Women systematically face problems of the genitourinary system, for example, they often visit a urologist with severe symptoms of cystitis or urethritis. In such cases, the doctor immediately prescribes antibiotics for a course of 5-7 days, but with the help of a treatment regimen with effective dietary supplements, you can do without antibacterial therapy and its unpleasant consequences.
The risk of complications and side effects is minimal, and the therapeutic effect is no weaker. Taking herbal preparations is possible only after preliminary consultation; self-medication is dangerous to health.
Types of infection
There are different types of urinary tract infections - there is a special extensive classification to distinguish them.
| By localization | |
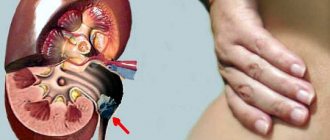
| Upper urinary tract lesions | The kidneys, renal tubules and pelvis and ureters are affected. Develop: pyelonephritis, renal carbuncle, abscesses. |
| Lesions of the lower urinary tract | The bladder and urethra are affected. |
| According to the degree of complexity | |
| Uncomplicated form | It is characterized by a slight deviation in the functioning of the urinary organs without structural anomalies. |
| Complicated form | Occurs with severe dysfunction of the urinary organs. In some cases, it is complicated by inflammation of nearby organs. |
| According to the nature of symptoms and form of course | |
| Clinical symptoms (acute form) | Symptoms are pronounced and occur frequently. |
| Asymptomatic infections (latent), chronic form | Characterized by the absence or mild symptoms, which may intensify when exposed to any factor (for example, cold or eating any product that has an irritating effect). They can accompany a person for a long time. |
| By method of infection | |
| Hospital | Infection occurs in a hospital setting during diagnostic or therapeutic procedures (for example, urethral catheterization). |
| Out-of-hospital | The infection is not associated with medical procedures and occurs outside the hospital. |
Classification of the disease
There are several classifications of infectious diseases of the urinary system.
By localization:
- upper urinary tract infections, these include inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis), ureters;
- lower urinary tract - bladder (cystitis) and urethra (urethritis).
According to the nature of the disease:
- Uncomplicated . They occur without structural changes in the tissues of the urinary apparatus, in the absence of obstructive uropathy or other concomitant diseases.
- Complicated . They occur against the background of difficulty urinating, when using instrumental methods of examination or treatment (catheterization).
Depending on the location of infection by the pathogen:
- Hospital . Also known as hospital-acquired or nosocomial. They develop when an infectious pathogen enters the body while in a medical institution.
- Out-of-hospital . They develop in an outpatient setting under circumstances favorable for infection.
According to the nature of symptoms:
- Clinically significant infections . They are characterized by obvious, often intense symptoms.
- Asymptomatic infections. The clinical picture is weak, the symptoms slightly worsen the patient’s quality of life.
Stages and degrees
All types of infectious diseases have 4 main stages:
- Incubation period. It begins from the moment a foreign agent enters the human body. Next, the pathogenic microorganism begins to actively multiply and create colonies (CFU).
- Prodormal period. It is characterized by the appearance of general signs of infectious infection without specific symptoms of a particular disease. The person begins to feel weak, loses appetite, and the patient’s body temperature rises.
- Period of development of the disease. At this stage, specific symptoms of the disease appear, on the basis of which tests and examinations are prescribed for further diagnosis. During the development of the disease, there is also an active restructuring of the immune system - it begins to synthesize specific antibodies aimed at destroying microbes and neutralizing the toxins they release.
- Reconvalescence (recovery period). During the recovery period, the symptoms of infection gradually disappear, and immunity to the type of microorganism that caused the disease is formed. In some cases, the pathology can become chronic.
Factors that predispose to the occurrence of UTIs in children
Urinary tract infections in children can occur due to:
- hypothermia (most often it occurs in cool seasons);
- respiratory infectious diseases. For example, with a sore throat, streptococcus may enter the kidneys through the bloodstream and this will provoke the development of severe pyelonephritis;
- decreased immunity (more often occurs in older age, as well as in patients who have immunodeficiency and severe chronic diseases);
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- developmental anomalies of the urinary tract (this pathology can be diagnosed in utero);
- obstructive uropathy (in this case, the outflow of urine is disrupted for various reasons).
