Why is ultrasound performed only on a full bladder?
An ultrasound scan is done of a full bladder - when it is maximally full, the inside is seen better, since in an empty state it is wrinkled and difficult to see by a specialist.
Before an ultrasound of the bladder, it is necessary to fill it with liquid, then the walls will straighten and stretch without unnecessary folds. When the organ is full, it can bring the intestinal loops closer to the abdominal cavity, to its front part.
Filling of the organ should occur in natural conditions and at a pace, but in some cases the patient may not know about the need for an ultrasound, or if the procedure is emergency and there is no time to prepare according to the rules. In this case, the bladder needs to be filled quickly and efficiently.
To do this, just drink a liter of clean water an hour before the intended procedure. Instead of water, it is allowed to use tea or fruit drink, juice or herbal infusions. Experts do not recommend drinking milk or highly carbonated drinks to ensure the reliability of the examination results.
The bladder of all people is different in volume, and if after an hour the patient does not have the urge to deurinate, then it is worth drinking another half liter of liquid. It is important to prevent overflow; if the urge to urinate appears long before the procedure, you can visit the toilet, but then be sure to replenish the lost volume of water.
As a rule, early urination indicates excellent functioning of the kidneys, which produce urine. Experts advise not to empty your bladder for several hours before the ultrasound, so as not to drink excess water and not put a strain on your kidneys. This is only possible if the patient has a good knowledge of his excretory system.
Preparing for the study
Competent preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is not particularly difficult. The main condition is a filled organ at the start of research. No diet or colon cleansing is required. You can fill your bladder in the following ways:
- an hour before the procedure, drink a liter of liquid;
- Avoid emptying your bladder for five hours before the procedure;
- if the patient has urinary incontinence, then before the examination, catheterization is performed with saline solution, which is used to fill the organ;
- You can take diuretics, but except in cases of kidney or heart disease, since excess fluid can be harmful or cause renal colic due to bladder blockage;
- if the ultrasound is scheduled for the morning, then you should avoid morning urination;
- In children under one year of age, feeding should be 10 minutes before the procedure.
More on the topic: What information is included in the bladder ultrasound protocol?
Each age group has its own criteria for assessing the liquid drunk, which should fill the organ:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | Children between one and two years old should drink as much as they can because their bladders are very small. |
| 2 | From 3 to 7 years old children need to drink a glass of water |
| 3 | from 8 years to 11 years 300 ml is enough |
| 4 | Teenagers over 12 years old and under 18 need to drink 400 ml of liquid |
| 5 | all patients over 18 years of age should wait for the organ to naturally fill with fluid and avoid emptying, and during an emergency examination, drink a liter of fluid an hour before the ultrasound |
Bladder examination algorithm: how to prepare for an ultrasound for women and men?
Ultrasound of the bladder in women and men: how to prepare correctly? This question worries all patients who are faced with the need to undergo an ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system for the first time. To answer this question, it is necessary to take into account all the features of the procedure.
In a man, the urethra passes through the prostate. With its diseases (adenoma, prostatitis), the urethra is compressed by the tissues of the enlarged gland, which causes incomplete emptying of the bladder. After a standard ultrasound procedure, the man is asked to urinate, and the residual amount of urine is measured by inserting an ultrasound probe into the rectal cavity.
Therefore, a man needs to do 2 enemas: one the night before, the other in the morning before the procedure, so that the lower part of the large intestine is free and does not contain fecal matter.
DETAILS: What disability group if there is no kidney
In women, if there are no contraindications, the most accurate source of information about the condition of the bladder is the transvaginal ultrasound method. For urgent indications, it is carried out even during menstruation and in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Indications
Frequent urination
The bladder is examined in the case of:
- pathological processes in various parts of the urinary system;
- determination of the source of erythrocyturia;
- complaints characteristic of prostatic hyperplasia, cystitis, kidney stones and urolithiasis;
- establishing the cause of acute urinary retention and other dysuric symptoms;
- suspicion of the presence of benign or malignant neoplasms;
- suspicion of diverticulosis;
- traumatic lesions of the bladder;
- control of therapy of various types of therapy.
Overactive bladder in women: treatment (medications)
To reduce hyperactivity syndrome, medications are used to help relax the walls of the organ. This:
- tolterodine (“Detrol”);
- oxybutynin in the form of a skin (transdermal) patch (“Oxytrol”);
- oxybutynin in;
- trospium;
- solifenacin;
- darifenacin;
- fesoterodine.
