Tuberculosis is a severe systemic disease that can affect not only the lungs, but also other organs (kidneys, bones, genitals, etc.). Kidney tuberculosis is a complex pathology in diagnostic and therapeutic terms.
It must be diagnosed early for therapy to be effective.
Symptoms and signs of kidney tuberculosis begin with general manifestations: malaise, fever, weakness, and only after that specific manifestations appear.
Kidney tuberculosis
This infectious disease is quite complex and severe. Treatment and rehabilitation after illness require enormous work.
Pulmonary tuberculosis is a primary disease, which in 30-40% of cases is complicated by damage to other body systems. Kidney tissue under the influence of tuberculosis infection in severe cases undergoes purulent melting - pyonephrosis.
As the infectious disease progresses, the formation of cavities and cavities is observed in the kidney tissues. The organ practically “melts” from the inside.
Its work is disrupted and sometimes may stop altogether. Often the process moves to nearby systems. In men, the prostate can be affected, in women - the ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus.
The most serious consequence of this disease is the cessation of organ functioning. This happens in advanced cases, with extensive tissue damage.
Causes of the disease in women, men and children
In adults and children, the cause of the development of the disease is the same: it is damage to the kidney tissue by the causative agent of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Less commonly, the disease first affects other organs of the genitourinary system, and then patients first develop pyelonephritis or urolithiasis, and only then renal tuberculosis appears.
provoke the development of pathology :
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- hypothermia of the body;
- colds of the upper respiratory tract;
- violation of diet, malnutrition;
- exposure to toxic chemicals for a long time (for example, when working in hazardous industries).
Also, this pathology can occur against the background of most urological diseases and injuries to the genitourinary system.
Causes
In the kidneys, tuberculosis appears as a result of long-term infection in the lungs or bones. This usually takes more than 3 years. The process is caused by the entry of Mycobacterium tuberculosis into the body.
They multiply in the lungs or other organs, and then travel through the bloodstream to the kidneys.
The infection spreads throughout the body predominantly by hematogenous route.
It takes time for the first specific symptoms to develop, as well as accompanying factors: a weakened immune system, pathologies of the urinary system, lack of treatment for the underlying disease (pulmonary tuberculosis).
In most cases, the human body can resist the spread of infection, but when the immune system is weakened, dissemination of bacteria is possible.
Prevention
Physiotherapy
The goal of preventive actions to prevent renal tuberculosis is regular examination of people at risk. These include citizens living in difficult conditions and already having symptoms of tuberculosis of non-renal origin. During the examination, doctors identify signs of the disease in the asymptomatic period based on a urine test.
Wellness treatments in sanatoriums located in favorable climatic conditions remain a traditional means of prevention. Physiotherapy and high-calorie nutrition help cope with the initial stage of the disease.
The course of the disease is influenced by the body’s ability to resist infection - immunity, as well as timely detection of the disease, therefore maintaining the human body with vitamin complexes is of particular importance.
For prevention purposes, doctors recommend the use of herbal infusions and decoctions that will support the immune system of both adults and children. The following medicinal plants will effectively support the immune system:
- birch leaf;
- Wheatgrass root;
- Silver cinquefoil;
- Potentilla gossamer;
- Yarrow;
- Veronica meadow;
- Burnet;
- Sage.
Burnet
It is recommended to use herbal remedies after consulting your doctor, although there are no clear contraindications for use.
Forms and stages of the disease
To diagnose renal tuberculosis, a complete examination is necessary. The process usually does not manifest itself with specific symptoms, so a comprehensive examination and study of test results is necessary.
This disease is usually classified according to x-ray data. This division is used in clinical urology. The classification is based on how deep the infection has spread into the kidney tissue.
Classification:
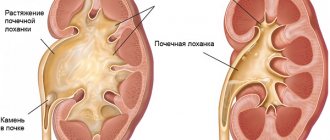
- Damage to the cortical and medullary layers of the organ.
- Damage to the papillae of the kidney tissue is tuberculous papillitis.
- An infection that occurs with the formation of cavities (cavities). There is a fusion of foci of destruction followed by encapsulation.
- The form in which obliteration of the renal calyces occurs and the formation of cavities with pus in them is called fibrous-cavernous.
- Caseous tuberculosis – deposits of calcium salts in pathological foci. In the process of damage, calcification of the kidney occurs.
Specific changes in the form of cavities with pus are formed during long-term processes. At this stage, not only by X-ray data, but also by clinical manifestations, a diagnosis can be assumed. The incubation period (the time from the introduction of the bacteria to the appearance of symptoms) can reach 2-3 years.
In its development, the disease goes through a number of stages:
- The infiltrative stage is the first stage of the disease. At the same time, the tissues are not yet subject to obvious changes that can be detected on an x-ray.
- Initial destruction is the stage of formation of cavities and cavities.
- Limited destruction - the number of cavities and their sizes increase.
- Total destruction. At this stage, the disease causes extensive damage to the kidney tissue, sometimes the kidney becomes one large cavity, the walls of which are the remains of the organ tissue.
This classification shows how the process spreads in tissues and, accordingly, the severity of the lesion increases. There is another division of kidney tuberculosis: into chronic form and miliary (acute).
In the first case, the disease is secondary.
In this case, the primary focus of tuberculosis already exists in the body, only in another organ. The acute form occurs when the infection first enters the kidney. It is characterized by the appearance of tuberculous tubercles (foci) in both organs.
The form or stage can be determined only after a complete examination of the patient. The results of all tests and instrumental studies, as well as anamnesis, are taken into account.
