Many people cannot fully understand whether renal pressure is upper or lower.
Due to incorrect interpretation of blood pressure indicators, self-treatment at home often only causes a worsening of the patient’s condition.
To determine what causes may affect blood pressure and its indicators, it is necessary to understand the terminology.
Main types of blood pressure
Blood circulation is the most important indicator of human life. It is with the blood that oxygen and important nutrients enter the body. The blood flow moves through large arteries, veins and capillaries with a certain speed and pressure on the vascular walls. You can measure its indicators using a device called a tonometer, but it gives two numbers at once. What is the renal pressure: upper or lower - and it’s worth figuring out.
Medicine distinguishes two types of blood pressure on the arteries:
- systolic _ This is how the upper pressure is called, that is, the first digit in the tonometer readings. With normal vital signs, systolic pressure varies from 90 to 120 millimeters of mercury. Systolic pressure is primarily determined by the work of the heart, namely, at what speed it pumps blood throughout the body;
- diastolic _ In medicine, diastolic pressure is called lower or renal. This is the second digit in the obtained measurement results with a tonometer. Within normal limits, the lower pressure should be between 60 and 80 millimeters of mercury.
Why is it rising?
The main reason for the increase is kidney pathology. An increase in lower values caused by damage to the renal artery is called renovascular hypertension. In this case, a decrease in the level of renal blood triggers the production of urgent plasma replenishment in the organ. The response to a decrease in blood flow is the production of hormones by the kidneys that improve vascular tone and normalize the functioning of the vascular wall. And due to an increase in blood levels in the kidneys, the load on the vessels also increases, which provokes a deterioration in the patient’s condition. The long course of this pathology leads to kidney dysfunction and subsequent necessary organ transplantation.
Causes of isolated increase in lower blood pressure
In medicine, the following increasing factors are identified:
- kidney pathologies;
- disruption of hormone levels;
- endocrine disorders;
- adrenal diseases;
- tumor formations in the area of the heart muscle;
- heart disease;
- improper functioning of the thyroid gland.
Why does the lower and upper pressure increase?
- the presence of a stressful situation or nervous tension;
- consuming excessive amounts of caffeine-containing products - coffee, dark chocolate, cola-based carbonated drinks;
- alcohol abuse;
- physical and emotional overload;
- drug overdose.
What are upper and lower blood pressure responsible for?
Systolic and diastolic pressure are responsible for the work and condition of the circulatory system of the human body as a whole.
Is the upper pressure renal or cardiac? The systolic (upper) pressure is formed when the heart pumps out the next batch of blood.
In other words, the tonometer records the force of the heart’s impulse, which is why it is called cardiac. There is an opinion that the more often the heart contracts, the higher the first number on the tonometer will be, but this is partly true, and partly misleading. For example, when consuming substances that promote vasodilation, such as alcohol, upper blood pressure increases, but the heart, to compensate for the load, slightly reduces its work.
Thus, after drinking alcohol, blood pressure first jumps sharply and later returns to normal. But such systematic experiments with the circulatory system can eventually provoke hypertension, which is already considered a disease requiring special drug treatment.
What does kidney pressure mean in humans?
Lower pressure, also known as diastolic pressure, characterizes the condition of the blood vessels.
This indicator is recorded at the moment when the heart has pumped out blood again and is in a relaxed state. At this moment, the tonometer records the blood pressure on the walls of large vessels in the human body.
It is called renal because it is the work of the kidneys that forms this indicator. With pathological kidney diseases, fluid stagnation can form in the patient’s body, sodium ions are retained in the blood, and this leads to swelling of the walls of blood vessels.
Kidneys and blood pressure: relationship with low blood pressure
High blood pressure is the scourge of today. The disease affects young and older people, but few people know how the kidneys affect blood pressure, and in medicine there is even a special term: renal hypertension. Statistics show that every 7th patient experiences trouble precisely because of the filtration organs. It is kidney pathologies that provoke high or low blood pressure in people under 30 years of age.
How do kidneys affect blood pressure?
Kidneys and blood pressure are interrelated concepts.
Kidneys and blood pressure are interrelated concepts. The slightest dysfunction of organs has a negative impact on blood flow. Due to the fact that organs are a filter of toxins, decay products, and removal of excess fluid, pathological processes disrupt normal functioning, which means that all harmful substances are not removed from the bloodstream. All these reasons lead to the patient experiencing low or high blood pressure.
