The kidneys are one of the most important organs of the urinary system. They are responsible for cleansing the blood of toxic products and harmful impurities and removing processed substances. In recent years, the number of kidney diseases, which are accompanied by a violation of the shape and size of the organ, has sharply increased. For primary diagnosis, many doctors resort to the palpation method, which helps to establish signs of various pathologies.
- Table: advantages and disadvantages of the technique
- Diagnostic value of this study
Photo gallery: what ailments can be detected this way
- How can a patient prepare for palpation of the kidneys?
- Procedure technique and results
Video: doctor talks about the procedure
Percussion and palpation of the kidneys
- Types of research
- Palpation technique
- Percussion
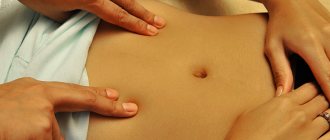
When a patient comes to see a doctor and presents his complaints, the specialist usually asks clarifying questions and conducts an examination. He feels with his hands where the organ is, how painful it is. The methods of conducting the examination will differ depending on which system of the body the failure occurred.
Palpation of the kidney does not cause pain to the patient if everything is in order with the organ. In addition, if the kidneys are in their place and have a normal size, it is quite difficult to palpate them. Already from these signs it is clear whether there are any deviations.
With pathologies such as nephroptosis, the kidney changes its position - it descends and becomes mobile. With neoplasms or inflammation, the organ becomes uneven, changes shape, enlarging in places where tumors are located.
Below we suggest familiarizing yourself with the pathologies for which it is possible to palpate the kidney:
- pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis;
- paranephritis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- neoplasms.
Types of research
There are two ways to palpate organs:
- superficial;
- deeper.
In the first option, the doctor receives generalized information about the kidneys. He will understand the body temperature, how tense the muscles are, and whether there are any lumps or infiltrates under the skin. With the deep method, the organ can be felt as accurately as possible. These include the following methods:
- palpation with sliding movements;
- bimanual method;
- jerky palpations.
The bimanual technique is most suitable for examining the kidneys.
Palpation technique
The patient will need to lie on their back or side, and the doctor may ask them to stand up. Sometimes the specialist is able to feel the edge of the right kidney. Usually it is located lower compared to the left. This is only possible in thin people or children.
If the patient is quite obese, then it is completely impossible to palpate the organs even with a pathological picture. In order for the doctor to somehow get to the kidneys, an overweight person must stand.
The doctor asks the patient to stand up and relax as much as possible and even out his breathing. It must be deep. When the patient inhales, the doctor from the back tries to slightly push the kidney forward. With his second hand he will feel it. It is this hand that must penetrate deeply.
Methods of palpation of the kidneys. Source: studopedia.su
Palpation of the kidney can be performed:
- according to Obraztsov, when the patient should lie on his back;
- according to Botkin, the patient is standing.
Palpation according to Obraztsov. The specialist places the thumb under the patient's front ribs. The remaining fingers are at the back. The doctor places his second hand on the front wall of the abdomen. When the patient inhales, the kidney will descend. The doctor will fix it with one hand and press on the stomach with the other. The organ, caught between the fingers, will slip out. At this moment, the kidney can be carefully palpated.
Palpation according to Botkin. This method of palpation of the kidneys has a similar algorithm to the previous one. The difference is that the patient must stand up and turn sideways towards the specialist. The torso leans slightly forward, and the arms should be folded on the chest.
Both methods are suitable for thin people with weak muscles and a soft stomach.
If the patient has well-developed muscles or is overweight, then the examination is carried out lying on his side.
Palpation of the kidneys in children is similar to the actions that the doctor performs when examining adults. In this case, the characteristics of young patients should be taken into account. Children are not always ready to stand still. That is why their internal organs are often palpated in a lying position.
Percussion
When examining the kidneys, percussion means tapping on the lower back. In this case, they focus on Pasternatsky’s symptom. If the pain is severe, the result is considered positive.
Often we are talking about urolithiasis, paranephritis, pyelonephritis. Pathologies such as radiculitis or myositis, which are not related to the urinary system, cannot be excluded.
In these diseases, percussion causes increased pain.
Percussion of the kidneys is performed in a sitting or standing position. The patient should fix his hand in the abdomen and lean forward slightly - bend over.
The doctor stands behind. He places his left hand in the area of the 12th rib, and with his right hand he makes gentle blows, but at the same time quite sharp. Then repeats the movements on the other side.
Thanks to this kind of tapping and palpating, a specialist can understand whether there is a pathology or not. To be on the safe side, additional studies will be ordered. Sometimes an ultrasound is enough. If doubts remain, a CT scan or a more in-depth examination will be prescribed. After this, it will be possible to make a diagnosis and begin choosing the optimal treatment option.
