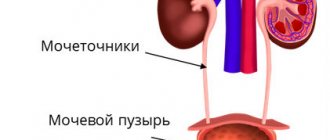
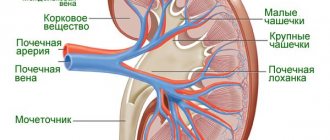
The genitourinary system is an interaction of several organs. The outlines of the buds resemble beans. Size: 10 X 5.5 X 3 cm. In the longitudinal section, the collecting apparatus is clearly visible. The pelvis is located centrally - a cavity where urine is collected from 3 cups, which in turn are formed from 11-12 smaller cups. On the outside, the organs are covered with a dense capsule.
The projection of the organs is the lumbar region, to the right and left of the spinal column. They are localized retroperitoneally. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left. By palpation, doctors identify them through the anterior abdominal wall at the height of inspiration. In the absence of pathology, the kidneys cannot be palpated.
The main task: blood filtration and urine formation is carried out through the work of about 1 million nephrons. This structural and functional apparatus forms the basis of the renal parenchyma. The nephron consists of a glomerulus of intertwined capillaries, covered with a two-layer capsule (Bowman-Shumlyansky), and tubules that form a system for draining urine.
Reproductive system
The male reproductive system includes the testes and epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, vas deferens, prostate gland, urethra and bladder. The external genitalia of men are represented by the penis and scrotum.
The female reproductive system includes the ovaries with appendages, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, labia majora and minora, and clitoris. Between the labia minora there is the vestibule of the vagina, into which the external opening of the urethra and the vaginal opening, as well as the ducts of the Bartholin glands, open.
Ureters and bladder
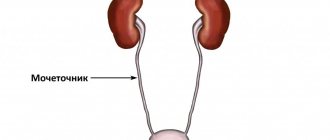
The ureters are hollow tube-shaped organs that emerge from the renal pelvis and transport urine to the bladder, flowing into it somewhat obliquely. Their length is about 25 cm. The bladder is a reservoir for collecting urine. It is similar to a muscle sac with a volume of 250 to 700 ml. When the walls of an organ are stretched by the collecting fluid, the baroreceptors inside the wall of the organ are irritated. A nerve impulse is formed that enters the brain. The person begins to feel the urge to empty the bladder. Further, under conditions of control of higher nervous activity, the sphincter of the urethra relaxes, which leads to the removal of urine from the body.
Development of the genitourinary system
During phylogenesis and embryogenesis, the structures of the genitourinary system go through several stages of development. The urinary and reproductive organs develop from the mesoderm with the formation of intermediate embryonic structures, some of which subsequently undergo complete reduction. The stages of development are: pronephros - preference; mesonephros - primary, trunk kidney; metanephros - pelvic kidney. In addition, the mesonephric (Wolffian) and paramesonephric (Müllerian) ducts are distinguished on both sides. In the female embryo, the mesonephros and mesonephric ducts are reduced, and the paramesonephric ducts intensively develop, resulting in the formation of the fallopian tubes, as well as the epithelium of the uterus and vagina. In the male embryo, on the contrary, the paramesonephric ducts are reduced, and the mesonephros and mesonephric ducts are transformed into the vas deferens.
Diseases of the reproductive organs
This type of disease of the genitourinary system is always characterized by impaired reproductive function in men or its complete loss. These diseases, the most common in urological and andrological practice, include:
- Epididymal cysts, or spermatoceles, are a common disease among patients over 40 years of age. The essence of the disease is the formation of cavities filled with fluid along the testicular appendages on their outer side. Symptoms of the disease are hidden. An effective diagnostic method is ultrasound examination. Treatment, as a rule, is not required - the disease does not damage either the reproductive function or the body as a whole.
- Epididymo-orchitis is an inflammatory disease that occurs under the pathological influence of infection. It is characterized by damage to the seminal appendages with the involvement of the testicular structure in the process. Often the cause of the disease is a cold. The symptoms of the disease are quite characteristic - swelling of the scrotum on the affected side and severe pain. The diagnosis of epididymo-orchitis is made on the basis of bacteriological analysis of urine. Ultrasound examination is ineffective. Treatment is antibiotic therapy, which can be adjusted after the results of bacteriological studies.
- Testicular torsion is a disease that most often occurs in adolescence and is characterized by twisting of the spermatic cord, which causes compression of the blood vessels supplying the testis. Symptoms of the disease include sudden pain in one of the scrotums, groin, lower abdomen, redness and tenderness of the affected area. Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound. Treatment is surgical, based on unwinding the spermatic cord and securing the testis for possible relapses.
- Testicular cancer is a common oncological pathology in men aged 20 to 40 years. Diagnosis using ultrasound is used in later stages, when the tumor becomes visible. A biopsy is used to make a diagnosis in the early stages of the disease. Symptoms of the disease reflect the chronic nature of the course - the presence of a hard painless tumor on the affected side, changes in the size of the testis, spontaneous sharp pain in the scrotum. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the testis.