The main method for diagnosing female genital organs is ultrasound examination. Ultrasound, thanks to a special sensor that emits ultrasound, allows you to find out the state of women's health. Through computer data processing, the doctor can see a high-quality image of the internal organs on the screen.
During the initial examination or for preventive purposes, the procedure can be performed at almost any time of the cycle, excluding the period of menstruation.
If a woman has previously been diagnosed with any diseases of the genitourinary system or has symptoms indicating pathology, ultrasound is prescribed on certain days or performed several times in order to be able to quickly monitor the patient’s condition.
If there are signs of pregnancy, the procedure is carried out 14 days after ovulation, however, a delay in menstruation can also indicate the appearance of a cyst in the ovaries or uterus.
The most favorable time for ultrasound examination is considered to be the period after menstruation (the first 3-6 days).
As a rule, during one procedure, the doctor examines not only the uterus, but also the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and cervix.
If the diagnosis is aimed at assessing the condition of the ovaries or corpus luteum, it is repeated several times during one menstrual cycle (usually on days 21-24 or 14-16). Preparing for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs for women involves certain actions. It directly affects how accurately the diagnosis will be made.
Depending on the method of the procedure, preparation for a gynecological ultrasound of the pelvis for women may differ.
For example, before a transabdominal examination, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids to ensure that the bladder is as full as possible.
Other methods of ultrasound diagnostics require diet, preliminary bowel cleansing and other preparatory measures. How to prepare for a pelvic ultrasound for women, depending on the purpose of the diagnosis?
This ultrasound examination technique is carried out using a special sensor (vaginal). Transvaginal diagnosis is carried out not only in gynecology, but even in urology (if the doctor suspects the presence of genitourinary diseases).
Preparing for a pelvic ultrasound for women does not require filling the bladder with fluid or taking any medications to cleanse the intestines. To carry out the diagnosis, you will need a disposable diaper/towel to lie on.
DETAILS: Neurogenic bladder in women and men: treatment, symptoms
If a doctor examines a pregnant woman, her bladder needs to be reasonably full. To do this, you should carry out appropriate preparation by drinking approximately 500 ml of liquid before the test (1-1.5 hours before).
What else you should know before the examination:
- It is impossible for there to be gases in the peritoneal organs during the study, so for 2-3 days it is worth reducing the consumption of foods that cause them (baked goods, vegetables/fruits, sugar, dairy products).
- It is not recommended to perform cleansing enemas before the procedure.
- You can eat in the evening before the diagnosis, but no later than 6 hours.
- To eliminate gases, it is allowed to take activated carbon or Enzistal.
The process of urine excretion
As soon as urine from the collecting duct enters the small calyx of the kidney, the process of urine formation ends. And the process of urine excretion begins.
If you remember, it was with this phrase that our last conversation about the human urinary system ended (Article “Further process of urine formation”). And today we will continue our series of conversations on this topic.
Let me remind you that the human urinary system is divided into two parts:
- urinary
- urinary
As you might guess, the first part of this system (urinary) is responsible for “forming” and producing urine. And the second one removes the resulting urine into the external environment.
Urologists in Moscow
Urologists of the Moscow region
Detailed information about the clinic and each doctor, photos, ratings, reviews, quick and convenient appointments.
Urine is formed in the kidney tissue
We have already discussed this rather complex process with you in previous articles. Now let's talk about how urine is eliminated from our body.
As soon as a tiny drop of urine appears on the pyramidal papilla (where the openings of the nephron's excretory tubules are located) and enters the small calyx of the kidney, the process of urine formation ends and the process of its excretion begins.
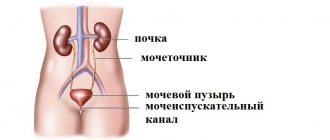
Urinary system
The following bodies take part in this less complex, but still very thoughtful and well-coordinated process:
- Small kidney cups
- Large kidney cups
- Pelvis
- Ureters
- Bladder
- Urethra
The small calyces, large calyces and pelvis are the renal pyelocalyceal system (or renal pelvis)
This system of collecting cavities is located directly in the kidney itself and consists of slit-like cavities that collapse when they are not filled with urine and expand as they are filled.
Why do the kidney cavities collapse, turning into narrow slits when they are empty?