Tuberculosis of the kidneys and urinary tract: contagious or not, diagnosis, symptoms and treatment, prognosis
Tuberculosis of the kidneys, urinary tract and bladder is a secondary disease that occurs in the organs of the urinary system, that is, it has an extrapulmonary localization. Such a defeat is provoked by Koch's wand. The most common cause of nephrotuberculosis is kidney damage. Much less often, mycobacteria affect the ureters and bladder in women and men. Symptoms and treatment of this pathology can be different, it all depends on the degree of damage to the organ and the individual characteristics of the body.
Description
At the beginning of the development of pathology, damage occurs in the renal cortical layer. The infection then spreads to the papillae. This disease can provoke complete shutdown of the organ with the development of pyonephrosis. When mycobacteria infect the mouth of the ureter, ulcers appear. As a result, the channel narrows.
The incubation period of this disease is long – 2-3 years. Statistics show that nephrotuberculosis occurs as a secondary manifestation in 30% of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis.
Is kidney tuberculosis contagious? The answer to this question is clear - it is contagious. This pathology is infectious and transmitted by airborne droplets. And besides this, there are other ways of transmission.
Infection
How is tuberculosis transmitted? Most often, nephrotuberculosis is transmitted hematogenously, that is, through the blood. And:
- By airborne droplets. In this case, you can become infected from another infected person. Mycobacteria are found in large quantities in the sputum of a person suffering from an open form of the disease. And only then they migrate throughout the body along with blood or lymph, entering the urinary system.
- Alimentary route of infection. In this case, Koch's bacillus enters the body through the gastrointestinal tract. That is, if a person eats contaminated meat or milk from sick cattle. In this case, mycobacteria enter the blood, and then enter the urinary system.
- Contact path. In this case, infection occurs through mucous membranes and lesions on the skin.
In view of this, we can conclude that renal tuberculosis is contagious, and there are many ways to become infected with mycobacteria.
Symptoms
In the initial stages, the disease is asymptomatic. Further, the symptoms of kidney tuberculosis manifest themselves in the form of weakness, general malaise, and increased body temperature. Sometimes patients feel mild pain in the lumbar region. Such signs are characteristic of damage to the cortical (surface) layer of the kidneys.
As the pathological process spreads inside the kidneys, the symptoms are more pronounced, since this condition manifests itself in the form of intoxication of the body, and renal colic additionally occurs.
For kidney tuberculosis, it is characteristic that the renal papillae become inflamed, and as a result, ulcers appear. Then caverns appear. The symptoms of kidney tuberculosis at this stage are pronounced. Namely, the person feels severe pain, and the general condition worsens significantly. Pyelonephrosis develops quickly or secondary shrinkage of the kidneys occurs.
Attention! When tuberculosis of the bladder occurs, that is, the infectious process has descended on the ureters and bladder, the symptoms are different, since in addition to the above signs of intoxication, dysuria (urinary disorder) is added.
Symptoms of kidney tuberculosis with damage to the bladder:
- The process of urination is painful;
- Frequent urge to urinate;
- There may be false urges;
- Incontinence.
In many patients, tuberculosis of the genitourinary system exhibits symptoms similar to cystitis, polycystic disease, urolithiasis, chronic pyelonephritis, etc. And in men, the prostate is also affected, with the manifestation of corresponding symptoms, such as urinary retention, difficulty urinating, and sensations of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Causes
The main factor that causes tuberculosis of the kidneys and urinary tract is a decrease in the body’s immune activity. Moreover, if the protective function is at a high level, then mycobacteria form small foci in the kidneys, which heal under the influence of the immune system. Otherwise, the lesions begin to enlarge with further decay.
Another important factor is the sanitary and epidemiological human environment. The likelihood of damage to the urinary system increases if there is a history of chronic inflammatory processes (cystitis, urolithiasis, etc.).
In addition, there are other factors that can affect the development of tuberculosis:
- Frequent occurrence of colds in humans;
- Wrong lifestyle;
- Unfavorable ecological state of the environment;
- Disturbances in the production of leukocytes in the red bone marrow.
Classification
There are 4 stages of development of tuberculosis of the urinary system:
- Stage 1 is tuberculous damage to the renal parenchyma. It is not yet destructive. If treatment is applied at this stage, kidney disease can be cured completely. Kidney tuberculosis in children at the first stage does not show any signs in a urine test, and in adults moderate leukocyturia is diagnosed (leukocytes in a general urine test).
- Stage 2 is a condition called tuberculous papillitis (inflammation of the renal papillae). It is characterized as a limited-destructive form. At this stage, the infection can already descend into the bladder. During diagnosis, multiple or single lesions can be determined.
- Stage 3 is a destructive lesion and is called cavernous tuberculosis of the kidney. Surgical treatment is necessary, which, however, does not guarantee a complete cure. Quite often, after treatment, the patient develops post-tuberculosis pyelonephritis. In this case, bladder tuberculosis is most often diagnosed.
- Stage 4 is a common destructive type of tuberculosis. It is also called polycavernous nephrotuberculosis. At the same time, cavities form in the organ, which significantly impair the functioning of the kidneys. Quite often, as a consequence of this stage, pyonephrosis develops with the manifestation of a fistula. This disease can be completely cured by removing the kidney.
Additionally, there are 2 more forms of renal tuberculosis: miliary and caseous. The first is an acute form, in which 2 kidneys are affected, but partially. At the same time, there is a rash on the cortex. The miliary form does not lead to tissue necrosis.
The caseous form is a chronic course of the pathology. In this case, ulcers form on the organ, which are accompanied by decay and necrosis of the kidney tissue.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of kidney tuberculosis in the early stages is extremely rare. This is explained by the fact that the incubation period is 2-3 years. The most common instrumental diagnostic method that can be used to determine the presence of mycobacteria in the urinary system is radiography. But often x-rays are performed several times, since it is necessary to identify tuberculous lesions from stones.
