Pathologies
Kidney hyperplasia is a special type of pathological changes in the structure of the kidney, which involves a sharp proliferation of organ tissue. This condition is not a malignant neoplasm. But the process of cell proliferation provokes a sharp increase in the size of the organ itself; this condition can negatively affect its functioning in the future.
Kidney hyperplasia differs from metastasis in its benign nature. During this process, the cells of one or both kidneys are characterized by the correct structure and have the correct chromosome composition. In very rare cases, if the pathological process in the tissues of an organ lasts a long time, and appropriate treatment of the organ is not carried out, it can become malignant (only under favorable conditions). Kidney hyperplasia most often appears if one of the organs is missing (congenital pathology or surgical intervention).
It is difficult for one organ to cope with the resulting load, so the process of enlargement of the kidney tissue begins and, as a result, kidney hyperplasia appears. This condition is also detected by ultrasound after serious mechanical damage to one of the kidneys. The second reason may be acute purulent pyelonephritis. In this case, one of the kidneys gradually loses its full function, and the second organ performs double duties.
Kidney hyperplasia can be false or true. A true increase in organ size is a consequence of the proliferation of actively functioning cells, while a false increase occurs in one or both kidneys as a result of the proliferation of lipid tissues.
Possible complications
The diagnosis of “hyperplasia” itself does not imply a pathological condition - after all, all the cells in the overgrown tissues have a normal structure and function accordingly. However, most often this phenomenon remains stable only in the vicarious (replacement) form, and then subject to certain preventive measures.
Extremely important! If the increase in tissue volume is caused by recurrent inflammation, hormonal imbalance, or is a false vicarious form, the condition becomes pathological and requires mandatory monitoring and treatment. Otherwise, tissue degeneration into malignant neoplasms and even loss of the organ itself is possible.
Causes
Any pathological process in the body necessarily arises due to certain reasons. Kidney hyperplasia does not appear on its own; the process of proliferation of renal tissue is caused by certain provoking factors. The most common cause of this pathology is inflammation and infection. Especially those that last for a long period of time and have a complicated course. Another common cause of renal hyperplasia is the absence of one of the kidneys.
This disease can occur regardless of age category, as well as the reasons for its occurrence. Enhanced cell functioning can occur under the influence of endocrine and neurogenic factors. Under the influence of such conditions, there is an accumulation of substances that have autocrine and paracrine effects. When certain hormones are produced, there is a direct effect on the kidney tissue, causing changes in their activity. This is due to the rapid growth of tissues.
Often, kidney hyperplasia begins to develop several weeks after the loss of one of them. Hyperplasia is not the norm, but according to some doctors, this condition is beneficial for the body, since with increased size, blood microcirculation significantly increases. And this helps the healthy kidney quickly absorb nutrients, despite the fact that the second one is not functioning.
Symptoms of hypertrophy
If the cause is pathological processes, the patient feels unwell, lethargic, and weak.
Symptoms of organ hypertrophy directly depend on the cause of the pathology. For example, if hypertrophy occurs after removal of a kidney, there are no symptoms, because the main load falls on one organ. But the neurohumoral form is a serious cause for concern, because it indicates the presence of a malignant formation in the kidney.
Important! Nephrectomy (removal of an organ) of one kidney leads to the formation of hypertrophy of the other.
If the cause is pathological processes, the patient feels:
- nagging pain in the lower back;
- malaise, lethargy, weakness;
- the color of the discharge changes;
- pain during urination.
Clinical picture
The characteristic signs of renal hyperplasia in the majority of cases do not appear in any way. And any abnormalities in the organ are usually discovered by chance during an ultrasound. Sometimes, in certain cases, the patient may experience minor pain in the affected area. Such sensations are complemented by hyperthermia. With hyperplasia of one of the kidneys, aching pain may appear in the lower back. When an infectious process is added to such a process, the general symptoms become more intense:
- Temperatures rise to subfebrile levels.
- The patient feels discomfort.
- Blood pressure increases.
The pain gradually increases in intensity. With the development of hyperplasia on the left, the pain syndrome is localized in the left hypochondrium, it is encircling. But in the majority of cases the disease develops asymptomatically.
Features of the development of the vicarious form of the disease
Vicarious or replacement hyperplasia is characterized by the proliferation of tissues that will replace the lost kidney. This is how kidney function is compensated - the remaining organ begins to actively perform its functions, simultaneously increasing in diameter.
