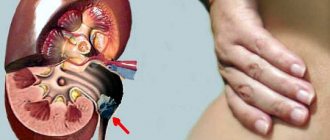
Diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract are associated with diseases of other organs. The pain that occurs may be a consequence of another disease that is not related to the kidneys and all adjacent canals.
The urinary system is a group of internal organs that ensures the removal of all unnecessary substances from the human body.
The main and most important organs in this chain are the kidneys.
They play an important role in processing and purifying all substances accumulated in the body.
The ureters are adjacent to them, then unnecessary substances pass through and are contained in the bladder, which plays the function of a storage device (a kind of reservoir) and exits out through the urethra.
The kidneys are located in the back region at the lumbar level. A vital organ, thanks to which the acid-base balance does not exceed the norm.
In a healthy person, there are 2 kidneys, which are evenly located relative to the spine. But a person is able to live with one working kidney. Of course, you will have to give up your old way of life and learn to live in a new way.
Take your medications on time, visit your doctor regularly, and most importantly, stick to proper nutrition. In structure, the kidney resembles a kind of biological filter.
The ureters are the channels that drain urine into the bladder.
How do you know if your kidneys are acting up?
Pathologies of the urinary tract occur in 30% of people (both sexes), and in half of the cases, the disease is initially asymptomatic. But there are also specific manifestations that make it possible to assume that there has been a disorder in the activity of these organs. The symptoms of kidney disease are the same in women and men. They look like this:
- pain in the lumbar region (right-left or both sides). It can be quite significant. The pain radiates to the pubis, thighs, and abdomen;
- hematuria – the presence of blood in the urine. It may acquire a pinkish tint, and if the ureter is injured by a stone, it becomes bright scarlet and opaque;
- swelling. Puffiness occurs (at first) in the morning. First of all, the legs swell; the upper extremities “swell” much less often;
- impaired urination - pain when trying to empty the bladder. Anuria is the absence of urine, oliguria is a significant reduction in its amount. Pollakiuria – increased fluid secretion (up to 10 liters per day);
- general poor health – weakness, fatigue, headache, attacks of nausea, decreased appetite;
- in some cases - an increase in temperature;
- increased sweating, chills;
- pale skin, dark circles around the eyes.
Treatment of kidneys and urinary tract
During acute colic, hot baths are practiced, although some doctors do not condone such actions, for the reason that a hot bath can negatively affect other organs, in particular the heart and raise blood pressure.
As medications, urolesan in the form of drops, canephrolin, and phytolit are used. No-shpa is used as pain relief.
But all of the above drugs are taken only after approval by a doctor.
If the diagnosis confirms the presence of stones rather than sand, removal occurs in several ways. It all depends on the size and structure.
In most cases, drug treatment is prescribed; if the size is large, the doctor refers it to a special crushing apparatus. Typically a laser or ultrasound procedure.
Kidney diseases: list and characteristic symptoms
Depending on the pathology, the following manifestations of the disease may be observed:
- nephrolithiasis, or kidney stones. A dull pain in the lower back that becomes more pronounced with exercise. When the disease becomes severe, unbearable pain, vomiting, tachycardia, and signs of shock occur: cold sweat, paleness, loss of consciousness. There is blood in the urine. Treatment – surgery or dissolution of stones using medications;
- glomerulonephritis. Manifested by edema, increased blood pressure, apathy, headache, fever, oliguria and hematuria. Then irritability, depression, and sleep disturbance are added to the listed symptoms. Treatment is carried out in a hospital, diuretics are prescribed, anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy is carried out (Aspirin), antibiotics are prescribed (Erythromycin, Clarithromycin);
- pyelonephritis. Symptoms (as well as treatment, they depend on the stage of the disease - chronic or acute) - temperature rise to 39 and above (it cannot be brought down with ordinary antipyretics), chills, sweating, nausea, lower back pain (radiates to the lower abdomen and groin), clouding urine, puffy face. Antibiotic therapy is carried out, drugs that improve microcirculation and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Diet is important;
- polycystic disease At first it doesn’t make itself felt; when the cysts are multiple, a number of signs are detected: aching pain in the abdomen and lower back, periodic appearance of blood in the urine, weakness, lack of desire to eat, weight loss, volumetric (up to 3 liters) urine output (it is light), itching. Therapy includes painkillers, antihypertensives and anti-inflammatory drugs. Surgery may be done to remove the cyst. The last resort measure is removal of the kidney;
- renal failure. The formation of urine decreases or completely stops, blood pressure drops, the pulse quickens, uremia develops - the smell of ammonia is felt in the breath, the patient is thirsty, cramps, and bone pain are noted. Treatment is in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit. An artificial kidney machine is connected, hemodialysis is performed, and in some cases a kidney transplant is required.