Symptoms
Urinary tract infections in women have common symptoms:
- too frequent urge to urinate, accompanied by pain and stinging;
- change in the color and odor of urine (it becomes darker and acquires a sharp, unpleasant odor).
Also, different types of infections have their own characteristic symptoms:
- Urethritis: burning and itching in the urethra and during urination, purulent mucous discharge from the urinary opening.
- Cystitis: a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
- Pyelonephritis: acute pain in the lower back and pelvis, fever, severe weakness of a person, vomiting, swelling.
Features of UTI in childhood
Frequent causes of infectious processes in the urinary tract in childhood are the appearance of:
- obstructive processes in the urinary system;
- various functional disorders;
- phimosis;
- congenital anomalies of the genitourinary tract;
- rare urination.
The clinical picture of UTI in children may be erased. Babies under 18 months are irritable, capricious, whiny, they have a decreased appetite, and they also experience an unreasonable increase in temperature.
At 2 years old, a child may already complain of pain in the abdomen or back, the number of urination increases, and the body temperature may also increase.
The prognosis of UTI in childhood is often favorable, but sometimes sclerosis of the kidney tissue, the appearance of arterial hypertension, protein in the urine, and functional disorders in the kidneys occur.
Reasons for appearance
Urinary tract infections in women (symptoms of the disease are specific, so it is impossible to make a wrong diagnosis) develop more often than in men. This is due to the fact that the urinary canal in the female body is short and narrow, and is also located close to the anus - because of this, it is easier for bacteria to enter the urethra and infect the urinary organs.
The most common cause of cystitis or urethritis is E. coli entering the urethral canal (this can happen if a person uses toilet paper from the back to the front after bowel movement).
Infection can also be caused by:
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules;
- sexual contact with an infected person without a condom;
- injuries and congenital anomalies in the structure of the urinary canal (in this case, the excretion of urine becomes difficult, which facilitates the penetration and reproduction of pathogenic organisms);
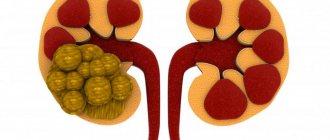
- the presence of stones or sand in the kidneys and bladder;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases of internal reproductive organs;
- vesicoureteral reflux or stagnation of urine;
- low immunity;
- diabetes mellitus (affects decreased immunity);
- use of internal contraceptives (uterine device, vaginal caps);
- the use of spermicides, as they irritate the mucous membrane of the genital organs and facilitate the penetration of bacteria.
Women during menopause and postmenopause are especially susceptible to developing genitourinary infections. Hormonal changes that occur during this period lead to the fact that the mucous membrane of the urinary tract becomes thinner and more susceptible to the penetration of pathogens.
Risk group for UTI
The risk group for infectious diseases of the urinary system includes:
- females (they occur five times more often).
Infectious diseases of the urinary tract are more often diagnosed in women. This happens because their urethra, vagina, anus are located closer, and also because their urethra is short and wide, thus pathogens penetrate the urinary tract faster;
- children under three years of age (due to immunodeficiency). UTI is one of the most common causes of fever of unknown etiology in boys under three years of age;
- elderly people (due to the fact that they develop age-related immunodeficiency);
- patients who have structural features of the urinary tract (for example, with an enlarged prostate gland, it may be difficult for urine to flow out of the bladder);
- patients who have renal pathology (for example, with urolithiasis, stones are an additional risk factor that contributes to the development of infectious processes);
- intensive care patients (they, albeit temporarily, have urine removed through a urinary catheter, which is the entrance gate for infection);
- patients who have chronic diseases (for example, with diabetes mellitus, there is a high likelihood of UTIs due to the fact that the body’s resistance decreases);
- women who use some kind of contraceptive method (an example is the use of a contraceptive ring).
