The bladder is an organ of the urinary system in which urine is accumulated, produced by the kidneys and flowing into the bladder cavity through the ureters. When a certain volume is reached, it is further removed from the body through the urethra.
Anatomy of the bladder
The normal bladder volume in men is between 350 and 700 ml. The muscle layer of its wall is capable of stretching and contracting, causing the cavity to increase and decrease depending on the amount of urine. Thus, the frequency of urination is regulated.
If the bladder is contracted and has a small volume, then the thickness of its muscular wall can reach 15 mm, and in a full state it can become significantly thinner and amount to 2 or 3 mm. Increased pressure in the cavity caused by the presence of urine leads to stretching of the muscle fibers. The receptor field perceives and transmits this information through the structures of the nervous system, resulting in the formation of the urge to urinate. The involuntary upper sphincter relaxes, the muscle wall of the bladder contracts, the lower sphincter, controlled by consciousness, also relaxes, and urine is released through the urethra.
What volume does a normal bladder have?
Adult bladder capacity is related to gender:
The fetal organ measures up to 8 ml, becoming larger over the weeks. The bladder of a newborn enlarges with age:
| Age, years | Normal values, ml |
| Up to a year | 50 |
| 1—3 | 70 |
| 3—8 | 200 |
| 9—10 | 300 |
| 11—13 | 400 |
Return to contents
What to do if the volume has changed?
First of all, the doctor will prescribe chromocystoscopy, excretory urography, ultrasound examination and, probably, cystoscopy. Based on the results of these surveys, he selects the best option for eliminating the problem that has arisen. The most important thing is to eliminate directly the cause that could lead to these changes.
If the bladder has become smaller, the following conservative treatment methods may be prescribed:
- injections of neurotoxins that are introduced through the urethra into the bladder tissue. Neurotoxins disrupt the functioning of nerves, thereby increasing the storage function of this organ and reducing the frequency of the urge to urinate;
- hydrodilation is a procedure in which fluid is pumped into the bladder and in this way gradually increases its size.
Surgical methods for increasing size:
- Transurethral detrusorotomy. A microsurgical instrument is inserted through the urinary canal into the cavity of the bladder, and the nerves are crossed with its help.
- Myomectomy. A certain part of the muscle fibers of the detrusor, the muscle that is responsible for contracting the bladder, is excised.
- Cystectomy. In this case, the bladder is completely removed and part of the intestine is replaced. This operation is usually performed in the case of malignant tumors in the urinary system.
- Augmentation cystoplasty. A part of the bladder is excised, which is replaced during the operation by a section of the intestine or stomach.
If the patient has an enlarged bladder, then treatment for the disease that provoked this condition is initially prescribed. At the same time, a catheter may be installed in the person to normalize urine output. Additional therapeutic measures that the doctor chooses individually:
- therapeutic exercises that can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles;
- physiotherapy (ultrasound, heating, electrophoresis and other procedures);
- medications, the effect of which is aimed at increasing the tone of the excretory organ.
If the increase in the volume of the excretory bladder was caused by malignant tumors, then in this case the patient undergoes a cystectomy - complete excision of the bladder with further replacement with tissues of the stomach or intestines.
If such changes in the body are left untreated, then a person can expect very unpleasant consequences in the future, which manifest themselves in the form of chronic pyelonephritis, vesicoureteral reflux, chronic renal failure and many others.
If you are faced with a similar situation, then there is no need to hide it and remain silent. As soon as possible, you need to visit a urologist who will prescribe therapeutic exercises, give you clear recommendations and prescribe medications if the situation requires it.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=YeMM98L9jIE
How to find out capacity using formulas?
To determine the capacity of an organ by age, use the following formula:
- Bladder capacity (BUC) = 73 + 32xN, where N is age.
For example, if the patient’s age is 35 years, the calculation will look like this:
If you need to find out the size of an organ based on the patient’s weight, then resort to the following formula:
- EMP = 10xM, where M is the person’s weight.
If a patient weighs 80 kg, then the volume of his organ is:
- 10×80=800 ml.
It is important to note that this formula is used only when the patient is not overweight or underweight. For calculations, the average weight is taken.
In newborns, the volume of the cavity varies, depending on how full it is. For older children, up to 10 years old, the size is calculated using the following formula:
- EMP=600+ (100x (N-1)), where N is age.