Execution techniques
According to Obraztsov-Strazhesko
First on the list of palpation techniques is the most common technique according to Obraztsov-Strazhesko - deep sliding palpation. Before the discovery of Vasily Parmenovich Obraztsov, it was believed that only serious changes in internal organs could be felt. Vasily Parmenovich proved that it is possible to palpate the abdominal cavity in a healthy patient, and not just in a sick one.
The Obraztsov technique is called methodological because it is performed sequentially: the examination begins with the sigmoid colon, then the cecum, the ileum (terminal section) and transverse colon, the ascending and descending part of the colon, the greater and lesser curvature of the stomach, the pylorus, and parts of the liver , spleen and pancreas.
The doctor monotonously penetrates the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity and probes the organ, sliding along it. During palpation, the patient is in a supine position (horizontally), with the limbs extended along the body.
Rules for performing the technique:
- We slightly bend the fingers on the right hand and begin to feel the necessary organ. Please note that to perform palpation you need to know in detail the location of a specific organ.
- Next, we form a skin fold.
- The tips of the fingers (or one finger) slide along the organ in the abdominal cavity towards the back wall.
Thanks to deep methodical sliding palpation, it is possible to determine the consistency (density), size, and level of pain of the organ. The video shows the technique for palpating the kidneys according to Obraztsov-Strazhesko:
According to Botkin
Sergei Petrovich Botkin was the first to propose performing binum palpation of the kidneys not in a supine, but in a standing (or sitting) position of the patient’s body. The method is applicable only for patients with normal or moderate weight, as well as in children - in overweight people, in an upright position, the enlarged abdominal wall overhangs. The Botkin technique is of particular importance for nephroptosis (wandering kidney or, more simply put, displacement of an organ in the pelvic area).
In a vertical position, the prolapse of the kidney occurs under the influence of its gravity, which allows the doctor to more accurately determine the anomaly - excessive mobility of the streamlined organ sliding between the fingers. In the video, palpation of the kidneys according to Botkin:
According to Glenar
The Glenard palpation technique is used much less frequently than the two methods described above.
Diagnostics are carried out as follows:
- The patient is placed in a supine position (on his back).
- The doctor's left hand clasps the patient's side so that the thumb goes into the hypochondrium and the other fingers into the lumbar region, behind.
- The second hand is placed in the hypochondrium, as if continuing the thumb of the left hand.
- The patient takes a deep breath, due to which the right or left kidney moves with its lower part towards the thumb of the left hand.
- The kidney is grabbed and under pressure it moves up to the hypochondrium.
- The fingers of the right hand perform sliding palpation of the anterior surface of the organ.
The Glenard method, like Botkin’s, is effective for determining the presence or absence of nephroptosis in a patient, as well as identifying tumors or enlarged kidneys.
Glenard kidney palpation technique
According to Guyon
Another modification of the Obraztsov-Strazhesko technique - the body is also positioned horizontally, but the difference is that the patient’s left hand slowly moves towards the right hand. The technique is used to diagnose diseases in children, and palpation is used with only one finger (this is due to the small size of the patient’s organs).
Guyon palpation is called kidney balloting and allows you to palpate the kidney when none of the other methods are suitable. It is performed in this way: bending the fingers, the doctor moves the kidney forward with jerking movements.
Method of palpation of the kidneys in the diagnosis of diseases
For any renal pathologies, examination of the patient begins with a visual examination, detailed questioning, auscultation, palpation and percussion of organs. Palpation and percussion are two types of examinations that the doctor performs with his hands. To make it clear, palpation is feeling, percussion is tapping.
Both palpation and percussion are ancient methods, known since ancient times. They are absolutely painless and safe for the patient, but, nevertheless, they allow the doctor to get an idea of the general condition of the body and the pathological changes in the internal organs. Let's take a closer look at them.
Types of palpation
There are superficial and deep palpation.
Kidney palpation technique
Palpation examination in medicine is of two types:
- superficial (thanks to it, the doctor determines the points of greatest pain sensitivity, and also makes a preliminary assessment of the patient’s general condition);
- deep (allows a specialist to directly examine the required organ, determine its main characteristics, location, size, etc.).
Superficial palpation should always precede a deep examination, since in some conditions sharp and intense pressure on the kidneys can cause a severe attack of pain and worsen the patient’s condition. Its implementation consists of uniform and soft palpation of the anterior abdominal wall, without deep immersion.
The following criteria are assessed:
- temperature reaction, skin moisture, pain points;
- the presence of infiltrates or compactions on the surface of the abdominal wall (under the skin);
- severity of protective muscle tension
.
Superficial palpation is performed over the entire surface of the palm (clockwise or counterclockwise), all movements should be smooth and gentle
Of greatest importance for diagnosis is deep palpation of the kidneys, which can be carried out in two positions of the patient: horizontal and vertical.
