Berger's disease (IgA nephropathy) is one of the types of chronic glomerulonephritis, namely a mesangioproliferative form, which is characterized by focal or mixed proliferation of renal connective tissue cells between the capillaries of the vascular renal glomeruli.
According to the international classification of diseases ICD-10, this nephropathy belongs to No. 02 - recurrent and persistent hematuria.
This pathology has a number of different names; it is commonly called IgA nephritis, Berger’s disease, idiopathic recurrent gross hematuria, sinpharyngitis hematuria, focal proliferative or focal hematuric glomerulonephritis. Such names were not given by chance, since the main manifestations of the disease are associated with a significant concentration of deposits of IgA-saturated immune complexes located in the tissues of the mesangium (capillary part of the renal glomerulus), as well as signs of hematuria.
This type of nephropathy is very common, accounting for about a quarter of nephritis worldwide, and some countries even classify it as a type of Bright's disease. Thus, in Europe, North America and Australia, IgA nephropathy accounts for 10-15%, in Asia - about 30-35%, in Japan it is almost half of all glomerulonephritis.
People of working age are more susceptible to the disease, more often men than women.
There are 2 main forms of the disease:
- primary IgA nephropathy - the so-called Berger's disease;
- IgA nephropathy of a secondary nature is a consequence of complications of other ailments.
Causes
The disease develops in the presence of a genetic predisposition and the action of provoking factors, among which are:
- hypothermia;
- reduced function of the immune system;
- viral diseases affecting the respiratory system;
- frequently recurring bacterial infections;
- lymphomas, lymphogranulomatosis;
- hepatitis B virus.
Etiology in children
The risk of Berger's disease increases in those children whose close relatives have this pathology. The pathological process can be started by:
- frequent sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis media;
- sherpetic infection;
- vaccination;
- food allergens (gluten, lactoalbumin).
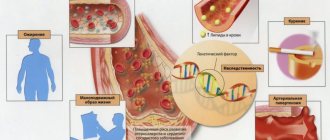
The disease is based on a pathological reaction of the immune system to an allergen (infectious, food), while a high content of immunoglobulin A is found in the blood.
Increased production of immunoglobulin A is associated with its overproduction in the bone marrow and its insufficient excretion by liver cells. The excess is excreted by the kidneys, but the IgA molecule is large, which leads to its accumulation in the glomerular apparatus.
The result is a diffuse (spread) inflammatory process, accompanied by damage to small vessels (blood appears in the urine) and a violation of the cleansing ability of the kidneys.
Inflammatory reactions and infections lead to increased production of immunoglobulin. Therefore, exacerbations of Berger's disease occur after tonsillitis, laryngitis, viral infection, etc.
The higher the concentration of immunocomplexes in the blood, the brighter the clinical manifestations of kidney pathology, up to acute renal failure, which threatens the patient’s life.
Immunological inflammation of the kidney: treatment
Despite the benign course of the disease, therapy is necessary during relapses. It is needed not only to alleviate the symptoms of the pathology, but also to prevent complications and preserve kidney function. Treatment begins with the sanitation of foci of infection. Most often, antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Cefazolin) and antiviral drugs (Viferon, Genferon) are prescribed for this purpose. In addition, to relieve inflammation in the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys, NSAIDs are needed. The most commonly used drugs are Canephron and Ibuprofen. For kidney diseases, medications based on herbs are effective. Special decoctions and infusions are also prescribed (knotweed, birch cones, bearberry).
If the disease is difficult to treat, frequent relapses or complications are observed, then hormonal therapy is performed. Usually the drug Prednisolone is prescribed, as well as cytostatic agents. In some cases, antiplatelet therapy and drugs to improve blood flow (medicine "Curantil") are necessary.
Clinical picture
Symptoms depend on the clinical form of Berger's disease. Highlight:
- Sinpharyngitis form . Characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. An exacerbation is manifested by pain in the lumbar region and a change in the color of urine from pink to rusty (hematuria). In severe cases, transient acute renal failure occurs. Symptoms are most pronounced one to two days after the infectious process. During the period of remission, there are no clinical and laboratory symptoms of the disease.
- Latent species . The patient does not make any complaints. The diagnosis is made on the basis of laboratory diagnostics, in which small amounts of red blood cells and protein are found in the urine. The cleansing ability of the kidneys is gradually impaired, which leads to chronic renal failure.
- Nephrotic stage . There is an edematous syndrome, a high content of protein and red blood cells in the urine (rust-colored urine). In rare cases, the disease begins with the nephrotic form. Usually it is the outcome of sinpharyngitis and latent.
