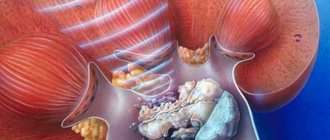
As a kidney disease, hydronephrosis is more typical for women, which is explained by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure - a short urethra, which is more susceptible to inflammation than in men. In 85% of cases, the right or left kidney is affected, and only in 15% is there a bilateral form. Treatment of kidney hydronephrosis is most often performed surgically, otherwise the patient will continue to suffer from exacerbations and even serious complications.
Causes of kidney hydronephrosis
As already mentioned, renal hydronephrosis can be congenital or acquired. Each of these forms of pathology has its own etiology. Congenital hydronephrosis is associated with the anatomical features of the child’s body. Certain changes can be noticed by an experienced specialist during an ultrasound examination of the fetus. Even then, the renal pelvis can be enlarged to varying degrees. Depending on how serious the deviations from the norm are, a decision is made to carry out appropriate treatment or even terminate the pregnancy if doctors assess the functions of the fetal kidneys as incompatible with life.
The causes of hydronephrosis can be divided into external, internal and functional. Pathological changes can affect both the ureter and the bladder. From the ureter, internal causes of hydronephrosis can be:
- blood clots;
- tumors of various etiologies;
- narrowing of the mouth of the ureter (urethrocele);
- endometriosis;
- tuberculosis;
- fibroepithelial polyps, etc.
Among the external causes that can cause ureteral dysfunction are the following:
- pregnancy;
- oncological diseases of the female reproductive system (cervical cancer, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc.);
- uterine prolapse;
- prostate tumors of various etiologies;
- aortic aneurysm in its abdominal section;
- anatomically incorrectly located renal artery, which in this case compresses the ureter.
If we are talking about the bladder, then among the internal factors contributing to the development of hydronephrosis, the following can be identified:
- contracture of the bladder neck;
- urolithiasis disease;
- prolapse of the bladder into the vagina in women (cystocele);
- carcinoma;
- bladder diverticulum, etc.
An external obstacle to the physiological outflow of urine from the bladder can be pelvic lipomatosis. Functional disorders include various disorders of bladder filling and emptying and retrograde vesicoureteral movement of urine (reflux).
From the urethra, the cause of hydronephrosis can be prostate cancer, its hyperplasia (external causes), as well as urethral strictures (pathological narrowing of the urethra) or urethral diverticula (internal causes).
Hydronephrosis can also be caused by various injuries, postoperative conditions, inflammatory diseases of various origins, obstruction of the urinary tract, etc.
Causes of the disease
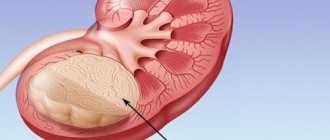
Hydronephrosis is an enlargement of the renal collecting system. This occurs due to the strong pressure of fluid from inside the organs, which has accumulated inside in large quantities. The disease can be congenital or acquired. In the first case, the disease is caused by the following factors:
- abnormal development of the genitourinary organs in the fetus;
- urinary tract obstruction;
- anomaly of kidney localization;
- ureteral strictures;
- narrowing of the lumen of the ureters.
In such situations, the child is born with hydronephrosis. The acquired form appears during life. The causes of this kidney hydronephrosis:
- tumor diseases of the prostate;
- disturbance of innervation of the bladder;
- embolism due to urinary tract injuries;
- tumors of the pelvis or ureter;
- tuberculosis of the kidneys or urinary tract;
- stones in the kidneys.
Hydronephrosis of the kidney during pregnancy occurs for the same reasons. The situation is simply aggravated by the uterus, which increases in size and thereby worsens the condition.
Symptoms of hydronephrosis
At the early stage of development of hydronephrosis, there are practically no symptoms. In some cases, the patient may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- colic;
- more frequent urination, which does not bring adequate relief;
- a feeling of heaviness in the area where the organ is located.
As congenital or acquired hydronephrosis develops, a dull, aching pain in the lumbar region may be felt. The localization of pain depends on which kidney is affected. The following symptoms can be observed:
- lower abdominal pain;
- weakness;
- elevated temperature;
- nausea;
- attacks of pain in the area where the organs are located;
- bloating;
- high blood pressure.
If a person has an elevated temperature (more than 37 oC), this indicates the onset of an infectious process, especially when hydronephrosis is suspected in children. In some cases, the patient does not experience the symptoms described above, except for one thing – urine mixed with blood. Such a violation requires immediate examination by a doctor.
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney is one of the most common diseases of the genitourinary system. The main trigger is a stone, which can block the flow of urine. In this case, if the stone enters the urinary canal, bilateral hydronephrosis is considered.
