Urinary tract infections in infants are the most common disease. Typically, specific bacteria that are present in the urinary tract are to blame for urinary tract infections in infants. Do you know what the symptoms of this disease are, how to help your child in such difficult moments, and what to do to prevent the infection from returning?
Causes of the disease
Sometimes parents notice that their child's urine smells strongly of rotten fish, and the smell is sometimes reminiscent of acetone. In such situations, the first thing that comes to mind is cystitis. However, the diagnosis may not always be correct. Before you begin treatment, research the reasons why your urine smells like acetone or rotten fish.
If the child has passed all the tests and the results indicate a urinary tract infection, the parents have a question - why and when did this happen? The causes of the disease can have different origins.
Main reasons:
- chronic neuralgia;
- contact with another patient in the pool (Escherichia coli);
- frequent hypothermia;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene rules;
- improper use of diapers;
- lack of a special diet for a small child (protein in urine is higher than the required level);
- the presence of a large amount of smoked and spicy foods in the diet.
All these factors can trigger the development of the disease. You need to carefully monitor the baby’s condition and, when he cries for no reason, immediately go to the doctor. If stones form, urination will be accompanied by severe pain.
Prevention
It is important to understand: urinary tract disease is an ascending infection. The most effective way of prevention: hygiene and proper nutrition. Use diapers correctly; when caring for newborns, it is useful to use folk remedies: bathing in chamomile, string.
For newborns, the best diet is breastfeeding. Mom should watch the foods she eats. It is necessary to exclude hot, spicy and sweet foods. Children need to be given plenty of protein and limit the consumption of sour fruits and vegetables.
Do not allow children wearing only swimming trunks to sit on the side of the pool or bench. The infection is transmitted by contact. Avoid hypothermia in your child.
Rate this article:
What are the symptoms of a urinary tract infection in a baby?
Symptoms of this disease may include not only burning and pain, difficulty urinating, but also fever, diarrhea, loss of appetite, vomiting, and pain in the sacrolumbar region. Your baby may wet himself at night, feel pressure on his bladder, or urinate too often (but in small quantities). In addition, blood may even appear in the urine. If you notice the symptoms listed above in your baby, you should not underestimate them. Be sure to consult with an experienced doctor and do all the necessary research. If the disease is not treated, the infection can cause pain and discomfort, and also become chronic, and then return with a vengeance. Difficulties in diagnosing urinary tract infections lie in nonspecific symptoms. This condition typically affects babies who use diapers and are unable to tell what hurts where.
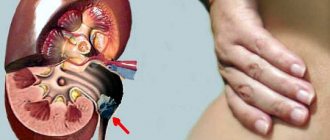
Causes and conditions of development
All diseases in children that cause stagnation of urine predispose to inflammation of the genitourinary system. A disturbance in the outflow of urine can be the result of a mechanical cause, or damage to the emptying mechanisms (adynamia in neuromuscular dystrophy, central nervous diseases - myelodysplasia and inflammatory diseases of the brain and spinal cord).
Mechanical obstacles are most often congenital. These are congenital defects of the ureter (expansion and insufficiency of the ureteral openings, ureterocele, hydronephrosis) or the bladder and urethra (valves, narrowing and folds of the urethra, etc.).
Acquired obstacles to the outflow of urine - stones, foreign bodies, tumors (rarely).
Most temporary pyuria are caused by some congenital or acquired abnormality of urinary tract emptying. Often, due to the weak contractility of the muscles of the renal pelvis, the slightest obstruction in the ureter can cause stagnation of urine. Sometimes such an obstacle in infants is invisible particles of urogenital acid. A known role, in addition to difficulties in the outflow of urine, in the occurrence of purulent inflammation of the genitourinary tract is played by all states of exhaustion of the body, in which the body’s resistance to infection is weakened (dehydration that occurs with gastrointestinal disorders in infants, vitamin deficiencies - mainly vitamin A, etc. ).
