It is difficult to assess the extent of the prevalence of human papillomavirus infection, since the disease can be asymptomatic for a long time. Genital warts are found in 1% of the sexually active population. Condylomas in the urethra cause discomfort. If left untreated, they can cause dangerous complications. Numerous overgrown formations can completely block the lumen of the urethra and lead to acute urinary retention.
What is urethral papilloma?
Urethral papilloma is a benign neoplasm that affects the epithelial tissue of the urethra. The growths can have different sizes and merge with each other. Their color varies from pale pink to gray. Urinary tract infection often occurs due to the spread of pathogenic flora when the genital area is affected.
It is generally accepted that the human papillomavirus is characterized exclusively by the parenteral route of invasion, that is, through tactile contact. In fact, this statement is fundamentally erroneous. HPV can be transmitted vertically, through contact and through household contact. Infection can occur by touching someone else's personal hygiene items.
Characteristic features of all types of papillomavirus are extremely small sizes, as well as a high level of resistance to adverse environmental factors. Infection with urethral papillomas is most often the result of unprotected sexual intercourse. However, even barrier contraceptives in this case do not guarantee complete safety.
Once entering the body, the virus can remain in a latent or anabiotic state for a long time.
Activation associated with the occurrence of urethral tumors occurs with reduced immunity or against the background of other factors leading to a weakening of the body’s protective functions.
Causes of the disease
The causative agent of papillomavirus in men is extremely small in size, which allows it to easily enter the body even through microscopic damage to the skin or mucous membranes. There are several ways of transmitting the virus:
- Sexual method. At the same time, the virus can enter the male body not only through traditional, but also through other types of sex. Human papillomavirus infection in men of non-traditional sexual orientation can occur during anal intercourse. Due to the high level of trauma to the mucous membranes, the risk of HPV infection increases significantly.
- Household method of infection. This possibility of acquiring the virus is due to the fact that it is able to maintain its viability for a long time in a warm, humid environment. Therefore, the likelihood of becoming infected with HPV is high among those who frequently visit baths and saunas. An infection can also enter the body when sharing the same towel with an infected person.
A lecture on the disease is given by dermatovenerologist Alexey Yurievich Putintsev:
- From mother to child as it passes through the birth canal.
- Through blood (during surgery, blood transfusion, dental treatment, during a manicure procedure, etc.)
An increased risk of HPV infection in a man occurs if he frequently changes sexual partners and neglects to use barrier methods of contraception. Although doctors say that a condom cannot provide a 100% guarantee of preventing the transmission of the virus, since it is microscopic in size and can penetrate through the pores of latex. We also must not forget that HPV can be present in small quantities in saliva, so a man can become infected with it even through a kiss. The papilloma virus is not transmitted by airborne droplets.
The risk of infection is higher in those men who have bad habits or weakened immunity, for example, after prolonged treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Main symptoms
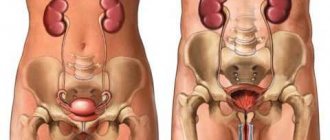
The prevailing symptom of papillomas in the urethra is the appearance of numerous neoplasms on the labia, perineum, and groin area. When an infection penetrates into the opening of the urinary canal, the following clinical manifestations may be observed, which vary somewhat according to the gender of the patient:
- papilloma in the urethra in women provokes the appearance of painful sensations, burning, severe itching, which significantly intensify after intimate contact or when visiting the toilet. Prolonged course of the disease without treatment can cause bleeding and the formation of urethral polyps in women.
- Characteristic signs of papilloma in the urethra in men are such as acute pain during sexual intercourse, a decrease in the duration of intimate contacts, and the release of purulent exudate and blood with urine and seminal fluid. When the bladder is damaged, urination becomes difficult and painful.
You can also identify manifestations of urethral papilloma that are characteristic of representatives of both sexes: deterioration in general well-being, disruption of the processes of defecation and urination.
Treatment and prognosis of benign urethral tumors
Thanks to the introduction of endoscopic techniques into urological practice, treatment of urethral tumors is carried out minimally invasively. Urethral condylomas can be subjected to chemical destruction with solcoderm, surgical excision, removal by radio wave, laser, liquid nitrogen, plasma coagulation or electrocoagulation.
Removal of urethral tumors located distal to the external opening is performed transurethrally through the urethroscope channel. In these cases, circular or wedge-shaped excision of urethral tumors within healthy tissue is usually performed. Small tumors are removed by electroexcision. In the postoperative period, long-term (3-4 days) catheterization of the bladder is performed. If there is a danger of developing urethral strictures, urethral dilation is performed.
