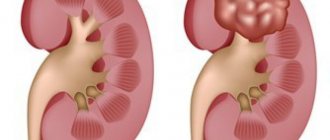
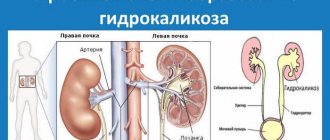
Renal calicoectasia (ICD-10 code: Q60) is a deadly pathology; the second name is hydrocalycosis. As this disease progresses, the renal calyx is damaged. The damage is due to the fact that the calyces become overfilled with urine and eventually expand. Hydrocalycosis leads to compression of the kidney tissue. As a result of such problems, the kidneys cannot function normally.
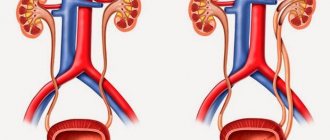
On the right is a healthy kidney, on the left is a kidney with hydrokaliosis
Causes
The main causes of this disease are:
- Urolithiasis, in which stones form in the kidneys and urinary ducts: they interfere with the normal outflow of urine.
- Nephroptosis: in some people, this pathology is associated with the special structure of the ureter.
- Congenital origin. Anomalies in the development of this organ also lead to pathologies, including hydrocalycosis.
- Impaired functioning of the pararenal veins.
- Sometimes pathology occurs against the background of a neoplasm. As you know, the tumor compresses the ureter, and because of this, the outflow of urine is disrupted.
- If pyelonephritis starts, many complications will appear, including hydrocalycosis.
- The cause of the pathology may be trauma to the ureter.
- Scar changes in the ureter are also dangerous to health: hydrocalycosis occurs against the background of this problem.
- Kidney tuberculosis, progression of parasitic infection in the genitourinary system.
Disease in children
Hydrocalycosis of the kidney can occur in a baby who is still in the womb. The doctor detects this in the fetus through abnormalities in the development of the urinary system. To confirm such violations, a screening examination is carried out. In older children it progresses gradually.
Symptoms
The main symptoms are:
- chills;
- urine has become dark and cloudy;
- frequent urination, but urine is not completely eliminated;
- there is pain in the lower back. They occur regardless of pressure: with pressure, the unpleasant sensations intensify;
- if the disease progresses, the person’s temperature rises;
- nausea with vomiting appears;
- blood spots in urine.
The symptoms of the pathology in question are similar to gastrointestinal diseases (cholecystitis and appendicitis). A nephrologist treats diseases related to the kidneys.
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys
DIAGNOSTIC METHODS, APPROACHES AND PROCEDURES [14,16,18]
Diagnostic criteria
Complaints and anamnesis:
Hydronephrosis is often asymptomatic. Most often manifested by: pain in the lumbar region; gross hematuria; hyperthermia; dysuria.
Anamnesis:
· the presence of the above symptoms and the time of their appearance from the moment of examination; · previous operations or pathological processes of the pelvic organs, abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
Physical examination:
· detection of a palpable formation in the hypochondrium, and in case of severe hydronephrosis - in the corresponding half of the abdomen; · tympanic sound during percussion characterizes the retroperitoneal location of the formation. A dull sound indicates significant hydronephrosis and displacement of the abdominal organs; rectal examination allows you to assess the condition of the prostate gland, vaginal examination - the genital organs.
Laboratory research:
· general blood test: leukocytosis, neutrophilic shift to the left, mild to moderate anemia, accelerated ESR. Leukocytosis with a shift of the formula to the left and an increase in ESR indicate the addition of a urinary infection. In bilateral hydronephrosis, a low hemoglobin level indicates the presence of renal failure. Possible leukocyturia, tubular proteinuria, hematuria, decreased relative density of urine with bilateral lesions; · general urine analysis (according to indications and according to Nechiporenko): leukocyturia, proteinuria, bacteriuria, hyposthenuria (decreased concentration function), micro-, macrohematuria; biochemical blood test: azotemia (increased level of creatinine), urea, decreased blood pressure, ferritin, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia. creatinine and urea, electrolytes (potassium and sodium). An increase in creatinine and urea levels may indicate a bilateral nature of the process. If secondary hydronephrosis is suspected, laboratory diagnosis includes the tests necessary to determine the underlying disease (PSA blood test, urine cytology).
Instrumental studies[16]:
· CT scan of the kidneys: expansion of the renal cavity system, the condition of the kidney parenchyma is assessed. · Ultrasound of the kidneys: expansion of the renal cavity system, the condition of the kidney parenchyma is assessed. · Dopplerography of the kidneys: the blood supply to the kidney is assessed, the presence of additional vessels is determined · An additional examination method is ultrasound with a diuretic load (Lasix at the rate of 0.5 mg/kg) - the size of the CL of both kidneys is determined, the dynamics of the collector system is assessed on the 15th, 30th th, 45 minutes into the study. Normally, the maximum expansion of the renal pelvis occurs 10-15 minutes after the administration of Lasix, and the return to its original size occurs by 20-30 minutes. Excretory urography: expansion of the renal collecting system of varying degrees, expansion of the pelvis (extra-, intrarenal), lack of contrast ureter, delayed evacuation of contrast agent from the collector system on delayed urograms. · Spiral CT with bolus contrast enhancement: shows the parenchymal, excretory and vascular phase, expansion of the pyelocaliceal system, the condition of the parenchyma, the presence of additional vessels, stones, volumetric formations of the retroperitoneal space, compressing the ureter from the outside. · Antegrade pyeloureterography: an additional examination method that allows you to determine the expansion of the collecting system and the localization of obstruction. · Retrograde ureteropyelography : an additional examination method that allows you to determine the level and extent of obstruction.
