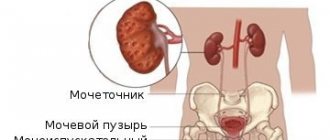
Kidneys are internal organs that cleanse the blood by removing toxic substances dissolved in urine and maintain the body’s water-salt balance. In a healthy person, the kidneys do not allow excess water to be retained in the body.
A variety of reasons lead to a slowdown in the removal of fluid from the body. Fluid in the kidneys fills the renal pelvis and calyces, creating additional stress on the organ, leading to the development of a disease called hydronephrosis.
Causes
The disease develops due to insufficient functioning of the ureteral valves, which leads to reverse flow of urine. It is not possible to determine the causes of the disease one hundred percent, but there are factors that provoke the accumulation of fluid in the kidney:
- Water can accumulate when the ducts are blocked by kidney stones.
- Blood clots formed during kidney injury can also become an obstacle to the drainage of water.
- Impairment of water outflow can occur when the ureter narrows as a result of surgery.
- Tumor involvement of the kidney and ureters.
Types and causes of hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis can be congenital, or primary, and acquired, or secondary. Hydronephrosis in children, as a rule, is congenital, in adults it is acquired.
The most common causes of hydronephrosis in children are congenital abnormalities of the structure of the kidney or its vessels. Secondary hydronephrosis is a consequence of changes in the structure of the kidney or urinary tract (ureter, urethra, and sometimes bladder) as a result of some disease. This may be inflammation of the renal pelvis or ureter, prostate adenoma, cysts and strictures (narrowing) of the urinary tract, etc.
Hydronephrosis can be unilateral, affecting only one kidney, or bilateral. Bilateral hydronephrosis occurs when the outflow of urine in the lower parts of the urinary tract - the bladder and urethra - is impaired, resulting in both kidneys suffering from increased fluid content. Hydronephrosis in children is usually unilateral.
In the case when not only the renal pelvis, but also the ureter has undergone pathological expansion under urine pressure, they speak of ureterohydronephrosis.
How to determine stagnation of urine in the bladder
The bladder is part of the urinary system. Nature has gifted it to perform two important functions in the human body: collecting urine and excreting it.
We do not even suspect how valuable tasks the bladder performs as long as it functions normally.
As soon as the system fails and stagnation appears in the bladder, we immediately begin to panic and look for the reasons, what caused the changes, and what could provoke the disorders.
Through the ureters, urine enters the bladder, from where the body removes it out through the urethra. Obstructed outflow of fluid from the kidneys provokes stagnation, which is medically called hydronephrosis. Symptoms of this condition require immediate medical attention.
Hydronephrosis
It is known that the kidneys are a paired organ, which is distinguished by its complex structure. The main function of the kidneys is to help eliminate toxins from the body through urine.
Its accumulation is observed in the calyces, after which it moves into the renal pelvis and bladder.
Improper functioning of the organ provokes stagnation of urine, and, as a result, pathological expansion of the system. It comes in two types:
- Infected.
- Aseptic.
Carrying a fetus and the development of neoplasms in women are the most commonly cited causes of the development of hydronephrosis. In representatives of the stronger half of humanity, such pathological disorders of kidney function are observed after the age of 45 years. The main stimulating factors are prostate diseases.
4 main causes of pathology
Impaired urine flow causes hydronephrosis. The main reasons that cause this process are the following:
- malfunction of the bladder and urethra,
- external compression of the ureter (neoplasms, enlarged lymph nodes)
- violation of the lumen of the ureter,
- failure of the renal pelvis.
Treatment of bladder congestion
Pain in the lumbar region, in most cases, is evidence that the natural functioning of the kidneys is impaired. Immediate contact with the clinic’s specialists will help prevent the development of serious diseases, including kidney failure.
The disease hydronephrosis can be diagnosed based on the results of an ultrasound examination or x-ray of the ureter. To determine the degree of development of the disease, the patient is prescribed to undergo a series of laboratory tests, based on the results of which the most effective and adequate treatment will be developed.
Doctors place the main emphasis in treatment on relieving pain and eliminating inflammation of the bladder and pathology in the kidneys. A properly developed treatment regimen allows you to eliminate the factors that stimulate urinary stagnation.
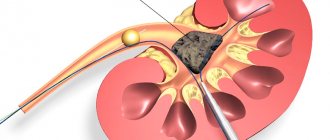
To restore the function of urine outflow from the bladder, it is often necessary to resort to surgery to eliminate stagnation. The operation is performed by urologists under the control of ultrasound diagnostics - percutaneous nephrectomy. During the operation, it is possible to install drainage in the kidneys, through which accumulated urine will be removed.
When hydronephrosis occurs as a result of the formation of kidney stones, doctors use a closed type of operation - endoscopic intervention. In severe cases, open surgery is performed.
Prevention of hydronephrosis
Doctors call personal hygiene the main preventive rules for preventing such a pathology as hydronephrosis. It is imperative to monitor the cleanliness of the genitals and avoid casual sexual intercourse. A number of infectious diseases can be caused by viruses and bacteria that are sexually transmitted
In addition, the development of urolithiasis and inflammation of the urinary system should not be allowed.
Monitor your diet. You need to understand that excessive salt consumption can cause urolithiasis.
Pregnancy and stagnation of urine are provoking factors
Stagnation of urine in the kidneys is often observed in women during pregnancy. This condition causes pain in the kidneys and increases the concern of women during such a crucial period. Hydronephrosis in pregnant women is caused by various provoking factors, in particular:
- pathological changes in the bladder or urethra;
- changes in the ureter - kinks, deformation, compression.
Doctors most often name the following provoking factors for stagnation of urine during pregnancy: compression of the ureter by an enlarged uterus and disrupted hormonal levels. Changes in hormonal levels can affect the contractile function of an organ such as the bladder.
Most often, the right kidney suffers during pregnancy. Reasons: displacement of the position of internal organs. This natural disorder can cause right-sided kidney prolapse.
To avoid such pathological development, it is important to know the main symptoms that indicate congestion in the kidneys:
- stage. The renal pelvis is dilated, renal function is preserved.
- stage. Slight enlargement of the kidney and expansion of its pelvis.
- stage. The kidney is enlarged by 2 times, and the pelvis and calyces in the kidneys expand significantly, forming a multi-cavity chamber. The third stage of the pathological disorder stimulates the development of renal failure.
The manifestation of symptoms of renal pathology directly depends on the development, course and cause of the disease. The woman feels a sharp pain during the attack, which is localized in the side of the abdomen.
The chronic course of the disease is not accompanied by any symptoms. But it is possible that pain in the lateral area, attacks of nausea and vomiting may occur.
Pregnant women complain of dull pain in the kidneys, which can radiate to the groin or thigh. Complaints of severe pain, which are characteristic of attacks of renal colic, are extremely rare. After delivery, symptoms of urinary stagnation in the kidneys gradually decrease.
