Diseases of the genitourinary system in men and their symptoms are a problem that the stronger sex often faces. The immune system in a man’s body controls many functions and also protects the genitourinary system from genitourinary diseases. World health statistics say that the organs of the reproductive and excretory systems are often susceptible to a process where inflammation occurs and no person is immune from it.
Sometimes a person is overtaken by a whole breakdown of symptoms and the disease seriously makes itself felt. The disease and inflammation can develop into a chronic form if treatment is not started in time. The man feels inferior and tries to drown out the acute pain. Treatment is prescribed only by an experienced doctor, only then will it be effective.
Symptoms of diseases of the male reproductive system
The inflammatory process is the main indicator of genitourinary disease.
The main symptom of most diseases of the genitourinary system is the inflammatory process. For example, with the development of urethritis, the patient experiences inflammation of the urethra, and with vesiculitis, inflammation of the seminal vesicles. Symptoms of inflammation of the genitourinary system:
- frequent, difficult or painful urination;
- nagging pain in the groove;
- purulent discharge from the penis;
- the appearance of blood in the urine or seminal fluid;
- decreased potency.
With the active development of acute infectious diseases, the patient may experience increased body temperature, general weakness and malaise. An additional symptom of the disease is a violation of spermatogenesis, which is accompanied by a decrease in the production of seminal fluid, as well as a decrease in the number of motile sperm in the ejaculate.
Classification of genitourinary infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are classified according to the following criteria:
- Localizations.
- The nature of the flow.
Infections are classified according to location:
- Upper urinary tract (kidneys and ureters).
- Lower parts of the bladder (bladder, urethra).
Reference! Most often, pathological processes occur in the lower parts of the urinary tract.
Depending on the nature of the disease, there are:
- Uncomplicated (without disturbances in the outflow of urine, structural changes in the urinary tract, or concomitant diseases).
- Complicated.
Any urinary tract infection in men is considered complicated. In women, UTIs that are complicated are:
- The causative agent of which was an atypical microorganism.
- With a functional or anatomical disorder, which causes an obstruction to the outflow of urine or a decrease in local or systemic immunity.
Specific and nonspecific infections are also distinguished. Specific genitourinary infections are sexually transmitted and are caused by gonococcus, ureaplasma, trichomonas, herpes virus, chlamydia, mycoplasma, etc. Nonspecific arise due to the increased activity of opportunistic (that is, provoking the development of pathological processes only under certain conditions) microorganisms: staphylococci, E. coli, streptococci, etc.
Reasons for appearance
In addition to infections, fungi and viruses, there are other causes of the development of certain diseases of the genitourinary system:
- hypothermia – in most cases is the cause of prostatitis;
- prolonged sexual abstinence – causes stagnation of seminal fluid and is an indirect cause of the development of prostate adenoma;
- low physical activity – leads to androgen deficiency and can cause infertility;
- injuries to the pelvic organs - disrupt the blood circulation of the reproductive system and cause various congestion.
Potency drugs compatible with alcohol
Viagra Soft from 76 rub.
Cialis tablets from 81 rub.
Levitra Tablets from 81 rub.
Chronic prostatitis
Treatment
In the absence of timely treatment, various infections, bacteria and microorganisms can enter the bladder and disrupt the functioning of the excretory and reproductive systems. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since dosage is an important fact in the process.
The following groups of drugs are used:
Medicines for treatment
- Antibiotics. They do an excellent job of restoring mucous membranes and killing foreign microorganisms.
- Means for enhancing and normalizing the immune system. With the help of such means, the immune system is stimulated and subsequently prevents the body from reoccurring the same type of disease.
- Medicines that relieve pain, eliminate unpleasant symptoms and make it possible to return to normal life.
- Antibiotics are selected by a doctor and prescribed in two forms - in the form of tablets and intravenous injections, it all depends on what stage of the disease and what causes the inflammatory process.
- Be sure to use chlorhexidine, iodine solution, miramistin for treating mucous and skin surfaces.
Diseases of the genitourinary system can occur repeatedly, sometimes developing into acute and chronic forms. In this case, treatment is no different from the initial diagnosis.
Infectious diseases
The most common infectious diseases of the genitourinary system are:
- urethritis - inflammation of the urethra;
- pyelonephritis - acute chronic inflammation of the kidney tissue;
- epididymitis - inflammation of the epididymis.
The causes of these and other diseases are pathogens such as:
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis;
- chlamydia;
- genital herpes;
- staphylococcus;
- streptococcus and others.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
In short, this pathology is called prostate adenoma. This disease is marked by the appearance of nodules on the prostate. If left untreated, the tumors grow and become larger. Most cases of the disease occur in males who are fifty years or older.