If the child is over 10 years old, the formula is as follows:
- EMP = 1500x (S: 1.73), where S is used to indicate the surface of the body.
Return to contents
The most accurate way to determine the size of the bubble is ultrasound examination. The device used for ultrasound examination calculates cavity size indicators independently in automatic mode. During the manipulation process, specialists are guided by the following indicators:
- height (B);
- width (W);
- length (L).
The following formula is used:
Why is it necessary to know the volume of the bubble, and how to take measurements
Why know what volumes will fit in the bladder of a man, woman or child? Such information is indispensable when conducting diagnostics. Obtaining this data is provided by ultrasound, which not only determines the capacity of the bladder, but also shows residual urine and its retention. If there are no deviations, the size of the bubble corresponds to the standards that we discussed above.
To calculate the capacity of the bubble, special formulas are used. In them, the shape is defined as an ellipse or a cylinder. Such techniques are suitable for detecting urine retention or determining the volume of residual fluid. However, the main difficulty in carrying out such calculations is problems in comparing the final data, since different formulas may be used in the studies. To eliminate all doubts, the calculations are double-checked manually, which makes it possible to verify the accuracy of the automatic calculations.
What correction methods can be used when changing the size of the bubble? To begin with, the attending physician refers the patient to undergo an ultrasound test, excretory urography, cystoscopy or chromocystoscopy. If the volume is reduced, conservative or surgical methods are used:
- Hydrodilatation. During this procedure, fluid is forcibly injected into the organ, increasing its size.
- Injection of neuro-toxins into the wall of the bladder through the urethra.
- Myomectomy, in which part of the contractile muscle is excised, transurethral detrusorotomy, cystectomy or augmentation cystoplasty.
When an organ is enlarged, the provoking disease is first eliminated. At the same time, a catheter can be installed to normalize the removal of urine from the body. Additionally, medications are prescribed to help improve tone, as well as physical therapy, including electrophoresis, ultrasound, warming and other procedures. Physical therapy is carried out to help strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor. If the size of the organ increases due to cancer, the patient is advised to undergo a cystectomy. This procedure involves complete removal of the bladder and subsequent replacement with intestinal tissue.
Should I pay attention to changes in tank volume? Undoubtedly, since if the problem is ignored, the consequences may include the formation of renal failure or chronic pyelonephritis, the formation of vesicoureteral reflux and other equally unpleasant diseases.
What is the normal thickness of the organ wall?
To obtain results about the thickness of the bladder wall, they resort to ultrasound examination. Only a specialist can decipher the data obtained from an ultrasound of the bladder. Health workers note that normally the organ has the following indicators:
- oval or round outlines;
- smooth borders;
- wall thickness 3-5 mm (with a full cavity the walls may be thinner);
- urine outflow - 14 seconds;
- bladder filling - 50 ml/60 min.;
- residual urine volume is 50 ml.
Return to contents
How to restore normal volume?
- Stretching sizes by filling liquid;
- Injections that reduce the number of urinations and increase storage capacity.
- Removal of part of the contractile muscle of the organ;
- Surgical effect on the nerves of the walls;
- Replacement of part of an organ with another part of the intestine or stomach;
- Complete removal of the bladder.
- The exercise technique involves drinking a significant amount of liquid while holding urination. The bladder gets used to the increase in volume;
- Each time you urinate, carry out the following actions: stop and start the outflow of urine. Strengthens the influence of the nervous system on the process;
- If you want to urinate, pat the front of your thighs or tap your knees. This will relax the muscles.
- A catheter is installed to drain urine;
- Medicines are prescribed;
- Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, amplipulse therapy, ultrasound, acupuncture, warming);
- Physiotherapy
It is recommended to have a bowel movement on a regular basis, every 2 or 2.5 hours. Regardless of desire.
- Cystectomy (removal of an organ for cancer);
- Lifestyle improvements (weight normalization, giving up bad habits, healthy eating, regular fluid intake).
The consequences of problems with urination make a man’s life difficult and problematic.
He becomes irritable, sleep disturbances begin, and his quality of life deteriorates.
Knowing the volume of a person’s bladder, correctly assess the potential of the organ, this will give you the opportunity to take care of urination on time, to be a healthy and full-fledged inhabitant of our planet.
What indicators affect the size of the organ?