Characteristic symptoms of diseases of the genitourinary system in women
The female genitourinary system is vulnerable due to its anatomical location.
Diseases of the genitourinary system in women and their symptoms often do not begin to appear immediately, so you should be attentive to your body, and when the first signs of disease appear, consult a doctor.
What applies to the organs of the genitourinary system in women?
The genitourinary system is a complex of interconnected internal human organs responsible for the urinary and reproductive systems.
The female urinary system includes organs:
- two kidneys located in the abdominal region. A paired organ that serves the purpose of maintaining chemical balance in the body. Cleanses it of toxins and harmful substances. On the kidneys there are pelvises - places where urine accumulates, which systematically enters the ureter;
- ureters. Paired tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder;
- bladder. Organ that collects urine fluid;
- urethra. An organ that facilitates the release of urinary fluid from the body to the outside.
The female reproductive system includes external and internal organs. External ones include:
- labia large. They are fatty folds of the skin that protect the organ from external influences;
- labia minora. Folds of skin that are located under the large lips. Between the small and large sponges there is a genital gap;
- clitoris. It is the organ responsible for sensitivity and has the main function of the erogenous zone. Surrounded by the labia minora and located under the superior junction of the labia majora;
- entrance to the vagina. This is a small opening located in front of the lower junction of the labia majora. Protected by the hymen, the Bartholin glands are located between it and the inner lips, which serve to provide lubrication during sexual intercourse.
The internal female genital organs include:
- ovaries. The organ has the appearance of two oval bodies, which are connected to the body of the uterus from its posterior wall. The ovaries produce a hormone important for reproduction, as well as for the entire female body, estrogen;
- uterus. The piriform muscle body is located in the pelvic area. Designed for carrying a fetus, as well as for its rejection at birth. In the uterine canal, which passes into the vagina, mucus is concentrated, it helps protect the organ;
- fallopian (uterine) tubes. They pass from the corners of the uterine fundus to the ovaries, promoting the advancement of the mature follicle into the uterine cavity;
- vagina. A muscular tube-like organ extending from the cervix to the genital slit. Covered from the inside with a mucous membrane, which provides protection against pathogenic organisms through the secretion of lactic acid.
The condition of a woman’s urinary system is monitored by a nephrologist, and the reproductive system by a gynecologist.
Common diseases
Diseases of the female genitourinary organs most often appear at a certain stage of development . If we consider the urinary system, its most common diseases are:
- pyelonephritis. An inflammatory disease that occurs in the kidneys is most often concentrated in the renal pelvis. It can occur on one kidney or on both. In most cases, it has a bacterial etiology;
- urethritis. The disease is caused by inflammation of the urethra (urethra), caused by a viral infection or the influence of pathogenic bacteria. The course of the disease can be acute or chronic;
- urolithiasis disease. Characterized by a large accumulation of protein and salts in the structure of urine, resulting in the formation of stones in the bladder or other ureters;
- cystitis. Inflammation of bladder tissue. The mucous membrane can be affected, as a result of which the functioning of the organ is disrupted.
(The picture is clickable, click to enlarge)
Read our article on how to treat cystitis during pregnancy.
