The stronger sex can be considered weak due to certain diseases. This is especially true for urolithiasis. According to statistics, men suffer from this disease several times more often than representatives of the fair half of humanity. It occurs in approximately 3% of the world's population and does not discriminate between ages. Neither a newborn nor an elderly person is immune from the occurrence of kidney stones.
Urolithiasis in men firmly occupies a silver position among diseases of the genitourinary system, accompanied by inflammatory processes. The deposition of salts and the resulting formation of sand and stones do not initially cause any discomfort. But when the movement of stones into the ureter begins, severe pain appears associated with acute inflammation of the kidneys and disruption of their functionality. If treatment for the disease is not started in time, life-threatening and serious complications may arise.
The disease has several names: urolithiasis, nephrolithiasis, kidney stones.
Causes
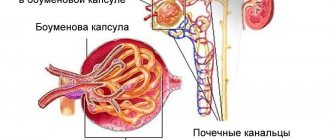
Urolithiasis in men is a pathological condition in which, as a result of metabolic disorders, crystalline formations are formed in the body: sand, kidney stones and bladder stones. Urolithiasis develops as a result of imbalances in the chemical composition of urine, which leads to the deposition of salts, mineral and protein components on the membranes of the genitourinary organs.
Causes of kidney stones in men:
- Living in a hot climate zone. At high temperatures, the process of sweating increases, which leads to the deposition of salts in the body.
- Living in places with a deficiency of ultraviolet rays.
- Drinking hard water.
- Abuse of coffee, cocoa, sour and spicy foods.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
- Diseases and pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
- Intoxication of the body when harmful viruses, infections, and fungi are introduced into the body against the background of which acute inflammatory processes develop.
- Chronic diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Long-term treatment with certain medications.
- Lack of physical activity.
- Enzyme deficiency.
- Living in environmentally polluted areas.
- Working with hazardous working conditions.
- Poor circulation in the pelvic organs.
- A congenital pathology that develops against the background of metabolic disorders and an increase in urinary levels of uric acid, phosphates, oxalates and calcium.
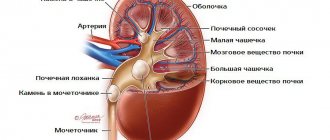
Sometimes stones fill the entire volume of the renal pelvis
Classification of formed stones
There are several types of kidney stones. Procedures aimed at treating the disease will depend on this. Certain types of stones can even dissolve in plain water.
The most common stones are calcium. They are the densest in consistency and the least susceptible to dissolution.
There are several types of stones:
- Oxalate stones have a very dense structure, gray or dark gray in color. On the surface of the stones there are thorns with which they damage the mucous membranes. They are formed from salts of oxalic acid. An overdose of vitamin C is also one of the factors in the development of stones.
- Phosphate stones have a softer structure, with a smooth surface, and a light gray color. They appear if metabolism is disrupted and shifts to the alkaline side. Their characteristic sign is the appearance of light and loose flakes in the urine. Can be dissolved by sour juices.
- Urate stones occur in 15% of cases. The factor causing their appearance is gout. But they cannot be seen in X-rays. But getting rid of them is quite easy.
- Struvite stones are formed under the influence of microorganisms. Their second name is infectious. They are diagnosed by coffin-shaped crystals found in the urine.
- Cystine stones are classified as a separate disease - cystinuria. Occurs in 2-3% and is inherited. Can be dissolved with the help of drugs.
Knowing the type of stones is very important when prescribing treatment and choosing a diet. Since with some stones one thing is possible, while with others certain categories of products are prohibited, violating the rules will lead to serious consequences.
Symptoms
Symptoms of urolithiasis in men are pronounced, which is associated with the physiological features of the structure of the genitourinary system: a long urethra, the walls of which are quite thin and low elasticity of the ureters, which increases sensitivity during the passage of crystalline formations.
Kidney stones symptoms in men:
- Feeling of pain in the lower back, increasing with movement and physical activity. The peak of pain occurs when the stone passes through the urethra.
- The appearance of colic in the kidneys is a muscle spasm due to irritation of organ tissue during the passage of sand or salt crystals. With renal colic, there is a sharp pain that quickly passes. Colic becomes intense with physical activity.
- There is a disruption in the functioning of the digestive organs: vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, flatulence, loss of appetite.
- Symptoms of general intoxication develop: chills, fever, weakness, poor sleep, decreased performance.
- Violation of the process of urine separation. The number of urges, which are often false, increases.
- When a kidney stone passes, the urine becomes cloudy and there is an accumulation of blood in it.
- Increased pressure.
The signs of kidney stones may vary slightly, which is due to the different localization of crystalline deposits in the organs. Blood in the urine is diagnosed if the stone is located in the kidneys. If the accumulation of salts is in the urethra, the pain is localized in the groin and thigh areas.