Such a disease can also be false and true. True kidney hyperplasia is an increase in cell size, this is a kind of protective reaction of the body to the lack of full functioning. The false form is characterized by increased growth in size of lipid and connective tissue. This is not the norm, but a pathology that negatively affects the functioning of the urinary organs.
Key Aspects
Data from studies and observations indicate that the disease is formed as a result of the death or removal of one of the organs.
There is an increase in the functioning of the preserved organ in order to compensate for the disruption of its functioning.
In medical practice, it is customary to divide vicarious hypertrophy into:
The peculiarity of this one is that it is endowed with an adaptive character. False, on the other hand, is characterized by pathological proliferation of kidney tissue, which negatively affects the functional ability of the surviving organ. In parallel with this, the development of atrophic processes is observed.
Diagnostics
Since this disease is asymptomatic in many cases, changes in the body can only be detected by undergoing an ultrasound.
The doctor may order additional tests to detect the disease and determine the cause of the organ's enlargement. Correct and effective treatment will depend on this:
- Blood test for creatinine level;
- Laboratory tests for sugar levels;
- General blood test;
- General urine examination;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- If a malignant process is suspected, the doctor prescribes an additional biopsy of the affected tissue;
- X-ray of the kidneys;
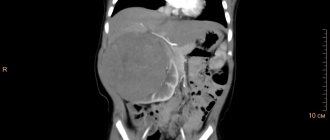
- CT scan.
Thanks to correctly prescribed diagnostic measures, it is possible to differentiate hyperplasia from other diseases.
Kidney hyperplasia
Kidney hyperplasia is a pathological condition of organ tissues, characterized by their rapid growth. Initially, the disease is benign in nature, so all functions of the filtration organ remain within normal limits. But in the absence of proper therapy, the disease is highly likely to become malignant.
The peculiarity of the pathology is that normal and overgrown tissue cells are completely identical, while the size of the organ remains normal. In medicine, there is hyperplasia of the left kidney, right and bilateral. When performing diagnostics, a special place is occupied by differentiation with hypertrophy and metaplasia.
Causes
Experts identify only three reasons under the influence of which the pathological process in question develops. Initially, these are prolonged and recurrent inflammations. They often accompany pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis and nephritis. Since the body independently fights the disease, the cells actively work, which triggers the occurrence of hyperplasia.
This condition can be observed in people who, for one reason or another, have lost one kidney, and it does not matter whether it was removed or simply stopped performing its functions. Pathology develops as a result of the fact that one kidney has to work simultaneously for a couple of organs.
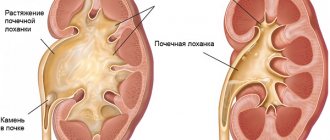
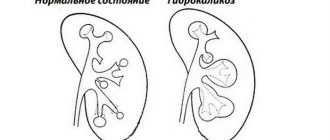
Changes in kidney size with hyperplasia of the filtration organ. Source: present5.com
The final provoking factors in which hyperplasia may occur are concomitant pathologies of the neurogenic or endocrine type. Since hormones are produced in excess, the functional abilities of the kidney are activated, and therefore the volume of the organ increases.
As mentioned earlier, a special place is given to differential diagnosis. For example, with hypertrophy there is also an increase in the size of the kidney. However, the trigger for such changes is an increase in the size of the existing cells, and not in their number. With metaplasia, a malignant process occurs.
Depending on what factors led to the pathological condition of the cells of the filtration organ, doctors present a classification of the disease. Accordingly, there is dishormonal and vicarious renal hyperplasia. The first occurs due to a hormonal imbalance, and the second occurs when there is a high load on one kidney due to the non-functionality of the other.
Symptoms
It often happens that hyperplasia is detected completely by accident, during a medical examination of the kidneys due to preventive monitoring or during examination for another disease. Accordingly, the pathological process proceeds for a long time without significant accompanying symptoms.
Only a small proportion of patients, shortly before diagnosis, felt a low degree of pain in the area of the affected organ. If the condition is advanced and complications begin to develop, then the symptom may be intense and widespread, affecting the back and lower back.
The latter is more typical for hyperplasia of the kidney located on the right side. With a left-sided lesion, the painful syndrome will be of the shingles type, with discomfort radiating to the left hypochondrium. Sometimes people noticed nonspecific symptoms, represented by an increase in body temperature and blood pressure, and a deterioration in their general health.