In order to verify the development of hydronephrosis during pregnancy, an ultrasound examination of the patient is performed or diagnostics are carried out by catheterization of the ureters with a contrast agent such as indigo carmine.
Impaired urinary flow is a serious disorder of the system that can cause unpleasant pain and discomfort. Therefore, immediate consultation with specialists is necessary, during whose examination the causes of the pathology of the ureter that caused congestion in the kidneys will be determined, and the correct treatment will be prescribed.
Source: https://pochkam.ru/mochevoj-puzyr-i-mocheispuskanie/zastoj-mochi-v-mochevom-puzyre.html
Degrees of hydronephrosis
There are three degrees of hydronephrosis:
- Hydronephrosis in the first degree. Stretching of the renal pelvis (pyelectasia) occurs as a result of increased urine pressure. At this stage, the function of the kidney is not yet impaired, but the kidney is already increased in size;
- Hydronephrosis in the second degree. There is a further, more significant expansion of the renal pelvis and renal calyces (hydrocalicosis). As a result, the fluid contained in the tubules compresses the kidney parenchyma, which thins (atrophies) under the influence of pressure. At this stage, kidney function is significantly impaired;
- Hydronephrosis in the third degree. Atrophy of renal tissue increases, becoming irreversible. Kidney function is gradually lost, and in the final stage of hydronephrosis the kidney dies. A kidney that has lost its function in this case poses a significant threat to health.
Hydronephrosis: definition, classification of pathology
Hydro - water, nephro - kidney, translated from Latin the translation of the name of the disease speaks for itself: the concentration of fluid at a local point. Moving into the acute stage, the pathology leads to the destruction of renal functions, disruption of metabolic processes and infection of the patient’s entire body.
The disease can be diagnosed immediately after birth - a congenital variant or during life - acquired. The pathology can affect one or both kidneys, while bilateral inflammation disrupts the outflow of urine in the lower reaches of the urinary tract: the ureter, urethra.
The disease is classified into three degrees:
- The first degree is manifested by a slight expansion of the pelvis due to increased pressure on its walls. At the same time, the organ still retains 100% of its functions.
- The second degree is a moderate or significant expansion of the pelvis and cups. The accumulated fluid in the kidneys puts pressure on the parenchyma, blocks the tubules, the functionality of the organs is preserved by 40-45%;
- The third degree is characterized by atrophy of organ tissue, and the process is already irreversible, leading to complete death of the kidney and a threat to the patient’s life.
Symptoms of hydronephrosis
The severity of the symptoms of hydronephrosis depends on the degree to which the disease occurs. Early symptoms of hydronephrosis are not pronounced, so the disease is sometimes detected in an advanced state.
Hydronephrosis in newborns, and indeed hydronephrosis in children in general, usually does not manifest itself in any way until the third degree of the disease, except that the baby’s increased anxiety may attract attention; sometimes with hydronephrosis in newborns, an admixture of blood is found in the urine. Hydronephrosis in newborns is usually known in advance, as it is detected during prenatal ultrasound diagnosis of the fetus. Hydronephrosis in older children, as in adults, can be discovered accidentally during examination for another reason.
Sometimes an early symptom of hydronephrosis is renal colic, this is especially true for hydronephrosis caused by urolithiasis. When the disease reaches a significant stage of development, the main symptoms of hydronephrosis are aching, dull and constant pain in the kidney area and signs of reduced renal function: edema, high blood pressure due to impaired water metabolism. One of the common symptoms of hydronephrosis is the appearance of blood in the urine (hematuria).
Diet therapy and drinking regime
Despite the simplicity of the advice, diet therapy, coupled with adherence to a drinking regime and a healthy lifestyle, can significantly reduce the symptoms of the disease, and then serve as an excellent prevention of pathology. When choosing a menu, it is better to avoid fatty, heavy dishes, giving preference to raw vegetables and fruits.
The volume of fluid consumed for a patient without additional diseases is at least 2-2.5 liters per day. The doctor will explain the details of the diet: the diet is selected individually, however, reducing the amount of spicy, sweet, and smoked foods will only come in handy, as will giving up alcohol, strong coffee, and tea. Dishes introduced into the diet should be rich in amino acids, which are not synthesized by the body, but are obtained only from foods.
Important! Limiting or completely eliminating table salt is a mandatory part of the diet for hydronephrosis. A potato-egg diet with a reduced calorie content and high levels of amino acids is considered the most suitable. In addition, the products do not increase the load on the gastrointestinal tract, remove excess cholesterol well and are processed by the body of a patient of any age. You cannot keep this diet for a long time! The timing of nutrition will be advised only by a highly specialized doctor, whose consultation is required.
Diagnosis of hydronephrosis
The leading method for diagnosing hydronephrosis is ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urinary tract. As a supplement, color Doppler mapping (CDC), radioisotope renography, and sometimes computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are used. Also, in some cases of hydronephrosis, endoscopic examination - urethrocystoscopy or ureteroscopy - can be used. All these methods are aimed at visualizing the internal structure of the kidney, ureters and the vessels supplying them.
Since hydronephrosis promotes infection, urine culture is performed. Functional urine tests (Zimnitsky test, Nechiporenko test) are performed to study kidney function.
Treatment of congestion in the kidneys
Prolonged progression of the pathology gradually worsens kidney function and leads to the development of renal failure. Stagnation in the kidneys is fraught with serious complications:
- pyelonephritis;
- formation of stones;
- spread of inflammation throughout the body (which can be fatal);
- secondary reduction in kidney size;
- increased blood pressure.
Therefore, it is important not to delay treatment of the pathology. To reduce pain and prevent infectious complications, antibacterial and painkillers are prescribed. But to restore normal urine flow, instrumental or surgical intervention is necessary. The choice of method depends on the causes of congestion.
1. Bladder catheterization.
It is carried out in the presence of benign or malignant formations in the prostate gland, with sclerosis of the bladder neck.
Using a ureteral stent, the narrowed area of the ureter is expanded. Then the patient is prepared for the introduction of an endoscope and retrograde pyelography.
2. Percutaneous nephrostomy.
Installation of external drainage into the renal cavity system under ultrasound guidance. With the help of drainage, urine enters external collection systems.
The method is used when it is impossible to place a stent or ureteral catheter.
3. Open surgery.
Indications for implementation:
- retroperitoneal fibrosis;
- aortic aneurysm;
- kidney stones that cannot be removed by endoscopy or shock wave lithotripsy;
- tumors in the retroperitoneal space.
4. Endoscopic method.
Used in the presence of stones and neoplasms that obstruct the outflow of urine.
Congestion in the kidneys can occur in the third trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the mechanical pressure of the uterus on the ureter and increased levels of progesterone. After childbirth, the pathology will go away.