Other signs of urolithiasis in men
As mentioned above, pain is the main symptom of this disease. However, there are a number of other signs that can also be classified as clinical manifestations. Accordingly, if they are accompanied by pain in the lumbar region, lower abdomen or groin, special attention must be paid to them.
With urolithiasis, the patient feels unwell
These signs include:
- dysuria;
- nausea and vomiting;
- general deterioration of the patient’s well-being;
- blood in the urine (especially during exacerbation of pain);
- various urinary disorders;
- urinary retention due to blockage of the bladder neck;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of edema.
Treatment
Urolithiasis symptoms and their treatment in men are carried out in close connection with the first ones on the basis of those obtained through laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods. For urolithiasis in men, there are two methods of treatment: conservative and surgical.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment is aimed at eliminating pain, eliminating inflammatory processes, normalizing urination and removing stones.
To eliminate pain and spasm, the urologist recommends medications that improve the general condition of the patient and help remove stones naturally. Among the painkillers used are No-shpa, Papaverine, Baralgin.
Antibacterial drugs, which are not recommended for use in diseases of the digestive system, which can cause complications, will help eliminate inflammation. Antibacterial therapy is always accompanied by the intake of probiotics to normalize the intestinal microflora.
Treatment of urolithiasis in men with drugs to destroy stones is necessarily accompanied by the use of mild diuretics. Together, these medications lead to a change in the acidic component of urine, which gradually breaks down stones and promotes their rapid elimination. Most often, Uralit, Blemaren, Phytolysin, Marelin are used to destroy stones in the kidney or urethra.
Diagnostic features
Considering the fact that this disease does not have many symptoms, diagnostic measures must be carried out at the proper level in order to recognize the type of disease. There are cases when doctors failed to diagnose urolithiasis - due to the provision of insufficient information by the patient himself or his own negligence, which inevitably led to serious complications.
Tests are required
To make a correct diagnosis, the following factors must be taken into account:
- the presence of characteristic symptoms - acute pain in the lumbar area, groin or abdomen, blood impurities, burning sensation, inability to completely empty the bladder, renal colic, etc.;
- visual and tactile examination of the patient. A qualitative examination allows you to identify many diseases of the urinary system. Palpation of the abdomen will help differentiate the disease from inflammatory processes in the peritoneum - for example, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis, etc. Examination of the lower back will make it possible to find out whether we are talking about radiculitis, pyelonephritis and other diseases that have nothing to do with stones. The doctor is also obliged to pay attention to the color of the patient’s skin, the presence or absence of swelling, and especially his posture - with urolithiasis, men often twist in pain;
- Ultrasound is a very effective diagnostic method with a high degree of reliability. A high-quality ultrasound examination allows not only to detect the location of stones, but also to determine their size and shape;
- indicators of a general urine test - the presence of red blood cells and an increased concentration of salts indicates this disease;
- X-ray contrast examination – required if it is necessary to identify exactly where the stone has blocked the duct;
- computed tomography - it is resorted to if ultrasound does not give a clear answer as to what features the detected pathology has.
Complications
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, urolithiasis can lead to serious consequences. The nature of the complications is influenced by the characteristics of the stones: composition, size, structure. Most often, if left untreated, urolithiasis leads to:
- To chronic inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, urethritis, cystitis, glomerulonephritis).
- The formation of pus in the kidneys and gradual necrosis of organ tissue lead to sepsis. This pathology is called paranephritis.
- Pyonephrosis is a pathological condition leading to complete cessation of kidney function and its death. The cause of the disease is the accumulation of stones, pus, and urine in the organ, under the influence of which tissue destruction occurs.
- During the passage of large stones or stones that are shaped like corals, bleeding may occur due to damage to the urinary canals.
- Development of renal failure.
Nature of the disease
If the metabolism is disturbed, all organs do not work properly. Such a disorder can be provoked not only by an incorrect lifestyle, but also by heredity. Due to such problems, urolithiasis occurs. Treatment, as well as symptoms, directly depend on the factor that provoked the disease. The formation of stones can occur in any part of the excretory system (kidneys, urethra). The pain may be periodic or completely absent. If there are no symptoms, this may indicate that the stones have not begun to move. With infectious and inflammatory diseases, the risk of stone formation increases.
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader got rid of PROSTATITIS using an effective method. He tested it on himself - the result was 100% - complete relief from prostatitis. This is a natural remedy based on honey. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast. EFFECTIVE METHOD.
Important. Men suffer from urolithiasis much more often than women.
Prevention
Prevention of urolithiasis includes simple and mandatory rules:
- Adjust your lifestyle: stop smoking, alcohol abuse, avoid nervous stress, lead an active lifestyle.
- Drink enough clean water daily, more than 2 liters. Water helps cleanse the urinary canals.
