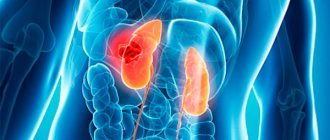
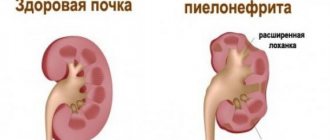
Hydrocalycosis (caliectasia) is a pathology in which the renal calyces expand. In the process of expansion, the calyx begins to put pressure on the kidney tissue and push it aside. As a result of this, the papillae located on the kidney begin to atrophy, thereby creating an obstacle to the outflow of urine, that is, the act of urination becomes difficult.
If treatment of the pathological process is started in a timely manner, then surgical intervention can be avoided in the future. Excessive expansion can lead to necrosis of the kidney tissue and the formation of stones. Unfortunately, the disease does not have pronounced symptoms and may not make itself felt for a very long time, so it is worth systematically undergoing a kidney examination. This will help to identify an anomaly in the early stages and begin to eliminate it as quickly as possible.
Causes of hydrocalycosis
The main cause of the development of hydrocalycosis is considered to be a violation of the circulation of urine in the renal calyces and pelvis. As a result, a load is created on all nearby organs. Enlargement of the calyx of the right kidney is much less common than the left one, but to a large extent it predominates in patients with excess body weight, since they usually sleep on the right side. Therefore, there is excessive pressure on the kidney, and as a result, deformation of the calyx.
Overweight people are more likely to suffer from enlarged renal calyces than those of normal weight.
In addition, the following reasons can be identified:
- flexure of the ureter;
- neurogenic bladder syndrome;
- drinking large amounts of liquid;
- the presence of stones in the lumen of the ureter;
- neoplasm, stones and other elements can compress the urethra;
- congenital anomalies;
- neurological diseases;
- the presence in the body of toxic substances that affect smooth muscles;
- infectious and inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system;
- muscle weakness of the renal apparatus.
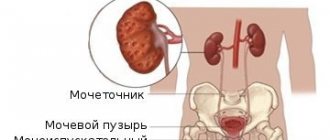
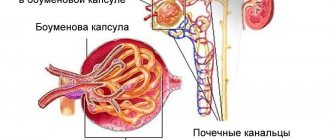
Pelvicalyceal system: structural features
The kidney joint serves as a functional unit of a paired organ, which is responsible for the accumulation and excretion of urine. The parenchyma contains the cortex and medulla; this is the so-called inner side of the kidney, in which the calyces are located. Then the latter exit into the pelvis through an anatomical structure - the cervix. The pelvis is presented in the form of a funnel-shaped cavity, which contains urine produced by the kidneys. Inside there is a mucous membrane, after which there are layers of smooth muscle that allow urine to move towards the ureter. Enlargement of the calyces of both kidneys is rare; as a rule, right-sided or left-sided pathology occurs and is caused by various disorders.
Organ sizes: what is the norm?
The pyelocaliceal system is a single whole that functions together. The parameters of the cups and pelvis may differ at different ages and in certain situations. A healthy person has 6-12 small cups and 2-4 large ones. The latter, when drained, form a pelvis. The table shows the normal sizes of the pelvis.
Types of pathological process
The presence of excessively large kidneys in a person can occur without a clear clinical picture: itching, pain, discomfort at the site of the lesion. This pathology is practically asymptomatic and may not make itself felt for a very long time, while gradually progressing. There are several distinctive symptoms that allow you to determine in which kidney the enlargement occurred.
Kaliectasia is an asymptomatic pathology, so at the first abnormalities in the kidneys, you should consult a doctor. There are several stages of expansion of the calyxes in the kidneys:
- First stage. The pathology manifests itself asymptomatically, no external changes are noticeable, any violations of the pyelocaliceal system can only be detected with the help of ultrasound examination.
- The middle stage involves a significant increase, the patient cannot empty the bladder normally, this process causes him certain difficulties.
- Development of a chronic process. The upper and lower extremities begin to swell, the urine changes color, since the kidneys are not working at full capacity. The process of urination becomes painful. Sometimes the patient feels painful shooting in the lumbar region.
Ultrasound diagnostics will help identify the disease at an early stage
If the inflammatory process progresses in the human body, fever may occur, as well as soreness in the sacral area. If a child has hydrocalycosis, it can be noted that he goes to the toilet more often, and also becomes very capricious. Despite significant swelling, the victim experiences a strong feeling of thirst and drinks water in large quantities.
If such manifestations are present, it is worth taking a general urine test. If there are deviations from the norm, immediately seek help from a doctor.
Diagnosis of kidney stones
To correctly establish the diagnosis, the urologist will definitely send the patient for laboratory tests
- To correctly establish the diagnosis, the urologist will definitely send the patient for laboratory tests. In particular, urine and blood will be taken from the patient for a general analysis. The type of stones will be determined by the concentration of salts in the urine.