Most often, purulent inflammation is caused by various types of intestinal molasses (mainly the common colon bacterium). In addition to E. coli, they are found either in pure culture or in combination with it, also streptococci, staphylococci, rarely enterococci, gonococci, pneumococci, etc. With secondary cystitis and pyelonephritis that began after acute infections of the upper respiratory tract, middle ear and tonsils, often in the first days of pyuria, streptococci and staphylococci are found, isolated or mixed with E. coli. They often, but not always, like other microbes secreted by the kidneys, reduce the resistance of the urinary tract mucosa and thereby contribute to the development of E. coli.
E. coli produces two types of toxins: endotoxin, which is enterotropic and causes diarrhea, bleeding and ulceration of the intestinal mucosa, and exotoxin, which is predominantly neurotropic and causes muscle weakness, drowsiness, general weakness, even coma with spastic tetanic convulsions.
Signs of a urinary tract infection
Not all parents immediately notice symptoms in their children. It is quite difficult to recognize a urinary tract infection in children under one year of age:
- the child does not speak yet, he is not able to describe his feelings;
- he is unable to regulate and control his urination;
- signs of the disease are also characteristic of other manifestations of the disease.
Urinary tract infection in infants is diagnosed in the same way as in adults. The signs are the same for all children:
- burning;
- frequent urination;
- pain in the lumbar region, in the abdomen.
Parents can understand that the child is in pain and it is associated with urination by the following signs:
- cries and becomes restless when urinating;
- shows anxiety, is capricious;
- reacts poorly to touch on the back, especially the lower back or tummy.
Treatment of UTIs in infants
The main method of treating UTIs in infants is due to:
- prescribing antibacterial drugs as early as possible, taking into account the resistance of microorganisms;
- timely detection and correction of urodynamic disorders;
- long-term antimicrobial prevention of recurrent processes;
- controlling intestinal functions;
- reducing the dosage of antibacterial agents in accordance with indicators of renal efficiency.
When treating infants, the presence of high fever and signs of toxicosis is an indicator of the immediate use of antibacterial drugs intravenously. It should be borne in mind that not all antibiotics can be used to treat infants. For parenteral administration, cephalosporins (Cefataximin, Ceftazidime, Ceftriaxone), penicillins (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid), etc. are prescribed.
The indicator for oral therapy is a decrease in signs of toxicosis and normalization of temperature throughout the day. Prescribed - "Ceftibuten", "Cefixime", "Cefpodoxime poxetil", "Cefuroxime axetil", "Cefaclor", etc. The duration of antibiotic therapy is one, one and a half weeks, but not less than 3 days; in case of complicated processes in newborns, it is permissible to extend the course to three weeks
Sick babies must be under constant medical supervision, so their treatment should be carried out under inpatient conditions.
How to treat a urinary tract infection in a baby
In addition to the treatment recommended by your doctor, you can try folk remedies. Here are some of them:
- Give your child plenty of fluids, which will flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Give cranberries (whole, drink, supplements). Its therapeutic effect on urinary tract infections has been questioned, but cranberry is a rich source of vitamin C, which oxidizes urine and also inhibits the development of bacteria and strengthens the body.
- Also take care of the hygiene of your intimate areas. Be sure to prevent irritation.
- Apply a heating pad and dress your baby warmly so as not to cool his body.
- Use warm baths that are relaxing and calming. Do not add irritating, strong-smelling cosmetics to it.
If a child feels the need to urinate during a warm bath, never prevent him from doing so.
What are the causes of urinary tract infection
In the vast majority of cases, this disease is caused by a natural element of the intestinal microflora, namely coli coli. The main cause of infection is considered to be the entry of this bacterium from the gastrointestinal tract into the urinary tract. These bacteria multiply quickly in the bladder, causing discomfort and severe pain. Urinary tract infections mainly affect girls. This is due to the short urethra, which allows bacteria to more easily enter the urinary system.