The size of the bladder in men and women sometimes changes throughout life. This is caused by the following reasons:
- surgical interventions on the genitourinary system;
- disruptions in the development of nearby organs;
- use of certain pharmaceuticals;
- bladder tumors;
- neurological disorders;
- pregnancy;
- old age.
Many studies have been carried out to determine the factors affecting the change in cavity size. Doctors note that severe stress can also affect the volume of an organ. To restore the normal volume of the urinary cavity, specialists prescribe psychological training and medications to the patient to relieve overstrain. At the end of the course of therapy, the person regains control of the urination process, and the bladder returns to its former size.
There are factors that provoke changes in bladder volume that are reversible. For example, after giving birth or finishing taking medications, the organ will independently take on the capacity it had before. As for changes in the size of the cavity caused by other reasons, a return to the original volume occurs only when a specialist prescribes the required course of treatment. In exceptional situations, they resort to operations.
Symptoms
Of course, a change in the volume of the excretory organ necessarily makes itself felt:
- First of all, in the form of a strong urge to urinate.
- Going to the toilet is becoming more and more frequent, at least 7-8 times a day, including at night.
- At the same time, very little urine comes out, and the process of getting rid of it can be painful.
If the organ is reduced, it fills with urine faster, and the desire to get rid of it will arise even more often than with an increase in volume.
Reasons for resizing
The diameter of the bladder becomes smaller mainly due to its overactivity. The disease is caused by a disturbance in the supply of nerves to the urinary cavity. But infectious and inflammatory diseases can also provoke organ shrinkage:
- Cystitis. When the disease occurs, inflammation occurs in the bladder. Patients complain of frequent urge to defecate, pain in the lower abdomen, and blood in the urine.
- Tuberculosis of the urinary cavity.
- Schistosomiasis.
- Artificial removal of urine using a catheter. Often used after surgery.
Return to contents
Bladder capacity increases when the patient has the following diseases:
- urinary retention;
- urolithiasis;
- stones in the ureters;
- tumors in the urethral canal;
- inflammation of prostate tissue;
- prostate tumors;
- formation of polyps.
Doctors note that the following reasons can provoke organ enlargement:
Diseases, neoplasms, parasites are the causes of bladder enlargement.
- inflammation localized in the gallbladder;
- diabetes;
- sclerosis;
- brain tumors, during which control of the urination process is not possible;
- inflammation of the appendages in women;
- incorrect placement of the catheter;
- operations that provoked inflammation in the bladder.
The organ also increases in size in situations where the following medications are used:
- medications to relieve spasms;
- medications to relieve severe pain;
- sedative pharmaceuticals;
- medications to lower blood pressure;
- anesthesia
Return to contents
Why does the organ shrink?
In both sexes, a small bladder may be due to the following groups of reasons:
- Functional. Observed due to malfunctions of the organ.
- Organic. Diagnosed in cases of pathologies in the structure of the wall of the urinary cavity.
Functional decline is characterized by bladder overactivity. This disease is caused by failures in the supply of nerves to the organ or by their poor functioning. During the disease, the patient experiences frequent urination. Organic causes arise in cases of the development of diseases, which are characterized by a long duration of inflammatory processes that have a detrimental effect on the walls of the bladder. In cases of such diseases, the tissues of the organ begin to be replaced by connective tissue, during which its capacity decreases. It is important to know what diseases cause this:
- Interstitial cystitis, which is an inflammatory process in the urinary cavity of a non-bacterial nature. When sick, the patient feels frequent urination, pain in the peritoneum, and often a small amount of blood in the urine.
- Organ tuberculosis, which is a bacterial disease caused by tuberculosis bacilli.
- Radiation cystitis is an inflammatory process in the urinary cavity due to chemotherapy.
- Schistosomiasis, which is a disease caused by infection with a flatworm.
- Long-term artificial withdrawal of urine, for example, after surgery.
How to normalize bubble size?
If a person feels discomfort in the bladder area and complains of an increased urge to urinate, he should visit a medical facility as soon as possible and not resort to traditional medicine. At the hospital, a specialist will perform an ultrasound scan of the person’s genitourinary system. In addition, excretory urography is sometimes prescribed, which is an X-ray method for examining the urethra. The study is based on the ability of the kidney to secrete radiopaque substances, which are introduced into the body before the procedure. After such an instrumental examination, the doctor receives results about the condition of the kidneys and urethra.