Has an extensive list of clinical symptoms. In some cases, the disease is asymptomatic. But most often these are the manifestations that are noticed:
- problems with urination (for example, pain or frequent urge);
- urine may be found in the blood;
- when emptying the bladder, it is not possible to empty it completely;
- often observed in the company of concomitant infections of the genitourinary system (for example, mumps);
Despite the benign nature of this pathology, the disease is quite capable of causing severe urinary retention, which will require urgent medical attention. The complications that most often accompany this disease include urolithiasis.
To treat the genitourinary system in men affected by this disease at the beginning of its development, they most often stop at a conservative form of treatment and it is enough. But if they notice that the formations begin to grow and develop rapidly, then surgical intervention is performed. New advances in medicine have made minimally invasive methods available to everyone. In this case, surgical treatment is carried out through the urethra.
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system
The method of treatment is selected depending on the diagnostic indications.
Therapy for diseases of the genitourinary system should be carried out in accordance with the diagnostic results, which in turn includes:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- analysis for the presence of infectious pathogens.
Additional types of laboratory tests (for example, a three-glass test or Nechiporenko test) are carried out if necessary and as prescribed by a doctor.
Regardless of the form of diseases of the genitourinary system, their treatment involves taking medications. If the disease is infectious in nature, the use of antibiotics is mandatory during therapy.
Diagnostics
When seeking highly qualified medical care, the doctor is obliged to collect a complete anamnesis and establish the clinical picture. Only then can an accurate diagnosis be made and effective treatment prescribed.
Diagnostics is as follows:
Analysis Study
- General and biochemical blood test. Any excess in the number of blood cells indicates that inflammatory or infectious processes have begun in the body.
- A specific smear from the urethra can also show bacteria that are common on the membranes.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity for a detailed examination of the internal organs, as well as their size.
- X-ray examination of the kidneys.
- Cystoscopy. Using an endoscope with a camera, which is inserted through the urethra, the bladder is examined.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography. An effective method for viewing many internal organs.
After passing all the necessary types of laboratory and instrumental studies, the doctor analyzes the results obtained and then prescribes treatment methods.
Prevention is the key to health
When the active stage of the disease is overcome, the patient must adhere to strict rules and not forget about prevention, since relapses often occur among diseases of the genitourinary organs.
Inattention to the disease after the first recovery leads to chronic forms.
Basic preventive measures
to maintain the health of the excretory and genital organs:
- avoid hypothermia;
- review your wardrobe and eliminate tight underwear and narrow-fitting trousers. Underwear should be made from natural materials;
- strict diet without fast food, spices, alcohol;
- an active lifestyle to reduce excess weight and get the blood flowing;
- drink as much water as possible daily. Natural juices and herbal drinks are suitable;
- have regular sex life;
- avoid unprotected sexual intercourse and casual relationships;
- take tests and undergo preventive examinations every six months.
A competent approach to any disease gives amazing results. Both young and mature men, with the timely intervention of doctors, not only recovered, but also lived full lives without discomfort, did not lose sexual potency, and even became fathers.
The worst consequences can be avoided
, if you carefully listen to the body’s signals, do not engage in home diagnostics and self-medication.
Find out how to rinse the urethra in men from the video:
Diseases of the genitourinary tract in men can be caused by a variety of reasons. In medical practice, the most frequently diagnosed pathologies of the urinary tract are infectious urological diseases, which cause psychological discomfort and can provoke serious health problems. Inflammation of the genitourinary system in men is most often associated with infections transmitted through sexual contact and diseases of the prostate gland.
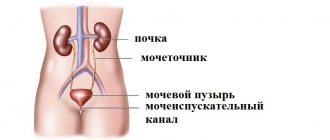
The health of a person as a whole depends on the proper functioning of the genitourinary system. From an anatomical point of view, the male genitourinary system (GUS) consists of the following parts:
- urinary (urinary), responsible for removing urine from the body;
- sexual, responsible for reproductive functions.
The genitourinary (urogenital) tract of men includes internal (vas deferens, spermatic appendages, prostate gland) and external organs.
Anatomically, the urinary tract is closely related to the organs of the reproductive system. The urinary duct is also the vas deferens during ejaculation. Most often, inflammation in men develops in the urethra, which is a narrow tube running along the entire length of the penis.
Consequences of prostatitis
Most men are not inclined to pay attention to such symptoms, and in vain. Chronic prostatitis serves as a constant source of infection, which, when the body's defenses are reduced, for example due to hypothermia, can cause damage to the kidneys, bladder, testicles and their appendages. In addition, the effect of inflammation on nerve fibers leads to potency disorders, and microorganisms “settled” in the prostate worsen the quality of sperm, which can lead to infertility. Therefore, diagnosis and treatment of prostatitis must be carried out as early as possible.
What causes male infertility?
