Who is being tested?
Most often, an ultrasound of the bladder is performed in women with clear signs of genitourinary dysfunction. These include:
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- difficulty urinating;
- presence of blood in the urine;
- presence of stones;
- vesicoureteral reflux;
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- pain above the pubis.
Ultrasound of the bladder is used as a complement to a gynecological examination, to assess the patient’s condition after undergoing surgery on the genitourinary system, to monitor the functioning of the kidneys.
Indications for use
Indications for ultrasound diagnostics are:
- pollakiuria;
- pain during urination;
- violation of urine evacuation;
- suspicion of nephrolithiasis;
- intense pain reaction in the lower abdomen.
The following procedures are performed under ultrasound guidance:
- surgical intervention for bladder cancer;
- cystolithotomy;
- resection of prostate adenoma;
- surgical treatment of pathologies of the ureter and urethra.
Preparation
Many women have a question about how to prepare for an ultrasound examination in order to get the most accurate results. Preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is based on good filling of the organ. This is a basic rule that applies to patients of any age. The main points are:
- two hours before the procedure you should drink at least 2 liters of liquid. This could be clean water, weak tea, dried fruit compote;
- you must refrain from going to the toilet 2 hours before the test;
- people who do not suffer from cardiovascular pathologies can take diuretics.
The basis of preparation is to fill the bladder with water.
The above measures will help the doctor conduct a quality study. If the diagnosis is performed transvaginally or transrectally, then filling of the bladder is also required. In addition, to carry out diagnostics, the last type of treatment is to do an enema cleansing. You can get unreliable results if there is increased gas formation in the intestines. Therefore, 3 days before the test, it is necessary to avoid eating a diet that increases the number of gases.
To do this, you need to adhere to a special diet that excludes the use of:
- legumes;
- tomato;
- cabbage;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- dairy products.
If a woman has difficulty refraining from urinating, which often happens during pregnancy, then she can visit the toilet. Next, you should drink 1 liter of water so that your bladder is well filled during the study. Women are examined on any day of the menstrual cycle.
Preparatory activities
A crowded intestine and excessive gas formation do not allow you to get an objective picture of the condition of the abdominal organs, so on the eve of the procedure it is not recommended to eat foods that cause fermentation. Black bread, raw fruits and vegetables, especially legumes, are excluded from the diet. You can't drink soda.
The day before the transrectal examination, it is important to empty the intestines as much as possible and, if necessary, use a laxative or enema.
You must come to the procedure with a full bladder for all types of ultrasound, except transvaginal. Therefore, you will have to drink at least 1 liter of plain water 1.5-2 hours before or not urinate for 5-6 hours before the test.
We have already looked at how an ultrasound of the bladder is performed, and what the procedure shows will be revealed by deviations from the norm discovered during the study.
How the research is carried out
Most often, diagnosis is carried out transabdominally, through the abdominal wall. During the procedure, the patient lies on the couch on her back. The doctor uses an ultrasound sensor with a special gel applied to it to perform the procedure. If during the diagnosis it is suggested that there are stones, sand, or a tumor process, then the patient may be asked to conduct the examination while standing.
To assess the condition of the bladder mucosa, it is recommended to conduct an examination on the side.
Typically the diagnosis lasts no more than 15 minutes. It may be necessary to assess how completely the organ is being devastated. To do this, the woman may be asked to visit the toilet and then examine the bladder again. If the patient is obese or there is an assumption of the presence of a tumor, then ultrasound can be performed using the following methods:
- Transvaginally. The sensor is inserted into the vaginal opening. The study can only be carried out on sexually active women.
- Transrectal. Using a special sensor inserted into the rectal opening. Diagnosis can be carried out both for women who are sexually active and for virgins.
Transvaginal diagnosis allows for simultaneous gynecological examination
How is the procedure done?
The ultrasound technique and algorithm depend on its type. It is important that the patient knows in advance what awaits him and how the study will proceed. The following types are distinguished:
Transabdominal
Transabdominal ultrasound of the bladder is suitable for everyone (children, men, women). Requires patient preparation. It consists of eliminating all foods that cause increased gas formation a few days before the procedure (baked goods, legumes, dairy and fermented milk products, coffee, mineral waters). For prevention, these days you need to drink 2 tablets of “Activated carbon” (not recommended for children). This is necessary so that gases do not block the view. In the evening, it is advisable to give a cleansing enema. Immediately before the procedure, you need to fill your bladder. During the procedure, the patient lies on his back. It is worth noting that this type is less accurate, but more common.
Transrectal ultrasound of the bladder is more suitable for people with low sexual activity.
Transrectal (TRUS)
TRUS is used to diagnose diseases in women who are not sexually active and men. During the procedure, the patient lies on his side with his back to the doctor (preferably on the left) with his legs pressed to himself. TRUS includes ultrasound of the prostate and bladder. TRUS of the prostate is performed. Going through this examination can be painful. It is necessary to prepare for the study in a special way. To do this, you must select one of the methods:
- drink a laxative;
- give a microenema;
- put a glycerin suppository.
TRUS shows a clearer picture than transabdominal ultrasound.
Transvaginal
Transvaginal ultrasound of the bladder is suitable only for women who are sexually active. The procedure is allowed during menstruation and pregnancy. It is important to inform the doctor about your piquant situation. This method is carried out when the bladder is empty. But preparation for the procedure is mandatory: diet and cleansing the body of gases. During menstruation, an ultrasound of the uterus may show abnormalities.