Diagnostics
Urinary tract infections in women, the symptoms of which are almost always noticeable, are diagnosed using special laboratory methods:
| Method | Description |
| General urine analysis | Allows you to determine the properties of urine (color, consistency, transparency). The presence of mucus and an increased number of leukocytes in the urine indicates an inflammatory process in the urinary organs. |
| Urinalysis using the Nechiporenko method | Using this analysis, you can determine the exact number of leukocytes and casts (protein molecules that are normally absent) in the urine and determine the severity of the inflammatory process. |
| Urine culture for flora with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics | Morning urine is used for testing. Using a flora analysis, you can determine what type of bacteria caused the inflammation and the appropriate type of antibiotics for treatment (since different types of bacteria can be resistant to certain types of antibiotics). |
| Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky | Directed to study kidney function. It consists in the fact that a person must collect urine in special containers every 3 hours during the day and record all liquid intake. |
The tests listed are the main ones in making a diagnosis. If there is a suspicion of kidney damage, then an additional blood serum test is prescribed - if the level of urea and creatinine in it is increased, this indicates that there is an active inflammatory process in the kidneys.
Also, additionally (if there are any diseases of the urinary organs or an unclear picture of the tests), instrumental studies may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder - shows the structure of organ tissues and allows you to identify the presence of stones in them.
- Computed tomography allows you to obtain three-dimensional images of the urinary organs and identify various diseases that could cause inflammation.
- Cystoscopy - designed to examine the inner walls of the bladder. An optical tube is inserted into the organ through the urethral canal, through which images are obtained.
Pathogens of UTIs in children
The causative agents of UTIs in children include:
- Escherichia coli. It is normally found in the large intestine, but when this pathogen enters the urethra, this disease occurs. 41 – 78% of all infectious processes in the organs of the urinary system occur due to it;
- protea It is the causative agent of 8.5% of UTIs;
- enterococci (also cause 8.5% of all urinary system infections);
- Klebsiella It is the causative agent of this pathology in 8.0%;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa. More often in 1 – 13.6% it is the cause of chronic latent pyelonephritis;
- staphylococci. They cause 3-5% of disease cases;
- other pathogens (7.2 – 8%).
When to see a doctor
Infectious infections of the urinary organs are very dangerous - they can lead to disruption of the functioning of the organs and cause severe intoxication of the body (due to the fact that the excretion of urine, which removes pathogenic bacteria from the body, will be impaired).
Therefore, you should consult a doctor immediately if characteristic symptoms of infection appear: pain and a burning sensation during urination, itching of the external genitalia, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Timely contact with a specialist will help prevent organ dysfunction.
With pyelonephritis, weakness and body temperature rise first, and a little later pain in the lower back appears.
Which doctor treats diseases of the genitourinary system?
The multiplicity of anatomical targets, symptoms and variants of the course of diseases of the genitourinary system does not imply the management of such patients by one specialist.
Disorders of the urinary tract are treated by a urologist, who also provides assistance with sexual disorders in men.
In women, diseases of the pelvic organs are predominantly managed by a gynecologist, excluding diseases of the urinary tract.
Kidney diseases are treated by a nephrologist.
Urogenital diseases of infectious origin can be observed by both urologists and venereologists (STDs).
However, with the first symptoms, the easiest way for the patient to contact a therapist or general practitioner.
He will refer him to the necessary specialist for specialized treatment
Prevention
Urinary tract infections in women whose symptoms interfere with normal life can be prevented by following the following rules of prevention:
- Promptly treat all inflammatory diseases in the body (regardless of their location, since the infection can penetrate the urinary canal through the blood or lymph).
- If you have the urge to urinate, do not endure it for a long time, but empty your bladder as quickly as possible.
- Maintain intimate hygiene (wash the vaginal and anal areas daily with clean hands from front to back - from the pubis to the anus).
- When having sexual contact with a stranger or an infected regular partner, use a condom.
UTI and dementia
If an older person with dementia or Alzheimer's disease develops a UTI, it can cause a noticeable change in their behavior within a few days, known as delirium.
Signs of delirium are:
- Excitement or restlessness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Hallucinations or delusions
- Unusual drowsiness
- Withdrawal
Because a person with dementia may not be able to discuss the problem, family members or caregivers should be aware of these signs of UTI. If you notice these signs, seek medical attention so that the patient can be examined and treated as soon as possible.