Indications for consultation with specialists:
· consultation with a therapist - to exclude concomitant somatic pathology (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, systemic diseases, allergic diseases, gastric ulcer, etc.); · consultation with a cardiologist - to exclude pathology of the cardiovascular system (arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, history of cardiac surgery, etc.); · consultation with a pulmonologist – to exclude pathology of the respiratory system (bronchial asthma, COPD, etc.); · consultation with an otolaryngologist – to exclude pathology of the nasopharynx; · consultation with a dentist – for sanitation oral cavity.
Diagnostic algorithm: (diagram)
Algorithm for diagnosis and treatment of hydronephrosis
Source: https://diseases.medelement.com/disease/%D0%B3%D0%B8%D0%B4%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B5%D1%84%D1%80 %D0%BE%D0%B7-%D0%BF%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BA/15069
Treatment
Therapy depends on how severe the hydrocalycosis is. When determining treatment tactics, the doctor takes into account the factors that led to the development of pathology. It is important to say that therapy should be comprehensive:
- Taking medications is aimed at eliminating pain. Additionally, medications are prescribed to help fight the infectious process.
- Painkillers are prescribed.
- If a patient's blood pressure rises, the doctor prescribes special medications. Depending on the nature of the symptoms, antipyretics may be required.
- At the same time, treatment is being carried out for the disease that could lead to caliectasis.
- If it is urolithiasis, medications are prescribed to help dissolve the stones. It is necessary to carry out therapy that will prevent complications.
- Endoscopy may be needed to treat hydrocalycosis. This is a modern treatment method comparable to a full-fledged operation. Surgical intervention is prescribed when taking medications does not lead to the expected result
Alternative medicine
Along with traditional medicine, you can use folk remedies, for example:
- To prepare an effective medicine, you need to take 50 g of eleutherococcus and ginseng. Plant roots are mixed with 300 ml of vodka. After 3 weeks you will have an infusion: it is taken 1 tbsp. l. once a day.
- To treat kidney-related diseases, rosehip decoction is used. To prepare the medicine, take not the fruits, but the roots of the plant. Grind 50 g of roots and pour 1 liter of boiled water. Determine the product in the dark, wait 12 hours. Then strain the infusion and take 1 tbsp. every 2 hours. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- You need to take blackcurrant leaves and berries. Wash the leaves thoroughly, chop, place in 0.5 liters of boiling water. The infusion is ready in 20 minutes: it is traced and put on fire. You need to boil it for 5 minutes, then put it on the fire and add 50 g of berries. Wait 10 minutes, then take 100 ml 4 times a day.
How does pathology manifest itself?
Wen in the mammary gland can pop out in any area. As a rule, a woman discovers it by accident while bathing or self-massage. It looks like a soft-to-touch lump that protrudes from under the skin. The formation should not hurt, and the skin should not change its appearance. If the lipoma occurs near the areola, the nipple and the area around it may become covered with small white pimples. These should not hurt or itch. Of course, if the wen grows greatly, or there are several formations, then the mammary gland itself also changes its shape and becomes asymmetrical.
As a rule, the nodular variety does not bother the woman much. There is no pain symptom. Removal occurs due to aesthetic rejection. Such a formation can degenerate into cancer (liposarcoma) if it is exposed to the negative effects of ultraviolet rays for a long time or is injured by poor-quality underwear.
Diffuse breast lipoma is much less common. The most dangerous thing is its calcification, that is, the appearance of calcium salt in fatty deposits. Symptoms in this case are accompanied by pain in the affected area. In most cases, the formation has a size of 1-5 cm. Less often, the size of the compaction exceeds 12 cm. The weight of the wen can reach 0.5 kg.
Diet
For this disease it is usually recommended:
- Baked and steamed vegetables (potatoes, carrots, beets, onions).
- Pumpkin porridge cooked with milk is very healthy.
- It is worth saying that eating raw cabbage leads to gas formation in the intestines: this product should be abandoned. The same goes for apples, but these fruits are not prohibited when baked.
- Rosehip decoction is ideal as a drink.
- Chamomile tea.
In conclusion, we note that treatment in the early stages gives good results.
Complications
Calicoectasia of the kidneys can lead to dangerous complications; therefore, the disease must be treated in a timely manner. Therapy in advanced stages is ineffective.
Complications may arise due to the addition of a bacterial infection. If this infection progresses through the urinary ducts, it can be fatal. A complication may be shrinkage of the kidney and loss of functionality of the organ. As the disease progresses, the parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue. The prognosis of the disease is favorable in case of successful treatment. If your doctor recommends abdominal surgery, you should not delay it.
You can also familiarize yourself with the main symptoms of kidney disease in this video.
Diagnostics
If a benign formation is detected, you should consult a dermatologist. The doctor will identify the wen by its appearance and differentiate it from atheroma or fibroma.
If in doubt, a biopsy may be prescribed - a procedure in which the skin is punctured with a thin needle. In this way, biological material is obtained from inside the lipoma, which is sent for histology. The study will show the presence of fat and the absence of atypical elements.
If the first examination reveals signs of localization of the wen on the internal organs, specialized specialists are involved in the examination of the patient. The list of diagnostic procedures is expanding to include instrumental examination methods.
Treatment tactics are developed taking into account the interpretation of the obtained tests, the stage of development of the lipoma, its size, the patient’s age and the severity of clinical symptoms. Lipomas are treated with radical methods. Those fatty tissues that grow quickly and compress internal tissues and nerve endings are subject to removal. It is worth immediately removing a lipoma that forms near the spinal column, natural openings or on the walls of internal organs.