Laboratory tests consist of urine analysis. It may contain mycobacteria.
Anamnesis and palpation examination are additionally important. The doctor analyzes all the symptoms that the patient has. And he conducts a physical examination, namely, palpating the kidneys. The diseased organ increases in size and can be easily felt. Sometimes palpation of the kidneys in women is carried out through the vagina.
Attention! To confirm the diagnosis, a person is prescribed magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound.
Treatment
In the case of kidney damage, it is very important to take into account all the individual characteristics of the body. Since anti-tuberculosis drugs often have a nephrotoxic effect, the doctor carefully selects the dosage.
In case of kidney infection, a complex of first-line drugs is prescribed. But in the presence of certain factors, they can be replaced by a reserve group of anti-tuberculosis drugs. These include cycloserine, ethionamidone, kanamycin, etc.
In addition, angioprotectors (drugs to protect the vascular wall) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also required. These funds are needed to prevent the formation of scars and atrophic processes in the kidneys.
Tuberculosis of the genitourinary system is treated for 1 year. This requires constant monitoring of the condition of the organ. Sometimes a person has a ureteral catheter or stent installed, as the outflow of urine may be reduced or completely stopped.
In case of advanced processes, surgical treatment is required. Depending on the degree of damage to the organ, a segment may be removed or a complete resection may be performed. After the operation, anti-tuberculosis therapy is prescribed to ensure that the infectious process does not affect the second kidney. It is good to use biologically active substances that help kidney function, such as Renon Duo.
Forecast
Tuberculosis of the genitourinary system has a positive prognosis if treatment begins in the early stages of its development. Treatment is carried out in a hospital. With extensive damage, the condition is assessed as more serious, and complications may occur. When tuberculosis of the bladder has already developed, doctors do not give favorable prognoses, since in this case there is a high probability of severe consequences that significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life.
It is known that all people encounter tubercle bacilli throughout their lives. Why do some people get sick and others not? It all depends on the immune system. Know that excess weight is the main factor contributing to decreased immunity. Lose weight with Lipo Star System and get a healthy immune system.
stoptubik.ru
Symptoms of kidney tuberculosis
This disease has no specific symptoms. At the initial stages, the patient develops weakness and malaise, and an elevated body temperature (37-37.5 degrees) persists for a long time.
Performance decreases, fatigue increases, and patients may notice weight loss. However, they often explain their condition by other reasons (stress, colds, lack of vitamins).
Kidney tuberculosis, the symptoms of which may not bother the patient for a long time, is an insidious disease. The most rapid progression of the disease and the appearance of symptoms that force one to seek help occurs in the later stages.
At this time, total damage to all kidney structures occurs, which leads to irreversible consequences.
Symptoms of kidney tuberculosis at the stage of the appearance of cavities can be different:
- Pain in the back and lower back.
- Difficulty urinating (dysuria, pain).
- The appearance of blood and pus in the urine.
- Increased body temperature.
- Arterial hypertension.
The disease is often diagnosed at a late stage, during the period when symptoms of renal failure and arterial hypertension appear.
In this case, changes appear in laboratory tests and pronounced signs of kidney damage on an x-ray.
Symptoms
The symptoms of kidney tuberculosis depend entirely on the degree of development of the disease. In slightly less than half of the cases, the initial stages of the pathological process do not have any symptoms and only in rare cases, pain in the lumbar region may be observed.
With prolonged progression of the disease, pain is observed in almost all patients
Clinical signs of renal tuberculosis, in addition to the stage, are closely related to the anatomical changes occurring in the patient. When lesions are localized in the area of the kidney parenchyma, the following symptoms are observed:
- temperature increase;
- weakness;
- slight malaise.
Symptoms of tuberculosis of the kidneys and urinary tract
However, urine analysis is absolutely not informative. Further development of the disease, accompanied by damage to the renal medulla, causes the following changes:
- an increase in the concentration of leukocytes in the urine, up to 10 per field of view;
- the appearance of a large amount of blood in the urine (gross hematuria);
- bacteriuria;
- increased blood pressure;
- increased pain symptoms, up to renal colic.
With the formation of multifocal lesions, severe intoxication of the body, deformation of the pyelocaliceal system and the formation of cavities can be observed.
All these changes trigger the process of tissue scarring, ultimately leading to the “isolation” of the affected calyx and its complete exclusion from the functioning parts of the organ. This course of the disease causes spontaneous disappearance of one of the signs of the disease - leukocyturia and normalization of urine analysis.
A good urine test for kidney tuberculosis is not evidence of recovery.
Multiple scar changes that form in tissues can lead to the development of shrunken kidney syndrome
Possible complications
Renal tuberculosis is dangerous because it causes irreversible changes in the kidney tissue. With the formation of cavities and cavities, the structures of the kidney are destroyed, which leads to a complete loss of organ function.
As the process spreads, pyonephrosis and death of kidney tissue occurs.
In rare cases, a complication may be amyloidosis - the deposition of a specific protein in the kidney tissue. As a result, organ function is impaired.
Chronic renal failure is one of the most serious complications of this disease. In this case, the cells of the organ (nephrons) die and its work stops.
The consequence of this is a violation of nitrogen, water and electrolyte balance in the body. All this leads to irreversible consequences, in particular to the death of the patient.
Treatment and prognosis
During treatment, patients are prescribed anti-tuberculosis drugs :
- Streptomycin;
- Ethambutol;
- Prothionamide;
- Rifampicin;
- Tubazid.
