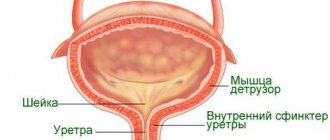
The condition when urine is released in drops after urination (in men is much more common than in women) is called post micturition dribbling (PMD). This is a kind of mild form of incontinence, in which the entire process of urination is controlled, except for the final stage. Normally, the remaining urine should be expelled with several strong contractions of the detrusor (bladder muscle), after which the urethral sphincters automatically close. When dribbling, urine continues to spontaneously leak and leak, which leads to poor hygiene and psychological problems.
Causes of urine leakage in men after urination
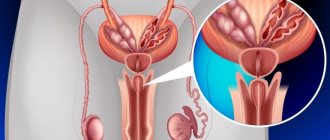
The reasons for the release of urine after urination are weakness or lack of controllability of the muscles of the bladder neck and urethral sphincters . They either constantly remain not completely closed, or they tighten only some time after urination. In the latter case, urine stops leaking. This condition of the sphincters can be caused by anatomical (mechanical) or neurogenic disorders.
Diagram of the location of the urethral sphincters
Prostate pathologies
Both the internal and external urethral sphincters are closely adjacent to the prostate. Inflammation, adenoma or tumor of the prostate gland almost always affects their functionality. During an exacerbation of prostatitis, the tissues swell and the sensitivity of the receptors is impaired. As a result, the nervous system partially loses control over the compression of the sphincter; after urination (usually with pain), residual urine gradually flows out.
The adenoma can grow towards the rectum, bladder or urethra. As the subvesical tumor grows, it raises the neck of the bladder, disrupts its anatomical position, and can compress the sphincters, interfering with their normal closure. With adenoma, dribbling is usually constant, and the amount of urine leaking increases as the bladder fills.
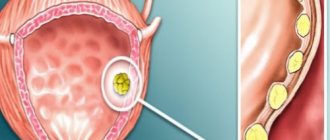
Hypertrophy and inflammation of the seminal tubercle
The seminal tubercle (mound) is located in the prostatic part of the urethra (essentially, in the prostate). With hypertrophy (tissue growth) or inflammation (colliculitis), it moves into the urethra. As a result, its lumen narrows. When urinating, you have to strain, squeezing out urine. The larger the swelling of the tubercle, the more urine remains in the bladder. Its walls and neck lose their sensitivity from constant tension, and urine begins to involuntarily be released drop by drop. The symptom is especially pronounced during coughing, sneezing, and sudden changes in body position.
Location of the seminiferous tubercle
Obstructions in the urethra
Men sometimes complain that they leak urine when they sit down. This can only be avoided by “milking” the penis after urinating. Doctors associate this symptom with prostatitis, provoked by a sedentary lifestyle. Additional signs: periodic tingling in the penis, painful urination.
This is also possible with chronic inflammation of the urethra or the presence of obstacles in it in the form of scars, condylomas, tumors or anatomical “pockets” - diverticula. During urination, part of the urine is poured into the diverticulum or remains behind the tumor. When changing position it flows out.
Bladder diverticula
The cause of urine leakage may be urolithiasis. Sand or small pebbles periodically begin to move “out”, damaging the neck of the bladder, sphincters, and the urethra itself along the way. A pebble can get stuck in the urethra, cause inflammation, become overgrown with fibrous tissue, which will also create an obstacle to the normal outflow of urine. In such cases, blood is often released along with it.
Weak pelvic floor muscles
The pressure of urine during urination is maintained by the bulbocavernosus muscle (also known as the bulbocavernosus muscle). It contracts and compresses the urethra.
The problem of weakening and sagging of the pelvic muscles is typical for older men, but can also occur in relatively young men due to a sedentary lifestyle.
Neurogenic disorders
Urinary incontinence after urination can be caused by a violation of the reflex function of the same bulbocavernosus muscle or urethral sphincters. The muscles relax even before the process of urination is completed, which is why residual urine flows out during any provocation: rapid movement, change of position, physical activity.
The cause of neurogenic dysfunction of the pelvic muscles can be trauma, pathology of the brain or spinal cord. The centers of the nervous system that control urination are located in these organs. When they are damaged, the connection with the receptors of the urinary muscles is disrupted or lost, as a result of which the reflexes are lost.
Involuntary leakage of urine is a common consequence of prostate surgery, during which the neurovascular bundles are damaged. The problem can also arise after a nerve-sparing technique due to damage to the urethra by an instrument or catheter.
Reflex impairment also occurs against the background of Alzheimer's disease, parkinsonism, and multiple sclerosis.
Other reasons
The problem of leakage is significantly aggravated by excess weight and chronic constipation. Visceral fat puts pressure on the bladder, preventing it from contracting normally. In a sitting position, the pressure increases, and the likelihood of urine leakage increases. With constipation, the swollen rectum puts pressure on the prostate, causing the sphincters to widen.
Involuntary leakage of urine is a common consequence of radiation therapy for prostate or urethral cancer. Radiation exposure damages functional tissues; it will take time to restore them.
Immediate and long-term complications of radiation therapy (%)
Sphincter insufficiency and urine leakage after visiting the toilet can also be a consequence of alcoholism, drug addiction, and smoking. The reason is damage to nerve endings, dulling of reflexes at the level of the central nervous system.