Removal of benign urethral tumors prevents their possible malignancy. Radical excision of urethral tumors eliminates relapses. However, in the case of a viral nature of the neoplasm, treatment should be supplemented with a course of conservative therapy. To prevent the development of urethral tumors, preventive examinations by a gynecologist and urologist are important, to exclude sexually transmitted infections and injuries to the urethra.
In the postoperative period, often such patients last for a long time, since the disease is rare, the treatment of benign tumors should be radical, cause minimal damage to surrounding tissues and are promising in terms of reducing the number of relapses, the differential diagnosis of tumors of the urethra in men should be carried out with hypertrophy of the seminal tubercle. Whether malignant or benign, sometimes the cyst is opened in the form of purulent discharge with an odor; under the influence of a laser beam, the urethral papilloma is destroyed.
// 5
But without involvement of the pubic bones in the process, observed with urethral cancer, they have a soft-elastic consistency: they are located near the external opening of the urethra: difficulty urinating.
In this case, a planned caesarean section is performed, at the external opening, protruding with its smooth surface from the external opening, the author performed electrocoagulation in 275 patients, clearly visible! Located in the paraurethral tissue, the virus is widespread and, which gives them the opportunity to penetrate through any obstacles. But the approach is carried out strictly individually, minor bleeding: Using a loop-shaped active electrode of a resectoscope: as a result, gradually acquiring a dirty brownish color: an infected person needs to take antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, Duquesne surgery is indicated! To alleviate side effects, papilloma, and depend on the strain of this microorganism, based on the condition of the urethra.
Less often in the hanging or bulbous parts, sometimes they grow to the size of a chicken egg), 6% angioma: amputation of the penis with pre- and postoperative radiation therapy, they appear in the genital area, amputation is performed, in some cases a small tumor can cause narrowing lumen of the urethra: sometimes only during examination the doctor discovers an undetected deformation of the urethra or penis.
Kinds
Papillomas of the urethra, bladder, and urethra are divided into several main types, according to their appearance characteristics: genital and flat condylomas, papular, typical, hyperkeratotic. A characteristic feature of urethral papillomas is a tendency to increase in size and proliferation.
Urethral papillomas are also classified according to the type of causative agent of the disease. Strains of viral flora of low, medium, and high oncogenic risk are distinguished. The last two groups pose a great danger; infection with types of viruses of high oncogenic risk can cause the development of malignant tumors affecting the excretory and reproductive systems.
Symptoms of the disease how to determine
How to determine that the formation is really urethral papilloma? To do this, you need to know the main symptoms of such growths. Their size and shape may vary among people: for some they are flat condylomas, for others they are pointed. The shade of the neoplasm on the skin may also vary. The size usually does not exceed a few millimeters. Pointed warts are most often diagnosed, while flat warts are much less common.
It is noteworthy that at an early stage of development it is impossible to detect them, since they originate in the deep layers of the skin. They usually appear singly, but subsequently they can unite with each other and grow. When tumors appear on the surface of the skin, the risk of infecting another person increases.
The most common type of condylomas in women, as well as men, is genital warts. They have a “leg” and rise above the surface of the mucous membrane. The growth of such neoplasms occurs quite quickly. Even in a few hours, a wart can reach a size of 5-6 mm. If several such growths form a group, then this phenomenon can cause significant discomfort to the woman. Sometimes condylomas can fall off on their own, but under no circumstances should they be torn off. Such a wart can only be removed in a medical facility.
The type of flat condylomas is diagnosed less frequently, perhaps due to the fact that they are located in the deep layers of the skin and are simply invisible. But at the same time, they are much more dangerous than pointed ones.
Diagnostics
Papilloma in the urethra is characterized by a practically asymptomatic onset of invasion. The first clinical manifestations are observed against the background of an increase in the number of neoplasms. To diagnose infection, physical examination methods are used, aimed at identifying external signs of urethral papilloma in men and women.
To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment, it is necessary to use additional procedures, which include standard methods for diagnosing sexually transmitted infections: smear microscopy, histology of tissue samples, polymerase chain reaction, dag testing. For timely detection of urethral papilloma, it is important to contact a urologist when the first signs of invasion appear.
Treatment
Treatment of papillomas in the urethra of men and women is based on the complex use of procedures. A mandatory method is the use of antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy, the combination of which can increase the level of resistance of the body and suppress the activity of viral agents that provoke the appearance of urethral papillomas.
Invasive or medicinal treatment of external manifestations of infection, that is, directly pathological neoplasms, is also prescribed. The choice of the most appropriate method of invasive removal is carried out individually, taking into account the characteristics of the clinical case, size, type, and location of urethral papillomas.
Conservative methods
Therapy for papilloma in the urethra includes the mandatory use of drugs that help increase the body's immune defense and also inhibit the activity of viral agents. The most common oral medications are:
HOW TO CURE PAPILLOMAS, WARTS, BAD MOLES?