Appears due to the occurrence of salt deposits in the renal pelvis in the form of sand or a dense formation. In the modern world, a mild degree of the disease can be found in 30% of the world's population. The grains of sand that form rarely exceed 1 mm in diameter, so they do not cause persistent pain and are independently washed out of the body along with urine. Large deposits over a long period of time form large stones that can reach 2 cm in diameter or more. It is difficult to remove such stones on your own; medical or surgical intervention is required. It is possible to get rid of small stones by significantly increasing the volume of fluid consumed or using a diet. An alternative method of treatment, according to experts, is mineral water.
Treatment of hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is treated only surgically.
Conservative treatment of hydronephrosis is used only to eliminate inflammation if a secondary infection has occurred, or as therapy to alleviate the symptoms of hydronephrosis before surgery. Surgery to treat hydronephrosis consists of removing the obstruction that interferes with the normal flow of urine. Each case requires an individual approach, so the choice of surgical treatment for hydronephrosis remains with the surgeon. Currently, surgical treatment of hydronephrosis is performed endoscopically, which does not require a large and traumatic incision to access the surgical field.
The endoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity through two small punctures; all manipulations are performed with a thin surgical instrument under the control of what is happening on the monitor. This method of treating hydronephrosis can significantly reduce the trauma of the operation, the risk of postoperative complications and is practically bloodless.
Hydronephrosis in young children at a minor stage may not require medical intervention. In such cases, dynamic monitoring with ultrasound is recommended two to four times a year. Hydronephrosis in children of the first and even second degree sometimes goes away on its own during the first year of life; surgical treatment of hydronephrosis is not required. However, the disease in the third degree, as well as the increase in symptoms of hydronephrosis in children, require urgent surgical intervention.
In case of hydronephrosis in the terminal stage, if the kidney dies, it is removed. Typically, this operation is performed in older people, when the regenerative functions of the body are significantly reduced.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Kidneys are internal organs that cleanse the blood by removing toxic substances dissolved in urine and maintain the body’s water-salt balance. In a healthy person, the kidneys do not allow excess water to be retained in the body.
A variety of reasons lead to a slowdown in the removal of fluid from the body. Fluid in the kidneys fills the renal pelvis and calyces, creating additional stress on the organ, leading to the development of a disease called hydronephrosis.
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys: what is it, symptoms, treatment, outcome of the disease
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys is an enlargement of the renal pelvis due to a deterioration in the outflow of urine, which leads to a decrease in the viability of the organ. It manifests itself as pain in the lower back, blood in the urine, increased blood pressure, and frequent urge to go to the toilet. For diagnosis, ultrasound of the bladder, CT scan of the kidneys, and urography are prescribed. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes that led to stagnation of urine in the kidneys.
What is hydronephrotic transformation
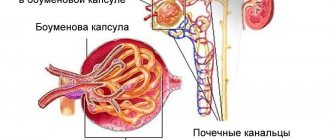
Hydronephrosis is a disease in which fluid stagnates in the kidneys. The organ consists of:
- parenchyma - tissue that cleanses the blood of toxins and produces urine;
- cavity system - consists of small cups that form large pelvis.
The cavity system is a reservoir for storing liquid. Outside, it is shrouded in parenchyma. If the passage (passage) of urine through the urinary tract is disrupted, the pelvis dilates. Subsequently, the pyelocaliceal system (PSS) becomes deformed, and the viability of the renal tissue decreases.
Deterioration of urine outflow from the renal cavity system leads to:
- violation of the filtration function of the organ;
- slowing down the circulation of blood and lymph in the parenchyma.
The outcome of the disease is the death of nephrons - structural units in which blood filtration and reabsorption of various substances occur.
Hydronephrosis is more often found in women 20-55 years old, which is associated with pregnancy and gynecological pathologies. And after 60 years, men with sluggish prostatitis and prostate adenoma suffer more from the disease.
Causes of hydronephrosis
Hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney is a multifactorial disease that is caused by various reasons. They are conventionally divided into 2 groups:
- caused by a decrease in the diameter of the urinary tract, chronic inflammation, tumors in the ureter, urethral canal, ureter;
- provoked by insufficient tone of the urinary valves and reverse urine flow.
Common reasons
In half of the cases, a violation of the passage of urine is caused by a narrowing of the diameter of the urinary tract, which is caused by:
- tumors;
- ureteral endometriosis;
- tuberculosis;
- stones in the ureter;
- blood clots
Hydronephrosis in an adult man occurs against the background of sluggish prostatitis, hyperplasia and prostate adenoma. It is possible that the urinary tract may narrow due to a sexually transmitted infection entering the urethral canal. In women, hydronephrosis is provoked by gynecological diseases - cervical cancer, vaginitis, uterine prolapse, cervicitis.
Difficulty in the outflow of urine from the pelvis is caused by urinary pathologies:
- prolapse of the bladder;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- stones;
- scarring of the cervix.
Disturbance in the passage of urine is caused by large pelvic lipomas, which compress the urinary tract. Sometimes fluid stagnates in the kidneys due to urethral obstruction, which is caused by:
- scarring of the urethral canal;
- pouch-like protrusion (diverticulum) of the urethra;
- obstruction of the urethra.
Hydronephrosis is provoked by injuries to the pelvic organs, inflammatory diseases of the urinary organs - urethritis, cystitis.
If the outflow of urine is disrupted below the pelvic level, not only the renal reservoirs expand, but also the ureter itself. This condition is called hydroureteronephrosis.
In children
In childhood, the congenital form of hydronephrosis is more common. It is caused by an abnormal structure, location or functioning of the organs of the urinary system:
- urinary tract dyskinesia;
- congenital narrowing of the urethral canal;
- ureteral atony;
- pathology of the valve apparatus of the ureter;
- the ureter departs from the pelvis in an atypical location;
- pathological location of the artery, creating pressure on the ureter.
Some diseases leading to hydronephrosis are noticed by a specialist at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. An ultrasound examination reveals an additional renal vessel for collecting urine, prolapse of the kidney, and incorrect location of the arteries. Timely organ plastic surgery prevents the loss of parenchyma viability.
During pregnancy
Hydronephrosis during pregnancy in 63% is caused by disorders at the level of the urinary ducts. Gradual enlargement of the uterus leads to:
- increased pressure in the pelvic organs;
- compression of the bladder and ureter.
In most women, dilation of the pelvis of the right kidney is detected, which is due to the peculiarities of the location of the fetus in the peritoneum. Hydronephrosis is provoked by:
- natural decrease in immunity;
- tubo-ovarian abscess;
- electrolyte imbalance;
- uterine prolapse;
- cysts on the gonads;
- aortic aneurysm in the abdominal region.
During pregnancy, the load on the body increases several times. To cleanse the blood of the mother and fetus, the kidneys function in an enhanced mode. To avoid gestational pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis, women should be examined by a doctor once every 2-3 months.
Classification and stages of hydronephrosis
In nephrology, left-sided and right-sided hydronephrosis are diagnosed with equal frequency. By location it can be one- or two-sided. Simultaneous damage to both kidneys is rarely detected - only in 5-7% of cases.
Depending on the time of origin, the forms of the disease are distinguished:
- congenital;
- acquired.