Diagnosis of the disease
Laboratory tests can confirm the presence of a urinary tract infection. First of all, a general urine test is performed. You can read more about how to properly collect urine from infants in this article. Detection of bacteria in the urine and a leukocyte level of more than 10 in 1 µl signal inflammation in the urinary tract . Bacterial culture of urine is mandatory. Detection of bacteria in the urine above 104 KUO/ml confirms the presence of a urinary tract infection. Bacterial culture allows you to determine the causative agent of the infection and immediately select a suitable antibiotic.
In addition, to clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound scan of the urinary system is indicated . The research method makes it possible to assess the structure and size of the renal parenchyma and identify possible anomalies in the development of the urinary organs. Young children with urinary tract infections also undergo voiding cystography (only during remission of the disease). This is an X-ray examination of the bladder, which is performed during urination. The method allows us to identify vesicoureteral reflux, which contributes to the development of inflammation in the urinary tract.
Why do girls get sick more often?
According to statistics, children under the age of 6 suffer from cystitis equally - both girls and boys. As for the age period from six to nine years, which we are talking about, here cystitis in girls occurs 2 times more often than in boys. This is due to the structural features of the female genitourinary system.
In a boy, the urethra is located far from the anus, and in a girl, the urethra is wide and short - this is a direct path to infection. This tendency to cystitis in females persists throughout life. That is why mothers of girls need to be especially attentive, monitor their child’s hygiene and teach girls proper hygiene.
Treatment
For cystitis manifestations, treatment can be carried out at home. The main thing is to choose the right drugs and antibiotics. If parents treat their children, strictly following the doctor’s recommendations and regularly administering the prescribed antibiotic and antispasmodic drugs, the child’s well-being can quickly return to normal.
The infection can be eliminated only with antibiotics - this is the only effective medicine. Painful sensations are relieved by antispasmodic drugs.
Timely treatment and properly selected antibiotics and uroantiseptic drugs are half the success. The treatment process is complex and exclusively individual. Without a doctor, it is impossible to eliminate the infection.
Treatment of pyelonephritis is carried out in a hospital setting. Especially children under two years of age. Inpatient treatment requires the following procedures: antibiotic administered parenterally, infusion therapy.
Bed rest is not a requirement. Exception: severe fever and pain. The most important condition: choose an effective antibiotic.
Antibiotics
Treatment of infection with antimicrobials: a prescribed antibiotic for a specific pathogen. An important nuance: nephrotoxic drugs are excluded. An antibiotic of the penicillin group, cephalosporins are prescribed.
For cystitis, antibiotics are taken for at least seven days. For pyelonephritis, an antibiotic is taken for at least two weeks. After a repeated urine test, a series of uroantiseptics are prescribed.
Diet
A special diet is prescribed: protein-plant products and dairy foods. Avoid eating sour and fried foods, smoked foods, citrus fruits, fruits, tomatoes, grapes, pickles, and sauerkraut.
After the pain syndrome has been relieved, you need to drink as much fluid as possible - this limits the effect of urine on the mucous membrane and promotes the rapid elimination of toxins. Preference: slightly alkaline liquids, fruit drinks.
To prevent the development of diarrhea, medications such as probiotics are prescribed. To prevent re-infection, your doctor may recommend taking herbal medicines.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is very effective. Preparations of St. John's wort and leaves of lingonberry, nettle, chamomile, rose hips and yarrow are used as teas and decoctions. Herbal teas are an excellent diuretic and anti-inflammatory agent. Folk remedies can relieve not only inflammation and uncomplicated symptoms, but also pain. A course of treatment with folk remedies can be prescribed for a long time.
Bakposev
To determine the main pathogen and whether the body is resistant to antibiotics, it is necessary to additionally submit urine for bacterial culture before starting treatment. The analysis is done no longer than 5-6 days.
The smell of urine, similar to acetone, is not a final diagnosis. Bacterial culture allows you to clearly determine whether there is a threat of kidney damage and whether there are oxalates in the urine.
How the material for analysis is collected:
- the child’s genitals are washed well;
- the container for collecting the analysis is sterilized;
- The morning portion of urine is collected, which is then poured into a prepared container, after which the latter is tightly closed.