A better result can be achieved if you combine these drugs with fluoroquinolone antibiotics (Lomefloxacin, Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin).
Such drugs should be taken for a year or longer to completely destroy pathogenic microflora.
In cases where the disease is complicated by problems with the ureter, the patient may undergo nephrostomy and installation of a urinary diversion stent . In advanced cases, when irreversible destructive processes develop in the affected organs, the patient's diseased kidney is completely removed.
Diagnostics
Methods for diagnosing kidney tuberculosis are divided into laboratory and instrumental. Appointed:
- urine culture for the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- blood test (ELISA method). It is carried out to detect antibodies to tuberculosis bacteria;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys. Is one of the main instrumental studies;
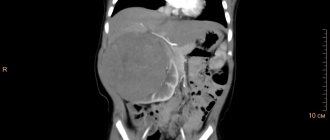
- X-ray studies: survey and excretory urography, as well as antegrade and retrograde angiography;
- radioisotope nephroscintigraphy;
- CT;
- MRI.
Cystoscopy with a biopsy of bladder tissue can be performed, but this increases the risk of spreading infection.
Diagnostic methods
An infected person may not feel the presence of pathogens in his body for three years, this is how long the incubation period lasts, therefore early diagnosis of kidney tuberculosis is difficult, especially in a child. There are several ways to determine infection:
- interviewing the patient to find out about the presence of unclear pain and possible tuberculosis in family members;
- urine collection for general analysis. The study helps determine the presence of mycobacteria and their quantity. Even with a slight accumulation of harmful organisms, a course of drug therapy is prescribed for preventive purposes;
- bacteriological blood test;
- cystoscopy is performed to detect problems in the urinary canals;
- X-ray.
After studying all the results of examinations and tests, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis of the disease.
Laboratory method
Laboratory diagnostics are carried out in the form of: clinical urine analysis, culture of urine on a nutrient medium, polymerase chain reaction studies, enzyme immunoassay of blood and provocative tests with tuberculin in the form of vaccination.
Urine examination is aimed at determining the nature of its composition. With tuberculosis, an acidic reaction occurs, and with other inflammatory processes it turns out to be alkaline.
Instrumental
The use of instrumental methods for the prognosis of renal tuberculosis cannot be considered the main method, but rather they are of an auxiliary nature of the study. More often used: ultrasound, excretory urography, MRI, computed tomography and dynamic nephroscintigraphy.
The use of ultrasound gives a picture of the disease in development, and nephroscintigraphy allows one to determine the degree of kidney activity and the level of their functioning.
These methods allow you to determine the location of tissue damage and the depth of penetration.
Treatment
If infection is suspected, patients undergo tuberculin tests and are given a consultation with a phthisiatrician. When collecting anamnesis, it may become clear that the patient himself or those in contact with him have a pulmonary form of tuberculosis.
Treatment of foci of tuberculosis in the kidneys depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s general condition. It can be only medicinal or complex.
Conservative treatment (medicines) is carried out with specific drugs that are taken in long courses for 6-12 months.
Examinations are carried out regularly to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Sometimes therapy lasts for years and is not interrupted after the symptoms of the disease are eliminated.
To treat tuberculosis infection in the kidneys, anti-tuberculosis drugs, NSAIDs and angioprotectors are used. Their action is aimed not only at destroying bacteria, but also at restoring normal kidney function.
It is also worth considering the possibility of scar deformation of the kidney tissue after healing of the cavities. This causes disturbances in the functioning of the organ.
To reduce the risk of scarring, patients are prescribed angioprotectors and drugs that relieve inflammation.
As scarring occurs, it may become difficult for urine to pass out of the kidney. In this case, surgery is performed to install a stent or form a nephrostomy.
Another treatment method is cavernectomy (cavity removal). In more severe cases, resection of the entire organ or part of it may be performed. The kidney is completely removed only in advanced cases, with total tissue damage.
Patients are warned that drug treatment for renal tuberculosis is long-term and can lead to serious complications.
Taking antibiotics can cause intestinal dysbiosis, so specific drugs are additionally prescribed to help maintain normal gastrointestinal flora.
Also, a side effect of anti-tuberculosis drugs is intoxication (nausea, vomiting, weakness) and allergic reactions.
Treatment of the disease
Therapy for the disease is very long-term, complex, and requires self-discipline and perseverance from the patient. Treatment tactics are chosen individually and, as a rule, include the use of specific anti-tuberculosis antibiotics, restoratives (vitamins, immunomodulators), anti-inflammatory, anti-sclerotic, antihypertensive drugs, angioprotectors, hepatoprotectors. Spa treatment is important. In severe advanced cases, surgery cannot be avoided.
At the initial stage of disease development, chemotherapy is used with first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs for 6–9 months; a deeper process requires combination therapy with first- and second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs for 10–12 months.
The cavernous form is treated with conservative and surgical methods - anti-tuberculosis, anti-sclerotic drugs and cavernotomy, resection of a segment of the affected kidney, in some cases (with a polycavernous course) complete removal of the organ is indicated.
For pyonephrosis, treatment is only surgical - nephrectomy is performed.
Early detected disease in a closed form without complications is treated on an outpatient basis under the systematic supervision of a local phthisiatrician. Hospitalization to an anti-tuberculosis dispensary is required if the prescribed treatment is insufficient, the disease progresses to the next stage after the initial stage (tuberculous papillitis or cavernous nephrotuberculosis), deterioration of the patient’s condition, additional complications, or serious impairment of kidney function.