According to the nature of the course, acute and sluggish (chronic) hydronephrosis is distinguished. In the first case, it is possible to restore kidney function in full, but in the second, organ dysfunction is irreversible.
Based on the presence of microbes, hydronephrosis is divided into types with aseptic or infectious inflammation. In case of infection, the disease is complicated by an abscess.
Stages of kidney disease:
- first - only the pelvis expands, but the functioning of the organ is practically not disrupted;
- second - the volume of the organ increases by 15%, its walls become thinner, and the performance of the pelvis decreases by 30-40%;
- third - the CL is transformed into a multi-chamber cavity, the kidneys are doubled in size, and the ability to discharge urine into the ureter is reduced by 80% or absent.
Based on the severity of renal tissue atrophy, there are 4 stages of hydronephrosis:
- first, there are no pathological changes in the parenchyma yet, but it is beginning to thin out;
- second - minor damage is detected on the surface of the organ;
- third – more nephrons die;
- fourth - the kidney tissue is missing, which is why the organ stops functioning.
Non-infectious hydronephrosis of the right or left kidney of the 2nd degree occurs in a latent form in 84% of patients.
The first symptoms occur when the organ’s performance decreases by 50%. Hydronephrosis of the left kidney of the 3rd degree is manifested by pain in the sacrum, which spreads to the groin and inner thighs.
Symptoms of kidney hydronephrosis
The symptoms of hydronephrosis in adults depend on various factors:
- location of the source of the disease;
- rate of progression;
- duration of narrowing of the urinary ducts.
Acute hydronephrosis is characterized by rapid progression and a clear clinical picture. The severity of pain depends on the degree of increase in the diameter of the renal pelvis. They are similar to renal colic. The pain spreads along the urinary ducts and radiates to the genitals, scrotum, and thighs.
The first signs of hydronephrosis:
- very frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- lack of appetite;
- lower back pain on the right or left;
- nausea;
- blood in the urine.
Non-infectious hydronephrosis is asymptomatic. Patients are concerned about:
- temporary back pain;
- discomfort in the lumbar-costal area;
- frequent urination.
As the pressure in the CLS increases, the functions of the organ are disrupted. Due to the accumulation of toxins in the blood, symptoms of poisoning occur:
- decreased performance;
- chronic fatigue;
- increased blood pressure.
If hydronephrosis is complicated by infectious inflammation, the clinical picture is supplemented by the following symptoms:
- feverish condition;
- temperature increase;
- impurities of pus in the urine.
Patients prefer to sleep on their stomach, which is due to increased intra-abdominal pressure and urine drainage from the kidney.
Why is the disease dangerous?
Improper treatment leads to the transition of the disease to a sluggish form. Hydronephrotic transformation of the right or left kidney is fraught with:
- urolithiasis (urolithiasis);
- hypertension;
- pyelonephritis;
- organ rupture.
With infectious inflammation of the kidneys, carbuncles form on the organ and sepsis occurs. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner leads to irreversible changes in the urinary system. Over time, kidney failure is diagnosed, which is accompanied by intoxication. Electrolyte imbalance and nitrogen poisoning lead to death.
Methods for diagnosing fluid in the kidneys
The diagnosis is made by a nephrologist or urologist. To assess the degree of kidney dysfunction, a comprehensive examination is performed, which includes:
- taking anamnesis;
- palpation of the abdomen;
- lab tests;
- hardware examination.
The defining methods for diagnosing urological disease are:
- Ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys;
- excretory urography;
- renal angiography;
- nephroscintigraphy;
- Kidney MRI.
To visualize the area of the urinary tract in which there are obstacles to the movement of urine, urethroscopy or cystoscopy is performed. Kidney dysfunction is determined by biochemical urine analysis. It contains high concentrations of protein, creatinine, potassium, and uric acid.
When making a diagnosis, hydronephrosis is distinguished from diseases with a similar clinical picture - nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis, prolapse, polycystic disease and kidney carcinoma.
Treatment of hydronephrosis
Before treating hydronephrosis, the degree of dilation of the pelvis and atrophy of the parenchyma is determined. Conservative therapy is used only to relieve symptoms. To restore kidney function, surgical intervention is used.
Drug therapy
Treatment of hydronephrosis without surgery does not bring the desired effect. Medicines are used to relieve symptoms:
- antispasmodics (Drospa Forte, No-shpa) - reduce spasm of the urinary tract, restore urine passage;
- antibiotics (Cefuroxime, Augmentin) - destroy bacterial flora in the kidneys;
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Canephron, Urofit) - relieve inflammation and pain, stimulate the outflow of urine from the kidneys;
- antihypertensive drugs (Nebivolol, Lisinopril) - reduce blood pressure, preventing further expansion of the pelvis and the progression of hydronephrosis.
Medicines reduce the severity of the symptoms of hydronephrosis, but do not eliminate the cause of the expansion of the collecting system.
Operation
To cure the disease, it is necessary to create an alternative path for the outflow of urine from the kidney. For this, different surgical methods are used:
- Transurethral catheterization. The operation is indicated for persistent bladder spasm. Using a catheter, a spring is inserted into the urethral canal, which is installed at the site of narrowing of the urethra. Due to this, its patency is restored.
- Nephrostomy placement. If the urinary duct is obstructed, an artificial pathway is created to remove fluid from the kidney. A tube is sewn to one of the renal pelvis, the second end of which is brought out.
If hydronephrosis occurs against the background of prostate adenoma or cancer, or urinary polyp, surgery is performed to remove the tumor. For stones, lithotripsy is prescribed - remote crushing of stones with a shock wave.
Nephrectomy - removal of the affected kidney - is performed in advanced forms of hydronephrosis, when there is a risk of infectious complications.
Diet
In people with hydronephrosis, the elimination of harmful substances by the kidneys slows down. To reduce the toxic load on the body, it is necessary to exclude from the diet:
- salt;
- fish;
- meat;
- confectionery;
- soda;
- aspic;
- fried foods.
Hydronephrosis of the kidney, stage 1, can be effectively treated. To prevent the progression of the disease, you should include watermelon, pumpkin, apples, sweet grapes, and cauliflower in your diet. Eat at least 600 g of healthy vegetables and fruits per day.
Folk remedies
To ease the course of hydronephrosis and support kidney function, use:
- Pumpkin decoction. The stalk is ground on a grater. 2 tbsp. l. raw materials are boiled in ½ liter of water. The filtered decoction is drunk 200 ml up to 3 times a day.
- Parsley decoction. 50 g of crushed roots are boiled in 300 ml of water for 15 minutes. Take 50 ml 4 times a day.
Folk remedies are used only after consultation with a nephrologist.
How long do people live with hydronephrosis?
The outcome of the disease depends on the timeliness of therapy. Hydronephrosis grades 1 and 2 are relatively easy to treat. When factors that impede urine passage are eliminated, 95-96% of patients recover.