Important! High pressure is the result of the accumulation of a large amount of excess fluid in the bloodstream, low pressure is the result of dehydration. Therefore, one of the recommendations for reducing blood pressure is to take diuretics that remove fluid from the body.
Hypertension is caused by damage to the kidney parenchyma or blood vessels, pathologies of the cardiovascular system. The causes of the development of pathological processes can be any kidney disease:
- Nephritis, including glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis;
- Hydronephrosis;
- Polycystic disease;
- Renal artery dysplasia.
There is also a connection between abnormal pressure and congenital obstructions of the renal tissues - in this case, the patient will only benefit from surgical treatment. The kidneys are an organ directly involved in maintaining normal blood pressure. Producing a number of substances that affect cardiac tone, the filtering organ at the slightest pathology will fail in the direction of increasing or decreasing blood pressure.
Important! Hypertension is a condition in which blood pressure rises, instrument readings range from 140/90 mmHg
How to distinguish renal hypertension from cardiac hypertension?
The symptoms of both pathologies are not very different, but there is still a clear difference: renal hypertension is not so often aggravated by crises, heart attack, stroke.
The symptoms of both pathologies are not very different, but there is still a clear difference: renal hypertension is not so often aggravated by crises, heart attack, stroke . In addition, with renal destruction, almost immediate swelling of the soft tissues is observed. A sign of an increase or decrease in the amount of urine will help to track low or high blood pressure. In particular, before blood pressure increases, urine volume decreases significantly.
Important! If the functionality of the kidneys is impaired, blood flow to the organs slows down, water and sodium accumulate - all this causes swelling. Exceeding the concentration of sodium ions in the blood leads to swelling of the walls of blood vessels, which exacerbates the sensitivity of the latter. Damaged receptors are activated with the production of renin, and being converted into angiothesin, then into aldosterone, the substance significantly increases vascular tone, narrowing the lumens. The result is an increase in pressure. Additionally, the problem is aggravated by the reduced production of substances that reduce tone, causing the organ’s receptors to become irritated with increasing dynamics. Such a vicious circle is constantly fed and helps maintain high blood pressure in the patient.
Any pathological process in the kidneys is associated with pressure and causes a decrease or increase in the production of pressor (increasing pressure) or depressor (lowering pressure) substances. But a change in pressure level leads to a slowdown in blood flow in the kidney, which provokes unpleasant symptoms in the patient.
Causes of increased pressure
A decrease in pressure due to renal pathologies is an extremely rare phenomenon and requires each time an individual examination by a specialist.
A decrease in pressure due to renal pathologies is an extremely rare phenomenon and each time requires an individual examination by a specialist. The most common option is increased blood pressure due to kidney problems, such as:
- hyperplasia is a congenital disease characterized by proliferation of the walls of the renal artery;
- coarctation - narrowing of the isthmus of the artery;
- arterial aneurysm;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- embolism – blockage of the renal artery;
- sclerosing pyelonephritis;
- external compression of the renal arteries.
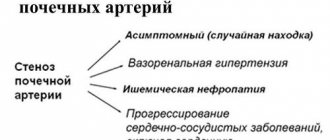
Kidney hypertension differs according to two indicators: renovascular or associated with diffuse (acquired) lesions.
- Vasorenal pathology is the most common, occurring even in children (90% of cases). With adult patients, the diagnosis is confirmed in 50-60% of cases.
- Diffuse hypertension is caused by damage to the tissue of the renal organs. There can be both congenital pathology in the form of: hypoplasia, absence of a part or a complete organ, the presence of cysts, formations, and an inflammatory process - this is pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis.
Important! Sometimes professionals discover a mixed version of the disease, in which destruction of the arteries is combined with pathology of the kidney tissue
Lower pressure – renal or cardiac?
The main and only symptom of renal hypertension is a sharp jump in lower pressure.
Systolic and diastolic (upper/lower) pressure is an indicator of the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Impaired kidney function may affect the indicators, but may indicate heart disease. Therefore, careful diagnosis and examination is required to identify the cause. The lower level, like the renal level, is judged by the presence of diseases of the filtering organs.
Important! The main and only symptom of renal hypertension is a sharp jump in lower pressure to 150 mm Hg. and more. At the same time, the upper indicator may remain normal. The standard numbers are as follows: lower pressure (diastolic) 80, upper (systolic) 120. When the lower bar rises above the reading of 120, you should monitor the symptoms of illness (pain, dizziness, vomiting, nausea) and consult a doctor as soon as possible
There are no special symptoms of pathology. The kidneys signal themselves only by swelling, usually of the lower extremities, some malaise, and pain in the lower back (of varying intensity). But all the signs can also indicate a malfunction of the cardiovascular system.