General recommendations
The most important recommendation for the patient is strict adherence to medical instructions. Treatment must be systematic and continuous - this is the key to its effectiveness.
The patient should avoid physical exertion, hypothermia, ensure that there is no urinary retention, follow a diet and daily routine. Alcohol is strictly contraindicated for patients. In the acute period, bed rest is recommended.
Medicines
Complex chemotherapy for nephrotuberculosis is developed taking into account the stage of the process.
The basis of treatment is a combination of:
- several first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs: Rifampicin;
- Isoniazid (Tubazid, Ftivazid);
- Pyrazinamide;
- Ethambutol;
- Prothionamide;
- Streptomycin;
- Lomefloxacin;
To enhance the effect, Thioacetazone or PAS (para-aminosalicylic acid) may be prescribed. The treatment regimen usually includes three anti-tuberculosis drugs, of which Rifampicin and Isoniazid are the main ones.
It is very important to take the prescribed medications regularly, since with unsystematic treatment, mycobacteria develop resistance to anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Long-term treatment with anti-tuberculosis drugs leads to disruption of healthy intestinal microflora, functional disorders of the liver and allergic reactions. Therefore, it is advisable to prescribe hepatoprotectors (Karsil, Essentiale), antihistamines and drugs to normalize the intestinal flora (Linex, Bifidumbacterin).
In cases of renal failure, the dosage of anti-tuberculosis drugs is reduced. In the terminal stage of chronic renal failure (CKD), treatment is carried out against the background of regular hemodialysis.
The patient is also prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and angioprotectors to restore microcirculation and prevent the replacement of infectious foci with fibrous tissue. In order to prevent scarring of the ureter, treatment is sometimes carried out against the background of its drainage with an internal stent (catheter).
To accelerate reparative processes, cleanse cavities from purulent-caseous masses, dissolve blood clots and exudates, relieve swelling and inflammation, enzymes are used - Lidaza (Hyaluronidase), proteolytic enzymes - Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Chymopsin (through physiotherapeutic procedures).
Photo gallery: drugs for the treatment of nephrotuberculosis
The main drugs for the treatment of nephrotuberculosis are Rifampicin and Isoniazid.
Streptomycin is often included in complex chemotherapy for tuberculosis
PAS is prescribed for nephrotuberculosis to enhance the effectiveness of therapy
Ofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic prescribed in the complex therapy of tuberculosis.
Ethambutanol is an anti-tuberculosis drug, often included in chemotherapy against resistant forms of mycobacteria
Traditional methods of treatment
Herbal medicine and other folk methods can serve as a complement to traditional treatment with anti-tuberculosis drugs. Folk remedies have an anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory effect, improve recovery and metabolic processes in the body.
Recommended herbal remedies for treatment
The use of some herbal infusions regularly produces positive dynamics in the condition of patients with nephrotuberculosis.
Collection with currants and yarrow to cleanse the kidneys:
- Take 1/2 tablespoon each of black currant leaves, birch leaves, yarrow herb, bean pods.
- Pour the raw material with water in a volume of 0.5 liters and bring to a boil, boil for 5 minutes and leave for 1.5–2 hours.
- Strain the finished product, divide into three servings and drink throughout the day, taking it an hour before meals.
Anti-inflammatory collection with analgesic effect:
- Take a tablespoon each of sage, Veronica officinalis and cinquefoil herbs.
- Pour two glasses of water over the herbs and bring to a boil.
- Infuse the product for 2 hours, then strain and take half a glass half an hour before meals three times a day.
Diuretic anti-inflammatory mixture with hernia:
- Mix dry nettle, wheatgrass and hernia grass in equal parts, add two parts of corn silk.
- Grind the raw materials to a powder state.
- Take a tablespoon of powder daily with plenty of water.
During the healing period, to accelerate reparative processes, it is recommended to take aloe juice as a biostimulant; at any stage of treatment, you can drink a decoction of oats and bran, an infusion of rose hips, lingonberry tea, and fresh pumpkin juice in small quantities.
Photo gallery: plants most often used to treat nephrotuberculosis
Hernia has a powerful diuretic and disinfectant effect
Cinquefoil anserina has the ability to relieve inflammation and cleanse the kidneys
Veronica officinalis is a plant with strong analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Rose hips in the form of infusions are used as a general tonic.
Wheatgrass is recommended for use in kidney pathologies
Pumpkin juice is recommended to be used daily for kidney tuberculosis
Motherwort has an anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effect
Nutrition rules for nephrotuberculosis
Proper nutrition when sick is important. The diet should be aimed at saturating the body with nutrients, vitamins and minerals, and improving metabolic processes.
In the early stages of the disease, without significant impairment of kidney function, diet No. 11 is allowed - complete, fortified, with the exception of extractives (meat, mushroom, fish broths), smoked meats, marinades, pickles, hot sauces and gravy. It is necessary to remove from the diet:
- spices;
- seasonings;
- fat meat;
- canned food;
- semi-finished products;
- alcohol.
Recommended for use:
- vegetable dishes;
- fermented milk and dairy products;
- various cereals;
- dishes from dietary meat and fish.
Nutrition for tuberculosis should be complete, fortified and reduce the load on the kidneys
In case of complications and renal failure, nutrition should correspond to diet No7, aimed at maximally reducing the load on the kidneys. In case of edema and impaired urine output, it is recommended to limit table salt and liquid. If your kidney function is intact, you need to drink 1.5–2 liters of fluid, which must include:
- alkaline still mineral waters;
- herbal teas;
- diluted juices;
- decoction of rose hips and bran.