Terminal hydronephrosis is complicated by renal failure and irreversible intoxication with nitrogenous substances. Survival depends on the presence of infectious complications, stones and other pathologies. In the worst case, a person dies a few months after stage 4 hydronephrosis is detected.
Can dropsy go away on its own?
Acute hydronephrosis of the 1st and 2nd degrees can go away on its own if the cause of the disturbance in the outflow of urine has resolved itself. This situation is possible with a temporary narrowing of the urethra due to inflammation and swelling of the prostate. The kidney has high reserve capacity, so when urine passage is restored, its function returns to normal.
With grade 3 hydronephrosis, the kidney tissue completely atrophies, that is, the changes are irreversible. Delayed organ removal is dangerous due to infectious complications.
Prevention
To avoid hydronephrosis, you should:
- timely treatment of urological diseases;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- avoid injuries to the pelvic organs;
- be examined by a urologist during pregnancy;
- eat rationally;
- Visit a gynecologist or andrologist two to three times a year.
Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating provoking factors. By maintaining personal hygiene and treating urogenital infections, the risk of exacerbation of hydronephrosis is reduced significantly.
Source: https://tden.ru/health/gidronefroz-pochek
Causes
The disease develops due to insufficient functioning of the ureteral valves, which leads to reverse flow of urine. It is not possible to determine the causes of the disease one hundred percent, but there are factors that provoke the accumulation of fluid in the kidney:
- Water can accumulate when the ducts are blocked by kidney stones.
- Blood clots formed during kidney injury can also become an obstacle to the drainage of water.
- Impairment of water outflow can occur when the ureter narrows as a result of surgery.
- Tumor involvement of the kidney and ureters.
Hydronephrosis during pregnancy
Hydronephrosis often appears in expectant mothers due to physiological changes caused by pregnancy. The cause of the disease is compression of the ureter by the enlarged uterus. In pregnant women, the right organ is most often affected by hydronephrosis. Hydronephrosis in pregnancy has the ability to resolve without treatment after the birth of the child.
This pathology is not an indicator for abortion; doctors call it true hydronephrosis of pregnancy. If a woman develops chronic hydronephrosis during pregnancy, this threatens severe complications during childbirth. Prevention of hydronephrosis - prevention and timely treatment of diseases that cause fluid in the kidney, general strengthening of the body's defenses.
Symptoms
Hydronephrosis can be congenital or acquired. The disease may affect one or two kidneys. The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. Signs of the disease depend on how rapidly the exit of water from the body is blocked. With rapid overflow of the renal pelvis, the patient feels severe pain in the lumbar region, on the side where the inflamed organ is located.
When the kidneys slowly fill with water, pain symptoms are often not felt. The development of hydronephrosis is indicated by signs: increased temperature, frequent urination, and the presence of blood traces in the urine. Abdominal cramps, nausea ending in vomiting, fatigue, and a decrease in daily urine volume occur.
Kidney congestion: clinical picture
Symptoms of congestion in the kidneys:
- organs are larger and heavier than normal;
- have a blue-red color;
- fatty degeneration of the kidney substance occurs;
- yellow spots are visible;
- the renal capsule is tense;
- the venous pattern is strongly pronounced;
- the surface of the kidneys is uneven (due to a heart attack or wrinkling of connective tissue);
- the section shows fatty degeneration of the cortex; it may be yellowish-spotted; the medulla is darker and therefore easily distinguishable;
- enlarged glomeruli stand out from the surrounding tissue as red spots;
- with prolonged stagnation, atrophy of the renal substance occurs and its replacement with connective tissue.
Hydronephrosis can be acute or chronic. In the acute form, patients note the following disorders:
- severe lumbar pain;
- painful sensations of varying intensity in the abdominal area, intensifying after eating, radiating to the genitals;
- Nausea and vomiting appear periodically;
- temperature rises;
- blood appears in the urine.
The chronic form of kidney congestion is most often asymptomatic. In some cases, there may be a gradual increase in signs of the acute form.
Diagnostics
Hydronephrosis must be diagnosed at an early stage; if the disease is recognized in the later stages, therapy will not help - irreversible processes will occur. The history of the disease includes the manifestation of pain in the kidneys and lumbar region.
During a conversation with a doctor, it becomes clear whether there have been surgical interventions on the pelvic organs or neurological diseases, since neurogenic disorders are often the cause of kidney pathologies. Visualization methods play a decisive role in diagnosing the disease, making it possible to examine dangerous changes in the kidney and adrenal glands.
Ultrasound determines the size, shape, and weight of the kidney. Detects stones, cysts and other pathologies. The study helps to identify the causes of hydronephrosis.
The most informative diagnostic procedure, with the help of which three-dimensional and two-dimensional images of organs are created, which makes it possible to determine the stage of the disease and changes in tissues.
A diagnostic procedure is used to evaluate the condition of the urinary system. X-ray images show the presence of urine backflow. Detects the presence of vesicouriteral reflux. The procedure is performed by inserting a catheter.
An X-ray examination performed when a special substance is introduced into the body, which allows one to clearly examine the structure of the kidneys. The method reveals changes in the structure of the organ and makes it possible to assess the condition of the excretory system of the kidneys.
The method is used to measure the pressure inside the bladder. The measurement is carried out in three options:
- with an empty bubble,
- when filled,
- when the bladder empties.
In addition to instrumental diagnostic methods for hydronephrosis, blood and urine are required to be examined. Blood is taken for a general analysis, urine is examined according to Nechiporenko’s method, and bacteriological studies are also performed.
Causes of the disease
Doctors find it difficult to determine the causes of the disease with 100% probability, but there are many factors that provoke the accumulation of fluid in the paired organ:
- Obstructions and/or genetic disorders of the direct flow of urine formed in the ureter, bladder;
- Insufficient functionality of the ureteral valves, leading to reverse flow of urine.
Important! Congenital hydronephrosis has the following main diseases: dysthenesia, abnormal development of the urinary system, obstruction. The acquired disease basically contains urolithiasis, benign/malignant neoplasms, and other urological pathologies
Treatment
Conservative treatment exists for a limited number of patients and is used only when there are contraindications to surgery. Conservative therapy is an antibacterial treatment that is prescribed if there is an infectious-inflammatory process, often associated with hydronephrosis.
An effective treatment is an operation performed using one of two methods: organ-preserving or organ-carrying. An organ-preserving operation is chosen in the case where a kidney that has lost its function cannot be preserved (development of a purulent process); a nephrectomy is performed, a prerequisite for which is the normal functioning of the second organ.
Diagnosis and treatment
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys is a concomitant pathology, therefore, without treating the underlying disease, all efforts will be ineffective. To diagnose the disease, the specialist, in addition to collecting anamnesis, invites the patient to undergo a full comprehensive examination:
- general urine and blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, which helps determine the size and dynamics of the disease;
- x-ray of organs to view enlarged pelvis;
- radioisotope scanning to determine the degree of impairment of functionality.