Transurethral ultrasound of the bladder is performed through the urethra of the male penis.
Transurethral
This method is used very rarely. Local anesthesia is used for this test because insertion of the device into the urethra may be painful. This method is used only in men. Before the procedure, you should not eat heavily, smoke, or drink alcohol. In addition, it is important to tell the doctor what drugs you are allergic to and whether you have chronic liver or kidney diseases. Transurethral examination of the bladder and urethra can detect bladder tumors.
Contraindications
Contraindications to an ultrasound examination of the bladder include in the abdominal form: urinary incontinence, since diagnosis is carried out exclusively on a full bladder, the presence of excess weight (since with an excess amount of subcutaneous fat, information content decreases), skin lesions in the area being examined, the presence of scars on bladder.
Transrectal examination is not done for intestinal inflammation, anal fissures, intestinal obstruction, or latex allergy. The transvaginal method is not indicated for allergic manifestations to latex, the presence of virgin pleura, pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, and infectious diseases of the genital organs.
Why is an ultrasound performed and what is determined?
Ultrasound diagnostics - analysis of the resulting graphic image of the elements of the body. Information is obtained in real time due to the reflective property of ultrasound waves from tissues of different densities. The procedure is safe with a competent diagnostician’s approach and is approved for clarifying problems in patients of any age.
The urologist uses ultrasound examination as one of the meaningful diagnostic methods. Ultrasound is informative, so the following goals are achieved:
- identification and confirmation of anomaly;
- differentiation of one disease from another;
- determining the degree of influence of pathologies of nearby organs on the element under study.
Doctors use ultrasound to find out whether the chosen treatment program is effective: control studies are carried out before, during and after therapy.
The equipment is used for visualization during surgery. Ultrasound helps with the following events:
- resection of the prostate using the transurethral method (endoscopic surgery);
- elimination of tumors in the organ;
- crushing and extraction of stones.
In some cases, with the help of diagnostics, operations on the pelvic organs are performed for the reason that the elements are located close to each other.
An ultrasound is prescribed if the patient has a history of the following complaints:
- to a painful or frequent urge to urinate;
- inability to fully empty;
- difficulty urinating or its absence for a long time;
- the presence of bacteria, admixtures of blood elements, or an increased amount of protein in the secreted fluid.
That is, ultrasound is used as an auxiliary and independent diagnostic technique.
The condition of the bladder is checked for frequent cystitis, urolithiasis and the following problems:
- congenital pathologies: dysplasia, polycystic kidney disease, absence of one of the elements;
- past diseases (infectious and other nature): pyelonephritis, urethritis;
- vesicoureteral reflux - the excreted contents are thrown back into the ureters;
- organ trauma: from impact, fall;
- when foreign objects enter.
Identified changes in the structure, shape of the bladder and adjacent elements allow doctors to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
What does the study show?
By developing pathology of the bladder, urologists, in tandem with ultrasound specialists, mean any deviation from the norm. Therefore, when using the ultrasound diagnostic method, specialists pay attention to the following criteria:
- clarity of contours, echogenicity;
- bladder size, shape, wall thickness;
- volume of remaining liquid;
- filling speed;
- location.
The images transmitted to the monitor by the sensor are printed by the diagnostician to record the results. He analyzes what exactly the ultrasound shows and provides a report to the attending physician.
results
During the study, the doctor, assessing the parameters of the bladder, can evaluate the following parameters:
- what shape is the bladder, deformation may indicate the presence of neoplasms;
- size. A reduced organ indicates fibrosis, frequent cystitis, an enlarged organ indicates hyperplasia, narrowing of the urethra, the presence of stones;
- contours;
- what contents does the organ have? This may be clots of pus, blood, hematomas, urine;
- the presence of neoplasms and their size, shape, mobility;
- integrity of the organ or the presence of damage.
If a woman has cystitis, then an ultrasound may show uneven contours and enlarged walls. Ultrasound examination makes it possible to identify various neoplasms, which include polyps, cysts, and tumor processes. As a result of the study, it is possible to diagnose the presence of patency of the ureteral canals, foreign neoplasms, sediment, inflammation, increased tone, atony, prolapse of the bladder, diverticulosis and pathology in the genital organs.
The attending physician deciphers the study picture
Research results
What does an ultrasound of the bladder show? Using this diagnostic method, you can determine the shape, size, external and internal contours, the nature of the contents, the thickness of the walls, their integrity, and traumatic damage to the organ. Thanks to this data, it is easy to establish a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
In acute cystitis, ultrasound may show the presence of small echogenic particles in the organ cavity (accumulations of red blood cells, leukocytes and other elements). In the absence of timely treatment, the contours of the bladder become uneven and the walls thicken. This indicates the transition of cystitis to the chronic stage.
The detection of echogenic formations of quite large sizes, which are tightly fused to the wall, indicates stones, polyps, ureterocele or prostate hypertrophy in males.
If the formations are mobile, one may suspect the presence of stones, a foreign body, or a blood clot. This phenomenon can also be caused by air that enters the bladder through a fistula or during insertion of a catheter.
When the organ increases in size, it is necessary to exclude prostate hyperplasia, a neurogenic bladder, the presence of a large number of stones, impaired urine outflow in the urethra in men and injuries to the urethra in women.