Deep palpation of the kidneys in the supine position
After the patient takes a horizontal position on the couch or other hard surface, he is asked to relax as much as possible and not strain the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
The palpation examination algorithm is presented below:
Kidney location
- the doctor takes a position to the right of the patient, after which the left hand is brought under the right lumbar region of the subject;
- with the right hand, the specialist begins to slowly plunge into the abdominal cavity of the corresponding side (the fingers should be slightly bent at the phalanges);
- on each exhalation of the patient, the doctor makes a deeper dive, trying to reach the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity (the movement goes towards the left hand, which lies under the lower back);
- if the patient does not have an enlarged kidney, then almost complete contact of both hands is possible, especially if we are talking about patients with low body weight and the absence of a pronounced fat layer on the anterior surface of the abdomen;
- layer on the anterior surface of the abdomen;
- when there is an increase in the size of the kidney, its lower edge or the entire organ can be easily identified with your fingertips (at this stage it is very important to palpate very carefully so as not to provoke an attack of severe pain);
- thanks to a digital examination, the doctor can determine the approximate size of the enlarged kidney, its shape, consistency, mobility, as well as the presence or absence of pain;
- after palpation on the right is completed, I move the hand placed under the lumbar region further until it reaches the left side of the back (projection of the left kidney), the technique for further examination is similar to the previous one.
Deep palpation of the kidneys in a standing position
It is advisable to examine the patient not only in a lying position, but also in a standing position. To do this, the patient is asked to stand on his feet, straighten up and place both hands behind his head. The doctor sits down on a chair in front of the patient and conducts a palpation examination, the course of which is described above.
There are many training videos that clearly show and explain all stages of palpation (they can be easily found in any Internet search engine).
If the doctor is not able to examine the patient’s kidneys in a horizontal position, he should begin palpating the kidneys in a standing position
Methods of conducting palpation examination
Deep palpation of the abdominal cavity is carried out in several ways:
Deep sliding palpation according to Obraztsov
The most common method for examining the abdominal cavity, proposed by Dr. Obraztsov. He was the first to prove that palpation of the abdominal cavity can be performed not only in a sick patient, but also in a healthy one. The technique of sliding palpation of the abdominal area allows you to assess the condition of the internal organs and is carried out methodically, starting with the sigmoid colon.
It is carried out in a lying position. With the bent fingers of his right hand, the doctor presses the anterior wall of the abdomen and forms a skin fold. Using sliding movements towards the abdominal wall, the doctor examines the organs. This technique allows you to determine the size, consistency and pain of the organ.
Bimanual palpation according to Botkin
The technique of examining a patient with both hands was proposed by Dr. Botkin, who for the first time decided to conduct a palpation examination with the patient standing. However, his technique is only applicable to people with moderate body weight and children. For overweight patients, the examination is performed in a lying position.
The patient stands facing the doctor, bending slightly forward. The doctor sits in front of the patient on a chair, placing his left hand on the lower back, and the half-bent fingers of his right hand in the area of the palpated organ.
It is important that the patient's abdominal muscles are relaxed. When the patient exhales deeply, the doctor presses the front wall of the abdomen towards the back with his fingers, forming a fold.
The patient takes a deep breath, the kidney lowers and becomes accessible for palpation.
The Botkin method of examining organs is of great importance for determining nephroptosis (prolapsed kidney). The technique of conducting a bimanual examination of the abdominal area requires the doctor to have deep anatomical knowledge and experience. Correctly performed palpation of the kidneys allows you to determine:
- condition of the organ and capsule;
- soreness;
- organ location (prolapse, displacement).
Guyon's balloting method (push-like palpation)
This technique is rarely used to examine the kidneys. The technique is one of the modifications of palpation according to Obraztsov; it is used only for enlarged or sharply lowered kidneys into the pelvic area.
The patient lies on his back, trying to relax his abdominal muscles as much as possible. The doctor presses the abdominal wall with two half-bent fingers of his right hand and palpates the surface of the organ with pushes, moving it towards the left one, which lies on the lower back.
How to interpret palpation results
Normally, in a patient without pathologies, the kidney cannot be palpated, the examination is painless. The kidneys are well palpated only in the presence of a disease of the urinary apparatus. It is important to pay attention to the consistency of the organs, the elasticity and smoothness of the surface of the kidney capsules, the presence of compactions and neoplasms, and pain.
With hydronephrosis and nephroptosis, a smooth and even kidney can be felt in the pelvic area. However, the consistency of organs in these diseases is different. With nephroptosis, the kidney is soft and elastic, does not change size, and is painless. Hydronephrosis hardens the organ, increases sensitivity - palpation causes moderate, tolerable pain.
In case of changes in the surface of the organ, the appearance of bumps and depressions, the doctor makes a conclusion about the presence of neoplasms. A dense, painful kidney may indicate the formation of tumors. In this case, a biopsy will be required.
Brief Anatomy of the Bladder
The bladder is a hollow muscular organ that serves as a reservoir for urine that flows through the ureters and is periodically excreted through the urethra.
The bladder is located in the pelvic cavity directly behind the pubic symphysis. The bladder is divided into a bottom, an apex, a body and a neck, which, tapering, passes into the urethra.