Treatment methods
In most cases, treatment of urinary tract infections occurs on an outpatient basis. But if the patient is in very poor condition, and the functioning of the organs is disrupted (most often this is observed with kidney damage), then hospitalization is required.
The goal of therapy is to destroy pathogenic microorganisms, relieve inflammation and pain, and normalize the functioning of the urinary organs.
Medications
For infectious lesions of the urinary tract, antibacterial drugs (antibiotics) are always prescribed. The choice of drug depends on the type of bacteria, the woman’s age and contraindications.
The most commonly prescribed types of antibiotics are:
- Broad spectrum antibiotics have a pronounced antimicrobial effect. It is important that the active substance of the antibiotic is excreted through the kidneys, therefore, for urinary tract infections, drugs such as Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Doxycycline are usually prescribed.
- Sulfonamide drugs — effectively fight infectious agents, are excreted through the kidneys and do not have a toxic effect on the kidneys. Sulfonamide drugs include: “Urosulfan”, “Biseptol”, “Etazol”.
- Nitrofuran drugs - have an effect on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. For internal use, Furazolidone and Negram are prescribed. To wash the genitals, solutions of “Furacilin” are prescribed.
Antibiotics may be prescribed in the form of tablets or injections, depending on the severity of the disease.
The following groups of drugs are also prescribed together with antibiotics:
| Group of drugs | Action | Facilities |
| NSAIDs | They have a complex effect: they relieve pain and inflammation. Helps reduce body temperature. | “Ibuprofen”, “Nise”, “Nimesulide”. |
| Antispasmodics | Helps relax the muscles of the urinary tract and normalize urine output. | “No-shpa”, “Drotaverine”. |
| Herbal remedies | They normalize the functioning of the urinary tract and have a slight analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. | “Phytolysin”, “Canephron”. |
| Probiotics and prebiotics | They populate the intestines with beneficial bacteria and help normalize digestion (since antibiotics negatively affect the state of the intestinal microflora). | “Linex”, “Hilak Forte”, “Acipol”, “Bifiform”. |
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are highly effective in treating urinary tract infections. With their help, you can achieve a significant improvement in the functioning of the kidneys and bladder and eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
However, traditional medicine is not a complete replacement for standard drug treatment, so they must be used together. Also, do not use folk remedies without a doctor’s permission.
Cranberries and lingonberries
Cranberries and lingonberries have pronounced anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and analgesic effects. The berries also have a diuretic effect, which is important for lesions of the urinary tract.
It is recommended to drink 200-300 ml of freshly squeezed cranberry or lingonberry juice or juice daily.
You can also prepare a healing infusion from plant leaves:
- Take 30-40 g of cranberry and lingonberry leaves and chop.
- Then pour hot water over the leaves (temperature no higher than 80 degrees) and leave the mixture to steep for 30 minutes.
- After 30 min. Filter the infusion and drink. The course of treatment is 1 week, 2-3 times a day.
Rosehip infusion
Rose hips are rich in vitamin C and also have anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects. Rosehip infusion helps speed up urine excretion and quickly eliminate the symptoms of cystitis.
To prepare the infusion, you need to put 100 g of berries in a thermos and fill them with hot water for 3 hours. After this, you can drink the drink instead of regular tea.
Decoction of birch buds
Birch buds have an antibacterial effect, so they are used in the treatment of infectious diseases.
In order to prepare the decoction you need:
- Grind 100 g of birch buds.
- Then pour 0.5 liters of hot water into the raw material and put it on medium heat.
- Wait for the water to boil and after 2-3 minutes. remove the broth from the heat.
- Cool the broth and take 150 ml 3 times a day before meals.
The course of treatment is 5-7 days.
Chamomile
Chamomile for urinary tract infections can be used both internally and externally to wash the genitals. The plant has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and regenerative effects.
To prepare the decoction you need:
- Pour 2 tbsp. l. chamomile flowers 0.5 liters of hot water and place the container with the raw materials on medium heat.