Common diseases of the female reproductive system include:
- vaginitis An inflammatory process occurring in the mucous membrane of the vaginal walls. Has a bacterial etiology;
- chlamydia. The disease, as a rule, is sexually transmitted and is characterized by the presence of pathogenic chlamydia bacteria in the vaginal microflora;
- thrush (candidiasis). Fungal pathology, which is caused by the spread of yeast fungi. May affect vaginal mucosa and skin;
- uterine fibroids. A benign formation of hormonal etiology, which can occur inside the uterus or in its outer walls;
- ovarian cyst. A benign formation located on the body of the ovary can transform into malignant;
- cervical erosion. Caused by damage to the epithelium or the wall of the uterine cervix;
- endometriosis. Characterized by the proliferation of the inner mucous layer of the uterus. In some cases, it may spread to the vagina or abdominal cavity.
Any disease of the female genitourinary system requires treatment. In some cases, surgery is necessary.
When should you see a doctor?
Diseases of the genitourinary system can be asymptomatic only at the initial stage. Most often, signs of the disease may appear as the pathology spreads.
The most common signs of diseases of the female genitourinary system are:
- urinary disturbance, characterized by too frequent urge (cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis);
- painful urination, as well as burning, pain, stinging and odor when emptying the bladder (cystitis, urethritis);
- itching and irritation in the external genitalia (candidiasis, chlamydia);
- swelling of the genital organs (urethritis, candidiasis);
- pain syndromes in the lower back (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- high temperature (pyelonephritis, chlamydia);
- sensation of a foreign body in the uterine area, heaviness (fibroids);
- copious discharge, presence of ichor in the discharge, discharge with a cheesy structure (thrush, chlamydia);
- pain during sexual intercourse (fibroids);
- bloody streaks in the urine (cystitis);
- rashes of various types on the genitals;
- abdominal pain (fibroids, endometriosis).
Any disease of the female genitourinary system manifests itself sooner or later and cannot be hidden. If a woman begins to experience frequent abdominal pain, uncharacteristic discharge, or itching or rashes on the genitals, she should immediately consult a doctor .
A woman cannot diagnose the disease on her own, since many diseases can have similar symptoms.
In addition, improper treatment can aggravate the course of the disease, which will negatively affect health.
How to check if there is a disease?
The doctor can prescribe diagnostic measures in accordance with the symptoms with which the woman came to the medical facility:
- After familiarizing yourself with the patient’s complaints, the doctor can palpate the abdominal cavity and feel the temperature of the muscles of the lower back and peritoneum.
- During a visual examination, the doctor can detect inflammation of the tissues of the external genital organs and palpate neoplasms.
- Examination with a speculum can help to examine the condition of the mucous membrane.
- Colposcopy helps determine the condition of the inner lining of the uterus, detect fibroids, erosion, and also take sections of tissue for histology.
After examination and palpation, the doctor prescribes the following measures related to laboratory diagnostics :
- general blood and urine analysis (characterizes the presence of inflammatory processes in the blood or urine);
- biochemical blood test (helps detect renal failure);
- examination of smears from the vagina, urethra (determine the presence or absence of pathogenic microorganisms);
- bacterial culture, cytology (bacterial culture helps identify genitourinary infectious pathogens, cytology determines the presence of infectious and cancerous diseases).
Hardware diagnostic methods provide detailed information about the condition and structure of a woman’s internal genitourinary organs:
- ultrasound examination of organs (urethra, uterus, abdominal cavity);
- MRI or computed tomography helps evaluate the condition of the kidneys, uterus, bladder, and urinary canals.
The set of diagnostic measures depends on the pathology expected during the initial examination. The doctor may limit himself to smears and a general blood test (for candidiasis), or prescribe a whole range of measures (for renal failure). In accordance with the results obtained, the specialist makes a diagnosis and selects treatment.
How to treat?
Diseases of the female genitourinary system are most often associated with inflammatory processes. Therefore, to suppress pathogens, you should take an antibacterial drug . However, only a doctor can prescribe an antibiotic based on tests and identification of the pathogen.
The course of antibiotics should be completed completely, otherwise untreated diseases may become chronic.
In addition, along with antibacterial tablets, the doctor may prescribe immunostimulating agents .