Upper pressure - renal or cardiac?
Systolic blood pressure clearly indicates disturbances in the functioning of the heart and its blood vessels. Pathologies of other organs do not affect this figure in any way! Therefore, when analyzing the question: is upper pressure cardiac or renal, the answer is cardiac.
What causes blood pressure to drop?
Low blood pressure with readings below normal is often caused by kidney failure.
If the relationship between kidney pathologies and high blood pressure has been tracked, you should know what causes low blood pressure. Low pressure does not always indicate renal pathologies, however, if the patient has already encountered problems with the filtration organs, you should check whether the low pressure indicates renal dysfunction.
Important! Low blood pressure readings below normal are often caused by kidney failure. When a minimum amount of the hormone renin, which is responsible for normalizing blood flow, is produced, lower pressure decreases, which is a consequence of either an existing renal pathology or its dynamic development. This indicator cannot be ignored; renal failure is a disease that, if left untreated, can lead to a fatal outcome.
What to do if you have high or low kidney pressure?
You should start by visiting a cardiologist to identify the exact cause of the increase in blood pressure.
You should start by visiting a cardiologist to identify the exact cause of the increase in blood pressure. But it is even more important to immediately visit a specialist if the lower pressure is low - the slightest delay can be critical, in this case, quick professional help is required and you cannot do without calling an ambulance.
You cannot lower your blood pressure readings on your own unless this treatment is prescribed by a doctor. The point is that the reasons are unclear: by lowering or increasing blood pressure on your own, you can completely “ruin” the kidneys and cause the development of pathology. Treatment is also prescribed after a preliminary examination, therapy is prescribed:
- Surgical/operating room in the presence of formations, cysts, and other pathologies;
- Medication in the form of tablets, if the cause is associated with insufficiency or excess of renin production;
- Diet therapy helps in cases where arterial hypertension is observed;
- Folk remedies and methods. This therapy can also be used as a preventive measure. Herbs, decoctions and tinctures help well, but you should still consult a doctor before taking them.
Important! If the blood pressure is too high, the ambulance is already on its way, but is a little late, a napkin soaked in apple cider vinegar, applied to the soles of the feet for 7-10 minutes, will help. The patient should be placed horizontally, given a warm drink, warm baths for the hands, and all stress/irritating factors should be removed as much as possible.
Despite taking measures to normalize blood pressure, sudden increases in blood pressure should be avoided. The use of medications should be prescribed taking into account the severity of renal pathology: starting with small doses, proceed to normal drug intake. Often, pressure changes are associated precisely with excessive use of medications, which also affects indicators. The most striking effect comes from complex treatment: medications supported by diet, proper lifestyle and a selected drinking regime will ensure the patient’s normal condition for many years.
lecheniepochki.ru
Causes of renal hypertension
Increased renal pressure, lower or upper cardiac pressure, signals problems in the body.
If the indicators jumped sharply and after a short period of time returned to normal, then there is no need to worry, because the reasons may be physical activity, nervous shocks, both alarming and joyful.
These are factors that can affect the circulatory system spontaneously, but do not bring a person much discomfort or affect well-being. High blood pressure signals heart problems, but unstable lower kidney pressure is considered a more acute problem.
What to do to normalize?
With high lower pressure, shortness of breath with difficulty in inhaling is observed.
An increase in pressure in the blood vessels is characterized by a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being, accompanied by heavy breathing, difficulty inhaling, shortness of breath, a feeling of tightness in the chest and confusion. In case of high lower pressure, regardless of the reasons that led to the violation, take the following measures:
- When the lower pressure is 100 and rising further, place the patient on a flat surface so that the head and shoulders are raised above body level to prevent suffocation.
- Open the windows in the room or fan the patient.
- Apply something cold to the collar area (for no more than 20 minutes) or constantly wipe the area with cool water.
- Massage the neck area to stimulate blood flow.
- If possible, soak your feet in warm water.
- Perform a massage by pressing pointwise on the earlobes and linearly along the collarbone area.
- Give high blood pressure pills (only if previously prescribed by a doctor).
- If chest pain is present, give the patient nitroglycerin under the tongue.
- If it worsens, call an ambulance.