An ultrasound examination of the bladder will help make a completely painless diagnosis. However, you cannot decipher the results yourself; only a specialist can do this. By following your doctor's recommendations, you can quickly get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Ultrasound is a modern method for diagnosing a huge number of diseases of various organs. It is believed to be absolutely safe, so this procedure is recommended for people of any age, including newborns, and gender.
Very often, ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the urinary system. But in order for the study to provide the most accurate information, some kind of preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is required.
Norm
After receiving the study picture, the doctor evaluates the results with normal indicators. A healthy woman is diagnosed with the following parameters:
- the bladder should be pear-shaped when the organ is full, and saucer-shaped after urination;
- on the device screen, the normal structure appears as dark spots;
- urine volume varies between 250–550 ml;
- walls with a thickness of 2 to 4 mm;
- filling speed is about 50 ml per hour;
- residual urine should have a volume of no more than 40 ml.
Decoding the results
The ultrasound examination of the bladder should be deciphered by a diagnostician immediately on the spot. In this case it is a urologist. Several indicators that are determined for the organ during diagnosis (the table shows the norms):
| Bubble capacity | Form | Organ outlines | Partition thickness | Interior | Urine flow rate (maximum) | Residual urine |
| 250-550 ml for women, 350-750 ml for men | round or oval, symmetrical | even, smooth | 3-5 mm | hollow | 145 mm/s | less than 50 mg |
Deviations from these norms may indicate various pathologies. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct not only an ultrasound, but also other examinations (blood tests, urine tests, etc.). They are prescribed by a doctor based on the specific situation.
What problems are detected on ultrasound?
Diagnostic data is provided as indicative information only. Based on this, a diagnosis is made. One of the signs of the pathological condition is thickened walls. Pathologies can be uniform and focal. They are characteristic of the closed lumen of the organ under study. This usually occurs as a result of urolithiasis, tumors, parasites, and tuberculosis.
Ultrasound of the bladder often shows obstructed urine flow. The causes of this pathology include the presence of stones, organ hyperplasia, innervation pathologies, and the presence of valves. A reduced bladder size is diagnosed as a result of congenital pathology, which is indicated by the presence of a reduced amount of residual urine. This occurs due to parasitic infestations, frequent cystitis, after surgery.
Diagnosis of sediment in the form of flakes occurs in cystitis. Often the sediment is formed from leukocytes, epithelial cells, phosphates and is a prerequisite for the development of urolithiasis. During diagnosis, flakes appear as hyperechoic formations. Formations characterized by increased echogenicity include the presence of stones, cysts, polyps, narrowed lumen in the urethra, and neoplasms.
The tumor on the ultrasound image does not have an acoustic shadow, such as stones
Formations with increased echogenicity can be mobile, such as stones, or immobile, such as polyps. On the screen of ultrasound equipment, stones are represented by light areas, while cysts are represented by darker areas. Often, the study determines the presence of urine reflux, which reaches the renal pelvis. This phenomenon occurs due to pathologies of the urinary tract, stones, flakes, formations.
In this case, ultrasound diagnostics is carried out simultaneously with Doppler. This type of study evaluates how much urine is thrown and remains, what its direction is, and is used to determine the severity of the disease. Ultrasound diagnosis of the bladder is an effective method for detecting pathologies at the very beginning of their development.
Thanks to ultrasound examination of the urinary system, a lot of urological diseases can be detected. The examination does not harm the body and can be performed on absolutely everyone: men, women and children, regardless of age. Experts say that various pathological processes of the urinary system are much easier to completely eliminate in the first stages of development. To prevent complications, it is recommended to do an ultrasound examination of the urinary system once a year as a preventative measure.
What diseases are detected during ultrasound?
During an ultrasound examination, urinary bladder pathologies are detected, including those that occur covertly. An experienced ultrasound specialist, looking at the image, can suggest a certain diagnosis.
Cloudy spots, which are a suspension of sand and mucus, appear in inflammatory diseases. They can form in the bladder with cystitis and come from the kidneys and ureter with damage to the upper urinary tract.
Dark spots on the wall are diverticula. This is the name given to bag-like protrusions filled with urine. Protruding areas cause problems with urination and can even lead to rupture of the wall. Such patients require constant ultrasound monitoring.
In case of injuries, dark lesions are visible inside the bladder wall - hematomas - accumulations of coagulated blood.
White elements on a dark background are stones (concretions). Their difference from tumors and other neoplasms is their displacement when the patient’s position changes. The largest stones can cast a shadow, which is called acoustic.
Large dense tumors have a similar appearance. Unlike stones, they do not cast shadows and do not move when the body position changes.
You can guess the type of tumor by its appearance. As a rule, a benign neoplasm has a more even shape and is delimited from neighboring tissues. Cancerous tumors are vague and can grow into other organs.
The protocol must indicate the presence of any neoplasms, their size, position and quantity.
What is included in the examination
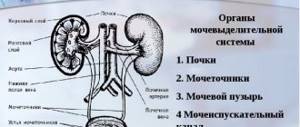
The urinary system includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters and adrenal glands. All these organs are examined during an ultrasound examination. If you do not want to wait your turn for an examination at a municipal clinic, ultrasound can be done in private diagnostic clinics for a fee.