Treatment of neoplasms (fibroids, cysts) may be limited to taking hormonal medications , or may lead to surgery.
In addition to drug treatment, you can, with the consent of your doctor, resort to traditional medicine. For this, herbal mixtures and berries are used as decoctions (chamomile, blueberries, leeks, dill seeds, steelberry roots). In addition to herbal decoctions, a decoction of viburnum with honey is used for inflammation of the urinary tract.
Prevention
In order to prevent female diseases, a girl should monitor genital hygiene from an early age: care in the intimate area should be done daily. In addition, you must adhere to simple rules:
- do not overcool;
- wear cotton underwear;
- use a condom during sexual intercourse.
It is important to eat right, not to get carried away with spices and fatty foods, and to avoid alcohol. If diseases occur, they should be treated in time and lead a healthy lifestyle. A systematic visit to the doctor will help identify diseases at an early stage of development.
Compliance with the above measures can protect a woman from various diseases associated with the genitourinary system.
A set of exercises to restore the genitourinary system of women in the video:
Source: https://opochke.com/mochevyvedenie/bolezni-mochepolovoj-sistemy-u-zhenshhin-simptomy.html
Diseases of the urinary organs and symptoms
The most common pathologies of the excretory system are:
- urethritis. Characterized by frequent painful urination, nagging pain in the groin; change in the smell and color of urine (in men - discharge from the urethra). Treatment is outpatient. The doctor prescribes antibiotics, sedatives, and physical therapy is used;
- cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) - symptoms: frequent urge, pain when urinating (increases at the end of the process), decreased urine volume, pain in the suprapubic area. Bed rest is indicated, the patient should drink plenty of fluids, follow a diet, and take herbal baths. Among the medications, antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine), antibiotics, herbal medicines (Canephron, Cyston) are prescribed;
- prostatitis. Pain in the lower abdomen, decreased sexual function, blood in the urine and semen. Antibiotics (Erythromycin, Ciprofloxacin), painkillers, and herbal infusions are required. Physiotherapy is widely used. A prostate massage is performed.
Diseases of the urinary system in adults and children: types and signs
The human urinary system includes not only the bladder and ureters, but also the kidneys and urethra. In the human body, the urinary system is connected to the reproductive system, so inflammation often spreads to the genital internal organs.
Diseases of the urinary system are invariably accompanied by discomfort, pain, disrupt the usual way of life and often lead to various complications. Such diseases are very common, affecting every ninth person. Moreover, inflammatory diseases are more common in women, and tumors of the urinary system are more common in men.
Causes and symptoms
There are many causes of urinary system diseases
Many diseases of the urinary system quickly become chronic, so when the first signs appear, an examination is prescribed to identify the causes and treatment is prescribed.
Diseases of the urinary system can occur for various reasons:
- Infection. The most common cause of kidney and bladder diseases. The infection can penetrate the organs of the urinary system in various ways: through blood and otitis media, sore throat, as a result of inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system and independently through the urinary canal, during hypothermia. Bacterial infections are especially dangerous for the urinary system.
- Injury or overexertion. Some diseases can occur due to heavy lifting, injury or bruise to the abdominal area.
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, the kidneys experience greater stress as the volume of fluid in the body increases. In this case, various kidney diseases, edema, and infections of the genitourinary system may occur due to reduced immunity.
- Hypothermia. Often it is hypothermia of the pelvic organs that leads to cystitis and other inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Cardiovascular diseases. Many of them cause kidney complications due to insufficient blood flow in the pelvic organs.
It is not difficult to recognize a disease of the urinary system when the symptoms are already obvious. However, some diseases are asymptomatic at first and can only be detected by test results (urine or blood).
Such diseases can begin with symptoms that seem to be unrelated to the urinary system: headaches, dizziness, increased fatigue, decreased appetite, nausea, elevated body temperature, shortness of breath, cardiac dysfunction.
Pain specifically indicates a disease of the urinary organs - it can occur in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, and intensify when urinating.