The size and shape, the relationship of the bladder to the peritoneum changes depending on the degree of its filling with urine. From the posterior surface of the bladder, the peritoneum in men passes to the surface of the rectum, in women - to the anterior surface of the uterus.
The empty bladder lies entirely on the urogenital diaphragm, slightly rising above the pubic symphysis. In a full bladder, the tip protrudes above the pubic symphysis by 5 cm or more.
In men, behind the bladder are the seminal vesicles, the ampulla of the vas deferens and the rectum, and the prostate gland is located below the neck of the bladder.
In women, the bladder is located directly on the urogenital diaphragm, the uterus with the upper part of the vagina is located back from it. The wall of the bladder, in addition to the serous layer partially covering it, has muscular and mucous membranes.
There are 3 mutually intertwined layers in the muscular layer; they form a single muscle that expels urine.
The most developed muscle layer is found in the area of the internal opening of the urethra, here it forms the sphincter of the bladder neck.
The inner surface of the bladder is covered with mucous membrane. In the lower part of the bladder there is an internal opening of the urethra, back from it there is a vesical triangle with the apex directed towards the internal opening, and at the corners of its base the openings of the ureters open.
How can a patient prepare for palpation of the kidneys?
Such a study is not invasive (does not involve the penetration of medical equipment into the body). This means that it is absolutely not necessary to follow a diet or not drink water or any other liquids. The only thing doctors recommend is not to eat food for 30 minutes before the start of the study. In patients with an extremely sensitive stomach, when it is full, palpation of the abdominal wall can cause heartburn or slight nausea, and is also accompanied by mild discomfort.
Don't forget that if you feel nervous before starting the test, you need to tell your doctor about it. I met one patient who was terrified of tickling and reacted extremely negatively to any touch to the abdominal wall. Since palpation was necessary for differential diagnosis, I tried to reassure the man as much as possible and explained in detail how the study was going. The patient relaxed and trusted me, and then we managed to carry out palpation without any funny incidents.
Kidney percussion
Percussion and palpation of the kidneys is carried out by a doctor to identify pathologies of the genitourinary system and make a preliminary diagnosis.
As a result of a survey and physical examination, including inspection, palpation and percussion, the attending physician can assume the presence or absence of urinary tract diseases.
Inspection and palpation are carried out with the patient lying, sitting or standing, bimanually (with both hands).
Diagnostic value
Percussion and palpation of the kidneys can determine the soreness of the organs, changes in appearance and size. After a survey and physical examination, the patient is prescribed additional tests necessary to make a differential diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment:
- General urine analysis;
- X-ray of the lumbar region with contrast agent;
- Ultrasound;
- Biopsy (if urgently needed).
Laboratory tests are prescribed based on the results of the examination and may vary and be supplemented.
Percussion
The use of percussion makes it possible to differentiate the presence of tumors (malignant, benign). If deep and superficial palpation is distinguished by stroking and pressing, then percussion is tapping (or tapping).
If there are compactions or neoplasms, the doctor will notice a percussion sound during the tapping process, similar to tapping on a box.
Sometimes during percussion you can hear a tympanic sound - this means that there is fluid formation or other abnormalities. It is not recommended to perform percussion on your own - tapping the kidneys requires a lot of experience and relevant skills. Video about kidney percussion:
Diagnostic method - palpation of the kidneys: how and why is it done?
Palpation is a method of examining the kidneys, when some abnormalities in the organ are detected using touch. It is actively used in everyday medical practice.
Examination methods
Palpation of the kidneys is carried out with both hands at once. In this case, different techniques are used. The most common method is the following: the patient lies on his back, when palpating the right kidney, the doctor places his right hand on the side of the abdomen, and places his left hand under the twelfth rib. When examining the left hand, they change. In this case, the patient should take deep breaths.
It is important!
The kidney is felt at the moment of a deep breath, which promotes its descent. To obtain more reliable information about the size and mobility of the organ, it is necessary to organize palpation with the patient lying on his side.
An additional method of palpation is to feel the kidneys with both hands at once with the patient standing with the torso slightly bent forward.
Sometimes, using this technique, it is possible to identify a wandering kidney when the organ moves freely over a fairly large distance.
When palpating moving kidneys, the following method is used: the left hand is positioned on the right side so that the thumb is under the costal arch, and the rest in the lumbar region. By squeezing the hand, the organ is, as it were, pushed toward the inside and at the same time can be better palpated with the right hand.
If there is a suspicion of the presence of fluid in the organ, the balloting method is used. The patient is placed on his back, while the doctor creates a push in the lumbar area with his left hand, which is also felt by the right hand located in front.
How is the examination carried out?
Most often, palpation of the kidney is carried out in a supine position with legs bent and slightly apart. The doctor stands on the side of the affected kidney and places his hand with straight fingers under the patient’s lumbar region, while they rest against the angle formed by the twelfth rib and the long dorsal muscles.