Indications
As a rule, a comprehensive diagnosis of the urinary system is prescribed in the following cases:
- Urinary retention
- Urinary incontinence
- Injuries
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Presence of stones in the kidneys or ureter
- Inflammatory or infectious diseases
- Pain when urinating
- Blood or pus in the urine
A diagnostic procedure is prescribed for a child if there is a poor urine test of unknown etiology. This procedure is often performed on pregnant women in the first trimester in order to exclude diseases of the urinary system.
What does a bladder examination show?
Examination of the bladder using ultrasound allows you to see many problems in an important organ:
- inflammation of the mucous membrane (acute or chronic);
- sand or stones of any size;
- tumors of various kinds;
- blockage of ducts with stones;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- pathologies of development of the ureters and bladder;
- wall diverticula;
- reflux (backflow) of urine from the bladder into the ducts of the ureters.
How to prepare for an ultrasound
A comprehensive examination of the urinary system requires special preparation. Only in this case can you find out an accurate diagnosis and find out detailed information about the organs. Despite the fact that the urinary system is in no way connected with the digestive organs, it is necessary to follow a dietary diet in order to prevent increased gas formation, which may interfere with the study.
- For two days, you need to stop eating black bread, whole milk, cabbage, fresh vegetables and fruits, and pickled foods.
- Drink enough water every day, up to 2.5 liters, if there are no contraindications.
- In the evening, before the ultrasound, have a light dinner around 19-20 hours.
- If you have problems with stool, you need to do a cleansing enema. If the study is carried out through the rectum, this point is mandatory.
- If you have flatulence, take carminatives for a couple of days.
- Come for an ultrasound examination on an empty stomach.
- Take a bottle of clean water with you. Drink about 700 ml of water over about 30 minutes and do not empty your bladder until a specialist requires it.
- Strictly exclude alcoholic drinks.
The doctor who ordered the test will tell you more about the preparation. Don't forget to take your passport and specialist referral with you. If you have pictures from a previous ultrasound, it is also advisable to have them with you.
Indications and features of the procedure
Patients may be referred for an ultrasound examination of the bladder if they have:
- changes in urine color;
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the suprapubic region;
- sediment in the urine visible to the naked eye;
- blood in urine, etc.
In addition to diagnosing various diseases, this procedure is carried out to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment by the presence or absence of positive dynamics. Most often this is necessary when undergoing a course of chemotherapy or after surgery.
Features of preparation
The procedure is performed on a full bladder, so the main preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is to fill it. This can be achieved by drinking approximately 1 liter of still water an hour before the procedure. In cases where the study is scheduled for the morning, you can go to the clinic immediately after waking up, without visiting the toilet. If it is impossible to refrain from urinating in the morning, it is recommended to set the alarm clock 2-3 hours earlier than the scheduled wake-up time, visit the restroom and go back to sleep. Moreover, after the final rise, the intensity of the urge will not be too great, which will allow you to get to the medical facility with a full bladder, ready for examination.
Important: water can be replaced with tea, compote or other non-carbonated drink, but not with milk or fermented milk products. If a patient is diagnosed with kidney pathologies, he may be advised to take diuretic medications.
In addition to filling the bladder, patients need to take care of the condition of the intestines before the study, since its overcrowding with gases can interfere with the procedure. Therefore, within a couple of days before the appointed date, it is recommended to take activated carbon or its analogue, as well as follow a diet that helps reduce gas formation. That is, on these days you should not consume:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- legumes;
- carbonated drinks;
- baked goods;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- alcohol.
Attention! The correct one allows you to conduct a full examination of not only the bladder, but also the prostate gland in men, as well as the ovaries and uterus in women.
If, even before the study is carried out, it is known that it will be carried out through the rectum, then, among other things, a cleansing enema or a glycerin suppository must be done a few hours before the procedure.
How is the procedure performed?
How an ultrasound of the bladder is done depends on its condition, degree of fullness, the presence of concomitant pathologies and some other factors. In general, the examination is usually performed using the transabdominal (through the abdomen) method. With this approach, the patient is placed on the couch on his back. He is asked to remove clothing from his lower abdomen, to which the doctor applies a special gel. After this, the doctor applies the sensor to the site where the gel is applied and, with slight pressure, runs it along the surface of the abdomen in different directions, examining the bladder and nearby organs.
Transabdominal ultrasound
Important: in certain cases, to clarify the situation, the specialist may ask the patient to visit the toilet and return to the ultrasound room to assess the condition of the bladder after emptying it. This is usually required to diagnose prostate pathologies.
As a rule, the procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes, after which the patient immediately receives a form with the examination results and is sent to his attending physician. But in some cases it may be necessary to conduct an examination through:
- Rectum. This type of examination is indicated when an ultrasound of the prostate and bladder is necessary, but it can also be used if the patient has fluid in the abdominal cavity, obesity, or other factors that make examination through the abdominal wall difficult. In addition, the indication for transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is the need to examine girls who have not lost their hymen, for whom transabdominal examination is difficult.
- Vagina. Ultrasound of the bladder in women is performed using the transvaginal method in the presence of obesity, adhesions, tumor formation, etc.
In such cases, a condom is placed on a special sensor, a small amount of conductive gel is applied and it is inserted shallowly into the natural openings.
Transrectal ultrasound
Sometimes patients are prescribed an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. It is carried out if it is necessary to evaluate the parameters of urine flow through the ureters and the state of blood flow in the organs being studied. This is required if there is a suspicion of vesicoureteral reflux, in which urine, for one reason or another, is thrown back from the bladder into the ureters. Doppler ultrasound is also indispensable in diagnosing tumor formations.
