Prostate adenoma is a serious male disease. It manifests itself in the pathological proliferation of prostate tissue located next to the urethra. The gradual development of the tumor leads to compression of the urethra and disruption of the urination process, as well as a number of other changes in the body, for example, blood appears in the urine.
Scheme of prostate adenoma
According to statistics, benign prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma) is diagnosed in 50% of men over 50 years of age and in almost everyone after 80, which indicates the widespread prevalence of the disease among older people. The first signs of the disease can be noticed already at 40. In addition to the age factor, there are other reasons that provoke the occurrence of prostate adenoma. Among them are:
- incorrect hormonal levels;
- diseases of the kidneys and the entire urinary system of an inflammatory nature;
- injuries;
- urinary tract infections;
- passive lifestyle;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits;
- lack of regular sex.
Some evidence also suggests that there is a hereditary predisposition to the disease.
Although prostate adenoma is considered a benign tumor, that is, it does not pose an immediate danger to the patient’s life, it is necessary to see a doctor. Prostate adenoma is dangerous, first of all, because as it develops it can provoke a lot of complications in the form of other diseases, the treatment of which will take a long time.
Features and possible complications of the bladder after removal of adenoma
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! The only remedy for CYSTITIS and its prevention, recommended by our subscribers! Read more…
After surgery to remove an adenoma, problems that occur for several months are normal and are considered part of the recovery period.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Need for a catheter
After removal of the adenoma, a special catheter is inserted through the urethra into the bladder for better wound healing. It is necessary for the outflow of urine and is a tube with an inflatable balloon attached to the end. After the procedure, the surgeon inflates the balloon and helps the patient secure it in place. In this case, the catheter is connected to a bag for collecting urine.
The need for a catheter is determined not only by wound healing, but also by preventing urinary retention, which occurs due to postoperative edema. The procedure helps clear blood clots after surgery.
The length of time the catheter remains in the bladder depends on the type of surgery. For example, laser vaporization allows you to remove it a day after the procedure. The use of transurethral resection of adenoma does not allow removing the catheter for 2–3 days.
Removing the catheter
The catheter removal procedure does not cause discomfort or pain to the patient. The balloon is deflated and carefully removed from the bladder. Painful sensations during urination may occur for some time, but will pass.
After removal of the catheter, it is normal to experience frequent urge to urinate, leakage of urine due to coughing or sneezing, and minor bleeding that should stop within 24 hours.
Urinary problems
The postoperative period for removal of prostate adenoma may be accompanied by pain and urgency. This is because when you urinate, urine enters the surgical wound, causing discomfort.
Sometimes patients observe a urine stream that has become stronger. The process of restoring the bladder after surgery to remove prostate adenoma takes about a month or a little longer. As a result, urination will become easier and the urge will become less frequent.
Urinary incontinence
During the process of rehabilitation of the patient, urination is gradually restored, and the bladder returns to normal. But, the recovery period may be associated with a problem in the form of urinary incontinence. This is primarily influenced by the degree of damage to the sphincter. There are incontinence that occurs due to stress on the urinary system and permanent (complete).
- Coughing, exercising, or laughing can trigger unwanted urination.
- Urinary incontinence (total) can be observed in those who have suppressed the urge to urinate for many years. This category includes people whose work was associated with a shift schedule (drivers, doctors, teachers). It is accompanied by a lack of urge.
- Among the reasons that caused the problem are Parkinson's disease, neurological pathologies, urinary tract infections, and constant stress.
Usually, after removal of an adenoma, urinary incontinence is not treated; it goes away over time, as the urinary system is restored. In individual cases, consult with a specialist.
Blood when urinating
In the first postoperative weeks, blood may appear in the urine. In many cases, their appearance does not indicate problems and goes away on their own. Often this situation occurs after transurethral resection and is the norm. The first days after surgery to remove an adenoma, the patient may observe urine that is intensely colored with bloody discharge. Over time, the amount of impurities will decrease.
An alarming signal will be the regular presence of blood in the urine, even while following the drinking regime. The patient also needs rest. In this case, it is important to consult a doctor who will determine the cause of the bleeding and take measures to eliminate it. In rare cases, a blood transfusion is required and is regarded as a complication of the postoperative period, which can be prevented by following strict doctor's recommendations. General rules include drinking plenty of fluids and limiting coffee. The patient should refrain from lifting heavy objects.