Most diseases of the urinary system are associated with dysfunction of urination. It may be painful, frequent, accompanied by pain, itching, the volume of urine may decrease significantly, there may be a frequent urge to urinate, and blood may appear in the urine.
Types and description of diseases
Features of the development of diseases of the urinary system
The category of “diseases of the urinary system” includes a large number of different diseases and pathologies. Conventionally, they can be divided into three large groups: diseases of the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract, and urolithiasis.
Let's take a closer look:
- Kidney diseases. The most common kidney diseases include pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, kidney tumors, nephropathy, and renal failure. These completely different diseases are united by damage to the kidney tissue, which as a result can lead to such a serious complication as kidney failure. All of them are accompanied by edema due to impaired kidney function and fluid retention in the body, lower back pain and urination problems. The most common is pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis), caused by a bacterial infection. This disease occurs in people of all ages and quickly becomes chronic.
- Diseases of the bladder and urinary tract. The most common disease in this group is cystitis. When the bladder becomes inflamed, urination becomes painful, nagging pain occurs in the lower abdomen, the urine becomes cloudy, and blood may appear in it. This disease can be primary, occurring when an infection enters the bladder, or secondary, which is a complication of other diseases. This group also includes vesicoureteral reflux, when the outflow of urine is disrupted and it flows back into the bladder or even into the kidneys.
- Urolithiasis disease. This disease also has its own varieties depending on where the stones are located and what they consist of. Any type of urolithiasis is accompanied by pain. It varies from mild to harsh and unbearable depending on the size and location of the stone. Pain, stinging, difficulty urinating, nausea and vomiting, sand and blood in the urine may also occur. At first, urolithiasis is asymptomatic, as long as the stones are small and do not interfere with the normal functioning of the urinary system. They can be detected using ultrasound.
Other urinary system disorders
Pathology of the urinary system: types and signs
There are a number of pathologies of the urinary organs that are less common. They may occur with different likelihood of occurrence in men and women. This is typical for all diseases of the urinary system. For example, cystitis is many times more common in women, and urolithiasis – in men.
Let's look at some pathologies of the urinary system:
- Acidosis. Acidosis disrupts the acid-base balance of the entire body. As acidity increases, the load on the kidneys increases significantly. In mild forms of this disease, it is asymptomatic, but severe forms can lead to heart attacks, thrombosis, coma and death. Causes of acidosis include diet disorders, cancer, pregnancy, dehydration, and increased blood sugar.
- Kidney cyst. Cysts are benign growths filled with fluid inside. The causes of renal cysts are still not fully understood, but risk factors include birth complications, age over 50, infections and trauma. This disease requires treatment, since in its absence the cyst can block the ureter, squeeze blood vessels and lead to the death of the kidney.
- Amyloidosis of the kidneys. This disease occurs due to the deposition of large amounts of starch in the kidney. Amyloidosis often occurs against the background of other, more dangerous diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis), and therefore requires careful examination and identification of the causes. Symptoms include weakness, swelling, high blood pressure, nausea and stool upset, cardiac dysfunction, muscle pain, and liver enlargement.
- Urinary incontinence. Urinary incontinence brings many inconveniences. Urine cannot be retained in the bladder and tract and is released involuntarily, which forces the patient to constantly wear special pads or diapers. Most often this disease occurs in women. It can be caused by postpartum complications, injuries, surgeries, infections, and heavy physical exertion. In male incontinence, which is not common, the cause is most often prostate adenoma.
Diagnosis and drug treatment
Ultrasound is an effective method for diagnosing diseases of the urinary system
Currently, there are many diagnostic methods in urology that make it possible to detect diseases of the genitourinary system in the early stages:
- Laboratory diagnostics comes first. Everyone had to donate urine. It is especially often taken by pregnant women. A general urine test allows you to identify abnormalities in kidney function and plan further diagnostics. This test looks for protein, occult blood, and salts in the urine.
- Instrumental examination is most often carried out using a catheter, which is inserted into the urethra. However, this method is not used if an acute inflammatory disease accompanied by severe pain is suspected.
- In cases where other examination methods seemed ineffective, a kidney biopsy is used to collect material for research.