Because nature has arranged it so that there is very low pressure in these cavities. Much lower than in the collecting ducts. Of course, this was done for a reason. We have already had a lot of opportunities to make sure that wise nature does not do anything for nothing. She never wastes her energy in vain.
This is done so that urine flows from the kidney tissue into the collecting system very easily and quickly.
The pyelocaliceal system does not simply “wait” for urine to fill its cavities. It literally “sucks” urine from the collecting ducts of the nephron. And all this is due to the fact that the pressure in the CLS is much lower than the pressure in the collecting ducts of the nephron.
So, the urine first fell into the small cups, then into the large cups, and finally into the renal pelvis
Here it collects until the gradually increasing pressure in these cavities allows it (urine) to slip through the narrow outlet from the pelvis into the ureter.
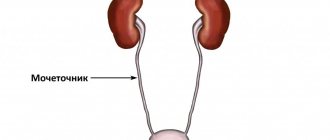
Ureter
The ureter is a long (about 30 cm) thin (3 - 4 mm) tube that begins at the outlet of the pelvis and ends in the bladder.
It is through this tube that urine moves from the kidney to the bladder.
There are two ureters in the human body - right and left. The right ureter comes out of the right kidney, and the left ureter comes out of the left. Both of them go down, behind the intestinal loops, to the bladder.
Having reached the bubble, they pierce its wall, each on its own side, and penetrate into its cavity. Urine formed in the kidneys enters the cavity of the bladder.
The place or opening through which the ureter connects to the bladder is called the ureteric orifice. As you understand, two ureters open into the bladder cavity through two orifices - right and left.
The ureters are very thin tubes, but their walls are designed in such a way that they can stretch surprisingly well if the need arises.
From the inside, the wall of the ureter, like any other hollow organ, is lined with a mucous membrane. In a calm state, it is folded and easily straightens if the ureter is stretched.
Beneath the mucous membrane is a submucosal layer of connective tissue. This layer contains nerve plexuses and vessels that feed the cells of the mucous layer. The glands that produce mucus and moisturize the mucous membrane of the ureter are also located here.
Next is a layer of muscle cells. Muscle cells are arranged in two layers. The inner layer is longitudinal muscle fibers. The outer layer is circular muscle fibers.
And finally, on top the ureter is covered with a loose connective tissue membrane.
The ureter's job is to deliver urine from the kidney to the bladder, which it does successfully.
To do this, the ureter produces smooth longitudinal peristaltic movements, gently pushing urine in the desired direction.
And so the urine entered the bladder
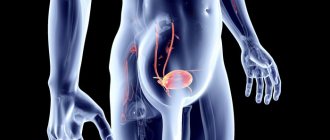
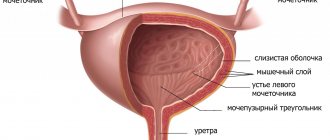
In a collapsed state, it is a small organ, a small sac, which is completely and easily hidden behind the pubic bone.
But a full bladder is a spherical (in men) or oval (in women) formation, which can have different sizes (depending on the degree of filling).
Sometimes the top of the bladder can reach the level of the navel. The capacity of the bladder is on average 500-700 ml.
The bladder is divided into several areas. The apex of the bladder is located above and slightly anteriorly. Below and slightly behind is its bottom. Between the bottom and the apex is the body of the bladder. The bottom smoothly passes into the neck and then the urethra begins.
Why is a bladder needed?
The only task of this sac-like formation is to accumulate and store urine until the moment of urination. That is, the bladder, just like the stomach, just like the rectum, is a reservoir. A reservoir that gives us great freedom of action. It is this that allows us to sleep peacefully, relax or work, and not have to visit the toilet every minute.
The bladder, like the ureters, is covered on the inside with a folded and easily extensible mucous membrane. Beneath it there is a submucosal layer with vessels, glands and nerve plexuses.
And then - a fairly thick layer of muscle tissue. In the wall of the bladder, the muscle layer is represented by three layers. Internal - longitudinal and circular muscle fibers. The middle layer is circular muscle fibers.
The outer layer is longitudinal muscle fibers.
All these muscle fibers of different directions make up a large and fairly strong muscle of the bladder, which anatomists have named mysteriously and beautifully: detrusor. This word, translated from Latin, means “to push out” and is fully consistent with the main task of this muscle: to push urine from the bladder into the urethra.
The process of removing urine does not end here, and we will continue our conversation in the next article.