The first and most common symptom of this disease is pain on the left side, which radiates to the leg. There is also a painful outflow of urine mixed with blood and mucus. In some cases, the patient cannot urinate, although the urge to urinate is present.
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and immediate treatment. Surgery is almost always prescribed.
Hydronephrosis of the right kidney
Hydronephrosis of the right kidney is a urological disease that is caused by blockage of the genitourinary tract. The main risk groups are elderly people and those who abuse alcohol.
The symptoms of hydronephrosis of the right kidney are the same as when the pathological process is localized in the area of the left kidney. The only difference is that with hydronephrosis of the right kidney, the pain radiates to the entire lower back.
Disease statistics
Statistical studies show that women are more likely to develop hydronephrosis. This is due to the structural features of their genitourinary organs. Pregnancy often contributes to the development of the disease, because the fetus compresses the vessels that feed the kidneys.
Elderly people and children are also at risk. People who deal with pesticides or heavy metals also get sick. Patients living in areas of radioactive damage also suffer from pathology.
People who move little often develop diseases, including hydronephrosis.
Disabled people, those suffering from cancer, overweight people, even healthy people who spend a lot of time at the computer or just sitting, move little. Teenage boys often suffer from this disorder.
Degrees
There are three degrees of hydronephrosis:
- Hydronephrosis in 1st degree. At this stage, the pyelocaliceal apparatus of the kidney is enlarged, but this is not accompanied by an increase in the organ itself. Kidney function is preserved; the clinical picture can manifest itself with symptoms such as aching pain in the lumbar region. Sometimes hematuria (blood in the urine) may occur. In the tests, protein may be slightly increased; with hematuria, red blood cells will also be present.
- Hydronephrosis in 2 degrees. At the second stage, simultaneously with the pelvis, the kidney itself enlarges. On average, it increases by 10 - 20 percent of its original volume. However, it is worth understanding that the enlargement of the kidney does not occur due to an increase in its tissue or function, but due to the stretching of the pelvis and the accumulation of urine in them. The kidney function itself is reduced by 30–40 percent. Protein (proteinuria) begins to appear in the urine, and toxic metabolic products - creatinine and urea - increase in the blood. At this stage, the first signs of renal failure begin to appear - blood pressure rises, and renal edema appears in the morning.
- Hydronephrosis grade 3. Represents renal failure. At this stage, the kidneys almost double in size, while their function decreases by more than 60 to 70 percent. The kidney parenchyma (its tissue) almost completely atrophies, and large cavities form in its place. The kidney takes on the appearance of a multi-chamber cavity, which, in turn, is filled with urine residues. Arterial hypertension becomes resistant (difficult to treat) and blood pressure is constantly elevated. Protein continues to be lost by the body; at the terminal stage, proteinuria reaches 3 grams per liter of urine. Such a massive loss of protein provokes large swelling. Patients at this stage are very swollen, swelling is observed not only in the eye area, but throughout the body.
Hydronephrosis is also classified according to the type of development. If the disease is complicated by an associated infection, then it proceeds according to the infected type. If not, such a disease proceeds aseptically, the symptoms in these two cases will be slightly different.
Types and stages of hydronephrosis
Depending on the degree of enlargement of the pyelocaliceal system, several degrees of severity of hydronephrosis are distinguished:
- Only a small amount of urine accumulates in the renal pelvis. The walls are not stretched too much, the kidney is working normally.
- The pelvis is stretched more strongly, which is why kidney function is impaired. If the disease develops only on one side, then the entire load falls on the other kidney.
- There is a complete loss of functionality of the affected kidney. Due to overload of a healthy kidney, renal failure develops, which can be fatal.
Features of hydronephrosis in pregnant women
The main reason for the development of this pathology in pregnant women is considered to be developmental anomalies of the urinary tract. Why is this happening? The development of the fetus does not occur unnoticed by the mother's body. While the baby is growing inside the uterus, the woman's kidneys have to do double duty. If the mother had certain malformations of the genitourinary system before conception that did not cause her discomfort, then with the birth of the child, the work of the kidneys is completely decompensated.
How does hydronephrosis manifest in pregnant women?
- in most cases, late gestosis develops (increased blood pressure, the appearance of edema and protein in the urine);
- an enlarged kidney can put pressure on the uterus, disrupting the blood supply to the fetus, which leads to intrauterine growth retardation. Also, the large size of the kidney prevents the mother from having a normal birth;
- The disease can be complicated by the development of pyelonephritis and chronic renal failure, as well as an increase in nitrogenous wastes (urea, creatinine) in the blood.
The development of hydronephrosis in some cases threatens a woman’s life, so pregnancy must be terminated if:
- the diagnosis of “bilateral hydronephrosis” was made before conception;
- the mother has only one functioning kidney;
- in case of complicated pathology;
- the disease is not amenable to conservative and surgical treatment.