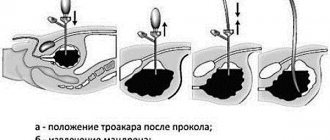
Another variation of this diagnostic method is intravesical or transurethral ultrasound. To carry it out, a special, thinnest sensor is used, which is inserted into the patient’s body through the urethra. It is prescribed if necessary:
- determine the degree of damage to the walls of the urethra and the neck of the bladder;
- differentiate or find the relationship between diseases of the bladder and urethra;
- assess the degree of damage to neighboring organs.
How is an ultrasound of the urinary system performed?
Let's take a closer look at how ultrasound of the urinary system is performed.
Kidney ultrasound
Depending on the patient's complaints and specific diagnoses, the kidney examination can be performed in various positions. Up to 40 years of age, a routine ultrasound examination is performed; older people are advised to undergo an additional examination with Doppler, which evaluates blood flow and possible problems with blood vessels in the kidney area.
A special gel is applied to the lumbar region for better glide of the sensor. The study takes no more than 20 minutes.
Ultrasound of the ureters
Ultrasound of the ureter is not performed separately, only in conjunction with other organs of the urinary system. This is due to the fact that using this diagnostic method it is practically impossible to detect the patency of the ureter.
Note that ultrasound is not entirely informative in this case, since the ureters are poorly visualized by ultrasound. For a more detailed study of the organ, other methods of examining the ureter are used.
The examination is also carried out with a full bladder. The sensor is installed in the area of the anterior abdominal wall; on average, the study takes 10-15 minutes.
Ultrasound of the bladder
The diagnostic procedure can be determined in various ways, most often through the abdominal wall. In women, a transvaginal ultrasound examination is possible, and in men, through the rectum. Note that this is practiced extremely rarely, for example, in cases of extreme obesity.
To make an adequate diagnosis, the organ is examined in two states: full and empty. First, before the ultrasound, the patient drinks a liter of water. The specialist conducts the study in a standard manner. Then it is necessary to empty the bladder, after which the condition of the bladder is assessed again.
Due to the good mobility of the organ, examination of the bladder is as informative as possible. With the help of such an examination, it is possible to identify various diseases, even cancer at the earliest stages.
Benefits of Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination has many positive aspects:
- the procedure is safe for patients of all ages, children and pregnant women;
- the examination takes no more than 15–20 minutes;
- minimum list of restrictions;
- no tissue damage, no risk of infection;
- preparation takes no more than three days: diet correction, drinking regime;
- according to the results of the study, all negative processes and diseases in the bladder are clearly visible in the photographs, including in the early stages;
- you can clearly distinguish bladder stones, tumors, various inclusions, sand, anomalies in the structure of the organ;
- the doctor sees the size of the bladder, the condition of the ureters, and the patency of the ducts;
- Ultrasound machines are available in almost all clinics, even in small towns.
Kidneys are not visible on ultrasound
It often happens that the doctor cannot “see” the kidneys on an ultrasound. What is it? According to statistics, this happens in 20% of cases. Sometimes this is due to increased echogenicity. In this case, it is necessary to replace ultrasound with magnetic resonance imaging. The following ailments may also be the cause:
- Ectopia is a non-standard localization of an organ.
- Atrophy - in this case we are talking about a reduced size of the kidney compared to normal.
- Missing one organ – sometimes children are born with only one kidney.
Features of ultrasound diagnostics
The transabdominal research method is most often used. The patient lies down on the couch and takes off her clothes.
An air-tight gel is applied to the front wall of her abdomen, and then the doctor places an ultrasound probe on it.
If the procedure is carried out using the transvaginal or transrectal method, their main difference is that a condom is placed on the tip of the device, which is also treated with gel. It is then inserted into the appropriate passage. According to patient reviews, this method of performing ultrasound does not cause discomfort and is absolutely painless.
The transurethral diagnostic method is carried out after the use of anesthesia. A flexible probe with a tip that transmits an ultrasound signal is inserted into the woman's urethra.
Typically, the study lasts about 15 minutes, after which the specialist gives the patient a protocol with a transcript and conclusion, as well as videos or photographs taken during the study, saved on a convenient medium.
Norms of the urinary system according to ultrasound
Each organ has its own normal indicators:
Kidneys
- Length up to 13 centimeters
- Width no more than 6 centimeters
- The thickness should not exceed 5 centimeters
- Parenchyma wall thickness up to 25 mm
Bladder
- Round shape
- Localized symmetrically
- Wall thickness from 0.3 to 0.5 centimeters
- The speed of urine flow is not more than 14.5 cm/s
- The residual amount of urine is not more than 40 ml
Ureters:
- Homogeneous fabrics
- No defects or anomalies
- Patency is normal
As a rule, diseases of the urinary system are accompanied by acute pain, which is difficult to ignore. It is very important to carry out diagnostic manipulation in a timely manner so as not to start the pathological process and avoid serious complications. Thanks to early diagnosis, you will get rid of unpleasant symptoms and eliminate the risk of the disease becoming chronic.
Ultrasound of the bladder is an examination that is based on the special properties of the ultrasound wave reflected from the organ, forming its image on a hardware monitor. Since women are more susceptible to diseases affecting the genitourinary area, they are much more often referred for an ultrasound examination.
To obtain accurate results, you must be well prepared for the examination. This method is widely used to diagnose all kinds of diseases.