CT, MRI, angiography may also be offered. All procedures are important for making the correct diagnosis and selecting treatment. Conservative methods often do not give the desired result and, as a rule, are used as a preparatory stage for surgery: to reduce pressure in the kidneys and reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process.
Surgery is the main path to healing. Today, surgeons prefer reconstructive techniques that preserve the organ. The choice of options is large and it all depends on the patient’s age, clinical picture and dynamics of the pathology.
Important! Nephrectomy is performed only in case of complete damage to the parenchyma, loss of functionality and a high threat to the patient’s life. Most often, complete removal of an organ occurs in older people.
At an early stage of the disease, therapeutic methods, maintaining a diet, regular examination and prevention of pathology are sufficient. If the doctor’s recommendations are followed, the disease is reversible and in 86% of cases patients do not experience negative manifestations of the disease.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of hydronephrosis
Folk remedies are used to treat hydronephrosis as an addition to drug therapy with mandatory medical supervision. Proven folk recipes below.
Recipe 1. Mix dry herb:
- Knotweed – 1 tbsp. spoon.
- Horsetail – 1 tbsp. spoon.
- Bean shells – 1 tbsp. spoon.
Add 5 tablespoons of birch leaves. 2 tbsp. Place spoons of the mixture into a thermos and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 7 hours. Drink in 2 doses 20 minutes before meals.
Recipe 2. Take in equal proportions:
2 tbsp. spoons of the mixture are poured with 1 glass of boiling water, leave for 7 hours. Drink in 2 doses 20 minutes before meals.
Diagnosis of dropsy
Initially, the doctor will listen to complaints, try to guess the causes of hydronephrosis, determine the duration of the illness and assess the patient’s general health. It is important if there were injuries and operations in the past, what kind, how was the rehabilitation, etc. To identify hydronephrosis, diagnosis includes the following measures:
- blood test - general and biochemical;
- urine test (general);
- Rehberg's test.
The listed tests are needed to confirm or refute the diagnosis of hydronephrosis, suggest the outcome of the disease, and exclude the development of renal failure. After the suspicions are confirmed, the doctor explains to the patient what renal hydronephrosis is, how to treat it, and prescribes an additional examination to clarify the data necessary for treatment. If necessary, the patient is prescribed and undergoes the following examinations:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. The study is carried out with a full and empty bladder to identify the remaining fluid;
- urography with contrast agent;
- CT and MRI;
- Nephroscintigraphy. The technique allows you to evaluate the functioning of the urinary organs using X-rays and a contrast agent. X-ray and other studies can not only determine the type and extent of the disease; when hydronephrosis is diagnosed, the causes can also be identified through diagnostics. The information obtained as a result of the diagnosis will help the doctor decide how to treat hydronephrosis.
Fluid in the kidneys in children
Hydronephrosis in children is more often a congenital pathology in which the kidney cavity is affected, impairing the patency of urine. There are 2 types of the disease: unilateral and bilateral. If one kidney is damaged, the child may not feel any manifestations of the disease, since the second kidney takes over all the functions of the affected one.
Bilateral pathology causes dangerous consequences in the child, including death from uremia. The congenital form of fluid in the kidneys is diagnosed more often, in most cases in a maternity hospital.
Treatment of hydronephrosis in a child is possible only surgically. With early diagnosis, children tolerate surgery well, and rehabilitation takes place in a short time.
Stagnation of urine in the kidneys and causes of the disease: symptoms and treatment methods
Hydronephrosis is stagnation of urine in the kidneys, enlargement of the renal system and its calyces. According to statistics, the disease affects women more often than men. The development of hydronephrosis in men most often ends with prostate cancer, urethral stricture, and in young people the disease is caused by urolithiasis.
Congestion in the kidneys is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the renal cups, as a result of which the functionality of the renal system is disrupted and a pyelocaliceal pathology is formed. Hydronephrosis can be infected or aseptic.
In this article we will tell you why urine stagnation occurs in the kidneys, we will analyze the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of the pathology.
How long does it take for 0.5 liters of drunk liquid to leave the stomach?
Answers (8)
It all depends on the state of the body, on the chemical composition of the liquid, its pH level. If you drink water after a run or sauna, then the kidneys will have almost nothing to excrete; all the water will be taken up by dehydrated cells. Along the longitudinal folds of the lesser curvature of the stomach, water quickly passes to the pylorus of the duodenum and quickly leaves the stomach, part of the water is absorbed through the walls of the stomach. Salt water will behave differently; it will not be absorbed by the mucous membrane of the stomach and excreted through the kidneys, but will go through the intestines. This property of water is used when cleansing the body. It only takes 15-20 minutes for the stomach to process water. During this time, water is split into molecules and passes through the walls of the stomach directly into the intercellular space. When we drink a glass of water, it immediately enters the intestines and is absorbed. However, after half an hour, exactly the same amount of water is released into the stomach through its glandular epithelium. It comes from below and enters the stomach, where it participates in the breakdown of food. Neutral or slightly alkaline liquids pass quickly and easily, while acidic ones are significantly retained in the stomach. Indeed, when food passes from the stomach to the duodenum, a change in the environment occurs; From an acidic environment, a liquid enters an alkaline environment. The acidic liquid must enter the duodenum in small portions in order to have time to be neutralized there and even, to a certain extent, alkalized. Neutral can enter the intestines much faster. Water comes out as sweat, as evaporation through the skin and through the lungs, and out through the bladder and rectum. On average, the human body excretes 3.5 liters of water per day.
Complain
881992881993881994881995881996881997881998881999
How long does it take for 0.5 liters of drunk liquid to leave the stomach? (Anatomy) - questions and answers for all occasions - reference book Anatomy moi-vopros.ru
anatomy.moi-vopros.ru
Why is hydronephrosis dangerous and how to prevent complications from developing?
Hydronephrosis develops at any age, including in infants. If you consult a doctor when the first clinical manifestations appear, the disease can be cured without damaging kidney function. However, if the disease is not diagnosed on time, then various consequences of hydronephrosis develop.
Among the complications that the disease leads to, the most common are:
- Attachment of a secondary infection
- The appearance of kidney stones
- Spontaneous kidney rupture
- Progressive decline in renal function with the development of renal failure.
Ultrasound examination is of greatest importance for diagnosing the disease. Moreover, with the help of ultrasound it is possible to diagnose congenital hydronephrosis of the fetus in the prenatal period.
Why do complications develop with hydronephrosis?
Hydronephrosis literally means fluid in the kidney. Due to the presence of an obstacle to the outflow of urine, it accumulates in the collecting apparatus. Every day the kidney increases in size, the substance of the organ atrophies and the parenchyma becomes thinner.
If the terminal phase of hydronephrotic lesions develops, then a moment comes when the walls of the organ are so thin that they cannot withstand the pressure exerted by the fluid.