Pregnancy is not a contraindication for reconstructive plastic surgery. In severe cases, kidney removal may be possible.
Treatment
Watchful waiting is used in the initial stages of kidney damage, with preserved calyx tone and minor pyelectasis.
Conservative treatment of incipient pyelectasis is ineffective and has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Additionally, medications are used to normalize the patient’s blood pressure, relieve symptoms of intoxication in renal failure, and provide preoperative preparation.
The main task in the treatment of hydronephrosis is to enable complete evacuation of urine from the kidney. Consists of two aspects: drainage of accumulated urine and removal of obstruction. Therefore, the choice of specific treatment tactics is directly related to the severity of the process and the level of obstruction.
Drainage of the renal pelvis is performed in the terminal stage of hydronephrosis or hydroureteronephrosis by percutaneous puncture nephrostomy.
In case of obstruction at the level of the lower urinary tract, decompression is carried out by installing a urinary catheter or cystostomy.
Minimally invasive outflow restoration is performed with preserved renal function:
- Balloon dilatation of the ureteropelvic segment;
- External lithotripsy;
- Laser removal of prostate adenoma;
- Ureteral stenting;
- Contact ureterolithotripsy;
- Endoprosthetics of the urinary tract;
- Endoureterotomy;
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy
- Nephrovesical shunting,
- Transurethral resection of prostate adenoma.
Reconstructive plastic surgery is used as an alternative when it is impossible to perform minimally invasive interventions to radically get rid of the causes of hydronephrosis:
- radical excision of obstructing scar tissue and fibrous tissue around the narrowed area;
- wide anastomosis of unchanged fragments of the urinary tract;
- elimination of obstruction of the lower polar vessels of the kidney without compromising their integrity.
Reconstructive plastic surgery is performed when the sphincter apparatus of the urinary tract is damaged:
- intestinal plastic surgery;
- plastic surgery with a bladder flap.
Removal of the kidney and ligation of the supplying vessels are performed in case of total atrophy of the kidney, mainly by endoscopic and minimally invasive methods.
Hydronephrosis in children
Hydronephrosis in children is usually congenital. Slowing the outflow of urine leads to its accumulation in the cups and pelvis and increased pressure in them. Additional elastic fibers appear in the walls of the pelvis and cups to counteract the increasing pressure. For a certain time the situation will stabilize. And, if the reason that inhibits the outflow of urine is eliminated, for example, the lumen of the ureter develops further, then hydronephrosis in children goes away.
Hydronephrosis in newborns is accompanied by the appearance of blood in the urine, urinary infections and abdominal pain. If the kidney is greatly enlarged, then the parents themselves can feel it as a round formation in the baby’s abdomen. An enlarged pelvis with hydronephrosis in newborns is easily detected by ultrasound. This is the very first study that needs to be done if hydronephrosis is suspected. Next, the doctor prescribes a more in-depth examination to determine the extent of the disease and the state of kidney function. As a rule, studies with contrast agents or radioisotopes are performed for this purpose.
Hydronephrosis of newborns is not diagnosed as a diagnosis during the first three to four weeks, since during this period the child’s body undergoes strong changes in the structure of the kidneys and water-salt metabolism, so the symptoms of hydronephrosis in newborns may spontaneously disappear.
Stages of transformation
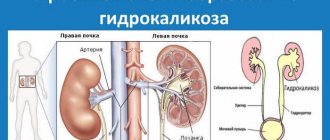
- The initial stage is observed with an isolated increase in the size of the pelvis (pyelectasia); The smooth muscle cells of the pelvis hypertrophy to compensate for the increased pressure. No functional manifestations are observed. Diagnosis of pathology at this stage is random.
- Pronounced manifestations include an increase in the size of the pelvis and calyces (hydrocalicosis). The smooth muscles of the calyces atrophy, the filtration capacity of the affected kidney is moderately reduced, which does not affect the general condition of the body while the function of the opposite kidney is preserved. A slight decrease in the thickness of the renal parenchyma is detected, often causing secondary arterial hypertension.
- The terminal stage is atrophy of the renal parenchyma and replacement of nephrons with connective tissue cells. There is a sharp decrease in the functional activity of the kidney, up to absolute absence. As a result, the kidney turns into a bladder formed from connective tissue and filled with liquid that slightly resembles urine. The volume of such a bag can be up to 5 liters.
Diagnostics
It is important not only to discern all the diagnostic signs of hydronephrosis, but also to identify the cause and assess the functional capacity of the contralateral kidney.