The ultrasound method is characterized as simple and operational. It has no contraindications and does not cause complications. A study is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- Presence of pain in the lumbar region;
- Painful sensations with cystitis located in the lower abdomen;
- Changes in the color of urine, cloudiness and the appearance of flakes, the presence of streaks of blood and sediment;
- Frequent or less frequent urination;
- Nocturnal diuresis prevails over daytime, the appearance of urinary incontinence;
- A sudden increase in body temperature in the absence of other symptoms;
- The appearance of edema of varying localization and intensity;
- Changes in clinical urine analysis parameters.
An ultrasound scan of the bladder allows us to identify a number of diseases and pathologies of the body, which include:
- Various types of tumor neoplasms arising in the bladder;
- The presence of stones in the organs of the urinary system;
- Inflammatory processes in acute or chronic phases;
- The presence of blindly ending invaginations (diverticula) of the bladder walls.
- All kinds of foreign bodies in the bladder;
- Pathologies of the structure of the organs of the urinary system;
- Urine from the bladder enters the ureters.
- The occurrence of blockage with stones and the appearance of obstacles to the exit of urine.
In addition, ultrasound of the genitourinary system can determine the presence of diseases such as cystitis or chronic pyelonephritis.
Ultrasound examinations in women are carried out to identify diseases of the pelvic organs. In some cases, ultrasound of the genitourinary system includes examination of the uterus and appendages. A sudden increase in temperature, accompanied by the appearance of sharp pain, is also an indication for research, as it may be a symptom of any disease of the excretory system. Experts recommend resorting to the procedure also for preventive purposes.
In addition to diagnosing various types of pathologies, ultrasound examination is carried out when it is necessary to more accurately assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Used after a course of chemotherapy or after surgery.
Video: How to prepare for an ultrasound examination
How to prepare for an ultrasound examination
Peculiarities of implementation in different groups of patients
Ultrasound in women
Everyone without exception undergoes research. Ultrasound of the genitourinary system in women is performed using both transabdominal and transvaginal methods. In the first case, sometimes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is also performed at the same time. Using ultrasound, you can detect many inflammatory diseases, as well as neoplasms, and determine whether they are benign or malignant. Before an ultrasound of the bladder, you need to make sure that the woman has no problems with the central circulation (especially during menstruation). An ultrasound of the kidneys clearly shows the neoplasm.
Ultrasound of the bladder during pregnancy does not have any special restrictions or prohibitions, because does not have a negative effect on the fetus.
During pregnancy
There is an opinion that pelvic ultrasound is contraindicated. This is wrong. Ultrasound does not have a negative effect on the fetus, the same applies to the placenta. Thus, this procedure is completely safe for a woman in an interesting position. But telling your doctor about pregnancy is very important. In this case (depending on the age and size of the fetus), he will be able to select the correct research method. This is important because in the later stages or if there is a threat of miscarriage, transvaginal ultrasound is prohibited. This may lead to undesirable consequences. Sometimes the test can detect the presence of a fetus.
Ultrasound in men
An ultrasound of the bladder is performed in men to show a full bladder. There is no need to do an ultrasound of the prostate and bladder separately; both organs are clearly visible in this study. In addition, you can look at the condition of the prostate gland. The most common type of this study is transabdominal. It is ideal for men. It is used to check for bladder tumors.
Ultrasound of the bladder can also be performed on children if problems arise with the urinary system.
Ultrasound of the bladder is an important part of the examination of a patient with suspected kidney and urinary tract diseases. This is a minimally invasive diagnostic method that has no contraindications for use. Approved for use by children, adults, and pregnant women, as it is completely safe.
Women
How is an ultrasound of the bladder performed in women? In order to obtain reliable examination results, the patient must adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations, in particular, carry out proper preparation for diagnosis.
This will allow you to obtain reliable data with which you can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. Manipulation is mainly performed transabdominally. However, in some cases, transvaginal access using a special sensor may be indicated.
For men
An ultrasound of the bladder in men is performed through the abdominal wall. And only in cases of severe obesity, ascites, or suspected prostate tumor, is it advisable to use a transrectal approach.
Features of preparing men for this study include conducting a cleansing enema or using a microenema several hours before diagnosis. This will clear the intestines of feces and ensure access of the sensor to the required depth into the rectum.
The main rule for a successful ultrasound is a full bladder. This can be done in two ways:
- Physiological. It involves the natural filling of the organ with urine over several hours. This method can only be used if the test is scheduled for early morning, because the bladder will fill overnight. However, this method is not suitable for all people, since many immediately after waking up experience a strong need to empty. Alternatively, you can set the alarm for 3:00-4:00, go to the toilet and be ready for research at the appointed time.
- Drinking large amounts of liquid. 1-1.5 hours before diagnosis, the patient should drink at least 2-3 glasses of clean still water. Drinking tea or compote is allowed; only milk is prohibited. If there is quite a lot of time left by the appointed hour, but there is already a strong urge to urinate, the patient can release a small amount of urine until relief occurs. However, after this you need to immediately drink 1 more glass of liquid.
- Use of diuretics. It is used quite rarely when there is no feeling of bladder filling for several hours after drinking 500-700 ml of liquid. This method is not recommended to be used independently, only in consultation with a specialist.