The presence of blood in the urine can be caused by rejection of the crust that has formed in the resection area. This problem does not require medical intervention and goes away on its own.
A flushing system that helps flush out blood clots and prevents blockage of the urinary canal can help prevent blood clots. After this, a catheter is installed.
Urinary retention
Acute urinary retention is caused by blockage in the urethra with a blood clot or a piece of tissue after resection. The problem can be avoided by inserting a catheter into the bladder.
Urinary retention after removal of an adenoma can be caused both by tissue changes during the long-term existence of the problem, and by technical errors on the part of the surgeon during the operation.
During an inflammatory disease, there is a possibility of narrowing of the urethra, which is called urethral stricture. Also, its occurrence is provoked by trauma as a result of the movement of medical instruments along the canal. In rare cases, the stricture is congenital.
The appearance of infections in the urinary system
In rare cases, a urinary tract infection may occur, which is accompanied by chills, pain in the lower abdomen, fever, nausea, or cloudy urine.
The situation arises due to the patient’s failure to comply with doctor’s recommendations and personal hygiene.
To prevent complications after surgery to remove an adenoma, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, which are taken as prescribed by a specialist.
By secret
- Incredible... Chronic cystitis can be cured forever!
- This time.
- Without taking antibiotics!
- That's two.
- During the week!
- That's three.
Follow the link and find out how our subscribers do it!
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
×
Blood in urine after catheter
Urinary catheters are used in cases of urinary incontinence or retention. The catheter is a hollow tube. In order to eliminate the possibility of injury to the patient, narrow tubes are used. Wide tubes are needed for long-term use. Catheters are installed in both men and women. Features of the physiological structure complicate the installation of a catheter in men.
The catheter is inserted into the urethra and advanced along the urethra. A urinal is attached to the end. Blood in the urine after insertion of a catheter is a normal symptom. Or rather, it indicates careless installation of the device. This should only be done by a qualified nurse. Under no circumstances should you do this procedure yourself, otherwise you may damage the urethra. Blood in the urine after this procedure should go away within a few days.
Bladder instillation - what is it?
The genitourinary system is often exposed to the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms that cause various pathologies, including: cystitis, urethritis, leukoplakia, malignant growths, as well as sexually transmitted diseases. Modern methods of treating diseases of the genitourinary system allow you to achieve quick results, avoiding the side effects of medications. One such method is bladder instillation.
The method involves administering medications using a catheter and syringe directly into the bladder. The method has earned popularity due to its effectiveness and the absence of negative effects on the kidneys, liver, blood and central nervous system.
Advantages of the method
Most often, local therapy, or instillation, is carried out using antiseptics, ozonated solutions or antibacterial drugs, and has undeniable advantages over general treatment methods. These include:
- penetration of injected drugs into the deepest layers of the walls of the bladder, which gives a quick antiseptic effect, even in cases of severe, chronic disorders;
- injection of the drug directly into the lumen of the bladder allows for a longer lasting effect;
- local infusion of drugs acts specifically on the affected area of the bladder and does not have any effect on other organs;
- allows the administration of much larger doses of medications, since they do not accumulate in the circulatory system.
Indications and contraindications
Instillation is indicated if it is necessary to restore the mucous membranes of the bladder. The procedure is prescribed for various inflammations and cystitis, even in fairly advanced, chronic conditions. The method is also used to treat malignant tumors, quite successfully destroying cancer cells.
Procedures are prescribed only after diagnostics and examination of the genitourinary system with a cystoscope. If the oncological nature of the disease is suspected, a biopsy is additionally analyzed.
Despite the fact that bladder instillations for chronic cystitis are considered the most effective treatment, the acute form of the same disease is a complete contraindication to the procedure. Therapy is not allowed for inflammatory processes in the area of the external genitalia in women and for tuberculosis of the genitourinary system.
Features of instillations in women
The indication for the procedure in women is most often regular chronic cystitis or other diseases that lead to damage to the mucous tissues of the bladder. In order to speed up the process of mucosal restoration, in addition to the mandatory antibiotics, patients are prescribed infusions of healing and anti-irritation drugs.
Bladder instillation in women with chronic cystitis can reduce or stop taking antibiotics completely. Possible side effects include the development of individual intolerance to a number of components and the patient’s tendency to allergies.