A clinical and urological examination is carried out in the following scope:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- bacterial culture of urine with identification of the pathogen;
- blood biochemistry;
- electrolytes;
- examination for genitourinary tuberculosis (with the constant presence of leukocytes in the urine, but sterile results of urine culture for flora);
- Kidney ultrasound with Doppler;
- survey and excretory urography;
- voiding cystoureterography;
- dynamic scintigraphy with assessment of the functional capacity of each kidney.
If a tumor pathology is suspected, an MRI may be performed. Additional examination methods may be performed according to indications.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with polycystic kidney disease (with a 2-sided process), solitary cyst, and malignant neoplasm. With concomitant pain syndrome, urolithiasis and nephroptosis are excluded. A combination of a prolapsed kidney with a stricture of the lumbar spine is often found. If there is pyuria and hematuria in the urine, oncology, pyonephrosis and tuberculosis are excluded.
Pyelocalicectasia, in addition to hydronephrosis, can occur in conditions such as:
- taking diuretics;
- diabetes insipidus;
- extrarenal pelvis;
- parapelvic cyst;
- papillary necrosis;
- cup diverticula;
- pregnancy.
Therapy methods
Hydronephrosis is treated with different methods. Their choice depends on the degree of development of the disease. The doctor will determine the necessary method for effective treatment of hydronephrosis.
Conservative approach
In the case of the initial stage of the disease, conservative methods of treatment can be used. But this happens rarely for the reason that the disease is not diagnosed at the very beginning, unless by accident.
The goal of treatment is always to remove accumulated urine and prevent permanent damage to the kidney.
Typically, conservative therapy is carried out to eliminate the symptoms of the disease that caused hydronephrosis or before surgery. This is preparation for surgery.
It involves the use of antibacterial medications for prophylactic purposes to avoid infection.
Ofloxacin and amoxicillin are usually prescribed. But the doctor prescribes antibiotics after testing the urine culture for bacteria and sensitivity to the medication.
If the patient has high blood pressure, antihypertensive medications are prescribed. It is difficult to select them, since this kidney pathology is often accompanied by uncontrolled hypertension. To improve blood flow in the kidneys, Trental is prescribed.
Impaired urine output leads to an increase in urea. In this case, sorbents are prescribed: Belosorb or Chofitol. It is possible to use polyphepane.
Surgery
In this case, surgery is mandatory. When it is carried out, the cause of impaired urine output is eliminated. If stones give this effect, they are crushed into sand using ultrasound or laser. This operation is performed with laser or ultrasound.
If the cause is a malignant tumor, it is removed and chemotherapy is given. This type of surgery is performed either conventionally or by laparoscopy. The choice depends on the degree of tumor growth and its spread to other organs.
More often the operation is performed using laparoscopy. This type of plastic surgery is distinguished by access to the operated site. The doctor makes several small incisions, inserts an endoscope into them, and performs the operation. Abdominal surgery is more traumatic, which is why it is used less often.
In the third stage of the disease, the kidney is completely removed. Laparoscopy cannot be used in this case.
In cases where hydronephrosis affects both kidneys, treatment is symptomatic to support the body and relieve pain.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies, like medications, can only be auxiliary in the preoperative period.
They relieve the symptoms accompanying hydronephrosis. But they bring more benefit after surgery, when gentle rehabilitation is required.
With the help of traditional medicine, you can relieve symptoms at home.
When restoring the body, folk remedies heal tissues, normalize metabolic processes, and have a moderate anti-inflammatory effect.
Herbal medicine has the most effective effect when combined with diet and fluid restriction.
Proper nutrition and diet
In case of hydronephrosis kidney disease it is necessary:
- fluid restriction (up to 1.5 l/day);
- consume a minimum amount of salt;
- exclude fried and spicy foods from the diet;
- It is unacceptable to consume products containing cocoa and coffee;
- remove any meat, fish dishes, beans from the menu;
- increase fruit in the menu;
- instead of meat you can eat chicken protein;
- steam food.
Violating the diet rules will quickly lead to a relapse.
Complications
Chronic hydronephrosis often contributes to the occurrence of urolithiasis and pyelonephritis, hypertension, which further aggravate the clinical picture of hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney. Sepsis sometimes develops against the background of infected hydronephrosis.
The course of hydronephrosis may be complicated by the development of renal failure. In this case, especially with bilateral hydronephrosis, the patient’s death occurs from intoxication with nitrogen metabolism products and disturbances in water-electrolyte balance. A life-threatening complication of hydronephrosis can be spontaneous rupture of the hydronephrotic sac, resulting in urine leakage into the retroperitoneal space.
Hydronephrosis, characteristic symptoms of kidney damage and modern treatment
Hydronephrosis usually manifests itself as aching pain that is not related to the severity of physical activity, time of day, or position adopted by the person.
Pain appears on the side of the affected kidney.