Symptoms
Doctors note that renal hypertension and cardiac hypertension are in many ways similar, judging by the patient’s well-being, but at advanced stages of diseases of the arteries or the kidneys themselves, the following symptoms appear:
- minimum gap between upper and lower blood pressure . With renal hypertension, the lower blood pressure can rise to the level of the upper one and the gap can fluctuate up to 5-10 mm Hg;
- deterioration of vision . Increased lower blood pressure can affect the optic nerve, the patient experiences causeless loss of vision, which does not recover on its own and requires medical attention;
- headache in the back of the head . Renal hypertension causes severe pain in the occipital region of the head, which does not go away even at rest. In addition, the patient experiences dizziness, nausea, and sometimes vomiting;
- legs and arms swell greatly. Fluid retention in the body due to impaired kidney function necessarily affects the condition of the limbs. Hands and feet may become very swollen after short walks; in the morning there is excessive swelling of the face, especially in the eye area;
- lower back pain. Kidney diseases are often accompanied by pain in the lower back and back. The pain is deeply aching in nature, and sometimes with severe attacks the patient loses ability to work.
With systematically elevated lower blood pressure, heart and kidney failure, atherosclerosis, partial or complete loss of vision, and in some cases myocardial infarction, micro-stroke and complete kidney failure can develop.
Nutrition and diet
When treating renal pressure, patients are prescribed a special diet. They are advised to exclude certain foods. These include:
- salt;
- fried and fatty foods;
- spicy foods;
- products with a high content of various seasonings.
All of these foods contribute to the worsening of nephrogenic hypertension. After their consumption, the level of blood pressure increases, which in turn destroys kidney tissue.
The performance of the excretory paired organ is significantly deteriorated. Experts also recommend avoiding drinking tea, coffee and other drinks that contain caffeine.
Drinking alcohol is also prohibited.
The patient is advised to give preference to only moderate physical activity. The sick person should include the following foods in their diet:
- Sea kale. This food component saturates the body with useful microelements. Sea kale contains a huge amount of vitamins.
- Onion and garlic. Such food products not only have a positive effect on kidney function, but also relieve a person of germs. They normalize blood pressure and restore the body's protective functions.
- Fresh juices from vegetables. They prevent the formation of kidney stones and include a large amount of vitamins. They can be prepared from celery, parsley and coriander.
- Cranberries and lingonberries. Such berries have a positive effect not only on the kidneys, but also on the entire body as a whole.
- Fish and fish oil. Such products contain phosphorus necessary for the body. There are also many useful microelements.
It is no coincidence that you need to stop eating salt. This food supplement retains excess fluid in the body. This negatively affects the health of not only people with kidney pressure, but also those who do not have any pathologies. You can consume no more than 4-5 grams of salt, and it is better to avoid it altogether.
The patient should avoid eating canned foods and various deli meats. As a rule, they contain a huge variety of seasonings. You should not eat salted fish. It contains an excessive amount of salt.
Video on the topic
General information about upper and lower blood pressure:
Having studied cardiac and renal pressure, and what these indicators are, we can conclude that this is a strictly adjusted balance of the circulatory system, which must be maintained for the normal functioning of all human organs and systems. Paying attention to body signals can protect a person from serious illnesses and health disorders.
- Eliminates the causes of pressure disorders
- Normalizes blood pressure within 10 minutes after administration
To assess the condition of the patient's body, doctors use various methods.
The activity of the cardiovascular system is assessed by measuring upper and lower pressure.
These indicators make it possible to timely identify pathological processes in the body and prevent irreversible complications.
Causes and symptoms of growth
All reasons for increased systole are divided into physiological, psychological and pathological. Sometimes an increase in blood pressure is simultaneously provoked by all these factors. A condition in which blood pressure remains above normal for a long period of time is called hypertension.
Physiological reasons for the increase in cardiac blood pressure:
- bad heredity;
- binge eating;
- lack of physical activity;
- abuse of salt in dishes, coffee, strong tea;
- aging of the body;
- excess body weight;
- overwork;
- addiction to tobacco and alcohol;
- taking medications that have a hypertensive effect.
Among women under 50 years of age, there are far fewer hypertensive patients than men of the same age. But the onset of menopause changes the situation: most representatives of the fairer sex have problems with fluctuations in blood pressure. The psychological reasons for the increase in blood pressure are experiences and stress.
Pathological factors of hypertension include:
- atherosclerosis;
- adrenal tumor;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- hormonal imbalances;
- diabetes;
- left ventricular hypertrophy;
- vegetative-vascular imbalance of the hypertensive type;
- kidney diseases (organ failure, pyelonephritis);
- malfunction of the aortic valve.