Photo gallery: recommended products for the initial stage of nephrotuberculosis
Vegetables and fruits are a source of a variety of vitamins and minerals
Cereals will not only enrich the body with useful substances, but will give strength and energy
If you have tuberculosis, you should definitely include a variety of fermented milk products in your diet, but it is better to choose ones that are not very fatty.
Dietary meat, such as turkey, is a source of natural protein and is easily absorbed by the body
Surgery
Severe forms of the disease, along with conservative treatment, require surgical treatment.
For large cavities, cavernotomy is performed - dissection of the wall of the pathological cavity and its sanitation, after which healing occurs. This operation is performed on patients in whom the cavity is the main source of infection and contributes to the progression of the disease.
If it is impossible to carry out such an intervention, an organ-preserving operation is performed - cavernectomy (resection of a section of the kidney with a cavity). For polycavernosis, nephrectomy is most often used, that is, complete removal of the affected organ.
In case of pyonephrosis, removal of the kidney is mandatory even with a mild clinical picture to prevent generalization of the process and the addition of a secondary infection.
Before surgery, conservative treatment is carried out for 1 month; the timing of postoperative therapy with anti-tuberculosis drugs depends on the degree of damage and the activity of the infectious process.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures used to treat pathology include electrophoresis, ultrasound treatment and inductothermy:
- Ultrasonic exposure does not directly affect mycobacteria, but can reduce the incidence of sclerotic changes in the kidneys.
- Electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory drugs and proteolytic enzymes has a resolving, restorative effect on the diseased organ.
- A high-frequency magnetic field (inductothermy) improves local blood circulation, stimulates the filtration functions of the kidneys, improves metabolic and trophic processes in tissues, promotes the rapid elimination of decay products and increased diuresis.
Magnetic therapy is aimed at restoring kidney function, improving metabolic processes, local circulation and diuresis
Sanatorium treatment in specialized anti-tuberculosis institutions is of great importance for patients with nephrotuberculosis.
Features of treatment of the disease in children
Nephrotuberculosis is most often diagnosed in adolescent children. As a rule, the pathology is asymptomatic. Unlike adult patients, in children the activity of Koch's bacilli persists simultaneously in the kidneys and in other organs (lymph nodes, lungs). Anti-tuberculosis therapy is based on the use of several drugs in combination with vitamin therapy and restorative procedures.
Video: Doctor Komarovsky about tuberculosis
Forecast
The main factor in the prognosis of treatment for renal tuberculosis is its stage and the degree of damage to the renal tissue. With early detection, superficial damage to the parenchyma and adequate therapy, the disease is completely cured.
In this case, the kidney tissue is completely restored. Severe cases of the disease can result in organ loss and disruption of the functioning of other body systems.
At a late stage of the disease, the prognosis is unfavorable. The organ stops functioning and it is impossible to restore its function. From the source of the lesion, the infection spreads throughout the body.
Nursing process in case of illness
Often, with complications of kidney tuberculosis, the patient requires nursing care, and the role of the transaction can be anyone close or not without special education. The main thing is to remember the main points of patient care:
- All prescribed medications must be given to the patient only in the dosage prescribed by the doctor, without decreasing or increasing it.
- Sometimes this pathology can lead to hemoptysis. In such cases, the patient must be positioned in bed so that his head is above waist level (to do this, it is enough to place several pillows under the person’s head).
- If a patient experiences adverse reactions while taking certain medications, they should be reported to the attending physician immediately, and the medication should be stopped immediately.
- It is necessary to constantly ensure that the patient has a clean bed and underwear; if necessary, the patient must be assisted in carrying out hygiene procedures.
- In the room in which the patient is located, it is necessary to regularly do wet cleaning and treat surfaces with disinfecting compounds - this is necessary to prevent the spread of pathogenic microflora.
In such situations, the diet remains the same, but hot food is completely excluded: dishes should be cool, but not cold.
Clinical picture
At the initial stage of the disease, a person rarely understands that he is sick. But there are a number of symptoms that accompany kidney tuberculosis. They are divided into indirect and direct.
Indirect symptoms
These include:
- general weakness of the body;
- increased body temperature;
- high fatigue threshold;
- vomiting, diarrhea, constipation;
- decrease in blood pressure.
All these symptoms are caused by decreased immunity. The red bone marrow receives a signal that a mycobacterium has entered the kidney and infection has begun.
It begins to actively produce leukocytes, which are sent to the affected area. And, naturally, the general condition of the body worsens. But that’s why they are called indirect.
It is not a fact that nausea and vomiting are a consequence of nephrotuberculosis. This could be normal poisoning. Taken together, of course, these signs may be a signal to go to the doctor.
Direct signs
The presence of the disease is indicated by the following symptoms:
- nocturnal dysuria (with tuberculosis, fibrous capsules can form on the walls of the renal parenchyma, which compress the bladder, hence frequent urination);
- skin pigmentation (impaired kidney function immediately affects the complexion, urine is not absorbed correctly and breakdown products make themselves felt, getting into the interstitial fluid, urobilin begins to affect the cells that are responsible for pigmentation);
- disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism (glucose is washed out of the body due to the fact that proteins are not processed correctly and only carbohydrates become a source of energy);
- sudden weight loss (increased breakdown of proteins takes a lot of energy from the body and therefore metabolism is disrupted, hence weight loss);
- constant aching pain in the lower back (one of the most common symptoms of nephrotuberculosis, the kidneys stop performing their natural functions and plus the affected parenchyma gives a signal to the brain that the organ cannot cope with the disease on its own and is waiting for a response as a flow of leukocytes) ;
- blood in the urine (this symptom will definitely force you to go to the hospital, it occurs already with necrosis of the kidney tissue due to rejection);
- painful colic in the kidney area (occurs due to impaired kidney function).