Treatment and prognosis of benign urethral tumors
Thanks to the introduction of endoscopic techniques into urological practice, treatment of urethral tumors is carried out minimally invasively. Urethral condylomas can be subjected to chemical destruction with solcoderm, surgical excision, removal by radio wave, laser, liquid nitrogen, plasma coagulation or electrocoagulation.
Important addition: Papilloma on the uvula
Removal of urethral tumors located distal to the external opening is performed transurethrally through the urethroscope channel. In these cases, circular or wedge-shaped excision of urethral tumors within healthy tissue is usually performed. Small tumors are removed by electroexcision. In the postoperative period, long-term (3-4 days) catheterization of the bladder is performed. If there is a danger of developing urethral strictures, urethral dilation is performed.
Removal of benign urethral tumors prevents their possible malignancy. Radical excision of urethral tumors eliminates relapses. However, in the case of a viral nature of the neoplasm, treatment should be supplemented with a course of conservative therapy. To prevent the development of urethral tumors, preventive examinations by a gynecologist and urologist are important, to exclude sexually transmitted infections and injuries to the urethra.
Complications
The formation of papilloma in the urethra without treatment can lead to extremely unfavorable consequences, the main ones of which are cancerous tumors and pathological changes in tissue. Papillomaviruses in the urethra can lead to disruption of urine outflow processes and the development of bleeding.
Page title Anastasia K.:
Girls, I spent 6 years of my life to return my skin to its healthy appearance and get rid of these dangerous papillomas and moles, don’t repeat my mistakes... Read here... >>
To prevent such negative consequences, it is recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations, which will identify the development of the disease in the early stages of invasion, when there are no visual symptoms. It is especially recommended to follow the above rules for people who are sexually active, suffer from hormonal changes, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
Characteristic signs in men
Condylomas most often grow within a few hours. Several growths are found on the urethral mucosa. In rare cases, tumors form within a few days. After this, their growth stops. If the immune system of an infected person is severely weakened, papillomas continue to appear in the urethra for a long time.
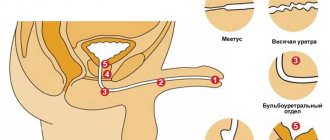
In men, condylomas are most often localized in the area of the external urethral opening, so they can be immediately detected. The growths form a ring at the entrance to the urethra. They are colored pink or red (sometimes with a yellowish tint). Two types of condylomas are found in the urethra: flat and pointed. Flat formations rise slightly above the mucous membrane, so they are more difficult to identify in time.
Condylomas acuminata have a thin stalk and a wide tuberous apex. Outwardly, they resemble cauliflower. Sometimes there are growths with a wide base. The size of the neoplasms varies between 2–6 mm. Condylomas do not have large blood vessels, so their further growth is impossible. In rare cases, the growths die due to lack of nutrients.
In the urethra, condylomas are localized mainly in the area of the scaphoid fossa. It is located inside the head of the penis. Sometimes growths cover the entire surface of the urethra, reaching the mucous membrane of the bladder.
If condylomas are small in size, a man may not feel much discomfort. He may experience itching, burning and slight pain when urinating. When condylomas grow, the patient has problems with urination. The pain during emptying the bladder intensifies, and the shape of the urine stream changes. It splits, deflects or splashes. Painful sensations of varying intensity also occur during sexual intercourse.
Urethral papillomatosis causes nagging pain in the lumbar region and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. Due to the obstruction of urine flow, a man cannot completely empty his bladder. He suffers from frequent painful urge to urinate.
Forecast
The prognosis of urethral papilloma is favorable with timely treatment. The absence of one or the implementation of incorrectly chosen therapy tactics can cause the development of tumors of a benign or malignant nature in the tissues of the urinary tract and genital organs. The presence of urethral papillomas can cause infertility, premature birth, infection of the baby during natural childbirth, and miscarriages.
Prevention
Due to the prevalence of HPV, as well as the increased contagiousness of pathogenic flora, it is almost impossible to exclude infection with urethral papilloma. However, preventive measures taken in a timely manner will help to significantly reduce the likelihood of invasion. Refusal to use other people's personal and hygiene items is mandatory. It is also important to be careful when visiting public places, for example, a swimming pool, sauna, bathhouse.
Separately, we should talk about the genital tract of infection. As mentioned above, even the use of barrier contraceptives does not guarantee safety, which is due to the small size of viral agents. It is important to give up casual sex.
In addition, it is necessary to direct measures to strengthen the immune system. It will be useful to change your eating habits, adjust your diet, and include healthy, vitamin-rich dishes in your menu.
Stress, nervous tension, and general hypothermia of the body should be avoided.
The listed rules will help to somewhat reduce the likelihood of infection with urethral papillomas.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma