territorial funds. In 2013, about seven hundred residents of other regions took advantage of the free services of nephrology centers on the Azov and Black Sea coasts.
Tweet