While a person is young, his arteries and heart are in good condition, compensatory mechanisms are immediately activated when blood pressure deviates from the norm. As we age, all organs and systems wear out and begin to function worse.
Many elderly people are diagnosed with atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy. Therefore, as you age, heart pressure standards increase. So, for an elderly person, a systole in the range of 140-155 units will be considered optimal.
Systolic hypertension is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the occipital area and temples;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- numbness of the limbs;
- fear of death;
- weakness;
- heart rhythm disturbance (tachycardia);
- increased irritability;
- redness of the epidermis;
- deterioration in the quality of vision;
- insomnia;
- tinnitus.
Types of pressure
There are several classifications to characterize blood pressure. Highlight:
- Upper (systolic). An indicator characterizing pressure during systole (heartbeat).
- Lower (diastolic). It is determined by a decrease in pressure during diastole (expansion of the cavities of the heart).
Based on the determined values, the following types of pressure are distinguished:
- elevated (hypertension) – defined when blood pressure is above 140/90 mmHg. Art.
- low (hypotension) – blood pressure readings are below 90/60 mm Hg. Art.
Diseases that lead to high blood pressure
Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands
The adrenal glands perform the task of producing hormones that are necessary for vital processes in the body. Their excess or deficiency leads to various diseases. For example, excess mineralocorticoids increase blood pressure and decrease potassium levels. Such problems can arise due to many diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands, many of which are chronic. A computed tomography (CT) scan is usually ordered to determine the connection.
A sharp decrease in hormones (acute adrenal failure) threatens a person’s life. This cause can be observed over a long period in people with one kidney.
Thyroid diseases
Diseases of this organ can completely change a person’s life. Changes in both appearance and mental health are possible. According to statistics, problems with the thyroid gland occur several times more often in women. A lack of hormones that it produces (hypothyroidism) occurs mainly in adulthood. The list of diseases is wide:
- endemic goiter, resulting from a lack of iodine in food;
- thyroid injuries;
- secondary hypothyroidism and others.
Due to excess hormones, thyrotoxicosis occurs. These painful conditions cause:
- toxic goiter;
- single or multiple thyroid nodules are pathological formations, usually benign, that appear in most people with age;
- pituitary diseases.
One of the possible symptoms of these diseases is low or high blood pressure. The early stages of thyroid disease can be characterized this way.
Pathology of the spinal canals
The canals of the spine can decrease in diameter - narrow. This leads to stenosis. Older people are more likely to suffer from the disease. But young people who have problems with the spine are also not immune. They are congenital. This may be indicated by aching pain in the lower back, radiating to the leg. The pain appears sharply and intensifies if you do not stop moving.
Fluid retention in the body
One of the most unpleasant sensations associated with fluid retention in the body is caused by an increase in “lower” pressure. The amount of fluid in the body is regulated by the kidneys, which is influenced by hormones. When the balance between sodium ions and water is disturbed, the kidneys are forced to accumulate water to dilute the sodium.
The most well-known causes of fluid retention in the female body are menstruation, pregnancy and overeating.
A possible reason could be heat or even allergies. There are several tips for removing fluid: move more, eat less, do not add too much salt to food, drink diuretic teas and products.
Atherosclerosis
If for a long time only the lower pressure is increased, then this may indicate problems with the muscle tone of the blood vessels, or the enzyme responsible for pressure (renin) is synthesized abnormally. One of the likely causes is atherosclerosis . With this disease, the elasticity and muscle tone of blood vessels decrease. This leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. It is usually caused by excess “bad” cholesterol.
Heart pressure
The top one is heart pressure. Its other name is systolic, it characterizes the work of the heart. Normal values of heart pressure are considered to be 110-140 mmHg. Art. On average, this value is 120 mmHg. Art.
The reasons leading to its increase are:
- Obesity. Excessive body weight provokes disorders of the cardiovascular system and also contributes to the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels, which is dangerous for the development of atherosclerosis.
- Emotional stress. Stressful situations cause a sharp increase in upper cardiac pressure. It can be short-term or long-term.
- Bad habits. Smoking and alcohol abuse lead to a decrease in capillary tone.
- Vascular damage. Narrowing of the lumen of the capillaries and blockage of blood vessels cause an increase in pressure and require immediate treatment.
- Somatic pathology. Damage to the endocrine, nervous, and urinary systems is the cause of the development of arterial hypertension.