Modern approach to diagnosis
In the early stages, it is difficult to diagnose this disease, since the incubation period for the spread of mycobacteria lasts from 2 to 3 years.
Today there are five main methods for diagnosing the disease:
- Anamnesis collection . Necessary in order to pre-diagnose the degree of the patient’s disease. From this survey, the doctor learns about previous illnesses and pain that the carrier of the bacteria has. This is not an easy blitz survey! The specialist asks questions regarding the general state of health in order to prescribe the correct treatment or give directions in the future.
- Study of urine composition . The specialist looks at the urine sediment, which may contain mycobacteria. If they already exist, then it is necessary to diagnose their quantity in order to prescribe treatment. If there are very few of them, then it is better to take preventative medications.
- Cystoscopy . An indigo carmine test is taken for kidney discharge. In a healthy organ, the rate of discharge varies from 15 to 22%. And the parenchyma is visible. If there are ulcers or bullous edema on it, then nephrotuberculosis may already exist.
- X-ray diagnostics . The most common method for diagnosing renal tuberculosis. X-rays are taken several times to avoid mistakes and not to confuse this disease with stones. The foci of caseosis do not move. They are always in one place. You can also see in the image whether the kidney is enlarged in size, which may indicate tuberculosis.
- Palpation examination . Basically, in patients almost immediately after the full stage of the incubation period, the kidney can be palpated. A healthy neighboring organ becomes increased in size. This is what they palpate. In women, this procedure is done through the vagina to exclude cystitis or other diseases of the genitourinary system.
Is it possible to become infected with tuberculosis?
Many people are interested in the question: is kidney tuberculosis contagious? This disease is infectious in nature, its causative agent is Koch's bacillus, or more simply put, tuberculosis bacteria, which can be transmitted through air and liquids.
Renal tuberculosis, like any other form of it, is transmitted from a carrier by airborne droplets.
Often people, not knowing how kidney tuberculosis is transmitted, put themselves in danger by coming into contact with a carrier of the infection. Meanwhile, the probability of a person becoming infected in this way is approximately 15%. In the remaining 85% of cases, the body develops immunity to the disease.
Complex of therapeutic measures
Treatment of kidney tuberculosis is carried out using three main methods.
Drug treatment
It involves taking a number of medications that are prescribed by the attending doctor. The main ones include:
- Ethambutol;
- Isoniazid;
- Rifampicin.
On average, such treatment lasts 4-6 months depending on the form of the disease, in rare cases about 1 year.
The drugs are taken in combination. Doctors also advise buying a complex of vitamins and taking them along with tablets, preferably immediately after the first meal.
In addition to this method, a visit to a sanatorium is necessary for the overall health of the body.
Specific medications and dosages are prescribed by a specialist!
Surgery
If kidney tuberculosis has reached the cavernous form, then surgery is no longer possible. In this situation, part or all of the organ is removed. Everything depends on the stage of the disease.
The operation requires preparation (on average 2 months). During this period, the patient takes medications and vitamins in tandem. Only after this are final tests done and surgery scheduled.
Resection of the entire kidney or part of it, less often the adrenal glands, is performed. The post-rehabilitation period can last from 12 to 18 months.
ethnoscience
If you decide to cure the disease yourself, then the following remedies will help in this matter:
- propolis oil;
- herbal collections (silver cinquefoil, sage, medicinal speedwell, wheatgrass rhizomes, yarrow, nettle root, black currant leaves).
To be treated with traditional methods, you need to know the exact dosages of herbal infusions. Only their ideal ratio will give a positive result.
There are two types of such fees:
- Grind 100 grams of silverweed and goosefoot until smooth, add 50 grams of veronica and sage, take a tablespoon once a day with plenty of water for 3 weeks;
- combine 5 grams of corn silk and burnet, 10 grams of speedwell, silver cinquefoil, nettle and wheatgrass rhizome, add 0.5 liters of water and boil; cool and take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day 20 minutes before meals.
Description of the disease
Renal tuberculosis ranks first among extrapulmonary types of this disease (it occurs in 30-40% of all cases). Adrenal tuberculosis develops extremely rarely.
In women, this pathology is less common. Male nephrotuberculosis often spreads to the prostate and testicles, and is severe.
The disease is most often diagnosed in people between 20 and 40 years of age. Recently, pathology has also been diagnosed in children, this is due to the unfavorable environmental situation.
The pathology develops over 2-3 years, in some cases this period extends to 15 years. In the later stages of the disease, tuberculous pyonephrosis (purulent liquefaction of the kidney) may occur, which subsequently causes damage to the bladder, ureter and genital organs.
In some cases, tuberculosis infection of the kidneys can occur simultaneously with pulmonary tuberculosis. But since the incubation period lasts for different times, diseases are diagnosed differently. In addition, due to obvious symptoms, pulmonary tuberculosis is detected faster than tuberculosis of the kidneys and urinary tract. Sometimes only in the last stages of the disease do doctors determine the pathology.
The main route of entry of Mycobacterium tuberculosis into the kidneys is through arterial blood. The structure of the kidneys itself influences the rapid progression of the disease. Due to the many small arteries, Koch's rod is provided with wide access to the organ, and in the renal glomeruli the blood flow is rather slow, which does not contribute to the rapid elimination of rods in a stream. Due to this, many primary foci are formed in the kidneys.
Let's look at the causes, symptoms and treatment of the disease.