They also resort to cystoscopy, an endoscopic method for examining the bladder and urethra, which involves examining the mucous membranes of organs using an endoscope. After the research results are received, the treating specialist will prescribe treatment that is aimed at eliminating the causes that led to the change in the capacity of the urinary cavity.
To make the urinary cavity larger, they often resort to conservative methods of therapy. Mostly doctors prescribe the following methods to the patient:
- stretching the organ by filling it with fluid;
- administering injections that reduce the number of urination urges and increase the time urine remains in the cavity.
What do they do when there are changes?
After an ultrasound is prescribed, they resort to other procedures to determine the disease and its nature:
- excretory urography;
- chromocystoscopy;
- cystoscopy.
Having received the results of the examination, the doctor prescribes current treatment aimed at restoring the previous size of the bladder. Naturally, we are talking about the priority elimination of the provoking factor.
When decreasing, prescribe:
- hydrodilation (injection of fluid into an organ);
- administration of injections aimed at restoring the functioning of nerve endings.
When increasing, the following is prescribed:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy (ultrasounds, heating, etc.);
- special exercises aimed at strengthening the pelvic muscle tissue.
If taking medications does not give the desired effect, then they resort to surgery.
Structure of the bladder
Urine is excreted by the kidney and sent through the ureters to the bladder. The ureter passes in the retroperitoneal space and has three physiological narrowings: at the point of transition of the pelvis into the ureter (pelvis-ureteric segment), at the point of intersection of the ureter with the iliac vessels (at the border of the middle and lower third) and at the place where it flows into the bladder.
The bladder is located behind the pubic bones: the empty one does not extend beyond the boundaries of the small pelvis, the filled one rises into the abdominal cavity. Above the bladder in men is the peritoneum and intestinal loops, in women - the uterus, peritoneum and intestinal loops. Behind the bladder in men are the seminal vesicles and rectum, in women the uterus, cervix and vagina. Below the bladder in men is the prostate gland, in women - the muscles of the perineum. From the sides - ischioanal fossa.
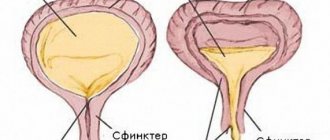
There are apex, body, bottom and neck of the bladder. The top is tilted forward, the bottom is at the back below, and the body is located between them. Tapering, the bladder passes into the neck, which ends with the urethra. The neck of the bladder is surrounded by a double circular muscle - the internal and external sphincter. The internal sphincter is composed of smooth muscle and works unconsciously, while the striated external sphincter can be influenced by muscle force.
The bladder is lined with transitional epithelium, which forms folds when the bladder is empty. The loose submucosal layer contains nerve endings, lymphatic and blood vessels. Three layers of smooth muscle unite to form the detrusor; near the orifices of the ureters, circular fibers form sphincters. The outside of the bladder is covered with adventitia, and in the body area with visceral peritoneum.
In the area of the bottom between the mouths of the ureters and the internal opening of the urethra, a vesical triangle is distinguished: the interureteric fold is the base, and the internal opening of the urethra is the apex. In the triangle, the mucosa is always smooth, the connective tissue of the submucosal layer is dense, and a powerful detrusor. This place is loved by inflammation and tumors.
Etiology of volume increase
Among the pathologies that affect the increase in organ size are:
- incomplete emptying even when overcrowded;
- the presence of mineral deposits in the bladder or urinary tract;
- foci of inflammation in the prostate (typical for men);
- formations of a malignant nature;
- polyps (benign neoplasms) in the organ cavity.
Secondary reasons include:
- inflammatory processes;
- neoplasms that are localized in the part of the brain responsible for the process of urine excretion;
- neurological pathologies;
- the age of the patient (often diagnosed after 40 years, especially in men due to prostate problems);
- diabetes;
- inflammatory processes in the appendages;
- incorrect placement of the catheter;
- long-term use of certain groups of drugs (sedatives, narcotics, etc.).
At the first unpleasant symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid the development of complications.
Ultrasound of the bladder transabdominal
Transabdominal ultrasound shows the entire bladder and surrounding anatomy. A full bladder serves as an acoustic window for examining the prostate gland in men and the pelvic organs in women. We are interested in the volume, shape, thickness of the bladder wall, as well as the distal ureters before and after urination.