The clinical picture of changes in cardiac pressure depends on the degree of its increase or decrease. When the upper pressure decreases, patients observe the following symptoms:
- weakness, fatigue;
- dyspnea;
- apathy;
- drowsiness;
- headache, dizziness.
Arterial hypertension is manifested by the following clinical symptoms:
- feeling of warmth in the head;
- skin hyperemia;
- pain in the back of the head, which subsequently spreads to the entire head;
- unsteady gait;
- dizziness.
What do lower blood pressure indicators indicate?
Blood pressure is one of the main characteristics of the circulatory system. Almost every person has measured their blood pressure at least once in their life, either independently, at home, or at a doctor’s appointment. But not everyone understands exactly what the readings of a tonometer, which uses 2 digits to indicate pressure, indicate. And if the top number is familiar to many, since it is the first thing people pay attention to when their health worsens, what the lower blood pressure shows is few people know.
What do the tonometer readings mean?
The first number, which is always higher, reflects the upper or systolic pressure (SD) observed at the time of systole. It occurs when the heart muscle contracts as much as possible, causing all the blood to be thrown into the artery.
The second number, the value of which is always smaller, means the lower or diastolic pressure (DP), observed with maximum relaxation of the heart muscle. This moment is called the moment of diastole.
When diagnosing various diseases, both meanings are of serious importance, since each of them indicates malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs.
Normal pressure values
For many years, it was believed that blood pressure (BP) should be 120/80 mmHg. Art., however, at present, when determining normal blood pressure, doctors began to take into account the individual physiological characteristics of each person. But still, there are certain restrictions, the excess of which indicates the presence of pathology and requires mandatory treatment. Stable level exceeding 140/90 mmHg. Art. indicates the presence of hypertension, while values below 90/60 indicate hypotension.
But the occurrence of a disease in the body can be indicated not only by changes in the upper and lower pressure values. Quite often, one of the indicators goes beyond the normal range, and when diagnosing a disease, the doctor takes into account these changes.
It is worth knowing that throughout the entire lifespan of a person, his lower pressure is not constant and its average parameters can be within 70 ± 10 mm. After reaching the age of fifty, DD levels may be slightly elevated, and the norm in this case is considered to be 90 mmHg. Art. It should also be taken into account that when diagnosing a disease, a single case of a rise or fall in lower pressure does not matter. Only those data that were observed over a long period of time, repeated several times a year, are of great importance.
What does an increase in DD indicate?
A blood pressure value of 120/80 confirms that the body is functioning normally, while changes in the blood pressure up or down may indicate malfunctions in its functioning.
- If the lower blood pressure is elevated, simultaneously with the upper ones, this means that the patient is experiencing pathological changes in the functioning of the organs of the cardiac system.
- An increase in DD alone may be a sign of disturbances in the normal functioning of the endocrine and renal systems.
If lower blood pressure is elevated, this primarily depends on the following reasons:
- Kidney diseases;
- Hyper-or hypothyroidism;
- Diseases of the cardiac system;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Failure in the functioning of the pituitary gland and adrenal glands.
If a patient has an increased value of diastolic pressure, then it is quite difficult to return it to normal, since it is practically not treated, either with traditional drugs or traditional medicine.
But it is worth knowing that increased DD may not necessarily develop against the background of diseases. Quite often the factors behind these changes are:
- frequent stressful situations;
- increased loads;
- alcohol abuse;
- drinking coffee.
In these situations, lower blood pressure rises simultaneously with upper blood pressure for a short period of time.
It is worth knowing that the initial signs of high DD at the initial stage of the disease are almost absent. The patient feels only the consequences of increased DD, in which internal organs are damaged, resulting in the following symptoms:
- chest pain;
- irritability;
- insomnia;
- noise and heaviness in the head, etc.
When seeking medical help, the doctor will first measure your blood pressure and then prescribe the necessary tests to diagnose the disease.
What does a decrease in DD indicate?
If high lower blood pressure is observed mainly in old age, then its reduced levels can also occur at a young age. If the DD shows a level below 70 mm Hg. Art., this means that the heart muscle is quite weak and does not cope well with its functions of pumping the required amount of blood, as a result of which the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- decreased concentration;
- forgetfulness and fatigue;
- weakness and dizziness;
- cold extremities;
- body temperature is below normal;
- darkening of the eyes;
- dyspnea;
- small spots before the eyes;
- gastrointestinal disorder.