- Varicocele is a varicose disease of the veins that drain blood from the testis. The symptoms of the disease are quite blurred, episodic paroxysmal pain in the area of the affected testis is possible. Examination - ultrasound and counting the number of sperm (with varicocele, their production decreases and, therefore, the number decreases). On an ultrasound, dilated and congested veins are clearly visible. Treatment is invasive surgery, which is based on the removal of the testes, which is carried out in especially severe cases.
It is worth noting that this is not a complete list of possible pathologies of the genitourinary system affecting the organs of the male genitourinary system. It is important to remember: if you notice any deviations in the functionality of the genitourinary system or the appearance of pain, you must immediately contact a urologist; any infections are particularly difficult. Most diseases are easily treatable in the early stages and are easily diagnosed using ultrasound.
Links
- Genitourinary system
- Genitourinary system // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
| Human organ systems | |
| Cardiovascular system (heart, blood vessels) • Lymphatic system • Digestive system • Endocrine system • Immune system • Sensory system (somatosensory system, visual system, olfactory sensory system, auditory sensory system, gustatory sensory system) • Integumentary system • Nervous system ( central, peripheral) • Musculoskeletal system (skeletal system, muscular system) • Genitourinary system (reproductive system, urinary system) • Respiratory system | |
Diseases in women
Women's diseases are very dangerous. Chronic inflammatory processes and prolonged infections of the genitourinary system in women can lead to disruption of menstruation, urination, but the most unpleasant thing is to infertility or ectopic pregnancy. If there is a symptom of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor to prevent undesirable consequences and the disease becoming chronic.
If pathogenic microorganisms increase in number in a woman’s vagina, the disease vaginitis and thrush develops. If bacteria infect the urethra, the disease urethritis occurs. Inflammation of the bladder is called cystitis. As a result of infection in the kidneys, the disease pyelonephritis develops. Hormonal imbalance results in various diseases: amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, premenstrual syndrome. The diseases are accompanied by pain before, during menstruation, or absence of pain at all.
Preventive measures, treatment
A healthy lifestyle is the best prevention of all diseases.
It can be concluded that the body is a single system, and disturbances in one area can lead to disturbances in a completely, as it seems at first glance, unrelated area of the body. If a symptom is present, you should consult a doctor, conduct an examination and only begin treatment if the diagnosis is confirmed.
However, diseases can be prevented by following certain rules. Avoid hypothermia. It is necessary to eat a balanced diet and give up bad habits. Underwear should be made of natural material and fit loosely to the body. Wash your genitals upon waking and before going to bed, after sex, and, if possible, after bowel movements. After sexual intercourse, you need to urinate so that possible infections come out along with the urine. Leading an active lifestyle, blood and lymphatic stagnation lead to inflammatory processes.
Women should not wear panty liners. It is necessary to wipe the genitals from the pubis to the anus. Males should wash the glans thoroughly, retracting the foreskin. Children should not be kept in diapers for a long time. After bathing, you must carefully dry your genitals. Conduct an annual preventive examination of the genitourinary system.
etopochki.ru
The anatomy of the genitourinary system, both men and women, has almost the same structure. These are the bladder, two ureters and, of course, two kidneys. They produce urine, which ends up in the calyces. They, in turn, form a kind of pelvis, from which urine enters the ureter, and then into the bladder. Its wall tends to increase, while facilitating urine retention so that a person can urinate at any time convenient for him. The bladder may also narrow. As a rule, during this, a cervix is formed, which passes directly into the urethra. The only difference between the genitourinary system of a woman and a man is that the female urethra is located separately from the genital tract.
Possible diseases
Diseases of the genitourinary system are very diverse. Women often suffer from ascending genital tract infections. This happens because their urethra is short and wide. That is why the pathogen easily penetrates the bladder, and then through the ureters directly to the kidneys. Some infectious diseases may be asymptomatic. The female genitourinary system is susceptible to diseases such as urethritis, cystitis, and pyelonephritis. Symptoms of urethritis include:
- Painful urination accompanied by burning.
- Discharge from the urethra, which causes redness and stickiness.
- The number of leukocytes in the urine increases.
This disease occurs due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, as a result of which an infection is introduced into the urethra.
The most common ailments of the genitourinary system
1. Cystitis. The disease is an acute or chronic disease. Symptoms of acute cystitis are painful urine discharge in small portions every ten minutes. The pain most often manifests itself in the pubic region. It can be burning, cutting or dull. Chronic cystitis is most often a pathology of the urethra, which is caused by the woman’s genitourinary system. The symptoms are no different from the acute form of the disease.
2. Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the renal pelvis. The genitourinary system of women after 55 years of age is most susceptible to this disease. This infection is considered the most dangerous for the urinary tract. Most often it is asymptomatic. It happens that a pregnant woman can get pyelonephritis due to the fact that the outflow of urine from the kidneys is disrupted. If a girl who is pregnant develops this disease, this indicates that it has already worsened to a chronic form. It can be primary and secondary. Acute primary pyelonephritis is accompanied by fever, pain in the side and lower back. During the examination, many bacteria, such as E. coli, may be found in the urine. In case of secondary pyelonephritis, computed tomography is necessary to identify the complexity of the disease.
Conclusion
As can be seen from this article, a woman’s genitourinary system is very susceptible to many diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor your health and consult a doctor in time.
fb.ru