- Timely treatment and prevention of diseases of the urinary system.
- After surgical, conservative or instrumental treatment, the patient needs to take medications and herbal remedies for some time that prevent the re-formation of stones.
- If you have a hereditary predisposition to urolithiasis, it is recommended to drink mild diuretics.
Treatment of nephrolithiasis at home
There are several ways to get rid of stones at home. Folk remedies are not suitable for serious cases of the disease, but at an early stage they can significantly reduce pain and eliminate problems:
- Oat infusion. 250 g of green oats must be poured with 500 ml of vodka. The tincture is placed in a dark place for 3 weeks. The product should be taken diluted, 30 drops per 1 tbsp. l. water 3 times a day before meals.
- Watermelon diet. Watermelon helps remove stones from the body. For 20 days, the fruit is eaten in large quantities, especially in the evening, when the activity of the male genitourinary system is activated.
- Infusion of oatmeal. For 1 liter of boiling water, 300 g of grain is used. It is necessary to infuse the product for about 12 hours in a dark, cool place. Take 100 ml infusion 4 times a day before meals.
- Herbal collections. Small stones are removed from the body by collecting various herbs: blueberry leaves, oat straw, clubfoot, corn silk. The herbal mixture is poured into 1 liter of water and boiled over high heat. The cooled product is taken within 3 hours, 1 tbsp. l. every 30 minutes.
Making herbal infusions and treating nephrolithiasis at home is only possible with the permission of the attending physician. Symptoms of the disease disappear after 2 weeks of taking medicinal herbs.
Nutrition
Nutrition for kidney stones plays a significant role in the education, treatment and prevention of the disease. Depending on the type of stones that are diagnosed in the urinary tract or kidneys, there are different dietary recommendations.
For stones of oxalate origin, it is necessary to exclude sorrel, citrus fruits and lettuce, dairy products and other foods rich in calcium, which lead to the development of urolithiasis.
When diagnosed with urate, a man should reduce the daily amount of meat products, liver, coffee and products containing cocoa.
For stones whose structure includes calcium or phosphates, you need to exclude foods that increase the acidity of urine: meat, fish, fruits.
Urolithiasis in men develops under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors and hereditary predisposition. The main manifestations of the disease are pain in the abdomen, lower back, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, diuretic disorders and symptoms of general intoxication. To combat stones, conservative, instrumental and surgical methods are used. During treatment and for the purpose of prevention, it is important to eat right and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Patient examination
In the anamnesis (medical history), all facts that may indicate urolithiasis are important. A family history of urolithiasis and risk factors help to easily identify the cause of pain. Surgery not only on the kidney itself, but also on the abdominal cavity in general can lead to the formation of crystals. Metabolic disorders—gout, cystinuria, hyperparathyroidism, or treatment with vitamin D supplements—may also provide important information to the physician.
The fundamental method of laboratory research is a general urinalysis. The doctor can determine the extent of possible bleeding and the nature of the stone. It also allows us to draw conclusions about the amount of protein and the presence of concomitant urinary tract infection.
Imaging techniques are necessary to determine the location, size, and number of stones. Ultrasound examination shows whether urinary tract obstruction is present. Using a urogram, you can determine the size and function of the kidneys, as well as the number and location of stones. However, it should be performed during colic as the contrast agent may lead to increased urinary urgency and therefore worsening symptoms.
The symptoms may be caused by various other diseases. Therefore, the doctor must exclude these diseases in his diagnosis. Such diseases are summarized by the term “differential diagnosis”:
- Biliary colic and acute inflammation of the gallbladder. The pain usually occurs above the right costal arch and may radiate to the shoulder.
- Gynecological diseases - ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy, stem fibroids can also cause severe pain. The pain is usually deeper and does not have a recurrent nature, unlike renal colic.
- Various acute abdominal diseases - sigmoid diverticulosis, diverticulitis, acute appendicitis or intestinal obstruction.
- Shingles (herpes): The disease can mimic colic.
What is the diagnosis?
At the first suspicion of possible formation of deposits in the kidneys, you should contact a specialist for a full diagnosis. You should not wait for the moment when the frightening symptoms of stone passage appear. A urologist will be able to make an accurate diagnosis after conducting a comprehensive examination, which consists of several stages:
- conducting a survey;
- initial examination;
- urography;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and ureters;
- urine and blood analysis.
In some cases, a modern diagnostic method is used - multislice computed tomography. It is this method that allows you to accurately determine the size of the formation and assess the condition of the damaged nearby tissues of the organ. Nephroscintigraphy is used to determine organ dysfunction. An integral part of the diagnosis is the collection of morning urine for bacterial culture. This analysis makes it possible to determine the degree of sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics of various groups, to assess the nature of inflammation and its scale. Complex treatment is prescribed based on the results obtained.