2 hours before the test, you should empty your bladder and drink at least 1 liter of water over the next hour (for children, 10 ml per kg of body weight). If the bladder is not stretched enough, the pathology may be hidden by folds.
The patient is in the supine position. A convex sensor of 3.5-6 MHz is used; a high-frequency linear sensor of 7 MHz and higher is suitable for children. Place the transducer sagittally in the midline just above the pubic symphysis and examine the right and left lateral fields. In the transverse plane, move from the apex to the base of the bladder.
A full bladder is a large anechoic formation in the pelvis. A full bubble has a round shape, while an empty one looks like a flat plate. In newborns, the bladder is spindle-shaped, in babies it is pear-shaped, at the age of 8-12 years it looks like an egg, in teenagers and adults it is spherical. The bladder is symmetrical in cross sections, has an even internal contour, and there is always a small amount of suspension in the lumen.
Human urine volume
The normal volume of the bladder reaches half a liter, and its size varies depending on the age category of the person, his height and weight. Based on the individual structure of the body, the organ can stretch and accommodate up to 1 liter of liquid. The size of the urinary cavity is determined using ultrasound or using special formulas.
Organ volume is normal
Sizes for women and men
The size of the bubble depends on the person’s gender and age. Let's look at the normal indicators:
- in women, the volume of the bladder varies from 250 to 500 milliliters;
- for men - from 350 to 700 milliliters.
Return to contents
Organ volume in newborns and older children
The bladder of a newborn baby is about 50 milliliters, increasing over the weeks. The size of the organ in older children also increases as they grow older and is:
- in children under 1 year - 35-50 ml;
- from 1 to 3 years - 50-70 ml;
- from 3 to 8 years - 100-200 ml;
- from 9 to 10 years - 200-300 ml;
- from 11 to 13 years - 300-400 ml.
Return to contents
Normal organ wall thickness
Ultrasound diagnostics will accurately determine all organ indicators.
To understand whether the walls of the bladder have enlarged, it is important to know exactly what wall thickness should be normal. The indicator is determined using an ultrasound examination of the urinary system, and only the doctor can correctly interpret the results of the analysis. A healthy organ must have the following characteristics:
- round shape;
- clear and even contours;
- wall thickness ranging from 3 to 5 millimeters (it is important to note that their thickness may be slightly smaller when the bubble is full);
- the rate of urine outflow is 14 seconds;
- bladder filling - 50 milliliters per hour;
- the remaining urine is within 50 milliliters.
Return to contents
What affects the size of the urinary cavity?
The capacity of the bubble sometimes changes throughout the life cycle. Changes in organ size depend on the following factors:
- pelvic surgeries;
- pathologies in the structure of neighboring organs;
- use of certain medications;
- benign and malignant neoplasms in the organ;
- neurological pathologies;
- pregnancy period;
- elderly.
Prostatitis in men can cause an increase in the size of the bladder.
The size of the bladder, according to many studies, can change due to severe stress, this is observed in women and men. To restore the former capacity of the bladder, specialists help the patient get rid of nervous tension and restore the emotional background. Thanks to this, the patient can again exercise control over the process of urination.
Some of the above changes are reversible, and the diameter of the bladder returns to its previous size. This applies to pregnancy and the use of certain types of medications. In cases of changes in the volume of the bladder due to other factors, it will be able to return to its previous size only after the doctor carries out the correct treatment or, in some cases, surgery.
Return to contents
How do changes in organ size manifest themselves?
Deviations in the thickness of the bladder walls and its size do not go unnoticed, since they change the patient’s life for the worse. Patients begin to experience the following symptoms:
- frequent urination (more than 5 times during the day and about 3 times at night);
- uncontrollable urge to urinate;
- reducing the amount of urine excreted.
In cases where the bladder shrinks, it is more likely to fill with urine, which causes the urge to urinate more often. If the organ increases in size, but the amount of urine does not increase, disruptions in the process of urination also begin, which are characterized by a constant urge to visit the toilet.
Return to contents
How to calculate organ size?
In adults
To determine the capacity of the organ, specialists perform an ultrasound of the bladder, which allows one to automatically determine its capacity. The information obtained is used to study the urinary cavity, check for the presence of diseases of the urinary system and study the volume of remaining urine. However, there is a way to determine the size of an organ without going for an ultrasound.