Then spontaneous rupture of the kidney occurs, and all the contents pour out. Internal bleeding begins and without urgent treatment the patient will not survive. Of course, if the correct treatment for hydronephrosis is prescribed, spontaneous rupture of the kidney does not occur, because the doctor does everything possible to restore the outflow of urine and preserve the function of the organ. But complications such as inflammation and urolithiasis occur quite often, and can develop even before the first signs of hydronephrosis appear.
Bacterial complications occur when infection enters the kidney cavity ascendingly from other parts of the urinary system. Hydronephrosis creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of these bacteria, resulting in the development of pyelonephritis. Moreover, pyelonephritis against the background of hydronephrosis is much more severe. If surgical treatment for hydronephrosis is planned, then before this you should undergo a course of antibacterial therapy to get rid of pyelonephritis.
Preoperative treatment of pyelonephritis is necessary because surgical interventions are not performed against the background of acute diseases. Indeed, in this case, the consequences after the operation are not predictable.
Urinary stones are formed from uric acid salts and other substances that are normally excreted in the urine. Stagnation of fluid in the cups and pelvis leads to the fact that salts settle and over time develop into stones of various sizes. These stones can move along the urinary tract and, getting into the narrowing site, completely block the lumen of the ureter. Then urine will not pass away at all and acute hydronephrosis will develop, which without emergency surgery is complicated by kidney rupture.
Why is hydronephrosis more dangerous?
The greatest danger lies in the development of chronic renal failure.
After all, urolithiasis and infectious complications can be cured, but chronic renal failure remains for life and the only method to completely get rid of the disease is to transplant a kidney.
Chronic renal failure
Chronic renal failure develops when the kidney is unable to perform its filtering function. Toxic metabolic products are not excreted in the urine, but remain in the blood, depressing the entire body. This complication is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Reduced amount of urine, up to its complete absence
- Violation of general condition: headaches, weakness, increased fatigue
- Loss of appetite, weight loss
- Dry mouth
- Lethargy, progressive impairment of brain function
- Increased blood pressure
- The appearance of a yellow tint to the skin
- Skin itching.
The dynamics of chronic renal failure depend on the causes of hydronephrosis and the treatment provided. With the therapy started, the failure does not progress, but it is no longer possible to restore kidney function.
Treatment of hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney
Treatment of the pathology is carried out through a combination of conservative and surgical measures. Conservative treatment is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. The patient is prescribed various medications that act on one or another complication of hydronephrosis. After complications have been eliminated, prophylactic medications are prescribed to restore renal function.
Surgical treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. During the operation, the doctor restores the patency of the ureter. Thanks to this, the outflow of fluid is normalized, pain goes away, blood pressure is normalized, and the amount and color of urine is restored after surgery. After the intervention, the patient remains for observation. In the hospital, regular changes of dressings are carried out, control over the quantity and quality of urine excreted, assessment of drainage discharge (mucus, blood, pus), and intravenous infusion of medications.
Constant dressing changes are performed not only to assess the condition of the wound, but also to prevent the most common complication after surgery - bacterial infection.
The postoperative period lasts from 5 to 10 days, depending on the type of surgical approach used and the general condition of the patient. If the doctor sees that the patient no longer needs further observation and intravenous administration of drugs, and the postoperative wound is in normal condition, then he can safely be sent home. The patient is scheduled for a follow-up appointment to remove sutures, assess general condition and further treatment.
Kidney transplantation: general information
Kidney transplantation is a complex and expensive operation, the main problem of which is the correct selection of the donor. In patients with kidney failure, the non-functioning kidney is removed and a donor organ is transplanted in its place.
Consequences after kidney transplant surgery vary. Most patients feel great and live for years without signs of complications. However, some people develop organ rejection and have to have their transplanted kidney removed. It should be noted that with the correct selection of a donor and the correct operation, complications are observed only in extreme cases.
Life after a kidney transplant involves constant use of medications, but this is still better than suffering from a disease that depresses the entire body.
In this video you can watch a story about kidney transplantation:
dvepochki.ru
The use of diet and traditional therapy for renal hydronephrosis – About the Kidneys
21.11.2019
Hydronephrosis is an inflammatory process that results in changes in the size and structure of the kidney and impaired urine output. Untimely treatment of the disease can lead to organ death, intoxication of the body with damage to the nervous system and brain.
Complex therapy for kidney hydronephrosis includes dietary nutrition, which must be balanced, consist of high-calorie and easily digestible dishes, and contain the necessary amino acids and vitamins. In addition, treatment with folk remedies is also indicated.
Prohibited Products
During the day, healthy human kidneys process about 2000 liters of blood and send more than 1.5 liters of urine to the excretory organs.
Hydronephrosis slows down the process of ridding the body of unnecessary metabolic components, waste, and toxins; that is why the diet for this pathology should facilitate and stimulate the functioning of the urinary system and restore the kidneys as a whole.
To do this, it is necessary to exclude from the diet food containing substances that negatively affect their functionality.
These include:
- fatty meat, fish, seafood;
- rich broths from poultry, meat, fish, mushrooms;
- chocolate confectionery;
- beans, beans;
- fried, smoked dishes;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- canned, salted, pickled foods;
- flavoring additives in the form of seasonings, sauces, ketchups, hot spices.
Previously, with this diagnosis, urologists completely excluded salt from the diet of patients. Currently, its daily amount is recommended by the attending physician for each patient individually.
There is no consensus among doctors on the consumption of protein foods. Some believe that due to the additional stress on the kidneys, it is advisable to remove it.
However, excluding it from the diet, especially in elderly patients, makes it difficult to restore the structure of the kidney tissue. Therefore, most nephrologists agree that the amount of protein consumed should be limited at the rate of ½ g per 1 kg. weight.
List of allowed dishes
Attention! It is not recommended to select dietary foods on your own. Diet is part of a comprehensive treatment, which is selected by the doctor, taking into account:
- results of tests and examinations;
- degree of disease;
- condition and age;
- concomitant diseases;
- arterial pressure;
- predisposition to an allergic reaction;
- medications used.
Depending on the presence of these factors, the prescribed diet for hydronephrosis may have specific features. Its basis is the daily consumption of at least 0.6 kg. fruits and vegetables, as well as 2 liters of liquid.
Products allowed for consumption include:
- Porridge (millet, buckwheat, rice).
- Vegetables in all types (except fried). Dishes with pumpkin, cauliflower, spinach, asparagus, parsley, and nettle are especially well digested.
- Dishes made from lean meat and fish products.
- Cottage cheese, milk, kefir.
- Sugar and eggs in small quantities.
- Fruits, berries, compotes, fruit drinks, juices from them. Valuable: blueberries, grapes, watermelon, cherries, raspberries, cranberries, citrus fruits, apples, plums.
- Baked, boiled potatoes.
Diet for concomitant diseases
If hydronephrosis has developed against the background of other diseases, dietary dishes in this case are slightly different. So, if the patient is prescribed diuretics, a diet with a predominant consumption of foods containing a lot of potassium is recommended. This:
- potatoes, baked in the oven (can be with vegetables), boiled;
- all types of dried fruits;
- dairy and fermented milk products.