Quite often, the appearance of low DD values does not depend on the presence of pathological processes in the body and is detected suddenly. This may be due to both heredity and the individual physiological characteristics of the patient.
As for serious health problems, a decrease in the DD level below 80 mm Hg. Art. depends on the following issues:
- renal or heart failure;
- osteochondrosis;
- VSD;
- tuberculosis;
- anemia;
- ulcer;
- infectious inflammation;
- hormonal disorders;
- stress and depression;
- exhaustion;
- lack of vitamins B, C, E;
- side effects of medications;
- sudden climate change.
When you contact a doctor, he prescribes the necessary tests and only after that prescribes treatment. In old age, reduced DD depends on the deterioration of the elasticity of blood vessels, as well as the appearance of cholesterol plaques on their walls. This condition of the arteries significantly increases the risk of developing complications of pathological conditions of the organs of the cardiac system, since it causes an increase in DM and a decrease in DD. All this can cause the development of a disease such as cardiac ischemia, which often leads to death.
Also, low DD in old age is responsible for the appearance of factors that cause the occurrence of Alzheimer's disease.
Reduced DD values can cause dehydration of the body, which in old age often occurs as a result of atherosclerosis, leading to deterioration of the elasticity of blood vessels.
Reduced DD values during pregnancy are of considerable importance, because as a result of these changes, the blood supply to the fetus may be disrupted. The result of this condition can be a miscarriage, as well as a neuropsychic or physical developmental delay of the unborn baby.
The ratio of SD and DD
It is not always possible to correctly determine the presence of pathological changes in the body based on changes in DD. Most often, diagnosis is based on a comparison of upper and lower pressure parameters. You also need to pay attention to pulse blood pressure, which is calculated as the number that is the difference between DM and DD and should be 40 mmHg. Art.
If pulse pressure values increase above 40 mm due to an increase in blood pressure, while the lower value remains at the same level, then we can talk about pathologies in the circulatory system.
If the difference is less than 40 mm due to an increase in the lower indicator, you need to pay special attention to the functioning of the renal system.
There is no general reason that would explain the deviation of DD from the norm, but you need to know that it shows the elasticity of blood vessels and the state of muscle tone, which is regulated by a substance that is secreted by the kidneys. This is why DD is often called renal.
It must be remembered that the lower or DD is no less important than the systolic. Therefore, long-term and regular fluctuations in indicators should be the reason for contacting a doctor, who will conduct a medical examination and, based on its results, prescribe treatment.
How to cure hypertension forever?!
In Russia, every year there are from 5 to 10 million calls to emergency medical care for high blood pressure. But Russian heart surgeon Irina Chazova claims that 67% of hypertensive patients do not even suspect that they are sick!
How can you protect yourself and overcome the disease? One of the many recovered patients, Oleg Tabakov, told in his interview how to forget about hypertension forever...
Read more "
(1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
sosudinfo.com
Kidney pressure
Renal is the lower pressure or diastolic. Impaired kidney function leads to its increase. The optimal value is considered to be in the range of 60-90 mmHg. Art.
- inflammatory kidney diseases;
- damage to the kidney vessels (vasculitis, developmental anomalies, thromboembolism, atherosclerosis);
- complications of diabetes mellitus, manifested in diabetic nephropathy;
- stones in the kidneys.
Symptoms of the disease are divided into 2 types. Some patients complain of a clinical picture characteristic of high blood pressure, while others suffer from renal symptoms.
In the first case, the leading clinical manifestations are:
- headache, frequent dizziness;
- feeling of heaviness in the head;
- gait disturbances;
- muscle weakness, fatigue, “chronic fatigue” syndrome;
- nausea, vomiting.
When renal symptoms appear, the main complaints include:
- pain in the lumbar region: the severity of the pain syndrome ranges from acute to aching nagging;
- frequent and painful urination;
- change in the quality of urine: darkening, the appearance of impurities in the form of white flakes or blood, a pungent odor;
- swelling of the lower extremities, face, possible swelling in the lumbar region.
The dangers of high diastolic blood pressure
In the absence of timely treatment of the cause that provoked the increase in lower blood pressure, the pathology progresses. And this is dangerous due to irreversible changes in the body. High diastolic pressure provokes the following consequences:
- sclerotic lesions. Healthy tissue is replaced with connective fibers. As a result, the organ stops working normally;
- increased likelihood of sudden rupture of vessel walls, heart attack, and cerebral hemorrhage;
- deterioration of blood circulation. In this case, there is a deficiency of nutrients in all internal organs, hypoxia develops;
- dementia;
- deterioration of the liver, brain, kidneys, heart.