The symptoms of hydronephrosis are superimposed on top of those characteristic of the pathologies that provoked its development:
- Urolithiasis disease. Characteristic is the appearance of sharp pain in the lower back, radiating to the perineum or along the ureter. Urination causes discomfort, which is aggravated by a burning sensation. There may be blood in the urine.
- Destruction of the innervation of the urinary tract. Symptoms include problems with urination. The urge will be too frequent, a change in the volume of urine provides the main provisions for nighttime diuresis. In advanced cases, the patient suffers from urinary incontinence.
Bilateral hydronephrosis has more symptoms. If there are deviations from the normal functioning of two kidneys at once, renal failure quickly develops. Symptoms include shortness of breath, swelling of the face in the morning and swelling of the legs in the evening, cardiac dysfunction src=»https://feedmed.ru/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/gidronefroz-normalnaya-pochka.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width =”620″ height=”410″[/img]
Hydronephrosis is not treated with conservative therapy. It is used only as a prophylaxis or a way to relieve pain. Surgery is considered the only effective way to eliminate hydronephrosis.
The appropriate surgical tactics depend on the patient’s condition:
- Reconstructive. The operation is permissible only in cases where the parenchyma retains its function. The doctor must be sure that the intervention will completely eliminate the cause of hydronephrosis.
- Organ-preserving.
- Organ removal. Removal of the kidney is indicated only if it is completely unable to cope with the assigned tasks, in cases of a high risk of complications.
Treatment of kidney hydronephrosis
Therapy for the disease should be aimed at eliminating its cause and preserving kidney function. Conservative and surgical treatment is possible. Drug therapy methods are used to relieve pain, lower blood pressure, eliminate uremia and destroy secondary infections.
What medications are prescribed for hydronephrosis:
- β2-adrenergic agonist hexoprenaline (ginipral) - it reduces the tone and expands the lumen of the ureter;
- broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs - protected penicillins (Augmentin), cephalosporins (Cefadox), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin);
- diuretics – often loop ones (furosemide, torsemide);
- myotropic antispasmodics – drotaverine (no-shpa), papaverine;
- painkillers - opioids (morphine, promedol) for renal colic or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substances (movalis, nimesil);
- antihypertensive drugs - ACE inhibitors (Enap, Prestarium) and calcium channel blockers (amlodipine) work best.
To eliminate uremia, afferent detoxification methods are used: plasmapheresis, hemodialysis.
What is hydronephrosis of the left kidney
The disease is associated with problematic urine outflow due to expansion of the collecting-pelvis system. If the pelvicalyceal part does not function properly, a large accumulation of urine occurs, causing poor outflow.
The disease has primary and secondary genesis. The reasons for its development are various.
The root cause of the primary form is the abnormal development of organ tissue, the genitourinary system, or the appearance of a large number of blood vessels during fetal ripening.
The causes of the secondary form of hydronephrosis: tumor formations, kidney stones or organ injury.
As a result of the overflow of the pelvicalyceal part with urine, it stretches to enormous sizes. The tubules and glomeruli of the kidney atrophy, wrinkle, and the renal part of the calyx becomes smaller. The disease requires emergency medical intervention, otherwise the consequences may adversely affect the patient’s body.
Operation
The goal of surgical treatment is to create an artificial pathway for the outflow of urine from the kidney and eliminate the root cause of the disease.
The choice of surgical intervention method depends on what exactly caused the hydronephrosis. There are two most common surgeries (with many modifications) used to treat hydronephrosis:
1. Transurethral catheterization followed by ureteral stenting, used for persistent ureteral spasm that cannot be corrected with medication.
The meaning of this operation is to insert a catheter through the urethra, equipped with a camera and carrying a stent - a special device that looks like a small spring. A stent is placed where the urinary tract is narrowed and then expanded. After the spring has straightened, the patency of this area is restored, the catheter is removed, and the patient is placed under observation. As a rule, such an operation does not take more than 40-60 minutes, and the patient can be discharged home the next day for outpatient observation.
2. The application of a nephrostomy (creation of an artificial path for the outflow of urine) is used in cases where the patency of the urinary tract cannot be restored urgently (for example, when it is compressed by a tumor, the removal of which requires a lengthy preliminary examination).
There are many modifications of this operation, which differ in the location and type of access, as well as the volume of intervention performed, but the main meaning of the surgical manipulations is as follows: by making an incision or puncture of the skin above the kidney, a catheter is inserted into the pelvis, the other end of which is secured with a special device on the skin. Thus, urine begins to flow out through the catheter, where it is collected in a sterile container - a urinal. The operation lasts up to 1 hour, and after a control ultrasound examination and receipt of recommendations for caring for the nephrostomy, the patient can be discharged home. Such a nephrostomy can function for quite a long time, which is necessary to identify and eliminate the main cause of urinary tract obstruction.