The main tasks of instillations for chronic cystitis:
- reduction of inflammatory foci and irritation;
- restoration of mucous tissues of the urinary tract;
- elimination of infection.
In order for the procedure to have a therapeutic effect, the necessary diagnostic measures must be completed before the procedure.
Instillations in men
For the stronger half of humanity, instillations are most often prescribed for prostate diseases or urethritis. The anatomical structure of the male genitourinary system is much more complex than the female one, and therefore longer treatment is required.
With the development of inflammation, the depressions located in the urethra in men shrink, as if fencing off from the surrounding tissues. Thus protecting the body from the spread of infection. Standard treatment in the form of taking tablets does not always give the desired result, since the concentration of medications is not enough to reach all areas of the bladder affected by bacteria. As a result, the infection remains untreated and after some time a relapse of the disease occurs. That is why most experts advise immediately starting therapy using the instillation method, which will allow achieving the required concentration of drugs in the affected areas.
The main symptoms of prostatitis and urethritis in men are:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- it becomes painful when urinating;
- itching and burning occurs in the genital area;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- potency becomes worse;
- blood or purulent inclusions may appear in the urine;
- urination becomes difficult, and the feeling of a full bladder does not leave;
- weakness, apathy and depression develop.
How is bladder instillation performed?
After collecting tests and making an accurate diagnosis for both men and women, the specialist begins treatment. Before instillation, the patient should refrain from urinating for 2–3 hours; it is not recommended to urinate immediately after the procedure.
To deliver the required volume of medication to the affected area, a special catheter is used, mounted on a syringe with medication. As a rule, a number of the following drugs are used for instillation:
- boric acid solutions;
- silver nitrate;
- corrosive sublimate;
- rivanol;
- instillogel;
- dioxin solution;
- collargol;
- disinfectants and antibacterial drugs;
- penicillin drugs;
- methylene blue solutions;
- oils from sea buckthorn, petroleum jelly, rosehip, etc.
Before inserting the catheter, the skin surface is treated with an antiseptic. The procedure does not cause any discomfort and does not require anesthesia. The diameter of the catheter and syringe is selected individually. Instillation of the bladder in men is carried out with a longer and thinner catheter, which can easily overcome all the bends of the rather narrow urethral canal. For women, instillations are performed in a gynecological chair. The volume of medications in one session should not exceed 100 ml.
In addition to the main functions: cure for chronic cystitis, urethritis and prostatitis, instillations can restore urodynamics in men, destroy existing stones in the bladder and much more. To restore positive microflora, in addition to medications, bladder instillations with sea buckthorn or rose hip oils are used. This type of therapy shows faster recovery dynamics in both women and men, making it possible to eliminate even the most advanced and severe disorders of the genitourinary system.
Blood in urine after biopsy
A biopsy is also an intervention through which tissue is taken. They are examined for the presence of tumors or other pathological changes. The intervention method has been around for a long time and is considered indicative and effective.
A biopsy can identify serious illnesses, but side effects may occur after any intervention. A biopsy may result in blood in the urine. The patient will probably be scared, but the symptom is not so terrible. This is banal damage to the mucous membranes during the procedure. The blood should disappear within a few days. Otherwise, you need to seek help from a doctor.
Surgical interventions, installation of probes and catheters - all these procedures, one way or another, are traumatic. It is also possible to develop complications that can cause symptoms such as blood in the urine. It is important to monitor your condition after operations and manipulations and not miss even those changes that seem insignificant. It is better to tell the doctor about them, and he himself will assess the degree of their danger.
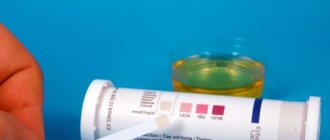
In some chronic and acute pathological processes, the key symptom is blood in the urine - hematuria; in men and women it is sometimes accompanied by pain and burning of the urethral opening. Urination may be painful, there is a deterioration in general condition, and a rise in body temperature. Diagnosis of hematuria is carried out using a visual examination of the color of urine (see examples in the photo) and laboratory tests.
Causes of difficulty urinating in women and methods of treatment
Difficulty urinating in women (strangury) is a group of symptoms caused by a violation of the natural emptying of the bladder. Manifestations of strangury are observed in 30-35% of cases when patients consult a doctor about gynecological or urological diseases. The causes of urinary disorders are pathologies of the urogenital and nervous systems.