With the simultaneous development of pyelonephritis, it is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day and eat 0.6-0.7 kg. fresh fruits and vegetables.
If uremia is detected, the egg-potato diet, which consists of 30 g of boiled eggs and 0.3 kg, can be quite effective. boiled potatoes.
The amount of salt, as well as the duration of consumption of the dish, is determined by the attending physician. He also makes adjustments to the patient’s diet, from which meat and fish should be completely excluded.
Nutrition also differs in case of kidney stones, as well as disorders of phosphate-calcium metabolic processes. The composition of food should be aimed at increasing the acidity of urine. To do this, it is recommended to sharply limit, and sometimes completely refuse, fresh vegetables, fruits, and dairy products. The exceptions are: green peas, pumpkin, lingonberries, cranberries, sour apples.
Dishes shown:
- fish, meat;
- from grains, legumes;
- with eggs.
- In addition, baked goods made primarily from coarse flour, as well as liquid in increased volumes, are introduced into the diet.
- If an increased amount of urate and uric acid falls out (uraturia), coffee drinks, cheeses, and poultry meat are completely prohibited.
- Oxaluria (acid-salt sediment in the urine) does not allow consumption of:
- legumes;
- sorrel;
- sour berry and fruit products;
- all types of canned food;
- dairy, chocolate products.
A gentle regime for the kidneys is ensured by the seventh treatment table prescribed by a nutritionist, which includes complex dietary dishes.
Fasting days
Often, to mobilize additional capabilities of the body, along with dietary meals, the doctor prescribes fasting days, on which it is recommended to take foods rich in carbohydrates. This:
- A slightly sweetened fruit compote, which the patient drinks 5 times a day (every 3 hours).
- Fruits that must be eaten daily at the same frequency are at least 0.3 kg. Watermelon is good for these purposes.
- Vegetable salad from 300 g of any vegetables, which is recommended to be eaten 5 times during the day.
The composition of dietary meals and fasting days is prescribed individually for each patient. The duration depends on the results of the examinations performed and the severity of the disease. For greater effectiveness, the doctor often recommends therapy to get rid of the disease with folk remedies, consisting of taking decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants.
Effective folk recipes
Treatment with folk remedies involves eliminating the causes of the disease. For this, effective compositions from the following mixtures are recommended:
- 50 g of adonis grass, 150 g of birch leaves, 50 g of nettle (leaves), 50 g of oat grains, 50 g of bearberry and the same amount of horsetail are poured with boiling water (1 l), kept for 10-15 minutes. in a glass jar with a lid. After which the composition is poured into a thermos, in which it infuses overnight. In the morning, the infusion must be filtered and taken 0.5 hours before meals in doses of 100 g. The composition is designed for daily use. Treatment is recommended for 4 months. If the result is not achieved, the course can be extended by taking a two-week break.
- 100 grams: birch buds, sedum leaves, hop cones, as well as horsetail, adonis and bedstraw herbs, mix and prepare an infusion in the manner described above.
- 2 tsp. each of the following plants: chamomile flowers, meadowsweet, knotweed, string, raspberry and currant leaves, calamus root, pour 1/2 liter of boiling water. The decoction is infused for at least 8 hours, drunk three times before meals. The composition is designed for a day, the course of treatment is 3 months. After a 10-day break, the dose is repeated.
No less effective folk remedies used to get rid of hydronephrosis are pumpkin and bean leaves. The recipes for their preparation are as follows:
- Dried pumpkin stalks (1 tbsp) are crushed with a coffee grinder into powder, which is poured into 1/2 liter. water and leave for 20-30 minutes. to a water bath. After which the mixture is wrapped and left in this state for 2-3 hours. Next, the decoction is filtered and taken warm, ½ cup before meals 4 times a day.
- Dry bean shells ground into powder (4 tablespoons) are poured into 1 liter. cold water and boil for 2 hours over a water bath. The composition is infused for a day in a wrapped state, then filtered and taken before meals, 100 grams 7-8 times a day.
Treatment with folk remedies is effective with regular and long-term use. The first positive changes were recorded in many patients after 2-3 weeks of treatment.
Attention! To avoid allergies and other adverse reactions, before using traditional methods, you should consult your doctor and carefully read the recommendations on the packaging of herbal remedies.
Diets, fasting days, treatment with folk remedies are just part of the complex therapy prescribed by specialists for hydronephrosis of both or one kidney.
Source:
Diet for kidney hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis of the kidney is a disease consisting of significant stretching of the pelvis and calyx of the kidney, resulting from impaired outflow of urine.
Improper removal of fluid from the body provokes an increase in pressure in the renal collecting system, which significantly increases the pressure on the vessels, causing the nutrition of the kidney to be disrupted.
Subsequent tissue atrophy provokes disturbances in the functioning of the entire genitourinary system.
Negative consequences for the body can be reduced by adjusting your diet. Our health almost completely depends on the right food, and a diet for kidney hydronephrosis is a mandatory step in the fight against the disease.
Why diet is so important
The functioning of the entire body is highly dependent on the functioning of the kidneys, because it is thanks to them that the body uninterruptedly filters all incoming fluid.
Due to expansion, these processes are disrupted, the kidneys lose their functions, and then the body does not have time to get rid of all harmful substances. Poor kidney function can leave creatinine and urea behind, and too much of these in the body is incredibly harmful.
Nutrition during hydronephrosis cannot be neglected, otherwise the person will suffer irreparable consequences, from coma to death.
The nephrologist will prescribe an organized and properly selected diet that helps eliminate toxins, improve the general condition of the body and properly saturate it with organic resources. It’s worth figuring out which dishes are worth paying attention to in the fight against kidney disease.
What you should pay attention to
Nutritional features are discussed with the doctor, because the required diet for hydronephrosis depends entirely on the patient. The diet must take into account the patient’s condition, his age restrictions, concomitant diseases, based on which the doctor draws up his diet, as well as the schedule of meals with breaks.
However, a common feature of the diet for all patients is a ban on the consumption of salt and salty foods.
Recommended Products
Food for hydronephrosis is determined by a general template - recommended diet No. 7. Patients need to eat:
- Dairy products;
- Fresh berries, vegetables and fruits;
- Low-fat fish, steamed or boiled;
- Vegetarian soups;
- Buckwheat, rice, pearl barley, groceries;
- Lean meat;
- Yeast pancakes, pancakes and bread;
- Sweet;
- Salads;
- Sauces.
Prohibited Products
The diet for hydronephrosis involves the complete exclusion of certain foods. Cheese, mushrooms, chocolate, as well as foods with a high fat content (fatty meat, rich broths, etc.
) should be removed from the diet. Garlic, spinach, radishes, onions, black pepper and legumes should also be replaced with other dietary foods.
Moreover, with hydronephrosis, carbonated drinks, strong teas and coffee are prohibited.