How to properly treat hydronephrosis
Treatment of renal hydronephrosis with medications is ineffective. Most often, conservative therapy is used as preparation for surgery to relieve an acute inflammatory process. The main treatment method for hydronephrosis is surgery. Surgery for kidney hydronephrosis in an adult can be performed in different ways:
- Open surgical operations. It is carried out in emergency cases or with a large volume of intervention.
- Endoscopy. Laparoscopy for kidney hydronephrosis involves surgery through several small incisions in the skin. This is a less traumatic operation with quick recovery.
Rice. Laparoscopic plastic surgery of the ureteropelvic segment for hydronephrosis.
Removal of the kidney for hydronephrosis (nephrectomy) is prescribed only at the terminal stage. In other situations, it is possible to save the organ and stabilize the condition. The State Urology Center uses organ-preserving surgeries, which result in fewer complications and allow one to avoid radical treatment methods. You can undergo diagnostics and treatment in our clinic completely free of charge. To do this, you only need a compulsory medical insurance policy. To prevent complications from developing, make an appointment with a urologist using the online form or contact number.
On weekdays you can get an appointment with a urologist on the day of your visit
Nutrition and diet
With hydronephrosis, the process of natural removal of decay products from the body is inhibited. To reduce the intoxication of the body with harmful substances, the patient must follow a special diet.
The diet for hydronephrosis is as follows:
- Limited consumption of animal protein;
- Exclusion of certain products;
- Consuming the required amount of plant foods.
For hydronephrosis, it is recommended to consume no more than 0.5 grams of protein per 1 kilogram of the sick person’s weight. So, if a patient weighs 70 kilograms, he can eat 35 grams of protein per day. You should replenish your protein intake with lean fish or meat, and low-fat dairy products. In this case, you need to choose natural (not frozen, not processed) products.
Foods that should be removed from the diet for hydronephrosis are:
- any types of meat or fish with high fat content;
- jellied meat and other types of rich broths from meat or fish;
- dishes prepared by frying, smoking, drying;
- industrial and home preservation (salted, pickled, pickled vegetables or fruits);
- sweets, cakes, pastries and other products with a lot of sugar;
- food products with a high salt content (chips, crackers, salty straws);
- any products that have an unnatural smell, color or taste.
- carbonated drinks, alcohol.
Products that are allowed for hydronephrosis are:
- meat (chicken, turkey, veal);
- offal (liver);
- fish (cod, pike perch, pike);
- dairy and fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir, milk, sour cream, yogurt).
It is also recommended to include at least 600 grams of fruits and vegetables in your daily diet. Plant products should be consumed mainly in raw form.
The most useful cultures for hydronephrosis are:
- watermelon;
- grape;
- apples;
- apricots;
- plums;
- pumpkin;
- beet;
- potato;
- cauliflower.
Diet
Diet plays an important role in treatment. The diet is prescribed by a doctor individually. The diet should be such as to help restore the flow of urine and kidneys.
The following foods should be excluded from the daily diet:
- salty;
- fat;
- smoked;
- sweets;
- alcohol;
- fried meat and spicy dishes.
Instead, the diet should include the following:
- vegetables and fruits;
- dairy products;
- proteins.
This diet, combined with proper treatment, gives positive results. By the way, diet can help improve metabolism, which is beneficial for the whole body.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies involves the use of various herbs and medicinal preparations that improve kidney function and alleviate the condition of patients with hydronephrosis. For this purpose the following is used:
- Pumpkin, namely the stalks. To prepare the medicine, the stalks are crushed, 500 ml of boiled water is poured in and infused in a water bath for 20 minutes. After this, the infusion must be removed, wrapped in a warm towel and left for about 2 hours. Take 4 times a day, half a glass per dose.
- 150 gr. birch leaves, 50 gr. nettle leaves, 50 gr. Adonis herbs, 50 gr. oat grains, 50 gr. bearberry and 50 gr. horsetail.
- In equal proportions take black currant leaves, raspberry leaves, calamus roots, kidney tea, string grass, chamomile flowers.
- Herbs for hydronephrosis are used in the form of preparations, which are recommended to be used for no longer than 3-4 months. It is necessary to change fees, after each course, waiting approximately 2 weeks. Plant infusions are taken on an empty stomach, approximately half an hour before meals.
- Chopped parsley root, 1 tbsp. l., pour 100 ml of boiling water. The product is infused all night. Carefully drain the liquid in the morning and drink 1 tbsp. l. on an empty stomach during the same day. If it is not possible to purchase plant roots, you can also use seeds. However, they give a less pronounced positive result. In the same way, you can prepare infusions for hydronephrosis from caraway seeds.