Almost all of the diseases listed in this article, if left untreated, can cause male infertility . This condition is treatable in most cases, but requires a thorough diagnostic search - in addition to disorders in the genitourinary system, it can be caused by genetic abnormalities, various diseases and methods of their treatment, nutritional deficiencies, as well as exposure to external factors.
With all the variety of diseases of the male reproductive system, they have one thing in common: they all require contacting a professional urologist, and the sooner the better. If this is not done on time, the risk of serious complications - irreversible sexual dysfunction, infertility, severe infections or tumors - increases significantly.
The editors would like to thank the specialists of the MedCentreService network of clinics for their assistance in preparing the material.
Modern methods of diagnosis
Diagnosis of diseases of the male genitourinary system is associated with an integrated approach. An initial examination is required, during which information about lifestyle and medical history will be collected. To obtain a detailed picture, a specialist will need the results of several studies:
- If there are external manifestations of the disease, an external examination is carried out.
- The patient must undergo tests. In the laboratory, samples of urine, semen and blood are taken for examination, a smear is taken to identify the flora, and tests are done.
- The internal condition of the urinary canals and organs is assessed by endoscopy. A special probe is inserted inside through the urethra.
- The presence of sand or stones is determined by installing catheters and introducing flexible rods to expand the lumens in the organ.
- An accurate diagnosis is impossible without ultrasound and radiographic examination. The doctor receives a detailed image of the entire system or a specific organ.
- Using the contrast method, you can obtain a clear image of even the thinnest tubules.
Diagnostic methods are selected based on the course of the disease
, because each clinical case is individual and requires a special approach. The anatomy of the patient, the degree of development of the disease, the age of the patient and many related factors also influence.
Therapy methods
- Regular measures - home bed rest or, if necessary, hospitalization in the urology inpatient department. Compliance with a special diet (for kidney pathologies, special nutrition No. 7, 7a, 7b according to Pevzner is indicated).
- Antibacterial treatment - carried out after making an accurate diagnosis. The patient may be prescribed drugs such as Trimethoprim, Bactrim, Ampicillin. If necessary, complex treatment is indicated. The course of therapy lasts on average 2 weeks. After completion of therapy, the effectiveness of treatment is monitored. For this purpose, various laboratory tests are carried out. Treatment for advanced genitourinary infections lasts several months.
- Syndromic treatment includes taking antipyretics, urological preparations, herbal uroseptics (“Fitolysin”).
- Herbal medicine - herbal infusions (from birch, horsetail herb, dandelion root) are taken after consultation with a doctor.
To treat pregnant women with a urinary tract infection, the symptoms of which are mild or severe, you will need to consult a doctor. Treatment of the disease should be carried out without delay. Otherwise, premature birth may occur. Antibacterial agents are selected by the doctor taking into account the duration of pregnancy and possible risks for the baby.
The main problem with urinary tract infections is frequent recurrence.
This problem is typical for women. According to statistics, every fifth woman after a primary infection suffers from repeated symptoms of the process in question. The main property of relapse is the ability of microorganisms to form new strains. This increases the frequency of relapses. Such modified strains of microbes are resistant to certain drugs. Experts include risk factors for relapse:
- unfinished treatment of a previous infection due to non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations;
- the pathogen has attached to the mucous membrane of the organ and remains in this area for a long time;
- development of an infectious process against the background of another pathogen.
What is prostatitis?
But the most common inflammation of the prostate gland is prostatitis . A sedentary lifestyle, irregular sexual intercourse, wearing tight underwear, frequent stress, hormonal changes and alcohol abuse predispose to its development. All this leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the gland and stagnation of secretions in its ducts. Stagnation creates a favorable environment for pathogenic organisms entering the prostate, which cause long-term, low-grade inflammation.
Treatment from folk remedies to the latest generation medications
After the diagnosis is made, a treatment scenario is determined. Drugs are effective against most diseases, but in the fight against advanced forms, surgical intervention is required. This is how phimosis, prostatitis, and prostate adenoma are treated.
The cause of many diseases is infection, so the main blow is dealt to the infectious agents. The patient is undergoing treatment with antibiotics or sulfonamides, prescribed based on test results and personal intolerance.
In case of suppuration, narrowing of the urethra, or problematic urine outflow, the urethra and bladder are washed. It can be carried out with proper preparation even at home, so as not to aggravate the condition by spreading the infection.
A catheter is inserted through the urethra, and urine, pus and mucus flow out of the bladder through the tube. Washing is carried out carefully to avoid injury. During the procedure, anti-inflammatory medications are administered through a tube for local treatment.
To improve urination, drugs from the group of alpha-blockers are used. Thanks to them, spasms of the muscles of the organs are relieved and the outflow of urine is facilitated. The list of decongestant drugs is extensive; a specific medicine is prescribed after examination. In some cases, hormonal therapy is also acceptable.
Traditional medicine against genitourinary diseases is a good help. They are natural and have no side effects.
