Causes of pathology
The main reasons for the development of hydronephrosis during pregnancy include the following:
- Pathological abnormalities in the functioning of the bladder or urethra, since the formation of obstacles in these sections provokes the occurrence of hydronephrosis.
- Changes in the ureters - their twisting, compression, kinks and other deformations. Changes in the ureter provoke the development of hydronephrosis on the affected side, which often occurs during pregnancy.
- Inflammatory process in the pelvic or retroperitoneal tissue.
- Formation of stones in the renal pelvis or ureter. They interfere with the proper passage of urine, and hydronephrosis is considered an early sign of the development of urolithiasis.
- Narrowing of the lumen in the ureter through connective tissue.
- Disorders of the urinary tract - hypotension in the ureters or renal pelvis, etc. Such processes cause a slowdown in ureteral peristalsis, causing hydronephrosis in pregnant women.
Regardless of the cause of the development of the disease, the expansion of the renal pelvis during pregnancy is complemented by a gradual disruption of urine flow, stagnation of urine and, as a consequence, an increase in the size of the renal pelvis. At the same time, an increase in pressure occurs in the kidney, blood flow is disrupted, filtration of the kidney and atrophy of parenchymal tissue manifests itself.
Over time, the walls of the renal pelvis are greatly stretched under the influence of hydrostatic pressure, and they become thinner. This process contributes to disruption of the excretory function of this organ.
Pyeelectasia: definition and course of pathology
Pyeelectasia is an expansion of the pelvis of the urinary organ relative to normal indicators.
Pyeelectasis is an expansion of the pelvis of the urinary organ relative to normal indicators. Often the pathology is diagnosed during intrauterine development. In some cases, it can be detected in children 7-10 years old or during periods of intensive growth and puberty.
Interesting: pyeloectasia during intrauterine development is more common in boys (about 5 times more often than in girls). However, a higher percentage of the pathology degenerating into the normal structure of the kidneys is also characteristic of boys. That is, in girls, dilation of the kidney cavities can be congenital and observed at birth. In boys, the pathology may disappear as the fetus grows in the womb and the structure of the internal organs changes.
It is worth knowing that pyeelectasis is noted as an independent disease only if its cause is the abnormal structure of the child’s kidneys. In this case, the identified size of the renal pelvis is only a structural feature of the urinary organ of a particular child. In other cases, the pathology is only a consequence of some disease of the kidneys or urinary system. Therefore, if pathology is detected, it is necessary to observe the child and look for a urological reason for the change in the size of the pelvis.
Important: it happens that an ultrasound specialist diagnoses a change in the parameters of the renal cavity in the child in utero at 17-20 weeks of pregnancy. However, when the ultrasound is repeated at 30-36 weeks, the size of the pelvis returns to normal. In this case, the pathology does not require observation and medical intervention. If the baby is born with an enlarged pelvis, then a consultation with a urologist and constant monitoring of the child is necessary.
Symptoms of pathology
The chronic form of the pathology can occur without clinical manifestations. Enlargement of the renal pelvis during pregnancy can cause nausea with vomiting and nagging pain in the side. With the development of a violation of the outflow of urine in the lower sections, pain appears due to stretching of the walls in the bladder.
During pregnancy, women most often complain of a dull pain radiating to the groin area or thigh. Severe pain, similar to an attack of renal colic, occurs less frequently. Such pain may occur against a background of persistent mild pain radiating to the lumbar region.
If a pregnant woman has severe kidney pain, such pain may be mistakenly confused with the threat of abortion or premature birth. Often the pain is accompanied by urinary retention, and after the birth of the child the pain gradually subsides.
A little about the structure of the renal collecting system
The renal pelvis and calyx are the most complex structure in this organ. They connect the kidney and ureters. Each of the pelvis contains about two or three large-sized cups, and those, in turn, consist of small-sized cups.
Radiologically, there are three types of pelvis:
- embryonic, in which there are no large cups, and small ones pass into the large pelvis;
- fetal - in this case there are no pelvises, and large calyces are connected to the ureter;
- mature, having the same structure as an adult.
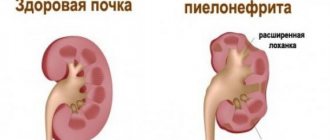
Normally, the parameters of the pelvis do not exceed 5 mm in the second trimester, and 7 mm in the third. If the size of the pelvis is expanded by more than 10 mm, then we are talking about hydronephrosis. It also represents an enlargement of the renal pelvis, but the reason for this will be a change in the outflow of urine of a pathological nature. There is also a decrease in the size of the pelvis (hypoplasia), up to the complete absence of the kidney.
There are two types of pyelectasis:
- unilateral;
- bilateral.
There is also the following classification of pyeloectasia:
- only the pelvis is dilated (pyelectasia);
- both the pelvis and the ureter are dilated (pyelourethroectasia);
- the pelvis and calyces are dilated (calicopyelectasia).