Help with 2.3 degrees
A more severe anomaly, and to restore the outflow of urine, surgery is more often prescribed. With degree 2 hydronephrosis, you can still limit yourself to using effective folk remedies that have saved people from illnesses before.
Herbs of refreshing fireweed, sensual mint, celandine and knotweed, merging together, form a medicinal collection. You can add marshmallow root, coriander and alder cones to the mixture.
Take 2 tbsp. spoons of the resulting mixture and pour 250 ml of boiling water. Drink 50 ml 3 times a day. Course duration is 2-3 weeks.
At the third, most advanced and difficult to treat stage, surgical intervention is indispensable. In 99.9 percent of cases, the outcome is favorable.
Prevention
It is difficult to prevent the congenital form of the disease. To do this, you need to plan your pregnancy and undergo a medical examination while carrying the baby. The expectant mother needs to avoid contact with teratogenic substances, not drink alcohol and not smoke. To prevent acquired hydronephrosis, it is necessary to:
- promptly treat diseases of the urethra, bladder and ureters;
- dress warmly in cold weather;
- Healthy food;
- drink more clean water;
- exclude injuries;
- observe the rules of intimate hygiene;
- do not engage in casual sex;
- empty your bladder in a timely manner;
- do not be stressed;
- to refuse from bad habits.
Development of the disease in the fetus
One of the congenital pathologies in children is a defect of the genitourinary system, which manifests itself in the form of renal hydronephrosis.
The disease begins with intrauterine development. The patient is on the verge of death and life. If the disease is detected in time, the opportunity to save the child’s life increases several times.
The most common causes of the disease:
- Urinary dysfunction;
- The presence of an additional vessel in the right or left kidney;
- The kidney has a horseshoe shape;
- The left kidney is affected by multicystic disease.
The exact causes of hydronephrosis have not been established.
Scientific research has found that the main risk categories include women carrying a child.
Aggravating factors contributing to the development of intrauterine renal hydronephrosis:
- Unfavorable environment;
- The impact of environmentally unfavorable zones on the intrauterine development of the baby;
- Effect of ionizing radiation;
- Genetic factor.
When a child is born with kidney pathology, a married couple needs to contact the family center with a request to conduct a genetic examination to avoid a recurrence of the pathology.
Therapeutic principles of treatment include the following steps:
- Lack of conservative therapy for the fetus;
- Carrying out surgical intervention in case of risk of kidney rupture;
- Hospitalization for the purpose of continuous monitoring of the fetus.
To ensure the normal course of pregnancy and eliminate the occurrence of contraindications, fetal catheterization is necessary.
After birth, if hydronephrosis of the kidney is confirmed, surgery is necessary. The prognosis for treating the disease can be said with confidence that it depends on the stage of development of the disease, its timing, and the characteristics of the mother.
Forecast
The outcome of the disease can give various indicators. The prognosis depends on the course of the operation and possible complications. After surgical intervention, half of the patients experience complications that lead to repeated operations, systematic hospitalization and continuous therapy. If hydronephrosis has developed only on the left or only on the right, then the prognosis is relatively favorable, since even with a severe form of the disease, one kidney can be removed, thereby saving the entire body from infection and further diseases.
In case of dual diagnosis, surgical intervention is not always effective. And although double hydronephrosis is too rare, the patient may not survive without transplantation of at least one kidney, since in most cases there are all indications for the removal of both kidneys, which is incompatible with life. If, nevertheless, both kidneys can be saved, then every second patient is diagnosed with renal failure. As with other diseases, the prognosis depends on the period and stage. The sooner the operation is completed, the greater the chances for a full, healthy life.
In 90% of cases, children under three years of age lead a normal life after surgery. Good results are determined in 80% of children aged 3 to 15 years. Adults recover completely in fifty percent of cases.
Pyelonephritis Urolithiasis Prostate adenoma - what is it? Symptoms and treatment Glomerulonephritis Hepatitis C: first signs and treatment regimen Diabetes mellitus
Degrees of development of left-sided flow
There are several stages of development of the disease; at the initial stage it is difficult to recognize.
Later, a list of characteristic signs appears that help to recognize and classify hydronephrosis.
First stage
At the initial stage of development, the pathological process is difficult to recognize, since the outflow of urine is not impaired. The kidney does not function fully, the ureteral duct is narrowed, but not completely blocked. A healthy kidney compensates for the work of the affected organ.
Second phase
At stage 2 of development, the pathological process is clearly expressed, but it is not possible to notice its development without carrying out characteristic diagnostic procedures.
But you can suspect the presence of hydronephrosis if you evaluate the characteristic symptoms, compare them and carry out a number of diagnostic procedures that can help make a diagnosis.
At the second stage, the outflow of urine is completely disrupted, the kidney cannot perform its functions, and various complications arise. This is what makes the disease dangerous.
