MRI of the bladder is usually performed as part of a general diagnosis of the condition of the pelvic organs. This inspection method is absolutely safe for human health. MRI of the bladder, like any other test, is prescribed according to the recommendations of the attending physician. If you have problems with this organ, such a study will be necessary to undergo a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Indications and contraindications for diagnostics
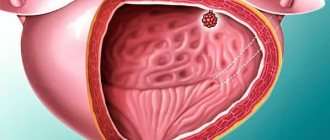
MRI allows you to see pathological changes in tissue from 1 mm in diameter, showing that urination in the urethra is difficult due to a stone or tumor. An accurate diagnostic technique makes it possible to determine the cause of the pathology, even if it is located in neighboring organs.
Symptoms of urinary tract diseases have similarities that make diagnosis difficult in the early stages. It is sometimes possible to distinguish oncology from cystitis and take timely measures to treat it only with the help of MRI. Indications for the procedure may include:
- difficulty urinating and painful process;
- change in urine odor;
- detection of traces of blood or hematuria in tests;
- enlarged inguinal lymph nodes;
- pelvic area injuries;
- thrombophlebitis.
Due to the high cost, examinations are most often prescribed only in cases of suspected severe pathologies associated with oncology or abnormalities in the structure of the bladder. For cancer patients, MRI is performed as a way to monitor the dynamics of the process during treatment or to prevent relapse.
Contraindications to the procedure are due to the effect of the magnetic field on the human body. The study cannot be performed if the patient has a pacemaker, a metal implant, or clips applied to the blood vessels of the brain.
Relative contraindications are:
- installed insulin pumps, nerve stimulators, or non-metallic implants;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
- claustrophobia;
- tattoos containing dyes with metallic compounds.
When using a contrast agent, renal failure is also a contraindication, since the reagent is excreted from the body through the urinary system.
The procedure is practically not prescribed for children due to the requirements for long-term immobility.
Using Contrast
As we have already said, a contrast agent provides a more accurate diagnosis. This is especially important if you suspect cancer.
Disadvantages of this method:
- Cost (almost doubles).
- Time costs (the procedure takes at least an hour).
However, the reward will be accurate research data. The fact is that here the contrast agent is produced on the basis of gadolinium salts, which clearly help to visualize the difference between affected and healthy tissues. New growths will be brighter and faster colored due to their developed vascular network. The contrast will thus allow you to see both the size and boundaries of the cancerous lesion.
What preparation will be needed?
To avoid distorting the results during the examination, it is advisable to limit the consumption of foods that cause gas (legumes, cabbage, brown bread, etc.). The diet must be followed for 1-2 days before the procedure.
On the eve of the MRI examination, it is advisable to do an enema so that the intestines are empty and do not distort the contours of the examined organ when visualizing its sections. Before the procedure you will have to abstain from eating.
On the day of the procedure, you need to drink about 2 liters of water 1-2 hours before the procedure and do not visit the toilet, since the pictures are taken with the organ filled with fluid. It is not recommended to apply creams to the skin before an MRI. When getting ready for the office, you should not wear watches, metal jewelry, or clothes with zippers or studs. The absence of metal parts will allow the patient not to even undress during the examination.
Preparation before MRI of the bladder
MRI or CT, like any other analysis, requires compliance with certain rules. No preparation is required for this procedure. You will only need to fulfill some conditions.
- A couple of days before the examination, you should refrain from eating vegetables, bread, fruits and drinks with gas.
- The bladder should be full and the intestines should be cleansed. It is recommended to take an enema in the evening before the procedure.
MRI of an organ can be performed without prior preparation. The only disadvantage of such an analysis will be the possible unclear image that is projected on the device’s monitor. With the timely detection of diseases using this study, the chances of a complete cure increase.
How is it done for women and men?
There are no differences in the examination between men and women. The patient is placed on a special couch that moves inside a magnetic ring. In this case, the device operates in automatic mode, the specialist does not touch the patient and does not perform any unpleasant manipulations with him. No radiation is generated during the examination, but the patient's body is in a strong magnetic field.
The only inconveniences that the subject experiences are the desire to visit the toilet and the need to remain completely still. Sensitive people may be uncomfortable with the sound the device makes during operation. The total duration of the study does not exceed 30 minutes, after which the patient can continue his usual lifestyle.
MRI of the pelvic organs in women examines:
- bladder;
- uterus and appendages;
- vagina;
- lymph nodes, blood vessels, other soft tissues.
In the photographs you can assess the man’s condition:
- bladder and urethra;
- prostate gland;
- testicle;
- vas deferens;
- blood vessels and lymph nodes.