- After the mixture boils, simmer it over low heat for another 5 minutes, then remove from the stove and cool.
The decoction should be used to wash the external genitalia 2 times a day. After the procedure, the broth does not need to be washed off the skin.
For internal use, it is recommended to prepare an infusion, as it brews faster: you need to pour 1 tsp. chamomile flowers with hot water, cover the container with a lid and leave for 15-20 minutes. After this, the mixture must be filtered. The infusion should be consumed 2-3 times a day after meals. The course of treatment is 7 days.
Pathogens and ways of their penetration into the body
Different types of microorganisms can provoke the appearance and development of inflammation in the organs of the urinary apparatus:
- bacteria (Escherichia coli, ureaplasma, gonococci, streptococci, Trichomonas, listeria, staphylococci);
- mushrooms (yeasts of the genus Candida);
- viruses (herpetic viruses, papillomaviruses, cytomegalovirus).
The most common causative agent of UTI is the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli). This bacterium is classified as opportunistic and is a normal component of the intestinal microflora.
If hygiene procedures are neglected, improper washing of the perineum (from the anus forward), in case of a drop in the body's defenses (hypothermia, the presence of viral diseases), severe forms of dysbacteriosis, E. coli begin to actively multiply in the skin and can migrate to the urethral mucosa, developing which causes inflammation.
There are several possible ways of penetration and spread of pathogens in the urinary tract:
- Contact . Unprotected sexual intercourse (vaginal or anal), migration along the skin from the anus, catheterization, cystoscopy.
- Hemorrhagic and lymphogenous . Entry of the pathogen through the system of body fluids (from the blood or lymph) in the event of the presence of infectious foci in the body. For example, carious teeth, tonsillitis, sinusitis, pneumonia (against the background of an advanced viral infection, a pathogenic pathogen can penetrate the bladder mucosa - hemorrhagic cystitis develops).
- Descending . Movement of the pathogen from the kidneys through the ureters, bladder to the urethra.
- Rising . Infectious inflammation spreads from bottom to top: from the urethra to the kidneys.
Newborns are prone to developing UTIs due to possible birth defects, underdevelopment or late formation of some parts of the urinary system (urethral valves, ureteric orifice). The occurrence of infectious and inflammatory diseases is possible due to improper use of diapers.
Diet and drinking regime
During treatment of urinary tract infections, it is necessary to increase fluid intake. This is necessary so that urine and the salts and bacteria in it are quickly removed from the body. It is recommended to drink water, herbal teas and decoctions.
It is also necessary to follow a diet that is aimed at reducing irritation of the urinary tract, reducing inflammation and the amount of salts in the body.
During treatment the following should be excluded from the diet:
- salted and pickled foods;
- fatty, spicy, smoked dishes;
- herbs and spices;
- legumes and sorrel;
- onion, garlic, horseradish;
- soy sauce, store-bought mayonnaise and ketchup;
- citrus;
- coffee and black, green tea;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- sweet dishes.
The diet for urinary tract infections should consist of low-fat broths, boiled chicken, fish, vegetables and fruits. Cereals and pasta are also allowed. Once every 2-3 days you can consume low-fat dairy products.
How do infectious processes of the urinary system proceed?
Symptoms during infectious processes of the urinary tract can be different and sometimes “make themselves felt” even in the initial stages of the disease. But there are cases when the clinical picture is asymptomatic for a long time.
Symptoms that may occur with infectious diseases of the urinary system:
- pain, pain, burning when urinating;
- increased urge to urinate or urinary retention;
- excretion of urine in small portions;
- change in the smell and color of urine;
- pain in the suprapubic, lumbar regions and lower abdomen;
- fever and intoxication symptoms.
If a child’s temperature rises to high levels and there are symptoms of a UTI, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance and hospitalize the baby in the hospital!
In newborns and infants, symptoms of the disease may be nonspecific. They become irritable and moody. In such children, appetite decreases, sleep deteriorates, vomiting and hyperthermia occur, and babies also gain weight poorly.
If a child has at least one of these symptoms, a mandatory consultation with a pediatrician is necessary!