- To understand exactly where the stones were located, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound scan. In this case, the ultrasound specialist will be able to accurately track where and in what quantity the stones have formed.
Important: Here it is worth remembering that my ureter will not be visible on an ultrasound. Since they are located in the retroperitoneal space.
- To confirm the type of stones, the doctor may order an x-ray. Here, X-ray positive stones of the pelvis space will be visible. If the stones do not appear on the image, then they are X-ray negative. In this case, patients are treated with an X-ray contrast agent, which will color the X-ray negative stones in the image.
Main symptoms
In most cases, the expansion of the renal calyx occurs in parallel with pyeloectasia (enlargement of the renal pelvis). But despite the presence of two pathologies, the symptoms are very dull. In young children, even with the dilation of the pelvis over 7 mm, there may be no symptoms of the disease. As mentioned above, hydrocalycosis develops due to stagnation and, as a result, the infectious-inflammatory process begins to actively operate, which leads to the appearance of the following symptoms:
- upon examination, leukocytes and red blood cells are detected in the urine;
- body temperature rises;
- painful sensations in the lumbar region, can be on both the left and right sides;
- pain during urination;
- nausea, sometimes turning into vomiting;
- urine changes color.
The brightness of the clinical picture depends on how dilated the calyx and pelvis are. Most often, symptoms begin to occur when the calyx has exceeded the limit of 4 mm, and the pelvis has exceeded 7 mm. If these indicators are lower, then there are practically no signs of pathology. But if problems with the genitourinary system have previously been observed, then it is worth conducting regular ultrasound examinations of the kidneys.
Ultrasound examination should be performed several times, as this will help to see the dynamics of the disease
In young patients, unlike adults, there is such a feature: when the pelvis dilates over 7 mm, clinical manifestations of the disease may be completely absent. Therefore, such patients require careful attention and timely diagnosis.
Diagnostic measures
Among diagnostic procedures, to detect dilation of the calyces of both kidneys, the greatest preference is given to x-ray and ultrasound manipulations. When performing excretory urography, there are two ways to administer a contrast agent: intravenously and through a probe. X-ray methods include intravenous (excretory) urography. This manipulation involves obtaining images of the entire genitourinary system at 7, 15 and 21 minutes after the injection of a special agent, Urografin, into a vein.
Using this manipulation, you can identify the following changes:
Hydrocalycosis of the kidneys during pregnancy
- the process of removing urinary fluid from the body slows down;
- During examination, dilated cups are clearly identified;
- change in the size of the ureter;
- the advancement of the contrast agent in narrow areas of the urethra slows down;
- smooth muscles lose their motor activity.
In the process of carrying out excretory urography, it is worth noting the fact that the contrast agent can be administered not only intravenously, but also using a probe that is inserted through the urethra. For a more thorough and informative diagnosis, Doppler ultrasound of blood vessels is used. Ultrasound diagnostics will help detect only the expansion of the renal calyces. But this method has proven itself very well for monitoring the process in dynamics.
For children, magnetic resonance imaging is used only in extreme cases. For a more thorough study of pathological changes in the genitourinary system, it is necessary to connect Dopplerography of blood vessels. This manipulation will allow you to monitor the state of the circulatory system, namely, determine the absence of blood clots.
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor pays attention to the following symptoms that are observed when the cups expand:
- in the area of changes, from the pelvis and calyces, increased echogenicity is noticeable;
- “Calcium milk” is a phenomenon in urology that combines positive and negative echo signals at the site where dilation and contraction occur.
X-ray and ultrasound diagnostics can be targeted and overview. Survey studies are necessary to find pathology in the human body. Targeted diagnosis is used if the doctor knew in advance which area of the kidney was affected. And therefore, in order to avoid the unnecessary influence of x-ray radiation on the human body, irradiation is directed only to the affected area.
In addition, modern medicine offers a research method such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This procedure allows you to examine the affected organ as accurately as possible. But MRI is used only in extreme cases, namely, when the patient has a pronounced expansion of the cups, when possible complications arise, and also before surgery, in order to determine the scope of work.
MRI is the most informative diagnostic method, but is mainly used in the presence of complications
For young patients, MRI is used only in cases of urgent need, since it is undesirable to irradiate the child’s body again.
Differences in the expansion of the left and right cups
There are no specific symptoms that would indicate an expansion of the calyx of the right or left kidney, but there are several small features. Quite often in medical practice one can encounter cases of severe inflammation on the right side. This is due to the fact that most people are right-handed, so their muscle tone is predominant on the right side. When the first signs of pathology appear, you should immediately contact a specialist.
In the presence of hydrocalycosis on the left side, the amount of renal tissue decreases. This is due to the fact that connective tissue grows in areas of the inflammatory process. And as a result, we can conclude that the more often inflammatory reactions occur in the human body, the greater the likelihood of the formation of areas with connective tissue.