Causes
Delayed urination (urination) can be caused by organic disorders of the genitourinary system:
- urolithiasis;
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- inflammatory diseases of the cervix and vagina;
- endometriosis;
- herpes zoster;
- periurethral abscess (damage to gonococcus);
- echinococcosis (formation of cysts in organs due to the introduction of echinococcus);
- anomalies in the development of the system.
Mechanical obstacles to urine excretion are caused by:
- compression of the urethra by a tumor or other neoplasms;
- tumors in adjacent organs;
- blocking the outflow with a calculus (stone);
- stricture or spasm of the urethra;
- accumulation of feces;
- aneurysm.
Urine excretion may be difficult due to disruption of the location of organs as a result of:
- weakening of the muscles that fix the organ;
- pregnancy;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Functional urination disorders in women are caused by:
- mental illness;
- injuries, surgical treatment of the brain or spinal cord;
- exposure to psychotropic drugs, narcotic substances, ethyl alcohol.
Difficulty urinating is influenced by external factors:
- low temperatures causing hypothermia;
- psycho-emotional overload, stress;
- limitation of physical activity, immobilization due to pathology.
Changes in hormonal levels, age-related characteristics and drug treatment also affect urination.
Urinary retention can be caused by ischuria, in which the bladder is filled with urine, but in the morning or during the day the outflow of fluid is scanty or stops altogether. Another type of pathology is anuria, in which fluid is not released into the reservoir.
Neurological diseases
Neurological causes of difficulty urinating in women are due to:
- Damage to peripheral innervation caused by diabetes mellitus, polio, surgical treatment of the pelvic organs, spinal cord injury, autoimmune polyradiculoneuropathy (muscle weakness), tick-borne borreliosis, autonomic neuropathy (nerve damage).
- Impaired functions or damage to the structure of the brain (BM), provoked by a concussion of the brain, pathology of the blood vessels of the brain, multiple sclerosis, neoplasms, Parkinson's disease, Shy-Dragen syndrome (death of nerve cells), hydrocephalus (dropsy of the brain).
- Pathologies of the spinal cord (SC) caused by intervertebral hernia, meningoencephalitis (inflammation of the brain matter and its membranes), multiple sclerosis, hemorrhage in the SC, narrowing of the lumen of the SC canal, impaired blood supply to the SC, tumors of the SC.
Urination is often difficult in patients who have had a stroke or heart attack. Frequent stress also leads to urinary dysfunction. The cause of reflex urinary retention can be hysterical neurosis.
Inflammatory processes
Difficulty urinating in women can be caused by inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system and gastrointestinal tract. Most often, problems with urination are caused by cystitis, which is diagnosed in women 30 times more often than in men.
The disease may be bacterial in nature or caused by sexually transmitted infections. Cystitis causes spasm of the bladder, which impairs urine output.
Inflammation of the bladder of various etiologies leads not only to reflex spasm, but also to pathological changes in the detrusor (muscle) - disruption of its functions and elasticity, which affects the volume of the bladder and the ability to consciously empty. The cause of urination problems can be peritonitis and general blood poisoning.
Mechanical damage
Strangury in women is caused by mechanical damage. Difficulty urinating develops against the background of fractures of the pelvic bones, rupture of the walls of the bladder, and damage to the urethra. Instrumental methods for examining the urinary system and placing a catheter may result in mechanical injury.
A blunt blow to the lumbar region or a fall on the back damages the kidneys, which can lead to difficulties with the outflow of urine. A blow to the suprapubic region with a full bladder leads to rupture of its walls, the formation of hematomas, blood clots that block the removal of fluid to the outside.
The cause of mechanical damage to the organs of the urinary system is a penetrating wound to the abdominal area. The causes of problems with urination in women may lie in injuries received as a result of difficult childbirth. The incidence of urinary retention in the postpartum period is 1.7-17.9% of cases. Risk factors are: cesarean section, instrumental obstetrics, epidural anesthesia (anesthetic is injected into the SM).
Main symptoms of urinary dysfunction
Difficulty urinating in women is accompanied by:
- pain due to stretching of the walls of the bladder when it overflows;
- discomfort - pain, burning, itching;
- long wait for the first jet;
- difficulty with the release of the first portion of urine, which requires tension in the abdominal muscles;
- the inability to completely empty the bladder at one time - urine is released after urination;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- hematuria;
- The stream during urination is sluggish and intermittent.