Ultrasound diagnostics is the ability of ultrasound waves to pass through the tissues of the human body. However, in some cases, for example, with severe flatulence, the results of the study may be distorted, since ultrasound does not pass through air and gases.
To avoid this, if you are prone to increased gas formation, you should follow a certain diet for 2-3 days before the diagnosis. To do this, you need to remove brown bread, legumes, raw fruits and vegetables, milk, sweets, baked goods, and carbonated drinks from the daily menu.
During this period, it is necessary to exclude fried, spicy and salty foods. It is advisable to cook food using steam. The diet should include dietary meat, lean fish, cereals, and eggs.
The last meal should be at least 8 hours before the diagnosis. Therefore, dinner should be planned for 18:00-19:00 in the evening. In the morning you can only drink still water, you cannot eat. The exception is people who need regular meals due to certain diseases.
How to prepare for a bladder ultrasound
The procedure for examining the bladder in women is carried out on a full bladder, therefore it is necessary to prepare for the ultrasound in a certain way.
- Some time before the appointed time, you need to drink a noticeable liter of water, compote or tea. It is important to remember that water should not contain gases. Do not replace liquid with milk. To keep your bladder full, you cannot urinate. If it is impossible to endure the urge to urinate, you can empty the bladder, but then you need to drink a few glasses of water again and by the appointed time the bladder will be filled to the desired level;
- You don’t have to drink the water, but wait for the bladder to fill on its own. To do this, you need to not empty it for three to four hours. Often the procedure is scheduled for the morning. At the same time, you can prepare for an ultrasound if you don’t urinate in the morning. If this is too difficult, you can go to the toilet a few hours before you finally wake up, but after getting up you shouldn’t do this anymore.
It is important to take into account the fact that a gas-filled intestine can prevent a correct procedure for diagnosing the bladder. For those people who suffer from bloating or constipation, it is recommended that a few days before the scheduled procedure follow a diet in which fresh fruits and vegetables, legumes, gas-containing drinks and alcoholic beverages are excluded from the diet.
If even before the start of the ultrasound it becomes known that the procedure will be carried out through the rectum, a few hours before visiting the office you should do a cleansing enema or use special suppositories.
Preparing for the study
It is imperative to prepare for the procedure, especially since the algorithm is simple: stick to a diet and drink a lot. A bladder examination involves a full bladder. Preparing a patient for a study is sometimes carried out according to the following scenario: a person should not go to the toilet for 5-6 hours before the procedure. This method is suitable for people who have severe swelling. If you can’t bear it, you can let out a little urine, but then quickly fill the bladder again. When the bladder is empty, its contours are poorly visible, the same applies to the prostate and appendages. The doctor should explain how a prostate ultrasound is performed. It is necessary to prepare not only the patient, but also the equipment: gel is generously applied to sensitive areas of the device. This will give a clear image. During transvaginal examination, a special disposable condom is put on it.
How to fill your bladder? How much fluid for ultrasound?
Preparing for an ultrasound of the bladder during menstruation requires drinking a lot of fluids. Approximately 2 liters of still water (water, compote, tea - it doesn’t matter). The amount of fluid may depend on approximately how much water a person drinks. In children this dose is much less. Carbonated drinks are not allowed because they cause increased gas formation, which closes the internal organs. It is also undesirable to drink alcohol before an ultrasound scan of organs. It is important to take a responsible approach to the preparation process. Otherwise the result will be inaccurate.
How to do an ultrasound of the bladder in women
Ultrasound examination of the bladder is usually performed in one of the following ways:
- Abdominal. With this type, the examination is carried out from the anterior abdominal cavity. Is an external type of research;
- Transurethral. The examination is performed through the urethra;
- Transrectal. The examination of the organ is carried out through the rectum.
The most often used is the first method, since the other two are used when it is necessary to confirm or refute problems identified during an external inspection and examination. Which ultrasound method will be used for each patient is determined by the attending physician, who prescribes this procedure. The position in which the patient will be during the examination is determined during the procedure. Usually the patient lies on his back or side; sometimes the doctor may ask the patient to stand up in order to examine the organ for the presence of formations inside it.
In addition to the bladder, women are additionally examined for the uterus and ovaries. Ultrasound provides the opportunity to measure the size of these organs, determine pathologies in their structure and location, as well as shape. In some cases, women undergo transvaginal ultrasound. This method is used for the most complete overview of the condition of internal organs and the most accurate diagnosis of certain diseases. Pregnancy and menstruation are not an obstacle to the procedure, but you should notify the doctor in advance so that he can choose the right examination method.
In some cases, patients are prescribed an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. It is used when it is necessary to evaluate the parameters of urine flow through the ureters and the state of blood flow in them. Such a study may be required if a specialist suspects the development of vesicoureteral reflux, in which urine flows back into the ureters.
The use of this method when it is necessary to diagnose tumor diseases is irreplaceable.
What is bladder filling and why do you need to drink water before an ultrasound?
Usually, the doctor recommends drinking 500-700 ml of water before an ultrasound examination. This is dictated by the structure of the organ, on the walls of which there are folds. Without filling, it will be difficult to see the pathological foci located inside the folds. In addition, through a filled bladder during transabdominal examination, adjacent structures are clearly visible.
Filling the bladder is also necessary to determine residual urine. In this case, the patient undergoes ultrasound diagnostics twice – before and after urination. Normally, after going to the toilet, 50 ml of urine should remain in the bladder space. Exceeding this indicator indicates a violation of urine flow, which is caused by:
- Enlarged prostate gland blocking the urethra.