Possible complications
Urinary tract infections, the symptoms of which can vary in intensity and severity, lead to serious consequences if left untreated. Inflammation caused by infection can become chronic, and then its symptoms will bother the person constantly.
Also, infection and inflammation can penetrate the reproductive organs and affect the uterus and fallopian tubes. This is dangerous because in the future a woman may become infertile or have problems bearing a fetus, since infections increase the risk of miscarriage.
In rare cases, the infectious process leads to sepsis or abscesses - usually these conditions develop only if left untreated for a long time. Sepsis and abscess are dangerous because they lead to human death.
A kidney infection can lead to kidney failure, which can also be fatal if left untreated. If kidney failure develops in a pregnant woman, her risk of premature birth and miscarriage greatly increases.
Since infectious lesions impair the excretion of urine, without treatment a person may experience incontinence or reflux (backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureters).
Incontinence leads to a deterioration in the patient’s quality of life and psychological problems, and in the second case, toxic shock may occur (since harmful substances will not be eliminated from the body).
Infectious lesions of the urinary tract can lead to infection of other organs, so it is important to detect the symptoms of pathology in time. If treatment is started in a timely manner, the infection can be completely cured in just 3-5 days.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
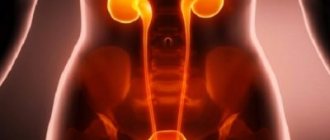
What is the urinary tract
The urinary system is the system responsible for the formation of urine and its removal from the body. It includes the following bodies:
- The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, about the size of your fists, that produce urine from blood waste.
- The ureters are connective tissue tubes that extend from the kidneys into the bladder.
- The bladder is an unpaired hollow organ that serves to store urine.
- The urethra is the tube that extends from the bladder through which urine exits the body.
Basic recommendations for the treatment of genitourinary infections in men
Treatment of genitourinary tract infections is recommended to begin only after an accurate diagnosis has been made. To prescribe the optimal medications, the doctor relies on test results, as well as medical history and examination data.
Antibiotics are primarily used for genitourinary tract infections. Antibacterial drugs are designed to help the patient get rid of pathogenic microorganisms of a bacterial nature.
The doctor selects the optimal antibiotic, focusing on the results of culture and determination of sensitivity to drugs. The higher the sensitivity based on the results of such culture, the better the results of therapy.
It is important to remember that in case of a genitourinary infection, treatment is recommended not only for the stronger sex, but also for his sexual partner. This is necessary to prevent re-infection once the course of treatment is completed.
The irrational use of antibiotics is frowned upon by doctors. You should not use drugs from this group if there is no clear certainty about the bacterial origin of the pathology.
It is important to remember that herpes and other viral infections are treated with antiviral drugs.
To combat fungal pathologies, it is worth using antimycotics.
If you try to treat a virus or fungus with antibiotics, this will not only not help the patient recover, but will also worsen his condition.
In addition to the main treatment, remedies aimed at general strengthening of the body are always recommended. Immunomodulators and vitamin complexes can be used. Their task is to activate the immune system to fight pathogenic microorganisms. Help the body win the fight against infectious processes.
Herpes and other viral infections in men
Herpes is often one of the causes of genitourinary tract infections in men. Unlike other pathologies, this is a viral disease, but it is also transmitted sexually.
With herpes, the urethra, the skin of the penis and surrounding tissues may become covered with small blisters filled with clear liquid. The blisters burst over time, and in their place moist skin defects are formed that are difficult to heal.
As doctors note, herpes quite often causes inflammation in the genital area. But besides it, other viruses are also capable of causing negative reactions. For example, characteristic complaints often appear in representatives of the stronger sex with HPV.
The human papillomavirus provokes the appearance of small formations on the skin and mucous membranes that are easily injured and irritated. In addition to HPV and herpes, inflammatory processes can be explained by HIV and a number of other viral pathologies.
Causes of urinary tract infection in women
Most UTIs develop in an ascending manner. This means that bacteria living around the opening of the urethra can enter and climb higher, causing inflammation of the bladder.
What factors predispose to UTI?