Most remedies relieve inflammation, disperse urine, and strengthen the immune system, which is important for fighting infections.
The patient is advised to drink plenty of fluids, so herbal infusions will come in handy. They should be consumed after meals 3 times a day, half a glass. The most effective plants against genitourinary ailments are horse chestnut, willow bark, rose hips, cornflower, currants, and chamomile.
What are sexual disorders?
Another large group of diseases of the male reproductive system consists of various sexual disorders . These include systematic difficulties that arise at any stage of sexual activity, and not just erectile dysfunction (impotence), as is commonly believed.
Sexual disorders include decreased sexual desire and arousal, problems with erection and orgasm, premature ejaculation, pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse, and some other disorders.
Male genitals
The genitourinary system of women and men is a complex system that is subject to the negative influence of various factors. Adverse effects provoke the development of a number of diseases that, without appropriate treatment, cause serious complications, including complete loss of reproductive function. Common pathologies of the genitourinary system include:
- cystitis - inflammation affecting the mucous membrane of the bladder;
- fibroma is a benign tumor neoplasm;
- urethritis - inflammation of the urethra, bacterial or viral etiology;
- cervical erosion – disruption of the integrity of the epithelial layer of the mucous membrane;
- prostatitis is an inflammatory process occurring in the prostate gland;
- vaginitis is a pathology of the vaginal mucosa caused by pathogenic microorganisms;
- pyelonephritis – inflammation occurring in the kidneys;
- vesiculitis (spermatocystitis) – a pathological disorder in the functioning of the seminal vesicles;
- endometritis - inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus caused by pathogenic flora;
- oophoritis is a disease of the ovaries that causes disruption of the functioning of the genitourinary system;
- orchitis – inflammation of testicular tissue;
- balanoposthitis - pathology of the skin of the penis;
- salpingitis - inflammation of the fallopian tubes, infectious etiology;
- KSD (urolithiasis, urolithiasis) is a disease accompanied by the formation of uroliths (stones) in the kidneys;
- amenorrhea – absence of menstruation, most often caused by hormonal imbalance;
- ectopic pregnancy is a pathological disorder in which the fetus develops outside the uterus;
- candidiasis (thrush) - an infection of the mucous membrane of the genital organs;
- dysmenorrhea is a pathological disorder manifested in the form of intense pain during menstruation;
- mastitis – inflammation of the mammary glands;
- renal failure - a pathological disorder of the functioning of the kidneys, leading to metabolic disorders;
- endometriosis is the growth of internal cells of the uterus outside of it.
In addition to the pathologies listed above, the genitourinary system is susceptible to the development of malignant neoplasms. A common reason for visiting a doctor is also infection of the reproductive system with various bacteria, fungi and other pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, the disease is observed in both partners, since urogenital infections are transmitted during sexual intercourse.
Pathologies of the genitourinary system can develop as a result of exposure to negative factors. In many ways, the treatment of pathological processes depends on the causes provoking the disorder. If the disease is caused by problems in other organs and systems, then without curing the underlying pathology there will be no improvement.
Pathologies associated with digestion cause an imbalance of nutrients in the body and also lead to disruption of metabolic processes. Deviations in liver function can also provoke the development of diseases of the genitourinary system. Infection with bacteria, viruses, fungi reduces the body's immune defense, and pathogenic microorganisms successfully multiply, affecting organs.
Due to the structural features of the male genitourinary system, diseases most often affect the lower segments of the system. Characteristic symptoms are pain and discomfort during urination and discomfort in the groin area. Manifestations are usually associated with urethritis and prostatitis. In women, pathological disorders most often affect high-lying organs. This is due to the fact that women have a short urethra, and pathogenic pathogens easily penetrate the body.
One of the most common pathologies in women is cystitis, which is often asymptomatic at first. Lack of treatment in the early stages leads to complications, including kidney inflammation. With pathologies of the genitourinary system in women, the following symptoms are noted: a burning sensation and itching in the genital area, the presence of discharge, pain when urinating, a feeling of inadequate emptying of the bladder. Diseases can also be expressed by neurological disorders.
A healthy genitourinary system is important for proper reproductive function. Having children is an important stage in the life of every person, and you need to start taking care of your future baby even before he is born. In many ways, the child’s health depends on the health status of the parents, so a preventive visit to the doctor should not be neglected.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
If one of the following manifestations occurs, you should contact a urologist as soon as possible. The sooner a man does this, the better.
A wake-up call could be:
- decreased potency;
- urinary disorders;
- prolonged and painful erection;
- decreased duration of sexual intercourse;
- painful sensations in the perineum, groin.
Back pain is another symptom that may indicate the presence of inflammatory kidney disease. This is a serious reason that requires immediate action.
Particular attention should be paid to nagging, pressing pain in the back.