Blood in the urine is observed both with inflammation of the bladder and with mechanical injuries to the organ or urethra. Painful urination is the most common symptom. Other manifestations may or may not occur, and the degree of their severity varies. In acute ischuria, the symptoms are most pronounced. In chronic cases, they are smoothed out or absent.
In women, urinary disturbances may be accompanied by discharge from the genital tract of varying color and consistency. Sometimes the pathological condition leads to a febrile syndrome.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods depend on the cause of the pathology and include:
- laboratory techniques: blood test - clinical, biochemical; urine tests; biochemical analysis of urine to determine the type of pathogen; determination of blood glucose levels;
- instrumental visualization methods: ultrasound, MRI and CT;
- other research methods: cystoscopy (examination of the inner surface of the bladder using an endoscope), uroflowmetry (determining the rate of urination with a uroflowmeter).
Other research methods are also used, for example, the size and filling of the bladder can be determined by palpating and tapping - percussion.
Women are required to undergo a gynecological examination and a smear test.
If a neurogenic bladder is suspected, specific tests and a complete neurological examination are performed.
Treatment
Based on the examination results, the patient is prescribed therapy, the regimen of which depends on the individual characteristics of the pathological condition. Treatment includes:
- conservative methods: drug therapy, physiotherapy, lifestyle correction, diet therapy;
- surgical treatment;
- traditional medicine methods.
Conservative
The initial stage of conservative treatment is the forced release of the bladder from its contents using a soft catheter. To restore urination after removing the tube, drugs from the group of α-blockers are prescribed - Tamsulosin, Omnic, Proflosin. In order to reduce the risk of relapse of the pathological condition, α-reductase inhibitors are prescribed - Avodart, Proscar.
When identifying and establishing the type of pathogen, it is necessary to use antibacterial, antiviral or antimycotic drugs under the supervision of a urologist.
If the balance of hormones is disturbed, hormonal therapy is carried out. The selection of drugs is determined by the individual characteristics of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, and allergic reactions.
For a neurogenic bladder, sedative medications are prescribed, and the patient is advised to visit a psychologist.
In combination with drug therapy, physiotherapy is used - electrical stimulation of the detrusor, baths, wraps, electrophoresis with drugs.
Of great importance in the effectiveness of conservative therapy is lifestyle correction - giving up bad habits, physical activity, and playing sports.
To normalize urination, diet therapy and vitamin therapy are used to strengthen the immune system, correct body weight, and stimulate plastic and recovery processes.
With the help of drug therapy, natural urination can be restored. If conservative methods do not give the expected effect, surgical treatment of the pathology is resorted to.
Surgical
Surgical intervention is indicated in the case of:
- mechanical disturbance of urine outflow;
- detection of tumors;
- malignant process;
- injuries;
- developmental anomalies;
- sphincter insufficiency.
Methods of plastic and reconstructive surgery, minimally invasive techniques using laser and ultrasound equipment are used.
What is vascular impotence and how to treat it?
Vascular impotence dysfunction, impotence (Latin impotens - powerless) - erectile dysfunction, in which the volume of a man's penis, its hardness and straightness are insufficient for sexual intercourse, is the main cause of developed erectile dysfunction in men. Taking into account the statistics of admitted patients, specialists record more than 55% of patients who are diagnosed with this particular pathology.
Anatomy of the penis
In order to understand the importance of proper and complete blood supply to the penis, an organ of the body (arm, leg, finger, ear, etc.), now often used in the meaning of “penis” (for the implementation of a healthy erection), it is necessary to have an idea of the structure of this organ.
The male penis consists of porous tissue, similar in structure to a sponge. The cavities that make up this sponge are called sinuses. They are supplied with blood through branches from 2 large arteries that run along the entire length of the penis and communicate directly through the walls that form them.
In addition, the structure of the penis is composed of 2 cavernous bodies, which also communicate with each other through a common blood flow. Visually, these bodies are separated by the same large vessels that go from the root of the member to the organ of the body (arm, leg, finger, ear, etc.), now often used in the meaning of “penis” to its head. In the same direction is the urethra, through which urine is removed from the body. It also goes from the root of the penis to its head and is surrounded by a dense layer of sinuses.