When telling a patient about a UTI, you need to pay attention to a number of predisposing factors. The most important of these in young women is recent sexual intercourse (the relative risk of acute cystitis increases 60-fold within 2 days after sexual intercourse). Risk factors should be explained to the patient so that she understands how her own behavior influences the development of a UTI. Physicians must also consider the possibility of more complex situations. The risk of pyelonephritis increases during pregnancy due to partial obstruction of the ureters.
Predisposing factors for UTI in women
- History of UTI.
- Sex life.
- Using a diaphragm or spermicide.
- First episode of UTI before age 15.
- History of maternal UTI.
- Condom use by partner.
- Taking antibiotics in the last 2-4 weeks.
- Genetic factors.
Within 2 days after sexual intercourse, the relative risk of acute cystitis increases 60 times.
What microorganisms often cause UTIs in general practice?
Approximately 80% of cases occur in. Escherichia coli, 13% - on Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
Pathogens of UTI
- Common causes of UTIs:
- Escherichia coli;
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus:
- Proteus mirabilis.
- Proteus vulgaris, Klebsiella species, Enterobacter species, Citrobacter species, Serratia marcescens, Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas spp., Staphylococcus aureus;
- candidiasis caused by Candida albicans is rare in the population, but a common occurrence in clinical patients with risk factors such as a bladder catheter, immunodeficiency, diabetes mellitus, and antibiotic treatment.
Causes of dysuria
Approximately 50% of women complaining of urinary problems do not have bacteremia. However, they have dysuria, frequent urination and a strong urge. There may be pyuria. In such cases, they speak of acute urethral syndrome, interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome.
The etiology of urethral syndrome is not completely clear. It can be caused by bacteria present in small quantities, bacteria that do not grow well in culture, nonspecific inflammation, or muscle disorders.
Other causes of dysuria and frequent urination include:
- the presence of microorganisms difficult to cultivate, for example Ureaplasma urealyticum;
- the presence of pathogens of sexually transmitted infections;
- vaginitis;
- infection with pinworms or polio;
- exposure to irritants (deodorants, bubble baths, detergents);
- atrophic urethritis.
Folk remedies against infections at home
Home remedies - herbal decoctions, herbal teas, alcohol tinctures - will help enhance the effect of medication treatment. Healing plants have diuretic and disinfectant properties . By activating the work of the kidneys, they help “wash” the genitourinary tract and cleanse it of pathogenic flora.
In addition, natural remedies enrich the body with vitamins and organic acids. These substances strengthen the immune system and increase internal reserves to fight infection.
The composition of diuretic and anti-inflammatory preparations includes the following raw materials:
- yarrow;
- sagebrush;
- oak bark;
- sage;
- Birch buds.
Cranberry is considered one of the best remedies against cystitis and urethritis. The proanthocyanidins it contains destroy the internal structure of many bacteria, and the vitamins increase resistance to infection .
The healing berry serves as a raw material for fruit drink. To prepare it, 200 g of cranberries are crushed in a blender. Then the juice is filtered, and the cake is poured with a liter of water and brought to a boil over low heat. The resulting liquid is passed through cheesecloth, mixed with juice and drunk three times a day, half a glass before meals.
A collection of lingonberry leaves, yarrow and rose hips has a diuretic and bactericidal effect. Place 1 tbsp in a glass jar. spoon of each ingredient, add a liter of boiling water. Cover with a saucer and leave for 2 hours. The resulting mixture is drunk 4-5 times a day, half a glass.
Herbal teas made from peppermint, blue cornflower or dried parsley are good for relieving pain and burning when urinating. For 1 cup of drink, 1 tbsp is required. spoon of any of the mentioned herbs. The raw material is brewed like regular tea, steeping for 10-15 minutes. Drink several sips throughout the day.
Folk remedies cannot completely replace antibiotic therapy. They are used together with medications, and are especially effective during periods of chronic exacerbations.
We recommend you look at these drugs
Generic Levitra from 1700 rub.
Boss Royal Viagra from 1170 rub.
VigRX Plus from 2650 rub.
How to get rid of and cure erectile dysfunction in men