Types of dribbling
Depending on the circumstances of occurrence, there are several types of dribbling:
- Urgentny . Develops against the background of diabetes mellitus (due to damage to nerve endings and cystitis), parkinsonism, and after a stroke.
- Stressful . Occurs when there is a sharp change in intra-abdominal pressure during sneezing, laughing, or lifting heavy objects.
- Postoperative . It is a complication of surgery on the prostate, urethra, and bladder neck.
- Temporary (transient) . Occurs under severe stress, taking certain groups of medications, and during infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Mixed. Usually urgent and stressful.
If the symptom recurs over several days, you should consult a urologist.
Diagnostic methods
When urologists complain of drip urine, they first try to exclude an infectious factor. To do this, a smear from the urethra, urine, blood, and prostate juice are taken for analysis. If there are deviations in the urine analysis, a clarifying study is performed according to Nechiporenko.
The Nechiporenko analysis is used to detect infection if abnormalities were detected in a clinical urine test
An important stage of diagnosis is uroflowmetry. Based on the nature of the urine flow, the doctor will determine the presence of narrowing of the urethra. To clarify its location and nature, radiography, urethroscopy, ultrasound, and TRUS of the prostate are prescribed. An ultrasound or x-ray of the bladder is done if urolithiasis is suspected.
If everything is in order regarding urology, then the patient is referred to a neurologist. He will assess the quality of nerve conduction, check the reflex of the bulbourethral muscle and urethral sphincters. If necessary, he will prescribe an MRI or CT scan of the brain and lumbar spine.
Important advice for patients
If a man spontaneously leaks urine, it is important to observe all standards of personal hygiene. Otherwise, favorable conditions will be created for the proliferation of dangerous microflora. It is important for patients to follow a few simple rules of self-care during illness:
- Wash your genitals regularly. For this purpose, use only special detergents intended for intimate hygiene.
- Take warm baths. You can add sea salt or decoctions of medicinal herbs, such as chamomile or calendula.
- Change your underwear as often as possible. If replacing the panties is not possible, wipe them with the sting solution. This will help wash away any remaining urine and eliminate the odor.
- For severe forms of dribbling, the use of sanitary pads is recommended.
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of water a day, even if you feel like walking too often. Otherwise, the urine will become too concentrated and have a strong odor.
- Avoid stressful situations, physical and mental stress.
- Specialized deodorizing tablets will help eliminate the strong smell of urine.
Dribbling is a common problem. You can cope with it only if you contact a specialist in a timely manner and begin adequate therapy. Modern means help to quickly restore full urination and cope with the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment of urine leakage in men
Treatment methods for urine leakage depend on diagnostic results. Drug treatment is used in the presence of infectious inflammation of the genitourinary tract, prostate hyperplasia in the early stages, and also to improve nerve conduction.
For prostatitis, urethritis, and colliculitis, the latest generation of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets and suppositories are used. Effective auxiliary agents are Fitolysin paste and Canephron tablets. In case of adenoma, alpha1-adrenergic receptors and suppositories are prescribed to improve urine outflow to reduce swelling of the gland (for example, Prostatilen).
Phytolysin is a combined herbal preparation that has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic effect. Price in pharmacies from 398 rubles.
Kegel exercises and electrical myostimulation help strengthen the tone of the pelvic muscles. If the functionality of the sphincters cannot be restored using conservative methods, artificial ones are implanted.
See also: Kegel exercises for men with urinary incontinence.
If polyps, condylomas, scar changes, or tumors are detected in the urethra, they are removed using minimally invasive methods.
- At the end of urination, make several sharp movements of the pelvis forward (as with frictions), then, with pressure, move along the penis from the base to the head. This way you can get rid of urine residues outside the sphincters.
- Do exercises regularly to strengthen your pelvic muscles.
- During treatment, use thin urological pads (for example, Tena Men Extra Light). They are invisible under clothing, absorb all urine and odor, and allow you to lead an active lifestyle.
A few recommendations for men suffering from non-infectious urine leakage (without obvious signs of inflammation):
- At the end of urination, make several sharp movements of the pelvis forward (as with frictions), then, with pressure, move along the penis from the base to the head. This way you can get rid of urine residues outside the sphincters.
- Do exercises regularly to strengthen your pelvic muscles.
- During treatment, use thin urological pads (for example, Tena Men Extra Light). They are invisible under clothing, absorb all urine and odor, and allow you to lead an active lifestyle.
How to use urological pads
In case of infectious leakage, for additional disinfection of the genitourinary tract, you can drink urological preparations, sage, chamomile, and propolis tincture.
How is a pathological phenomenon diagnosed?
In case of incontinence of urine discharge after emptying the bladder, in order to determine the causes of the pathology, a comprehensive diagnosis of the state of men's health is necessary.
To do this, a man must undergo a series of tests:
Diagnostic measures
- general blood and urine analysis;
- Ultrasound examinations of the pelvic organs and kidneys;
- utetrociscopy to determine the condition of the bladder and urethral canal;
- X-ray;
- profilometry;
- cytometry;
- sphincterometry.
Urine is recorded for three days with the calculation of portions of excretion during the day and night. The patient is interviewed about his lifestyle to obtain a complete medical history. Sometimes a cough test is prescribed for diagnosis.