Structure of the penis
The circulatory system is a set of elements that are in relationships and connections with each other, which forms a certain integrity; the unity of the penis is a closed hydrodynamic system. That is, blood is supplied through the artery to the sinuses of the corpora cavernosa, from where it flows into a spiral-shaped vein that runs around the entire penis to its root.
There is a set of muscles involved in erection during sexual arousal. However, a man cannot control these muscles; they are very different in structure from skeletal ones.
Erection: the order of passing through all stages of the process
If we consider an erection in relation to the simplest mechanics, it becomes clear what vascular impotence is in principle. Sexual arousal, transmitted by signals from the central nervous system, is a set of elements that are in relationships and connections with each other, which forms a certain integrity, unity, increases the lumen in the arteries that supply blood to the sinuses of the cavernous bodies. At the same time, the muscles at the root of the penis (arm, leg, finger, ear, etc.), which are now often used in the meaning of “penis,” contract, which compress the veins that ensure the outflow of blood. That is, blood is a liquid, mobile connective tissue of the internal environment of the body, which consists of a liquid medium - plasma and cells suspended in it - formed elements: leukocyte cells, post-cellular structures, enters the penis, but does not flow out of it. Under the influence of blood, the sinuses stretch, thereby enlarging the penis several times and making it hard and elastic.
Disruption of this process occurs at 2 points - incomplete and insufficient blood supply through the arteries, or too rapid outflow of blood through the veins.
How does an erection occur?
Causes of vascular impotence
Impotence of vascular origin can occur for a number of reasons:
- The arteries supplying blood to the cavernous bodies of the penis are completely or partially blocked by atherosclerotic plaques. They, in turn, form on the walls of arteries from excessive cholesterol in the blood or as a result of damage to the walls of the vessel.
- Systemic arterial activity is impaired in diabetes mellitus. As soon as the blood sugar level changes, blood flow can be disrupted in any part of the body, including the pelvis, which will affect sexual power.
- Heart disease leads to the fact that it cannot maintain the required pressure in the arteries of the reproductive system. Such pathologies include coronary heart disease or myocardial infarction.
- Long-term high blood pressure, called hypertension, leads to disruption of the vascular system; many elements are in relationships and connections with each other, which forms a certain integrity, the unity of the body. The reproductive system of a man, a person of male sex or gender, also suffers from this, since it is extremely sensitive to any malfunctions. In addition, taking antihypertensive drugs has a side effect in the form of impotence.
- There is a possibility of disruption of the proper functioning of the vascular system in the pelvic organs as a result of physical trauma. This phenomenon is most often observed in young men living an active social and sports life.
- The causes of impotence in men can be caused by dangerous habits such as smoking, alcohol abuse, spicy and fatty foods. All these actions lead to the fact that the walls of blood vessels Vessels - a tubular organ in animals and plants through which a liquid medium moves - lose their elasticity, the outflow of blood, the liquid mobile connective tissue of the internal environment of the body, which consists of a liquid medium - plasma and cells suspended in it - formed elements: leukocyte cells, post-cellular structures through veins dilated, for example by alcohol, stops an erection of any strength.
- The most common cause of vascular impotence is old age. Over the years, the functions of the reproductive system fade away along with the entire body.
- Vascular disorders in the reproductive system occur after surgical operations on organs adjacent to the penis.
- A sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity, in particular on the pelvic muscles, lead to the fact that the arteries, veins and muscles in the male reproductive system lose their tone and ability to contract and expand.
A sedentary lifestyle is one of the causes of vascular impotence!
Diagnosis of vascular impotence
As soon as symptoms of impotence appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. After all, any disease of the blood vessels and organs of the reproductive system can be cured if the pathology is recognized correctly and in time and does not lead to a severe and sometimes incurable form.
First of all, the doctor interviews the patient. Finds out his habits, diet and daily routine.
Then the patient is sent for laboratory blood tests. During these tests, the presence and level of cholesterol in the blood is determined to exclude or confirm atherosclerosis.
An electrocardiogram is required. This is necessary to determine whether the patient has heart diseases that can affect the condition of blood vessels throughout the body and in the reproductive system, including. The main method for diagnosing vascular diseases in this situation is Doppler ultrasound of the arteries and veins in the male reproductive system. Only a comprehensive study of the problem can help to correctly diagnose not only vascular impotence itself, but also the causes of its occurrence.