Formulas used to determine the capacity of an adult female and male organ:
- Bladder capacity (in milliliters) = 73 + 32 x N (N is the patient's age);
- EMF = 10 x M (M is the patient’s body weight);
- EMP = 0.75 x A x L x H (A is the width, L is the length, and H is the height of the bladder, which can be determined by catheterization of the organ).
Return to contents
In newborns and children
What should be the organ capacity of a child? In a newborn, the bladder is determined only at the 12th week of pregnancy. The size of the organ in newborns will vary depending on the fullness of the cavity. In children under 10 years of age, the bladder capacity is determined according to the following formula: 600 + (100 x (N -1)), where N is the child’s age. For children over 10 years old, the formula changes: 1500 x (S: 1.73), where S is the surface of the body. Body surface parameters can be taken from the table below.
A table with a ready-made calculation of the body surface depending on a person’s weight and height:
| Weight height | 40 kg | 45 kg | 50 kg | 55 kg | 60 kg | 70 kg | 80 kg | 90 kg | 100 kg | 120 kg |
| 110 cm | 1,04 | 1,09 | 1,14 | 1,19 | 1,24 | 1,32 | 1,40 | 1,47 | 1,54 | 1,66 |
| 120 cm | 1,11 | 1,17 | 1,22 | 1,27 | 1,32 | 1,41 | 1,49 | 1,56 | 1,64 | 1,77 |
| 130 cm | 1,17 | 1,23 | 1,29 | 1,34 | 1,40 | 1,49 | 1,58 | 1,66 | 1,73 | 1,87 |
| 140 cm | 1,24 | 1,30 | 1,36 | 1,42 | 1,47 | 1,57 | 1,66 | 1,75 | 1,83 | 1,98 |
| 150 cm | 1,30 | 1,37 | 1,43 | 1,49 | 1,55 | 1,65 | 1,75 | 1,84 | 1,92 | 2,08 |
| 160 cm | 1,37 | 1,44 | 1,50 | 1,56 | 1,62 | 1,73 | 1,83 | 1,93 | 2,02 | 2,18 |
| 170 cm | 1,43 | 1,50 | 1,57 | 1,63 | 1,69 | 1,81 | 1,92 | 2,01 | 2,11 | 2,28 |
| 180 cm | 1,49 | 1,56 | 1,63 | 1,70 | 1,77 | 1,89 | 2,00 | 2,10 | 2,20 | 2,37 |
| 190 cm | 1,55 | 1,63 | 1,70 | 1,77 | 1,84 | 1,96 | 2,08 | 2,18 | 2,28 | 2,47 |
| 200 cm | 1,61 | 1,69 | 1,76 | 1,84 | 1,91 | 2,04 | 2,15 | 2,27 | 2,37 | 2,5 |
Return to contents
Why does the organ shrink?
In both sexes, a small bladder may be due to the following groups of reasons:
- Functional. Observed due to malfunctions of the organ.
- Organic. Diagnosed in cases of pathologies in the structure of the wall of the urinary cavity.
With interstitial cystitis, a functional decrease in the bladder is observed.
Functional decline is characterized by bladder overactivity. This disease is caused by failures in the supply of nerves to the organ or by their poor functioning. During the disease, the patient experiences frequent urination. Organic causes arise in cases of the development of diseases, which are characterized by a long duration of inflammatory processes that have a detrimental effect on the walls of the bladder. In cases of such diseases, the tissues of the organ begin to be replaced by connective tissue, during which its capacity decreases. It is important to know what diseases cause this:
- Interstitial cystitis, which is an inflammatory process in the urinary cavity of a non-bacterial nature. When sick, the patient feels frequent urination, pain in the peritoneum, and often a small amount of blood in the urine.
- Organ tuberculosis, which is a bacterial disease caused by tuberculosis bacilli.
- Radiation cystitis is an inflammatory process in the urinary cavity due to chemotherapy.
- Schistosomiasis, which is a disease caused by infection with a flatworm.
- Long-term artificial withdrawal of urine, for example, after surgery.
Return to contents
Causes of increased bladder volume
Indicators of an enlarged bladder appear in the case of the following diseases:
- ischuria (urinary retention when the organ is full but cannot excrete urine);
- urolithiasis disease;
- stones in the ureters;
- neoplasms in the urinary canal;
- prostatitis;
- neoplasms in the prostate gland;
- polyps.