Diagnosis of pathology
If the renal pelvis is enlarged during pregnancy, then the diagnostic process consists of studying complaints and collecting medical history data. The suspected diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
In the first stages, a slight dilation of the renal pelvis is detected. Subsequently, the process involves the calyxes, and the entire pyelocaliceal system in the kidney enlarges. At the terminal stage of development of the pathology, the kidney is a formation similar to a large cyst.
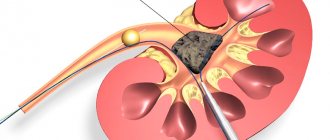
To diagnose the disease in a pregnant woman, catheterization of the ureters is organized. In this case, a catheter is inserted into the pelvis, emptying it, and then a contrast agent is injected.
Treatment of pathology
If hydronephrosis develops, management of pregnancy will depend on how long ago the pathology began, during or before pregnancy, whether additional infections are present, and whether normal kidney function is maintained.
If hydronephrosis first appeared during pregnancy, then it can be preserved except in cases of acute forms of the disease. The infection is treatable. Pain can be relieved with the knee-elbow position. Such signs have diagnostic value.
If hydronephrosis began to develop even before pregnancy, then the doctor may raise the question of its artificial termination. The decision should be made in a hospital setting and only after a full examination of the capabilities of the kidney, the presence of infections, and also taking into account the cause that provoked the development of hydronephrosis.
Treatment
In order to determine treatment tactics, pyelectasia is divided into three degrees: mild, moderate and severe. For mild cases, only monitoring is required. With an average degree, the monitoring period increases, the probability of a successful outcome is high. The urethra develops, and the disease goes away on its own. Observation is carried out via ultrasound.
Severe severity requires only surgical intervention. The operation is performed using very small instruments so as not to damage the tissue. The instrument itself is inserted through the baby's urethra. Before surgical treatment, in order to avoid complications, babies are given anti-inflammatory drugs approved for use by newborns. As a result of the operation, the outflow of urine is restored, and the reflux of urine from the ureter into the bladder disappears.
After surgical treatment, a special diet is prescribed with the exclusion of foods that irritate the ureteral mucosa.
Degrees of dilation of the renal pelvis
Treatment with medications is not used, because it is not effective.
The prognosis for such a child does not imply any guarantees; the pathology may make itself known many years later. That is why such young patients need to be monitored very carefully. They are registered at the dispensary all their lives. Such patients are especially carefully monitored during the so-called periods dangerous in terms of relapse. The first period occurs at the age of 6 years, when intensive growth of the skeleton and muscles occurs, but organs do not have time to grow. The second occurs during puberty.
Diagnosis and treatment of dilated pelvis
In cases where the renal pelvis is enlarged during pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct a specialized diagnostic examination. The process under consideration includes the collection of all data on a specific case, as well as the examination of complaints, on the basis of which a further conclusion is prepared. The alleged diagnosis, which in any case should be called by a medical specialist, is confirmed or refuted by a special ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
At the time of diagnosis of the disease in women, catheterization of the ureter is formed. A catheter is inserted into the pelvis, which empties it and then injects a contrast agent.
Treatment of the pathology directly depends on the history of the disease, the statute of limitations, and the presence of any other infectious diseases. In cases where hydronephrosis appears for the first time during pregnancy, preservation of the fetus is not excluded. The only nuance is considered to be the acute form of the disease. In situations where hydronephrosis has formed even before the actual pregnancy, the doctor may raise the question of artificial termination. Any decision is made only during inpatient treatment, where a full examination of the activity of the affected kidney is carried out.
Source: medic-sovet.ru
Symptoms of enlarged renal pelvis
Chronic pathologies during pregnancy may well occur without any clinical manifestations. As the renal pelvis enlarges, it can provoke nausea and vomiting, and unpleasant painful pulling sensations in the side. When disturbances occur in the outflow of urine, pain appears in the lower sections. This process is formed due to the stretching of the walls in the bubble.
Dull pain is one of the symptoms of the disease
During pregnancy, women most often complain of dull pain that radiates to the thigh and groin area. Symptoms such as attacks of renal colic appear much less frequently. The ailments in question may well appear as a result of regular mild pain, which, in turn, radiates to the lumbar area.
In cases where the kidneys suffer greatly during pregnancy, women may confuse this sensation with the threat of spontaneous miscarriage or premature labor. Quite often, pain can be accompanied by urinary retention. It is important to note that after childbirth, the pain gradually begins to subside.
Kidney function during pregnancy
In addition to the permanent tasks performed by the body, additional ones are added. The fact is that during pregnancy the kidneys must process and remove the baby’s life products that enter the woman’s blood through the placenta. The amount of urine excreted increases - approximately 1200-1600 ml. Under the influence of progesterone, the tone of the bladder decreases. Because of this, kidney problems occur during pregnancy - urine stagnates. Infection occurs faster, so the risk of getting sick increases. In some cases, the gestation period becomes a trigger for the “dormant” process.