The doctor places the bent fingers of the second hand in front under the ribs, strictly parallel and outward from the edge of the rectus muscle on the abdomen. Palpation is carried out by bringing the fingers of both hands together, but the fingers on the hand in the lumbar region slightly lift the kidney towards the front hand.
If the size of the kidney is increased, then it is possible to grasp it between the fingers of two hands, and this makes it possible to identify violations not only in size, but also in the shape and structure of the organ.
If the kidney is not enlarged in size and the preliminary diagnosis is its pathological mobility, then it will be necessary to lift it slightly more towards the front side with the fingers located on the lower back - the patient should take a deep breath. The organ begins to move down and is grabbed by the fingers of the hand from the front, and after it is released while exhaling, it returns to its place.
It is important!
Each kidney should be palpated from the same side: the right one - on the right, the left one - on the left.
In urology, palpation is considered a very informative way of clinical examination of the genitourinary organs, in particular the kidneys.
How is palpation performed in an adult and a child?
The kidneys can be palpated only if the patient has an asthenic physique or if the peritoneal wall is very thin. In patients, the kidneys are palpated if they are displaced or increased in size. Palpation of the organ, lying on its side or standing, must be organized for all patients - this way, it is possible to identify a violation of the localization of the organ or its pathological mobility.
If the doctor was unable to establish contact with the child, then subsequently it becomes quite difficult to palpate. It is necessary that the specialist’s hands are warm.
In infants, due to the great weakness of the abdominal wall, the more depressed position of the kidneys and the relatively large size of this organ, it is much easier to palpate it compared to this examination in children of school age.
When carrying out this method, it is possible to diagnose an increase in its size in a child, which often accompanies hydronephrosis, tumor neoplasm, polycystic disease, horseshoe kidney, hypertrophy in the presence of only one kidney.
It is important!
Sometimes the doctor is able to feel the dystopic kidney, and if hypoplasia or muscle aplasia develops in the abdominal wall, healthy organs are felt.
When palpating the lower abdomen in children with low body weight, it is sometimes possible to feel a certain formation with a dough-like consistency, which is located on the side of the midline in the area of the bladder. This manifestation may cause the presence of a large diverticulum in the bladder.
(Not yet )
When the kidney is palpable
The kidneys are well palpated only with pathological changes in the organ. The doctor can palpate them if they are drooping, if there are cystic or other neoplasms. For pathologies such as hydro- and pyonephrosis, palpation is successfully carried out using the balloting method. These are jerky movements under the lumbar region, which the doctor feels with his second hand through the organ being examined.
It should be noted that normally no organs except the kidneys are running.
Manual examination of the ureteral points is used if pathology in this area is suspected. Normally, the ureters are painless and cannot be palpated. If there is pain in one of the 4 points of projection of the ureters, a pathological process can be suspected.
Child's kidney examination
The same manual examination methods are used in children as in adults. In healthy children, the kidneys cannot be palpated, but in case of pathologies they can be detected. When performing a manual examination in children, the doctor prefers to palpate the kidneys in the supine and lateral decubitus position. Feeling while standing is not always possible, especially if the child is restless.
Deep and superficial palpation of the kidneys and percussion: methods, techniques, video
There are 2 types of palpation of the kidneys: superficial palpation (which does not require strong pressure deep into the body) and deep. During the diagnostic process, the patient should be in a supine position. Exceptions include the Obraztsov school - the examination is performed both horizontally and in a vertical position of the patient (standing, sitting).
Superficial
The examination is based on light palpation for primary conclusions about the condition of the kidneys. The straightened hands of the doctor simultaneously perform symmetrical stroking to palpate the body (without pressure).
Superficial palpation allows you to determine:
- Sensitivity (presence of pain), temperature, humidity level and density of the patient's skin.
- Seals and infiltrates under the skin.
- The tone of the abdominal muscles and their level of tension.
Deep
For a more accurate examination of the kidneys, deep palpation is used. Palpation is performed with several fingers (or one) with pressure deep into the patient’s body.
The deep type of palpation defines the following types:
- Bimanual - palpation with two hands is considered the most optimal method for diagnosing kidneys. It is performed as follows: the left hand holds the organ in a comfortable position, and the right hand palpates the kidney. Hands move towards each other.
- Sliding - sequential slow palpation of the kidneys and other internal organs. The organ, pressed against the back wall, is felt with several fingers of the doctor.
There is also a third type of deep palpation - jerky, but it is used to diagnose the kidneys. Used to examine the liver and spleen.
Application of bimanual technique of palpation of the kidney
Thanks to deep palpation, it is possible to diagnose diseases such as:
- Nephroptosis - prolapse of the kidney.
- Tumor.
- Dystopia is an abnormal location (displacement) of the kidney.
- Hydronephrosis is an enlargement of organ cavities.
- Polycystic disease – cysts in the kidneys.
Palpation of internal organs can take place in a lying position (on the side, on the back), in the knee-elbow position, sitting, and also standing.