In addition, the urinary cavity can increase due to the following factors:
- inflammatory processes in the gallbladder;
- neoplasms in the brain, due to which control over the process of urination becomes impossible;
- multiple sclerosis;
- pathologies of the prostate gland (in male patients over 40 years old);
- diabetes mellitus;
- inflammation of the female appendages;
- catheterization of the urinary cavity (in cases where the catheter was installed incorrectly):
- surgical operations, due to which irritation of the urinary system appeared, and subsequently - swelling of the urinary cavity and urinary retention.
The increase in cavity size is also influenced by the use of medications such as:
- parasympatholytics (used to prevent or eliminate spasms);
- opiates (used to relieve severe pain);
- sedatives;
- ganglion blockers (used to lower blood pressure);
- some types of anesthesia.
Return to contents
What to do when changing the bubble size?
An x-ray shows a picture of the kidneys and genitourinary system.
After the patient feels any changes in the functioning of the organ, it is important for him to immediately seek help from a specialist and not try to self-medicate. The attending physician will send the patient for an ultrasound examination of the urinary system. Often, excretory urography is prescribed for these purposes, which is an x-ray method for examining the urinary tract, based on the ability of the kidney to secrete certain radiopaque substances introduced into the body, after which the x-ray shows a picture of the kidneys and urinary tract. Cystoscopy is also used, in which doctors examine the inner surface of the urinary cavity using an endoscope.
After studying the results of the examination, the doctor prescribes the correct therapy, in which the main emphasis is on eliminating the factors that provoked disturbances in the size of the bladder. If its capacity is reduced, hydrodilation is used, with which doctors can increase the size of the organ by pumping fluid into it. In addition, neurotoxins (toxins that specifically affect nerve cells) are injected through the urethra. Sometimes doctors have to resort to surgical interventions, the most common of which is a cystectomy. It is a difficult abdominal operation, during which the bladder is completely or incompletely removed, and in particularly difficult situations, both nearby lymph nodes and neighboring organs of the genitourinary system.
If the patient is diagnosed with an enlarged bladder, it is catheterized. To do this, a hollow tube (catheter) is inserted into the urinary canal to regulate the output of urine. In addition, drug treatment, therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy are prescribed. In cases where the increase in the size of the bladder began due to cancerous tumors, the patient is also prescribed a cystectomy.
etopochki.ru
Reasons for the decrease in volume
In women and men they are absolutely the same and are divided into two groups:
- Organic, which arise due to a violation of the structure of the bladder wall.
- Functional, which are associated with disruption of the functioning of this organ.
The last group includes a disease called overactive bladder. This pathology is associated with insufficient functioning of the organ or a disruption in the supply of nerves to it. The disease is manifested by an imperative and frequent urge to defecate.
Organic causes include diseases that occur with prolonged inflammation, which provokes changes in cells in the walls of the bladder. As a result of this process, the walls are replaced with connective tissue over time, and the size decreases. These reasons include:
- tuberculosis of the excretory bladder is a disease of bacterial etiology, the causative agent of which is the tuberculosis bacillus;
- interstitial cystitis is an inflamed process in the bladder of non-bacterial etiology, which is manifested by frequent urination, prolonged pain in the lower abdomen and blood in the urine;
- artificial excretion of urine for a long time (for example, postoperative recovery period);
- schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by a flatworm;
- radiation cystitis is an inflammatory disease of the bladder that develops after radiation treatment (performed with ionizing radiation to treat cancer).
In most cases, these changes are irreversible, so returning to the previous volume is only possible with the help of surgery.
Features of the unpaired genital organ
On average, the maximum capacity of the bladder is approximately 750 milliliters. However, a person feels the need to go to the toilet with a volume of 150-250 ml. Capacity primarily depends on age, gender and general health. In women it is characterized by smaller sizes. This is due to the fact that they have internal genital organs in the pelvic area.
For women, the normal volume is from 250 to 500 ml. For men, this value is insignificant, but it is increasingly higher and amounts to about 650 ml. The amount of urine content in an organ is primarily influenced by the individual structure and extensibility of the walls of the organ. Depending on this, a person is able to hold up to one liter of urine.