MRI of the bladder with contrast
The introduction of a contrast agent makes it possible to most clearly identify pathologically altered areas of soft tissue in the organ under study and neighboring areas. Gadolinium metal compounds are administered intravenously, and through the bloodstream they penetrate into all the soft tissues of the small pelvis. Most often, contrast agents (Dotarem, Gadovist, etc.) are administered to patients with suspected cancer.
Tumor tissues are penetrated by numerous blood vessels. The contrast agent is concentrated in them more strongly than in the surrounding healthy tissue, so the tumor will stand out more clearly in sections. Only an oncologist can judge its malignancy.
Contrast agents may cause individual intolerance, so a test is required before the procedure.
Technique
The procedure takes no more than half an hour. If with contrast, then an hour. And the cost of the second option will be more expensive.
Some patients are afraid of the device because it makes noise and is a closed structure. Before starting the study, they need to take a sedative. If the situation is so difficult that the patient refuses to go inside a closed machine, there is the option of an open tomograph.
Before the study begins, the medical professional will explain in detail how the study will be carried out. Then the patient lies down on the couch and it slides inside the tomograph. If the patient becomes ill during the process, you can stop the procedure by pressing a special button.
After the examination, there are no restrictions - the tomograph does not affect the patient’s condition in any way.
What pathologies are diagnosed: interpretation of the results
Only a specially trained doctor can correctly decipher the tomograph readings. When a response is received during the procedure, all sections are recorded on digital media, and for diagnostics a printout is made in the form of many images. On them, a specialist can see the presence of a malignant tumor in the prostate or uterus, lymph glands and other pelvic organs and in the retroperitoneal space. The accuracy of the method allows you to assess the size and stage of tumor development, the presence of metastases in cancer.
Symptoms associated with difficulty urinating or hematuria may be caused by bladder pathology or compression. On a computer image, it is easy to detect stones stuck in the urethra or located in the cavity, and any inflammation of the mucous membrane or muscle layer of the bladder. When using contrast, pathologies of blood vessels or areas of their excessive growth (for tumors) are diagnosed.
Often, along with a bladder examination, diseases of the female and male genital organs are diagnosed:
- prostate adenomas;
- uterine fibroids;
- ovarian cysts;
- prostatitis, etc.
Their pathologies are often expressed by similar symptoms, and sometimes it is not possible to determine the location of the neoplasm in early-stage oncology using other methods.
After a pelvic injury, an MRI can help identify hidden bleeding, bone fractures, or organ damage.
Characteristics of the procedure
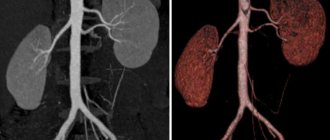
Most often, MRI of the bladder is performed in conjunction with magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvic organs. However, it can also be an independent procedure. For highly accurate results, the study must be performed on a high-field magnetic tomograph with a magnetic force of 1.5 Tesla. The power of the device is reflected in the informative accuracy of the results. Can be prescribed after ultrasound, CT (computed tomography) of the organ.
MRI of the bladder is characterized as a safe, non-invasive (without penetration of the device through the patient’s skin or mucous membranes), highly informative examination. It is also painless for the patient.
The procedure often involves the introduction of a special contrast agent. Why is this being done? First of all, to ensure more accurate research results, an MRI of bladder cancer is performed. The contrast substance allows you to show characteristic tumor clots, actual sizes, and location of the malignant neoplasm more clearly and brightly in the image.
Contraindications
Please note that there are few prohibitions on the procedure:
- An absolute contraindication is vessel clipping. Under the influence of a magnetic field, the clip moves.
- A relative contraindication is hip replacement. May cause some noise in the image. Therefore, the question of the advisability of MRI is decided individually.
- Orthopedic plates for osteosynthesis, other joint endoprostheses, a pacemaker, and a cochlear implant will not be obstacles to the procedure. But you need to warn a specialist about their presence, and also have with you the passport for the device, the conclusion of the surgeon who implanted it, about the possibility of performing an MRI.
Indications
Typically, an MRI of the kidneys and bladder is prescribed if the development of oncological tumors in these organs is suspected, namely bladder cancer. Magnetic field examination will not only confirm the diagnosis, but also determine the exact location of the tumor with an accuracy of one millimeter. It may also indicate:
- pathology of bladder tissue;
- presence of blood in the urine;
- congenital anomaly of the genitourinary organs;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- problems with urination;
- clarification of indications for surgical or radiation therapy.
At the same time, this research method is used to track the dynamics of tumor development and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. The procedure is safe, so it can be performed several times if necessary.
Difference between CT and MRI