One or two days after the infection, patients notice the appearance of blood in the urine and pain in the lower back. Also, Berger's disease can manifest itself as edematous syndrome (this is due to the loss of protein along with urine), a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, and high blood pressure.
Symptoms in a child
Children become dehydrated more quickly than adults, leading to kidney failure. Changes in the color of urine, restlessness of the child, and the appearance of swelling on the face are reasons for urgently seeking medical help.
Identification of a pathological condition
Berger's disease is diagnosed by a doctor taking a medical history, identifying hematuria, and changes in blood pressure. Next, the doctor examines the patient using palpation, percussion and others.
Next, the patient is sent for laboratory tests. A urine test shows the presence of blood and protein in the fluid. An increase in the level of class A immunoglobulins is observed in the blood. A biopsy of renal tissue reveals granular inclusions and complement in the expanded and overgrown mesangial layer of the renal glomeruli.
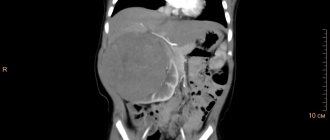
Additionally, radiation diagnostic techniques are used to determine the condition of the kidneys. These are ultrasound, magnetic resonance and radiographic tomography. Hardware diagnostics also help in differentiating this form of the disease from other pathologies of a urological nature. These include urolithiasis, oncological pathologies of organs and tuberculosis of the urinary tract.
Who to contact and how to diagnose
When the first signs of the disease appear, you should consult a therapist (adults) or a pediatrician (children). To prevent the development of acute renal failure, hospitalization of the patient is necessary.
The doctor clarifies the patient’s complaints, whether there were such manifestations in relatives, prescribes laboratory and instrumental studies and, if necessary, a kidney biopsy.
Laboratory research
In a general urine test after an infection, red blood cells are detected; with frequent exacerbations, renal failure develops, which is manifested by proteinuria (the presence of protein in the urine) and a decrease in urine density.
When performing a urine test according to Zimnitsky, daily diuresis (all urine excreted per day) and urine density are examined to determine kidney function.
The Nechiporenko analysis is intended for diagnosing the cellular composition of urine. During exacerbations, red blood cells are detected (normally absent).
Blood chemistry. Urea and creatinine, electrolytes are examined. It is necessary to monitor these indicators for timely diagnosis of violations of the cleansing function of the organ.
Ultrasound examination allows you to determine the size of the kidneys, the structural features of the cortex and medulla.
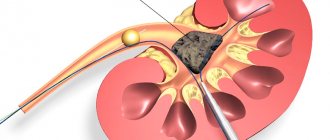
It is a reliable method. A small section of organ tissue is collected. In Berger's disease, deposition of immune complexes in the kidney tissues is detected.
What is Berger's disease
Damage to the glomerular apparatus is a consequence of the layering of IgA immune complexes on the intercapillary parenchyma of the kidney; its main, and often only, manifestation is periodically appearing hematuria.
It is characterized by diffuse or limited proliferation of intervascular parenchymal tissue of the kidney, adhesion of IgA immune complexes to it, and the capillary endothelium.
The outcome of the disease is the development of chronic renal failure.
The most common type of IgA nephritis affects mostly young men (women get sick three to four times less often).
Therapy methods
Treatment of Berger's disease depends on the stage of the disease (exacerbation, remission), kidney function, and concomitant pathology. They use traditional and folk methods.
During the acute stage, it is necessary to adhere to a diet that consists of excluding spicy, smoked, pickled and fried foods.
The daily protein content should not exceed one gram, and salt intake should be limited as much as possible. If there are signs of renal failure, the patient should keep track of the amount of fluid drunk and excreted.
When blood pressure rises, antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors) are prescribed. These include:
- Lisinopril;
- Perindopril, etc.
The above medications not only lower blood pressure, but also have nephroprotective properties (protect the kidneys).
To relieve edema syndrome, diuretics are prescribed (furosemide 40 mg).
To improve microcirculation in the kidneys, pentoxifylline is prescribed. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are contraindicated for this disease, as their side effects are nephrotoxic.
The severe nature of the attack is an indication for glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone 60 mg/day every other day). The drugs have a large number of side effects (increased blood pressure, blood sugar levels, atrophy of the adrenal cortex).
Therefore, treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. Steroid withdrawal is done gradually. In some cases, it is necessary to prescribe cytostatics; their side effects include suppression of hematopoiesis, decreased immunity, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
If acute renal failure develops, the patient undergoes hemodialysis (the essence of the procedure is to cleanse the blood of metabolic end products that have a toxic effect on the body).