Kidney anatomy
Before proceeding with a targeted examination of an organ, it is necessary to accurately imagine its topical location in the human body, only then can one judge about any violations (for example, their prolapse on one or both sides).
The kidneys are a vital organ; it is a paired formation whose main tasks include the process of formation and excretion of urine. It is thanks to them that the body “gets rid” of unnecessary and harmful products of metabolic processes, waste and toxins.
Anatomically, they are located along the posterior surface of the abdominal cavity on opposite sides of the spine (right and left). The organ occupies the space from the XII thoracic to the II lumbar vertebra, however, the right kidney, as a rule, is located below the left, which is due to the close location of the liver, to which it is adjacent to the upper pole.
The upper pole reaches the level of the 11th rib, and its lower edge does not reach the ilium by about 4-5 cm.
Normally, the renal surface is smooth and even throughout its entire length, which is explained by the presence of a dense capsule (fibrous membrane). There is a powerful ligamentous apparatus, thanks to which the organ is fixed in the anatomical bed.
The liver puts pressure on the right kidney, so it is 1-1.5 cm lower than the right one
According to Obraztsov-Strazhesko
First on the list of palpation techniques is the most common technique according to Obraztsov-Strazhesko - deep sliding palpation. Before the discovery of Vasily Parmenovich Obraztsov, it was believed that only serious changes in internal organs could be felt. Vasily Parmenovich proved that it is possible to palpate the abdominal cavity in a healthy patient, and not just in a sick one.
The Obraztsov technique is called methodological because it is performed sequentially: the examination begins with the sigmoid colon, then the cecum, the ileum (terminal section) and transverse colon, the ascending and descending part of the colon, the greater and lesser curvature of the stomach, the pylorus, and parts of the liver , spleen and pancreas.
The doctor monotonously penetrates the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity and probes the organ, sliding along it. During palpation, the patient is in a supine position (horizontally), with the limbs extended along the body.
Rules for performing the technique:
Indications and methods of examination
Healthy kidneys cannot be palpated; when palpated, the patient will also not feel any discomfort. Enlarged or displaced organs may be accessible for inspection. The palpation technique is carried out when:
tumors;- nephroptosis;
- polycystic diseases.
However, healthy organs can be palpated in thin people, as well as in people with thin peritoneum.
Moreover, only the right kidney can be examined, since it is located below the level of the left.
In children, it will be possible to palpate the kidneys only if contact with the baby has been established, otherwise it will be impossible to conduct an examination. In this case, the doctor’s hands should be warm.
It is easier to conduct research on children in their first year of life due to the fact that their abdominal wall is weaker and thinner than that of school-age children. Usually this technique has no contraindications, but it should be used with caution when:
- bleeding;
- purulent process;
- muscle rigidity.
In addition, there are difficulties in conducting the survey, which include:
- bloating;
the patient is overweight. If the patient is obese, then it is quite difficult to examine his internal organs.
For better results, you can ask the patient to take a semi-recumbent lateral position;
- pregnancy requires a more careful attitude;
- ascites.
If, upon examination, the doctor suspects an inflammatory process, a tumor condition, or cystosis, then there is a need to conduct a more detailed examination, which includes:
- general urine analysis;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- general blood analysis;
- bacterial culture of urine;
- Ultrasound diagnostics;
- organ x-ray;
- kidney biopsy;
- radiological examination;
- functional testing;
- CT, MRI.
There are 2 methods of palpation used when examining patients:
- Deep palpation is necessary for a more thorough examination of the kidneys. It is performed by a specialist by pressing the fingers of the right hand on the abdominal area. With strong pressure, the specialist presses the organ to the posterior wall of the peritoneum, while carefully palpating it.
For a more thorough examination, a sliding deep impact with a clear sequence will be required.
- A superficial examination is carried out at the first examination and allows you to determine the presence or absence of a pathological process. Using this method, you can make a primary assumption about a person’s condition. For a more accurate result, the patient should stand with his arms down.
The specialist touches the kidneys with light strokes, without making any pressing movements. In a similar way, he can determine the skin, the state of muscle tone, and whether there is excessive tension in the organ.
Types of palpation
Research can be conducted in several ways. The main condition is an empty bladder. Otherwise, the diagnosis will be incorrect. Palpation methods:
The procedure occurs differently in both sexes:
- men
- rectally; - women
– vaginally.
Examination technique:
- The person lies down or gets on all fours.
- The doctor presses on the pubic area with one hand, inserts a finger of the other hand into the anus (vagina) and presses on the bladder.
Difference from percussion
Palpation (or palpating) is a method in which the kidney area is felt.
Along with palpation, the percussion method can also be used, but it performs other tasks. Percussion is tapping
area of the kidneys, which is important if it is necessary to determine the presence of neoplasms or compactions in the kidneys, while in the event of such pathological compactions the sound will be dull and dense.