- Neurological diseases in which the nervous system poorly regulates bowel movements.
- Atony - in this case, due to low tone, the detrusor cannot expel urine.
- Spasm of the sphincter, blocking the exit to the urethra.
- Blocking of the urethra by a tumor, cyst, polyp.
- Urolithiasis, in which stones interfere with the flow of urine.
- Prolapse of the uterus and vaginal wall, in which the urethra is displaced.
The filling of the urea should normally be satisfactory. The reason for unsatisfactory filling is poor preparation for the study, in which the patient drank little water or urinated immediately before the procedure. Sometimes a small volume of urine indicates kidney disease, in which urine is poorly excreted.
Preparation and procedure
Conducting an ultrasound of the pelvic organs requires special preparation:
- 72 hours before the procedure, foods that provoke flatulence are excluded from the diet: beans, peas, white cabbage, beans, fresh fruits and vegetables, sparkling water, alcohol. This is important for clear visualization so that bowel gas does not interfere with the examination.
- If diet alone is not enough to combat flatulence, doctors prescribe special medications: activated carbon, Espumisan, Polysorb, enzyme agents.
- An ultrasound is performed with a full bladder so that the structure of its wall and the nature of the contents can be clearly seen. To do this, approximately 1.5 hours before the procedure, you need to drink 1.5 liters of still water and not go to the toilet until the examination. When the procedure is scheduled for early in the morning, you can simply not relieve yourself in the morning. If it becomes impossible to tolerate, then you are allowed to release a small volume of urine, but immediately drink another 2 glasses of liquid.
- Before transrectal and transvaginal ultrasound, it is important to carry out standard hygiene procedures.
- In addition, before transrectal diagnosis, you need to cleanse the rectum using a cleansing enema with warm water, microenemas or laxatives.
- You need to take with you to the ultrasound procedure a medical insurance policy, an outpatient card, the results of a previous examination, a sheet, and napkins. For inspection with a vaginal or rectal probe - a condom. The list of required items can be clarified at the registration desk.
An ultrasound usually lasts no more than 20-30 minutes, the result is given immediately after the examination is completed and the protocol is filled out.
The essence of the ultrasound method
Ultrasound diagnostics are possible due to the ability of high-frequency sound waves to be reflected differently from dense, soft and liquid media. The fluid is anechoic - it absorbs ultrasound and is visible on the monitor during an ultrasound as a black area. Bones almost completely reflect the ultrasound wave and are therefore visualized in white. Soft tissue structures give a gray color on ultrasound, the shade of which depends on the density of the tissue.
The ultrasound machine's sensor simultaneously serves as a source of sound waves and a receiving device. This is a convenient technical solution that simplifies the procedure.
Ultrasound diagnosis of cystitis is carried out in four ways:
- The transrectal (through the rectum) ultrasound method is used in male patients, since bladder diseases in men are often associated with prostate pathology. This technique visualizes both organs well.
- Transvaginal (through the vagina) scanning is important for women in whom the inflammatory process simultaneously occurs in the genital and urinary tracts.
- Transurethral (through the urethra) diagnosis is the most rarely used type of ultrasound due to the complex technique and risk of complications. It is used only in a hospital setting when planning surgical treatment.
- The most universal ultrasound option is considered to be transabdominal (through the anterior abdominal wall). It is easy to implement and quite informative for both men and women.
Summary
For modern patients, ultrasound has become an ordinary procedure, and everyone knows how this procedure is done. Its appearance can be called a real breakthrough in medicine.
Such non-invasive examination of the body has become widespread. It enjoys general recognition because it shows results quickly and safely, and this is an important factor for diagnosing a number of diseases. The whole procedure is quite simple, however, it is necessary to remember that there are some nuances in preparation for men and women, but for both, it should be equally thorough, since this ensures the accuracy of the study.
Telemedicine in St. Petersburg https://medi-center.ru/telemedicina - online medical consultations without breaks or weekends. We interpret test results, give treatment recommendations, and help patients in other cities and abroad via video communication.
Types of procedure
Ultrasound examination of the urinary system is carried out in different ways:
- along the surface of the abdomen - transabdominal;
- through the urethra - transurethral;
- the sensor is inserted into the vagina - transvaginally;
- the sensor is inserted into the rectum - transrectally.
Ultrasound for suspected bladder disease is most often performed transabdominally. This method is the least traumatic, completely safe for the patient, and is not accompanied by any discomfort. The doctor performs the examination through the anterior abdominal wall.
- What does an ultrasound scan of the adrenal glands show and how to properly prepare for the study?
The transrectal examination method is used for men and girls who are not sexually active. In men, the method allows you to assess the condition of the seminiferous tubules, prostate gland, and bladder. The transvaginal method is indicated for adult women if they need to obtain more information about the condition of the bladder.
Transurethral ultrasound requires special specialist skills and complex equipment, so it is used very rarely.
The doctor will tell you about ultrasound examination in the video:
What to take with you to the examination
To undergo an ultrasound examination of the urinary system, you must have:
- Referral from the attending physician.
- Medical insurance, cash.
- Wipes to wipe the skin after a transabdominal ultrasound.
- A towel or diaper to put under you.
- A water bottle in case you need to refill your bladder.
If an ultrasound is performed in a paid clinic, you do not need to take napkins and a diaper - everything is provided on the spot.