Complications of bilateral hydrocalycosis
With indicators that are within the normal range of calyx expansion, symptoms of the disease may be completely absent. If no pathological changes occur for a long time, then for several years, sometimes decades, the patient may not be aware of the presence of pathology.
Hydrocalycosis of both kidneys can lead to certain complications, namely:
- pressure on the urethra increases;
- pathogenic microorganisms infect the kidney tissue;
- venous outflow increases;
- An active redistribution of blood flow begins, as a result of which the blood supply to the kidneys increases.
To eliminate pain, NSAIDs are used in the form of suppositories.
With double dilatation, urinary tract obstruction may occur. This can trigger the renin-angiotensin system to become active, which affects blood pressure.
Potential danger of kidney stones
It is worth knowing that urolithiasis can cause a lot of trouble to its “owner”
It is worth knowing that urolithiasis can cause a lot of trouble to its “owner”. Their severity and course depend entirely on the type of stone formed in the pelvis. Thus, the simplest and most potentially harmless are urate stones, which dissolve well on their own if you follow a certain diet and drinking regimen. In the future, such sand simply comes out with urine. All other stones dissolve more difficultly or cannot be dissolved at all. In this case, the danger is that the stone can grow and eventually fill the entire cavity of the pelvis. With this pathology, hydronephrosis occurs (accumulation of excess urine in the kidney cavity and its subsequent rupture). It is worth knowing that fixed stones lead to hydronephrosis. But there is one peculiarity here: it is the stationary stones that grow very slowly. Therefore, they are classified as conditionally favorable.
It's a different matter when it comes to moving stones. Here the patient may periodically experience renal colic, which occurs when a pebble moves. The size of movable stones is much smaller than immobile ones. However, the very shape of the stones poses a threat to the patient. So, if the stone has sharp edges or spikes, when moving, such a formation can injure the inner surface of the urinary tract. And with their high sensitivity, the patient will feel sharp pain. In the worst case, the stone, when moved, can rupture the ureter, causing urine to leak into the abdominal cavity. This will lead to additional problems, surgery and possible complications.
Therapeutic measures
This pathology can be treated with the help of medications, and it is also possible to use folk recipes. It is possible to use surgical intervention, but only in cases where hydrocalycosis is combined with urolithiasis or abnormalities of the genitourinary system.
Use of medications
Medicines for the treatment of enlarged renal calyces are used to eliminate the symptoms of the pathology. In the presence of a pronounced inflammatory process, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Among them are: Dicloberl, Diclak, Voltaren, Indomethacin.
Folk recipe
Traditional methods are most often used for preventive purposes, very rarely for treatment. If there is an expansion in the pelvicalyceal area, infusions and decoctions from medicinal plant materials are used to restore it, namely:
- A decoction of lingonberry leaves: to prepare it you will need 2 tbsp. l. leaves and 200 ml of fresh boiling water.
- Decoction of bearberry herb: 1 tbsp. l. raw materials must be mixed with 200 ml of boiling water.
On sale you can find medicines that contain medicinal plants: Phytolysin, Trinephron, Canephron, Uronephron, Cyston.
Before using traditional recipes, you should consult your doctor.
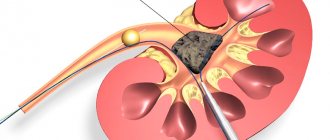
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is used if there are problems associated with the outflow of urine. It is necessary to restore the patency of the urethra; for this, shock wave lithotripsy can be used in the presence of small stones. To avoid such health problems, you should listen carefully to your body, undergo the necessary examinations in a timely manner, and also lead a healthy lifestyle. By following these simple rules, kidney problems can be avoided.
How is the treatment carried out?
If the tendency of the cups to enlarge is confirmed by various studies, then, in most cases, this is a reason for surgery. This is also explained by the fact that quite often hydrokaliosis is accompanied by the addition of an infection, which in turn contributes to the accumulation of amorphous phosphates, which subsequently block the urinary ducts.
Note! Today, operations are performed in a gentle, minimally invasive way, using an endoscope. This significantly reduces the level of postoperative complications for the patient.
Drug treatment is prescribed when surgery, in the opinion of the attending physician, is inappropriate at this stage of the disease. During this treatment, antibacterial therapy and mandatory instrumental and laboratory observation of the dynamics of processes occurring in the urinary system are used.
The patient, regardless of the type of treatment, is prescribed a special diet. It involves excluding from the diet fatty, fried, protein foods, salty, sour and spicy foods, as well as sausages and fast food, coffee, strong tea and alcohol. It is allowed to consume fermented milk products and a large amount of fruits and vegetables. Decoctions of bearberry and lingonberry leaves are also useful. Herbal medicines are used, for example, phytolysin and canephron. By following all the recommendations of your doctor and taking a conscious approach to your health, you can significantly speed up the healing process.