Treatment of vascular impotence
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment begins. It is clear that first of all, the disease that caused disruption of the functioning of blood vessels in the reproductive system is treated. For example, with ischemic disease, attention is paid to the heart, with atherosclerosis, treatment of atherosclerotic plaques begins, with hypertension, blood pressure is normalized, etc. Of course, treatment is carried out on the veins and arteries that directly supply the penis with blood; the liquid mobile connective tissue of the internal environment of the body, which consists of liquid medium - plasma and cells suspended in it - formed elements: leukocyte cells, postcellular structures. The operation of the valves on the veins that drain blood from the penis is adjusted.
When conservative treatment, a process whose goal is to alleviate, relieve or eliminate the symptoms and manifestations of a disease or injury, pathological condition or other disability, does not bring results, vascular disorders are treated surgically. The bypass method is widely used - when a donor vessel is laid around the blocked artery, ensuring normal blood circulation in the penis. To reduce the risk of rejection, an artery taken from the patient's own thigh is used.
In a situation where an enlarged vein has an increased outflow of blood, such a place on the vessel is cut out, that is, a resection is performed. Treatment of vascular impotence with this method often ends in relapse, so resection is carried out on the extensive network of veins that provide blood flow from the penis. In this case, the erection remains until old age.
How to prevent the development of vascular impotence?
Prevention of vascular impotence
Whatever the origin of vascular pathology, it is much wiser and easier to prevent its development by using some prevention methods:
- In order for the blood vessels to keep their walls elastic and strong, you should adhere to a proper diet - you should not eat spicy, fatty, smoked, or fried foods. You should consume more fresh vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins.
- You should not abuse alcohol or smoke cigarettes. This destroys the walls of blood vessels in just a few years.
- To keep muscles and blood vessels in good shape, it is necessary to exercise regularly, especially if a man is engaged in a sedentary job. You need to walk or bike more.
- The nervous system also needs proper care. After all, without the correct functioning of the central nervous system, the signal about sexual arousal simply will not be generated or will not reach the reproductive system. To do this, you should follow a certain daily routine - you need to get up and go to bed at the same time, you need to sleep at least 7 hours a day.
- Stressful situations should be avoided. If work becomes the source of your worries, then you should look at it from a different perspective and perhaps even change your field of activity. After all, nothing compares to the health of the body and the opportunity to live a full sex life until old age.
In addition, it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations (at least once a year); you should not spare any money or effort on this. It will pay off in the end with a long and happy life.
What to do if there is blood in your urine
First of all, you need to visit a therapist and take a general urine test. Next, the results of the analysis are sent to a specialized specialist - a urologist. To identify the presence of a particular pathology, ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys is used. Concomitant symptoms play an important role, so the doctor questions the patient for their presence. Let's look at how hematuria is treated depending on the cause of its occurrence.
- If this symptom is caused by an inflammatory disease, a course of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed. As an additional therapy, medicinal baths can be prescribed.
- If we are talking about serious kidney damage (polycystic disease), surgery may be necessary. As an operation, sometimes they resort to the complete removal of one of the kidneys.
- If the bleeding is caused by the presence of kidney stones, surgery is prescribed. Depending on the size of the stones, a crushing method or a full-fledged operation to remove them may be used.
- If there is a suspicion of cancer, it is necessary to take kidney biomaterial (biopsy). If a malignant tumor is detected, the doctor suggests surgery and a course of chemotherapy.
Preventive actions
In order to prevent the development of such an unpleasant symptom as the presence of blood clots in the urine, it is recommended to follow preventive measures.
- use thongs as little as possible;
- maintain hygiene daily;
- empty your bladder at the first urge;
- undergo medical examinations and general tests once a year;
- Before taking any medication, consult your doctor.
In any case, hematuria in the urine is not normal. Even if nothing besides the main symptom bothers you, be sure to contact a specialized specialist to identify the nature of this symptom. Even if there is no pain, blood in the urine may indicate serious pathologies that need to be treated promptly.
What is blood in urine
Hematuria is the presence of red blood cells - erythrocytes - in the urine. They are present due to inflammatory processes of tissues, organs, mechanical damage, and internal bleeding. The condition is a marker of chronic infections in the genitourinary system. Hematuria is divided into macrohematuria and microhematuria (occult blood) based on the number of red blood cells. Microscopic hematuria cannot be detected without the help of a microscope. Large blood clots are found with injuries to the urethra.