If there are no neoplasms, but the patient has pathologies that lead to fluid accumulation in the kidneys, the sound will be louder. Percussion also allows you to accurately determine whether the tumor is located on the organ itself or in close proximity to it in the abdominal cavity.
Unlike percussion, palpation has a wide range of applications and allows you to identify not only disorders in the pathological organ, but also determine its location
(displacement of the kidneys is a deviation from the norm, which indicates possible diseases and injuries).
In general, palpation is used for:
- determining the direction in which the kidney is displaced;
- determining its mobility or immobility;
- identifying the size of the kidney;
- obtaining information about the consistency and shape of the organ.
General rules of palpation require the examination to be carried out when the patient is in a supine, relaxed position.
.
The doctor uses one hand as a support, placing it behind the patient’s lower back in the area of the kidney being examined. The second hand is slowly inserted into the abdominal cavity, and if there are no pathologies, the specialist can feel the organ with both hands without causing any pain to the patient.
Types of palpation
During the initial examination, the doctor performs superficial and deep palpation of the kidneys. Both methods provide different amounts of information necessary to make a preliminary diagnosis.
Superficial palpation
The doctor gets the first idea about the presence or absence of kidney pathology through superficial palpation. The examination is carried out with two straightened arms. Using symmetrical, sliding movements, the doctor examines the patient’s abdomen and lower back without pressing on the abdominal wall. Superficial palpation allows you to determine:
- skin condition (temperature, humidity, sensitivity);
- muscle tone of the abdominal wall, lower back;
- the presence of subcutaneous formations, seals.
Deep palpation
To conduct an in-depth examination, it is necessary to have anatomical knowledge of the projection of organs on the abdominal wall and experience. Thus, the doctor will receive more complete and clear information about the presence of the disease. Deep palpation of the kidneys is carried out using fingers, pressing on the abdominal wall with sufficient force. The technique allows you to determine:
- size, consistency of the kidneys and renal capsule;
- location of the organ relative to anatomical structures;
- presence of formations.
Bladder palpation
For a long time, doctors have used the palpation method to make an accurate diagnosis.
After all, they did not always have such extensive examination methods at their disposal. Palpation of the bladder is precisely the main technique with which the examination of the patient will begin if he comes with complaints of disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system.
This approach has been known since the very beginning of the 19th century, and is still actively used today.
A little about the structure
The bladder is a hollow muscular organ that is located in the pelvic cavity. It functions as a urine reservoir; urine from the kidneys flows from it through the ureters, and it is discharged out through the urethra.
This removes a large number of toxic substances from the body. The urinary reservoir is divided into a bottom, an apex, a body, and a neck. The latter continues into the urinary canal. The posterior part of this organ in the male part of the population is adjacent to the rectum and seminal vesicles, and in women it is adjacent to part of the vagina and the uterus.
This organ has three layers: serous, muscular and mucous. Due to the contraction of the muscle layer, urine is expelled from the organ.
It is impossible to examine the bladder when empty, since it is located in the pelvic cavity behind the articulation of the womb. But if it is filled with urine, it begins to gradually appear from behind the symphysis. This changes the contours of the abdomen. And then it is available for palpation.
Doctors palpate only the filled organ
Visually, a filled reservoir with urine looks like an oval-shaped dome; with very strong overflow, its upper part can reach the navel. It is worth noting that severe overcrowding of the bladder is possible due to urinary retention by force of will, but usually this indicates the following pathology:
- neoplasm in the area of the bladder neck;
- narrowing of the urethra;
- BPH;
- inability to expose the head of the penis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- neurological diseases (paresis of the bladder muscles due to injury, infection, also pathology of the central nervous system, loss of consciousness, pathological processes in the spinal column).
Types and techniques
Palpation of the bladder is divided into deep and superficial. When this organ is well filled and the patient does not have a significant layer of fat, then even upon palpation, the superficial bladder will be found in the form of an oval, softish formation. But the most informative is the deep technique.
The patient should lie down on the couch, positioned on his back, legs extended, body relaxed, abdominal muscles not tense. The doctor sits down next to you; his hands should not be cold, especially when examining children.
Palpation of the kidneys (video)
So, the examination begins from the navel. With the palmar surface, the doctor places his hand in the middle of the abdomen, with his fingers directed towards the umbilical region.
Taking into account the rhythm of breathing movements, the fingers slowly sink into the abdominal area; if the bladder is not detected, the doctor lowers the fingers 3 cm down and repeats the movements. So he moves towards the pubic connection.
When an organ is found, palpation does not stop, but its depth is reduced to prevent pain in the patient. But the most reliable picture of the bubble can be obtained only with deep palpation. It is carried out according to topographic lines, like the percussion method.
It is worth noting that if there is an excess of urine in the bladder, then even the lightest touches can cause significant discomfort.
Sometimes, if indicated, the urinary reservoir is examined with both hands. To distinguish it from a uterus or ovarian cyst in females, you need to empty your bladder. If necessary, conduct an examination by a gynecologist.