Treatment of children
During an exacerbation, a child needs to follow a diet. The amount of fluid consumed and excreted per day is recorded. If necessary, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed (prednisolone, dexamethasone, methylprednisolone). Cytostatics cause inhibition of growth and development, therefore they are not used to treat a child.
Acute renal failure is an indication for hemodialysis.
ethnoscience
Used in conjunction with traditional ones. You can use medicinal herbs only after consulting your doctor.
A decoction of bearberry (bear ears) has a good diuretic, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare it you need:
- pour one tablespoon of herb into one glass of boiling water;
- keep the mixture in a water bath for 30 minutes;
- cool and strain the broth.
Directions for use: Divide the decoction into three equal parts and drink in the morning, lunch and evening.
To prepare a medicinal infusion, you need to take valerian root, 20 g of lemon balm leaves, 20 g each of cinquefoil and rue. For one tablespoon of the mixture you need to take one glass of boiling water. Leave until cool. Dosage regimen: half a glass of warm infusion twice a day.
Elimination of the disease
Berger's disease begins to be treated after establishing a complete symptomatic picture and examining the patient. First, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the development of the pathology. Afterwards, fight the signs of the disease, monitoring the patient’s condition in order to provide timely assistance in the event of a complication or relapse.
Treatment of nephropathy begins with eliminating foci of infection. The doctor prescribes antibacterial therapy (Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Cefazolin and the like) and antiviral agents (Genferon, Viferon, Anaferon).
To remove inflammation in the glomeruli of the kidneys, doctors use diuretic herbal medicines, non-steroidal antiviral drugs, medicinal herbal decoctions and ACE inhibitors. In case of relapses or complications, therapy with hormones, immunosuppressive drugs and cytostatics is indicated.
If drug therapy does not restore kidney function and does not produce the expected results, a relapsing form of the disease develops. If Berger's disease progresses to renal failure, hemodialysis and donor organ transplantation are performed.
For the success of the treatment, the patient must adhere to a special diet. To do this, you need to exclude meat, milk, gluten from your daily diet, that is, all foods that provoke allergic reactions. Salt is limited to 5 grams per day. If the patient suffers from extra pounds, it is prohibited to consume animal fats and carbohydrates, which tend to be quickly absorbed.
If there are no contraindications, the amount of proteins is significantly reduced.
Prevention and prognosis
With timely and adequately prescribed therapy, the prognosis is favorable. In Berger's disease, prevention of exacerbations plays an important fundamental role.
The main preventive measures include:
- avoiding hypothermia;
- increasing immunity (healthy diet, active lifestyle);
- rehabilitation of chronic foci of infection (caries, tonsillitis, sinusitis, etc.);
- consultation with a doctor before vaccination;
- if you have allergies, completely avoid contact with allergens;
- undergoing preventive examinations.
Berger's disease is a genetically determined disease that occurs when exposed to provoking factors. Pathology most often manifests itself in childhood and young age.
A timely visit to a specialist will help avoid complications and also help maintain a high quality of life.
Forecast
Prognosis for nephropathy
Nephropathy usually progresses slowly. Arterial hypertension, as well as renal failure, develops in 15–20% of patients over 10 years. The disease progresses to end-stage renal failure in 25% of patients suffering from nephropathy for more than 20 years. If IgA nephropathy was diagnosed in childhood, the prognosis is favorable.
However, persistent hematuria invariably leads to renal failure, proteinuria and arterial hypertension. If the disease began at an older age, then risk factors for the development of renal failure are diseases such as tubulointerstitial pathology, transformation of GN into rapidly progressive, severe glomerular sclerosis, an increase in creatinine concentration, the absence of recurrent gross hematuria, persistently severe proteinuria and arterial hypertension.
Preventive recommendations
A few simple rules will help reduce the risk of Berger's disease:
- regularly monitor blood pressure;
- control cholesterol levels;
- reduce the amount of fat in the diet, eat fresh vegetables and cereals;
- avoid stressful conditions;
- give up alcoholic beverages;
- monitor your weight, if you have extra pounds, get rid of them;
- the nephrologist should know about the presence of a similar disease in close relatives;
- Visit a urologist twice a year for preventive purposes.
Berger's disease or IgA nephropathy is a renal pathology that requires complex therapy. If unpleasant symptoms appear, it is important to visit a urologist or nephrologist, get a consultation, be examined, and undergo the necessary treatment.