Prognosis and possible complications
Hydronephrosis is a very serious pathology. But with timely access to doctors, according to statistics, 95 out of 100 patients recover . With bilateral kidney damage, the prognosis is not so favorable, but even in this case, doctors find an opportunity to save the patient by prescribing regular hemodialysis.
If you contact doctors late, the prognosis is disappointing. Advanced hydronephrosis can lead to:
- urolithiasis (prolonged stagnation of urine leads to the formation of kidney stones);
- nephrogenic hypertension (against the background of renal dysfunction, hypertension (high blood pressure) develops, which is difficult to treat with medication);
- pyelonephritis (inflammation occurring in the kidneys);
- sepsis (infection can spread throughout the body);
- renal failure (due to prolonged stagnation of urine, the kidney may lose the ability to produce it);
- lethal outcome (prolonged stagnation of urine can lead to rupture of the kidneys and spillage of contents into the abdominal cavity, resulting in the development of uremic coma, and subsequent death may occur).
Hydronephrosis that does not receive adequate treatment can lead to the development of pyelonephritis
It is useful for patients who have suffered hydronephrosis to exercise, but only in gentle forms. Heavy physical activity (for example, weightlifting) is strictly prohibited. Yoga classes are very useful. In each case, the recommended amount of physical activity is discussed with the doctor individually.
Conservative treatment
Quite long-term therapy is prescribed when pathology occurs as a result of inflammation in the genitourinary organs (due to urolithiasis). The specialist prescribes a course of medications and determines the diet. All medications are prescribed to eliminate infectious and inflammatory processes. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents are used. To dissolve and further remove stones, diuretics and uroseptics are prescribed. Pain can be relieved with the help of antispasmodic and painkillers. To treat hypertension, ACE inhibitors are prescribed, which normalize the patient's blood pressure.
Urolithiasis
Among the acquired causes, the most often cited is a violation of the outflow of urine due to obstruction of the tract by stones - urolithiasis. Inflammatory and infectious pathologies and tumor-type formations in the organs of the urinary system and prostate gland can lead to defects in the passage of urine in men. Hydronephrotic transformation of the left kidney in women occurs due to fungal and viral infections, against which various inflammations, malignant and benign formations of the genitourinary organs develop.
Hydronephrosis during pregnancy
Hydronephrosis often appears in expectant mothers due to physiological changes caused by pregnancy. The cause of the disease is compression of the ureter by the enlarged uterus. In pregnant women, the right organ is most often affected by hydronephrosis. Hydronephrosis in pregnancy has the ability to resolve without treatment after the birth of the child.
This pathology is not an indicator for abortion; doctors call it true hydronephrosis of pregnancy. If a woman develops chronic hydronephrosis during pregnancy, this threatens severe complications during childbirth. Prevention of hydronephrosis - prevention and timely treatment of diseases that cause fluid in the kidney, general strengthening of the body's defenses.
Diagnostic methods
If renal pathologies are suspected, the patient should consult a urologist or nephrologist. The doctor will initially examine the patient and ask him about bothersome symptoms. During palpation (feeling), the doctor may detect a stretched bladder or an enlarged kidney, but such data is not enough to make a diagnosis, so doctors prescribe a comprehensive examination.
Diagnostics includes the following studies:
- Analysis of urine. This study allows us to identify typical signs of kidney dysfunction. Blood streaks, leukocytes, and purulent discharge may be found in the urine.
- Blood analysis. An increase in ESR and leukocytes in the blood indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Blood biochemistry. This analysis in case of development of hydronephrosis will show increased levels of creatinine and urea.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys. Diagnosis is carried out in different positions (on the back, side, stomach). Ultrasound determines the size of the kidneys, assesses the condition of the parenchyma, cups, and pelvis. The study gives an idea of the patency of the ureter and the presence of stones in the kidneys.
The doctor can see the pathological enlargement of the kidney using an ultrasound examination.
- X-ray contrast studies. Using a contrast liquid injected into the urethra or vein, the rate of urine accumulation in the kidneys is determined, narrowing of the ureter is detected, and the location of blockage with stones is identified.
- Endoscopic examination. An endoscope is used to examine the condition of the urinary tract.
An endoscopic examination method helps determine the condition of the urethra, bladder and lower ureters
- Dynamic nephroscintigraphy. This is a radioisotope method that allows you to assess the degree of impairment of renal blood flow.
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography. MRI and CT are recognized as the most accurate diagnostic methods. Such studies make it possible to determine the causes of obstruction and clarify the degree of kidney damage.
Hydronephrosis causes symptoms similar to some other ailments. Therefore, the urologist must carry out a differential diagnosis with urolithiasis, nephroptosis (prolapse of the kidney), and polycystic disease.