Deep palpation is carried out according to topographic lines
If there is a tumor in this area, it can be felt. As a rule, it is lumpy. Concretions are less easily detected during such a study. It happens that during palpation it is possible to detect pain along the location of the ureters.
By palpation you can detect diveticulosis of the bladder, inflammation of the peri-vesical fatty tissue (there is infiltration of a dense consistency, which is not eliminated even after placing a catheter).
What parameters are studied during palpation?
During the diagnosis, the doctor draws conclusions about the presence of a particular disease.
He pays attention to the following characteristics:
- skin temperature;
- skin and muscle tone;
- degree of skin moisture;
- patient's sensitivity level;
- the presence of painful points and areas of increased density.
All this information can be easily collected by an attentive and sensitive doctor. Despite the abundance of various instrumental and laboratory methods for making a diagnosis, palpation of the bladder is a safe, non-invasive technique that every doctor should know.
Source: https://2pochki.com/diagnostika/palpaciya-mochevogo-puzyrya
Kidneys are normal
If the kidneys are healthy, then, as a rule, they are not felt during palpation, and the patient does not feel any pain or discomfort during the procedure. The examination can be carried out with the patient standing or lying down. The kidneys become accessible for palpation, that is, palpable by the doctor when palpated, when the organ enlarges by one and a half to two times or changes its normal location.
Diseases when the kidneys are palpated:
- Tumor development
- Polycystic,
- Nephroptosis.
With normal kidneys, they can be palpated in very thin people, and, as a rule, only the right kidney, which is usually located below the left, can be palpated.
Conditions in which the kidneys can be palpated
You can identify the kidneys by palpation in the following situations:
- an asthenic physique of a person or pronounced thinness (complete absence of fat), as a result of which the lower edge of the organ is easily determined by deep palpation;
- prolapse of the kidneys of varying degrees of severity (unilateral or bilateral nephroptosis), in which the kidneys are partially or completely displaced from their anatomical bed, up to their descent into the pelvic cavity;
- a significant increase in organ size is possible in a number of diseases.
These conditions include:
- cystic kidney disease (replacement of normal tissues with multiple cysts of different sizes);
- hydronephrosis (prolonged stagnation leads to a sharp expansion of the collecting apparatus, while progressive atrophy of healthy tissues is observed);
- mass formations in the kidneys (for example, an abscess) or oncological processes of benign or malignant origin.
Thanks to correctly performed palpation, the doctor is able to determine the prolapse of the kidneys in the early stages of the development of the disease (1st degree nephroptosis)
Technique of the procedure
The palpation method is based on the sensations experienced by the patient when pressing on the corresponding organ. Using this method, you can determine the current condition of the genitourinary organs.
By palpating the lower abdomen, you can clearly determine the strength of the tension in the abdominal muscles. At a time when there were no modern diagnostic devices in medicine (ultrasound, CT, X-ray), this method was quite relevant. However, in modern practice, palpation is still relevant.
Performing percussion step by step:
- The patient is placed on his back.
- The action is carried out from the navel to the womb (from top to bottom). A finger (pessimeter) is placed on the stomach, and with the other hand the doctor applies light blows to it with a gradual decrease of 2 cm. The bottom of the organ is determined by the occurrence of dullness.
To diagnose certain types of pathologies, a special technique is used - “”. To do this, a person must sit or stand. Method for identifying a symptom: the doctor performs percussion at the site of the 12th rib and moves towards the spinal column. If a patient experiences pain, it can be assumed that there is a bladder pathology.
To examine the internal organs of the genitourinary area, the method of deep palpation is used. When a person's bladder is healthy and empty, it is difficult to palpate, so it must be emptied before the procedure. How is palpation performed:
- The patient takes a lying position and relaxes.
- The doctor gently presses his hand on the lower abdomen, gradually increasing the pressure in the umbilical area, to feel the contour of the organ.
During the process, the patient must talk about what he feels (localization of the pain syndrome, how it manifests itself).
Features of the female gender
Since the structure of the pelvis in women is special, diagnosis is carried out 2 times:
- With a full bladder.
- With a devastated organ.
Diagnostics in 2 stages is necessary so as not to confuse the organ being examined with the uterus, which is stretched when carrying a baby, or with a tumor. The method of bimanual vaginal palpation is often practiced. The bottom line is this: one hand is in the woman’s vagina, the other presses on the pubic area.
This technique allows you to detect neoplasms, organ compaction, determine density, and determine a treatment regimen. It should be noted that the appearance of pain does not always indicate the development of pathology.
Palpation of the bladder in young children
In childhood, palpation of the bladder is carried out by a doctor using both hands simultaneously. Before the examination, the child must go to the toilet. In acute, chronic urinary retention, the organ is palpated as a flexible, fluctuating formation, the apex of which sometimes reaches the navel. Normally, a full bladder is palpable in infants.