As for vicarious hyperplasia, there are two types. In the true form, the development of pathology occurs as a result of the absence or inability of the second kidney. False hyperplasia progresses against the background of an increase in the volume of subcutaneous fatty tissue, as well as connective tissue, which also affects the functioning of the urinary system.
In most cases, true form of vicarious renal hyperplasia develops within one or two months in patients who have undergone nephrectomy. Since this pathological process is of a replacement nature, this condition is considered more favorable for the patient’s body.
Diagnostics
If the patient notices that he has long-term problems with urination, or more characteristic signs have arisen indicating the possibility of developing kidney pathology, he should go for an examination to a therapist, urologist and nephrologist. Each specialist will be able to examine the patient and make a preliminary diagnosis.
The principle of performing ultrasound screening of the kidneys. Source: prourinu.ru
To confirm or refute it, it is recommended to take a blood and urine test, in particular:
- Determining the level of creatinine in the blood, which will allow you to estimate glomerular filtration;
- Performing a test to determine the amount of glucose, which helps determine diseases of the vascular system;
- A study on the amount of urea nitrogen, as a result of which the filtration capacity of the kidneys and the quality of protein metabolism are assessed;
- General urine analysis with determination of protein, acidity level and other substances.
In addition, you may need to undergo certain instrumental diagnostic methods. They will make it possible to determine the size of the kidneys and the correct functioning of the vascular circulatory system in the organ area. Therefore, ultrasound screening, MRI, radiography are prescribed, and if cancer is suspected, a biopsy is necessary.
Treatment
In order for a specialist to be able to select the most appropriate treatment tactics, it is very important to fully study the functional abilities of the filtration organ in which the hyperplastic process is noted. If this indicator is normal and there are no deviations, then there is no need for treatment.
However, it is worth remembering that since one kidney performs the functions of two, it becomes more vulnerable.
To maintain its normal operation, it is recommended to carry out some preventive measures.
In the presence of hyperplasia with an infectious process, outpatient or inpatient treatment with uroseptics and antiseptics may be required, depending on the severity of the case.
To maintain kidney function, you can drink chamomile tea. Source: 4geo.ru
Medicines created on a plant basis have a good therapeutic effect. You can also take a variety of infusions and decoctions prepared according to traditional medicine recipes. It can be golden mustache, madder, burdock root, chamomile, nettle, horsetail. However, all actions must first be agreed upon with a leading specialist.
Particular attention should be paid to diet.
It is better to give preference to food that is easily absorbed by the body, but at the same time it should contain the maximum amount of vitamins, for example, it is better to use honey instead of sugar, fresh vegetables and dairy products should predominate in the diet. You can eat lean meat and fish. It is better to steam or boil. You need to drink at least two liters of water per day.
If the patient feels well, his kidneys function normally and concomitant pathological processes do not develop, then, with quality monitoring of his lifestyle, the prognosis will be positive. But at the same time, we should not forget about the likelihood, albeit low, of transformation of the disease into a malignant process, so it is worth regularly undergoing a preventive examination.
Kidney abnormalities (video)
Source: https://uran.help/diseases/giperplaziya-pochek.html
Treatment
In almost all cases, treatment of hyperplasia is not carried out, since this condition is defined as normal while maintaining all functions of the organ. If this is normal, the doctor prescribes maintenance therapy to ease the function of the urinary system and help remove fluid.
If hyperplasia is accompanied by an infectious process, drug therapy is selected by the treating specialist, taking into account the existing disease and its stage. In the presence of severe kidney pathologies, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting; in uncomplicated cases of the disease, therapy is carried out at home, with the use of diuretics and other medications prescribed by a specialist.
Additionally, hyperplasia is treated using physiotherapeutic procedures - ozokerite and paraffin lotions, electrophoresis. It is important to facilitate the function of the second kidney, since the first one does not carry out its work.
Prevention
If 1 kidney is missing, the second one fully performs all functions, so there is no specific therapy. It is very important not to self-medicate if you have hyperplasia. If the functions are not impaired, this condition is the norm.
All preventive measures are aimed at stopping the process of deterioration of the organ’s performance. To do this, you should eliminate bad habits, regularly monitor blood sugar levels, and maintain a drinking regime. Hyperplasia also requires modern treatment to a specialist. It is important to undergo timely treatment for all infectious diseases and strengthen the immune system.