Causes of the disease
As already mentioned, the source of the disease is infection with the tuberculosis bacillus. It can occur both through the development of an internal source of infection, and through its external influence. Tuberculosis is often transmitted by airborne droplets if there is an infectious source nearby (an already sick person). In most cases, renal tuberculosis is a consequence of neglected or untreated pulmonary tuberculosis. Why do these organs suffer? As a rule, the disease affects the kidney structure if there is low specific immunity and the organ simply cannot resist infection. In addition to the infection itself, there are other causes of the disease:
- lack of adequate nutrition or starvation;
- severe hypothermia and colds;
- harmful working conditions;
- injuries to the kidneys and adjacent organs;
- urinary tract diseases;
- endocrine pathologies.
Like any other disease, kidney tuberculosis varies in form and also has several stages of development.
According to the form of the disease, they are distinguished:
- Acute miliary tuberculosis. Accompanied by the active release of Koch bacilli into the blood. At the same time, other organs also suffer.
- Chronic tuberculosis. It develops in cases where the infection is transmitted from already affected organs. The main danger of this form is that its diagnosis is difficult, and there are often no characteristic symptoms. In this case, tubercles form on the kidneys, which increase in size over time, and the organ itself also increases in size.
By stage, renal tuberculosis is divided into:
- The first (non-destructive). It is characterized by maintaining the integrity of the organ.
- The second (with initial destruction). Inflammation and death of the renal papillae occur, and tuberculous cavities, the so-called cavities, begin to form on the tissues.
- Third (with limited destruction). It is characterized by an increase in the number and size of the cavity.
- Fourth (with complete destruction of kidney tissue). Complete destruction occurs, which is accompanied by the “degeneration” of the kidney into a system of caverns.
Diagnosis of the disease
Initially, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints and collects anamnesis. Important information will include the following data:
- Have you been diagnosed with tuberculosis of the lungs, bones, etc. in the past?
- Are there people with tuberculosis in the person’s surroundings?
- Have you had contact with carriers of the infection?
Then an X-ray examination is carried out, the results of which will reveal signs characteristic of this disease.
Diagnostics carried out when kidney tuberculosis is suspected includes the following research methods:
- Urinalysis for kidney tuberculosis reveals the presence of protein, red blood cells and white blood cells.
- Urine culture is done: it is placed in a nutrient medium, where Mycobacterium tuberculosis is detected.
- Polymer chain reaction (PCR) method. This test gives results with 95% accuracy.
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). Identifies the characteristic antibodies that the body produces in response to the presence of a pathogen.
- Provocative tests using the substance tuberculin. If there is a tuberculosis infection in the body, it means that after using tuberculin, characteristic impurities will appear in the urine.
Disease prevention
To prevent kidney disease from developing and being accompanied by complications, it should be detected at an early stage, when the symptoms of kidney tuberculosis do not manifest themselves.
Of particular importance is an annual full examination of the body and general tests. This especially applies to people at risk.
Next, all possible problems with the outflow of urine are eliminated. In this case, medicinal herbs such as yarrow, birch leaves, burnet, and wheatgrass can come to the rescue.
An important role is played by sanatorium treatment, good nutrition and a course of vitamin complexes.
The prognosis for recovery from kidney tuberculosis will depend on the following important indicators:
- Conditions of the immune system.
- Timely diagnosis of the disease.
- Correctly selected treatment.
If tuberculosis foci appear in the kidney parenchyma, then with proper therapy it is possible to achieve long-term regression of the disease. This is achieved due to the fact that these organs form scars.
Unfortunately, complete regeneration of damaged tissue cannot occur, because the parenchyma does not have the ability to fully recover. But if the treatment is long-term and targeted, then partial functionality of the affected kidney will remain.
A small child, while still in the maternity hospital, receives a special anti-tuberculosis vaccination, which is repeated as he grows up.
Renal tuberculosis is an infectious kidney disease that affects the renal parenchyma and develops as a result of the activity of special tuberculosis bacteria (mycobacteria or MBT for short).
Renal tuberculosis leads among all extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis. The disease affects both sexes equally.
The main problem in diagnosing this disease is that its first symptoms do not directly indicate renal tuberculosis, only indirectly. Its initial manifestations include low-grade body temperature, blood in the urine, girdling back pain and difficulty urinating (may be completely absent).
To treat this disease, the patient requires patience and consistency in action, because due to kidney tuberculosis, the entire body suffers.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment will depend on the stage of kidney tuberculosis and symptoms. There are 2 main methods of therapy - conservative and surgical. The patient is placed in a specialized dispensary, where he remains until the disease takes a form that is safe for others, because It is well known that kidney tuberculosis is contagious. Treatment lasts on average 12 months or more.
If the disease is diagnosed at a late stage, then surgical intervention becomes appropriate.
The choice of treatment for tuberculosis will depend on the lesion:
- Damage to the parenchyma or papillae of the kidneys requires a conservative approach to treatment.
- The third stage of cavernous tuberculosis is also treated with medication. To preserve the function of the urinary systems, surgery may be performed on a separate area of the kidney.
- Polycavernous tuberculosis or pyonephrosis can only be treated surgically.
Despite the individual approach to the treatment of nephrotuberculosis, there are similarities in therapy. So, at any stage of the disease it is necessary to take a loading dose of antibiotics. Therapy is carried out according to the following scheme:
- First, first-line antibiotics are prescribed - these are Ethambutol, Streptomycin, Rifampicin. If one of the drugs causes an allergy, it is replaced with other drugs. Most often these are Ethionamide, Kanamycin, Cycloserine, Prothionamide.
- The purpose of such drugs is to destroy the causative agent of the disease, while the foci of infection are gradually replaced by connective tissue. To keep the number of such scars as small as possible, the doctor prescribes angioprotectors and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to the patient.