Important: Diastolic hypertension can occur over a long period without visible symptoms. A sharp jump in blood pressure can provoke a hypertensive crisis
During a hypertensive crisis, the patient experiences severe headache, nausea, dizziness, and spots appear before the eyes. Sometimes there are convulsions, temporary paralysis of the limbs, hallucinations, loss of sensitivity in different parts of the body (it can be complete/partial).
In case of a hypertensive crisis, it is important to immediately provide assistance to the patient. You need to call a doctor, put a cold compress on the back of your neck, provide air flow, and give a quick-acting drug (Nifedipine, Capoten).
Prevention and recommendations
To minimize the risk of developing hypertension, you must adhere to the following preventive measures:
- Balanced, rational and nutritious nutrition. Food should be enriched with vitamins, minerals and trace elements. It is recommended to limit your salt intake.
- Active lifestyle. Regular physical activity, as well as walks in the fresh air, help enrich the blood with oxygen. This has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system.
- Calm. It is important to avoid stressful situations and nervous tension. Emotional experiences are a powerful provocateur of increased blood pressure.
- Rejection of bad habits. It is recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Regular monitoring by a doctor. A comprehensive examination, including an electrocardiogram and tests, will allow timely diagnosis of changes in the cardiovascular system.
Complex treatment
If your lower blood pressure is elevated, consult a cardiologist. Self-treatment, accompanied by taking medications that normalize basic indicators, leads to irreversible consequences or has no effect. A cardiologist will help identify the cause that triggered the increase. The main goal of therapy is to get rid of the physiological factors that lead to deviations from normal lower pressure. Great importance is given to the therapeutic diet. In general, to treat a patient, a comprehensive approach is required, which includes:
- balanced diet;
- establishing a daily routine;
- normalization of the patient's weight;
- feasible physical activity;
- walks in the open air;
- drug therapy;
- folk remedies.
How to reduce using medications?
Medicines are taken after a comprehensive examination.
Medicines are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician after conducting a comprehensive examination of the patient and establishing the etiology of the pathological condition. More often, doctors prescribe beta blockers, which normalize the condition by regulating the functioning of the heart. Taking such medications increases the oxygen content in the heart and reduces tension in the organ. Stable heart function ensures unimpeded blood flow and stabilizes the load on blood vessels. They are also prescribed to take medications of the calcium antagonist group, used for advanced disease. Medications to reduce elevated readings:
- "Concor";
- "Carvedirol";
- "Celiprolol";
- "Diltiazem"
- "Metoprolol";
- "Falipamil"
- "Propranolol";
- "Amplodipine".
Therapeutic diet
The list of prohibited and permitted products is shown in the table:
| Authorized Products |
|
| Products that are limited to a minimum or excluded |
|
| Prohibited Products |
|
Medicines
High lower blood pressure can rise either independently or together with cardiac indicators. In this case, the pulse often increases and tachycardia occurs. The attending physician should select medications. The main problem in the treatment of isolated diastolic hypertension is that not only renal, but also systolic parameters decrease. Therefore, the doctor has to prescribe several drugs at the same time in order to maintain both the upper and lower numbers normal.
For moderate and severe forms of the disease, a complex of drugs aimed at reducing blood pressure is prescribed. The composition includes diuretics, beta blockers, inhibitors, peripheral substances.
Beta blockers are widely used in the treatment of hypertension, tachycardia, and heart failure. They limit the flow of adrenaline to the heart, thereby relaxing the muscle. Reduce heart rate, lower pulse. The most common medications are Metoprolol, Anaprilin, Atenolol.
Thanks to ACE inhibitors, it is possible to increase vascular patency; sometimes they are prescribed for a greater diuretic effect. These include: Lisinopril, Ramipril, Enalapril, Captopril.
Diuretic drugs are Hypothiazide, Uretit, Furosemide, Veroshpiron. If there is a high pulse (90 or more), Xipamide is prescribed to normalize the heart rate.
Calcium antagonists lower blood pressure as a result of vasodilation and normalize cardiac activity. Reduce calcium content at the cellular level, thereby relaxing the muscles of blood vessels. Widely used - Amlodipine, Verapamil, Nifedipine.
Sympatholytic drugs reduce heart contraction, dilate arterial and venous vessels (Octadine, Isobarine, Diltiazem).