- Endoscopy is also widely used in urology. This is a fairly informative research method in which an endoscope is inserted into the urethra and advanced all the way to the kidney. This way you can see the urinary canal, bladder, and renal pelvis from the inside.
- Ultrasound remains one of the most popular methods for examining the organs of the urinary system. This is a painless, inexpensive and informative research method that allows you to identify kidney stones, tumors, cysts and other diseases.
— Disease of the kidneys and urinary system.
Drug treatment is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician after a thorough examination and diagnosis.
Diseases caused by bacterial infections, such as bacterial cystitis, cannot be treated without antibiotics.
The choice of antibiotic and its dosage is determined by the doctor depending on the causative agent of the disease and the severity of the patient’s condition.
For urolithiasis, medications are prescribed that crush and soften stones. Sometimes folk remedies are prescribed for the same purpose, for example, celery roots, knotweed, and dandelion roots. For diseases of the urinary system, anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers are mandatory to relieve pain.
Diseases of the urinary system in children
Features of the development of diseases of the urinary system in children: types and description
In young children, the most common infection is a urinary tract infection. It occurs in children more often than in adults due to immature immunity and immaturity of the pelvic organs.
Acute pyelonephritis often occurs in infants, which can only manifest as weakness and high fever. Only a pediatrician can determine the disease after examination.
In addition to the temperature, the child develops painful sensations that he cannot report due to his age, so children often cry, sleep poorly, refuse to eat, and you may notice frequent urination.
Unfortunately, such infections in children progress and spread very quickly. At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor. If treatment is not started within 24 hours, serious complications may occur, such as kidney failure.
In older children who are accustomed to using the potty, it is somewhat easier to determine a disease of the urinary system. The child himself may complain of pain, cries during urination and urinates involuntarily, which was not the case before.
Mothers may also notice a decrease in the volume of urine and a frequent urge to urinate in the child.
If, on the contrary, the amount of urine has increased, the child experiences thirst, weakness, and loses weight; these are signs of diabetes.
After a year, girls are much more likely to suffer from such infections and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system. In boys, the percentage of diseases decreases significantly by the age of one year.
Girls can often get sick until they are 4 years old. Also, violations are indicated by bedwetting over the age of 5 years.
Such a pathology requires examination, as it may indicate various inflammations, stress, and neurological disorders.
In newborns and older children, cystitis often occurs, caused by hypothermia or direct infection in the membranes of the bladder. It is treated with gentle antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and herbal sitz baths. In case of chronic cystitis, it is important to accustom the child to daily hygiene and normalize his diet.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostics is carried out using the following laboratory and instrumental methods:
- Ultrasound examination;
- urography with contrast agents;
- CT;
- radiography,
- blood chemistry;
- Analysis of urine;
- scraping of discharge from the genitals;
- cystoscopy of the bladder;
- biopsy.
Kidney pain
The main cause of pain and renal colic is the presence of stone or sand.
Diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract are associated with abnormal or impaired metabolism. This is болезни щитовидной железы, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
The so-called urolithiasis has several varieties. Depending on your diet, kidney stones have different structures and sizes. May be phosphate, loss or oxalate based.
For minor but frequently recurring pain, you should seek medical help. The doctor will prescribe a urine test, sometimes a blood test, and refer you for an ultrasound examination.
The main thing is to correctly determine the diagnosis and be sure that the cause of acute pain is the kidneys, since similar symptoms are possible with stomach pain.
Herbal treatment
Treatment of kidney diseases is carried out according to indications using herbal medicine. A doctor's consultation is required in advance. Herbal therapy is represented by the use of:
- Horsetail.
- Daisies.
- Mint.
- Parsley.
- St. John's wort.
- Lingonberry leaves.
- Bearberry.
- Dandelion.
The folk remedy is prepared as follows: the herb (1 tablespoon) is poured with boiling water (200 ml) and left for 20 minutes. Take the medicine before meals for two weeks.