Treatment
If blood appears in the urine, a thorough diagnosis and examination of the patient should be carried out and the cause of the veins and blood clots should be identified. It is necessary to begin therapy for the pathology that caused hematuria. Treatment includes:
- stopping bleeding;
- prescription of medications;
- restrictions on movement, bed rest;
- taking vitamins and iron-containing medications if necessary;
- in case of massive blood loss, the patient is indicated for a blood transfusion.
Sign in young women
In young girls, blood usually appears in the urine due to the presence of an inflammatory process. The female genitourinary system is designed in such a way that it is very easy for infections or bacteria to enter the urinary tract cavity. Often the pathology occurs in women who wear thongs.
The most commonly diagnosed cystitis is the hemorrhagic form. In this case, in addition to blood in the urine, accompanying symptoms are observed. For example, a woman complains that it hurts to pee when trying to empty her bladder, this means that there is an infection in the genitourinary system.
If blood in a woman’s urine is observed only during menstruation, this may be the first signal of the development of endometriosis. To diagnose this situation yourself, urine must be collected carefully so that menstrual fluid does not get into the urine from the vagina. To do this, you should thoroughly clean the genitals and close the vagina with a tampon. Your doctor will tell you how to give urine before your period correctly.
Carrying out the procedure in men
Due to the anatomical features of the male genital organ, urologists recommend entrusting the procedure only to specialists. The narrow and long urethra makes it difficult to install drainage into the opening of the urethra.
In addition to a length of up to 25 cm, the canal has 2 physiological narrowings. Manipulations are allowed to be carried out by healthcare workers who have extensive experience and are fluent in the technique of catheterization of the male bladder. Amateurs can only do harm.
Algorithm for performing bladder catheterization in men:
- a previously prepared patient lies on his back on an oilcloth, slightly bending and spreading his knees, between which the reservoir is installed,
- with a hand with a sterile napkin, the specialist supports the penis under the head, providing access to the opening of the urinary canal,
- wipe the head of the penis with a cotton pad soaked in a disinfectant solution,
- a few drops of gel are applied to the opening of the urethra when catheterizing the bladder with a soft or hard catheter for pain relief,
- a flexible catheter is grabbed with tweezers, the rounded edge of which is moistened in Vaseline or glycerin, after which, supporting the head, the tube is inserted 5 cm,
- subsequent insertion of a catheter into men requires care. Grasping the instrument with tweezers, it is carefully moved further along the canal,
- if muscle spasm occurs due to resistance when passing the spongy and membranous section of the canal, you should wait a couple of minutes and continue advancing the catheter,
- the following resistance is felt when the instrument is inserted into the bladder through a physiological narrowing,
- the outer end of the catheter should be lowered into the tray, flowing urine indicates successful drainage of the urethra,
- when the process of urine excretion is completed, using a Janet syringe, 150 ml of furatsilin is injected through the tube to disinfect the inner walls of the bladder, after which the remaining liquid is removed through the drainage,
- using rotational movements, remove a tube 25-30 cm long,
- Gently wipe the head of the penis with a cotton pad soaked in a disinfectant solution,
- all devices are disinfected.
If it was not possible to install a flexible catheter, the doctor independently inserts a hard metal one. This happens in exceptional cases.
The installation technique of such a device requires skill from a specialist. If pain occurs in the patient, the specialist must be informed immediately.
Symptom after childbirth
Blood may appear in the urine after childbirth. There are many reasons for this factor. Most often, blood indicates inflammation of the bladder. The disease can occur for many reasons.
- If a woman gave birth through surgery (caesarean section), then after delivery the woman is given a catheter to collect urine. Blood may occur due to tissue damage during insertion of the catheter, or due to infection in the bladder. In this case, urine after childbirth without blood is very rare.
- Immediately after childbirth, for several days, the woman does not feel that her bladder is full and it is time to empty it. Stagnation of urine provokes an inflammatory process, which is commonly called cystitis.
- After childbirth, a woman’s body is greatly weakened. For this reason, the infection can easily enter the bladder and multiply. Hemorrhagic cystitis often occurs, which is characterized by this symptom.