Ultrasound is the main method for diagnosing pyelectasis in the fetus
Dilated renal pelvises in the fetus are easily visualized using ultrasound. Most often, such a disorder in the structure of the urinary organs is diagnosed from 17 to 22 weeks of antenatal development. Experts say that an increase in the size of the pelvis by 0.5-1 mm often resolves on its own, without medical intervention. But the pelvis, dilated by 2-3 or more millimeters, requires careful monitoring by a doctor.
If dilatation of the renal pelvis diagnosed in the fetus does not resolve by birth, the child is prescribed additional examination, including:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys (repeated);
- intravenous urography;
- cystography;
- laboratory tests of blood and urine (UAC, OAM, BAC, etc.).
In this case, it is important to identify not only how enlarged the renal pelvis is, but also why such a congenital anomaly developed. Depending on the cause of pyelectasis, the doctor draws up a plan for monitoring and, if necessary, treating the child.
In addition, all couples whose children were born with congenital developmental anomalies are recommended to consult a geneticist.
In utero detection of pyelectasis
The pathological phenomenon is diagnosed starting from the 16th week of pregnancy. If the pelvis is dilated by no more than one millimeter, there is a high probability that the deviation will go away on its own. When they increase by more than 10 millimeters, there is a risk of developing complications, which is extremely dangerous for the health of the unborn baby.
The disease is detected using ultrasound. If the pathology has not been eliminated during the period of intrauterine development, the baby is observed after birth by doctors. Additional diagnostics are carried out by intravenous urography and cystography.
When sick, a newborn’s body temperature rises and he eats poorly. Pain is observed in the lower back and abdomen. Signs of gastrointestinal distress appear: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting.
Causes of kidney hydronephrosis in pregnant women
The main reason that kidney hydronephrosis develops during pregnancy is an enlarged uterus. It compresses the ureters and thereby disrupts the outflow of urine, which accumulates in the renal pelvis, causing enlargement and deformation of the organs themselves. There are other factors and internal diseases of a pregnant woman that contribute to the development of the disease:
injuries; congenital anomalies of this organ; infections; urolithiasis disease; tumors of various origins (including metastases); spinal cord damage; pathologies of pregnancy, in which this organ cannot cope with increased loads; cystitis (read more about the effect of cystitis on pregnancy).
If it was not possible to avoid the disease, you need to try to identify it as soon as possible, especially since the first signs can be guessed already at home.
Total information
This pathology is an enlargement of the kidneys or their pelvis, and this condition predominantly affects one side, usually on the right.
The fact that the disease manifests itself precisely during the period of bearing a child is due to the fact that during this period the hormonal level changes, and the uterus increases significantly, which causes stagnation of urine. This condition often goes away on its own after childbirth.
But the situation is much more difficult if the renal pelvis is dilated during pregnancy due to infections and stone formation. In these situations, surgical intervention is the only way out of the situation.
The first option is a pathological process of the urinary system, and the second is only a temporary disruption of the functionality of the body, which occurs during pregnancy.
Prevention
To avoid having to undergo kidney treatment during pregnancy, you must adhere to some rules:
- Healthy food excluding fried, spicy and fatty foods.
- Daily fluid intake of at least two liters.
- You should empty your bladder when you feel like it.
- Maintain personal hygiene - after visiting the toilet, you need to wipe yourself from top to bottom, otherwise you can get an infection.
- Wearing tight underwear is prohibited.
- The composition of the linen should be made only from natural fabrics.
- It is better to give preference to a shower, since being in the bathroom is undesirable for several reasons.
- It is advisable to undergo an examination of the urinary system before pregnancy and, if necessary, carry out treatment.
- It is necessary to perform special gymnastics to ease the load on the spine. The most common exercise is a stand on all fours, which should be performed several times a day for about 15 minutes.
If you follow such recommendations, you can reduce the risk of pathologies such as kidney prolapse during pregnancy and others. It will be possible to carry the baby to term without complications, and the birth will be favorable.
If you cannot avoid unpleasant manifestations, you should definitely consult a doctor. Only he should decide how to treat the kidneys during pregnancy. Any unpleasant symptom should not be ignored. If the kidney is pulled during pregnancy, this is a signal for alarm. It is better to play it safe and immediately report your complaints to your doctor. After all, this will help preserve the fetus and not disrupt the functioning of the body.
Author: Irina Levchenko, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
Pyeelectasia during pregnancy
Congenital pathology of the fetal kidneys can be provoked by the discovery of pyeelectasis in the mother during gestation.
The causes of the disease may be:
- pressure of the uterus on the ureter;
- low tone of the smooth muscles of the urinary reservoir;
- hormonal changes;
- exacerbation of chronic kidney disease.
It is best to plan a pregnancy after all treatment methods for kidney diseases have been completed.
After delivery, if there are physiological causes of the disease, the mother’s kidney function is restored.