Antibiotics for illness
Treatment of kidney diseases necessarily includes the prescription of antibacterial drugs. The specific medicine and dosage are determined by the doctor. Priority is given to drugs with a wide spectrum of action: antiviral, antibacterial and antifungal.
The most common medications prescribed for kidney disease are:
- Ofloxacin, which is commonly prescribed for pyelonephritis.
- Netilmicin, which has a pronounced bactericidal effect.
- Amoxicillin, prescribed for severe inflammation.
- Flemoklav Solutab, which is indicated during pregnancy.
- Cephalosporin drugs, which are natural, low-toxic drugs.
Despite the good tolerability of some antibiotics, they should be prescribed by the attending physician. Self-therapy can result in negative consequences and the formation of adaptation of pathogenic microflora to them. As a result, repeated treatment will require the use of more powerful drugs.
Diet for kidney disease
One of the areas of treatment for pathologies of the urinary system is diet therapy. Its main principles are: reducing the amount of protein-rich foods and reducing the dosage of salt consumed. It is allowed to add salt to the finished dish immediately before serving. Prohibited foods for kidney diseases include:
- fatty meats, smoked meats,
- canned and semi-finished products,
- products with a high inclusion of salt and preservatives,
- marinades, pickles,
- animal fats,
- egg yolk,
- hard cheeses,
- mushrooms,
- chocolate products,
- coffee,
- fatty sauces, ketchup,
- alcoholic drinks,
- sweet carbonated drinks,
- packaged juices.
Important attention should be paid to the drinking regime. The minimum amount of liquid is about 2 liters. For drinking, you can use not only water, but also homemade fruit juice, rosehip decoction, and compote.
The optimal nutrition option would be to follow a diet that combines dairy and plant products. A sample menu might include:
- vegetable soups,
- salads containing fresh vegetables and vegetable oil,
- fruits,
- fermented milk products with low fat content,
- lean meats and fish (up to 3 times a week),
- vegetable stew,
- mashed potatoes,
- porridge (preferably buckwheat and oatmeal).
The peculiarity of preparing the dish is to avoid frying. Products can be stewed or boiled. You should not practice fasting, as this does not always have a positive effect on the functioning of the kidneys.
Glomerulonephritis
This is a disease that is inflammatory and autoimmune in nature. With glomerulonephritis, damage to the renal glomeruli and tubules occurs. The disease can develop independently, as well as accompany other ailments. Most often, the cause of this kidney disease is streptococcal infection ; in more rare cases, it develops against the background of tuberculosis and malaria . Also, the cause of the disease is sometimes hypothermia and the influence of toxic substances.
There are acute , subacute and chronic glomerulonephritis. In the acute form, the patient is bothered by pain in the kidneys, swelling in the eye area on the face, as well as swelling of the limbs, attacks of arterial hypertension , changes in the state of urine are observed, the temperature rises, pain in the lower back, in the right or left part, increases. As a rule, this disease manifests itself in a person several weeks after suffering an infectious disease.
In the chronic form, which develops in most cases as a consequence of acute glomerulonephritis, the symptoms are similar to those of the acute form of the disease. Doctors distinguish hypertensive , nephrotic , mixed and latent forms of the disease.
In the process of diagnosing glomerulonephritis, not only the results of instrumental and laboratory studies are taken into account. If necessary, biopsy .
It takes a long time to treat this disease, sometimes therapy lasts several years. The patient is prescribed a diet, antihypertensive and diuretic drugs, as well as long-term treatment with corticosteroids. If necessary, other treatment methods are practiced.
Nephroptosis
Nephroptosis is a pathological phenomenon associated with too much mobility of the kidney, the so-called wandering kidney. Due to the anatomical features, women are more likely to suffer from this disease. Due to the fact that the fatty receptacle in their kidneys is shorter and wider, and at the same time there is also a weakening of the abdominal press due to pregnancy and childbirth, the disease develops quite often. In addition to these reasons, factors that provoke the development of nephroptosis can be very sudden weight loss, injuries, and heavy physical activity. Three stages of nephroptosis are defined, which are differentiated depending on the degree of kidney mobility.