Causes
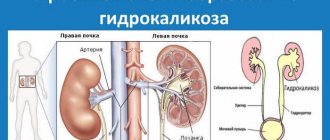
During pregnancy, the right renal pelvis expands, which is due to physiological reasons. The enlarging uterus puts pressure on the internal organs and ureter. This leads to incomplete excretion of urine and expansion of the pelvis system. This process is reversible; at the birth of a child, the kidney structures return to their normal size. The presence of physiological hydronephrosis is considered normal. During pregnancy, it occurs in the right kidney in 90% of cases. As for the left, the probability is up to 67%. Rarely both ureters are compressed.
Increased renal blood flow leads to an increase in kidney size by 1-1.5 cm. The process reaches its maximum by mid-pregnancy. Progesterone promotes smooth muscle relaxation and reduces peristalsis in the ureter. In addition, the renal systems dilate moderately due to mechanical pressure on the ureter. More often during pregnancy, right-sided pyeloectasia is observed, which is associated with the anatomical features of the position of the ureter, crossing the iliac and ovarian vessels at an angle before the entrance to the pelvis. Stagnation of urine in the dilated renal system predisposes pregnant women to asymptomatic bacteriuria.
The right kidney is more distended than the left due to dextrorotation of the uterus and the protective effect of the sigmoid colon, which is located above the left ureter. Dilatation on the right begins as early as 6 weeks after conception and decreases 1.5 months after birth.
Pathological pyelectasia
Pregnancy is associated with hormonal changes that directly and indirectly affect kidney function.
Increased GFR (glomerular filtration rate) mainly results from decreased mean oncotic pressure and increased ultrafiltration capacity.
Renal dysfunction is a common complication during pregnancy.
Causes of obstruction of the urinary organs:
- urolithiasis disease;
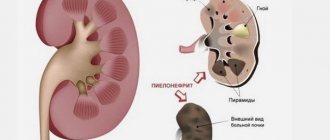
- pyelonephritis;
- bladder hernia;
- congenital pathology of the abdominal, pelvic or urinary systems;
- tumors or abscesses;
- inflammation of the urethra;
- fibrosis and scarring in the perineum;
- injuries;
- purulent and hemorrhagic occlusions with cystitis;
- ascending urinary tract infections (UTI);
- purulent urethritis.
Pyeelectasis of the right kidney can be caused by infectious processes in the urinary tract, cancer and hormonal disorders. This condition of the organ can lead to atrophy and necrosis of its tissues.
Renal plasma flow and glomerular filtration rate increase by more than 50% during pregnancy. This leads to increased urinary excretion of calcium, uric acid, sodium and oxalates. All these substances are lithogenic. Reabsorption in renal tissues is reduced due to suppression of parathyroid hormone. These changes and stagnation of urine contribute to the formation of stones during pregnancy.
Recommended topic:
Treatment of renal pyelectasis
Pathological enlargement of the renal pelvis in an expectant mother during pregnancy requires urgent medical or surgical treatment.
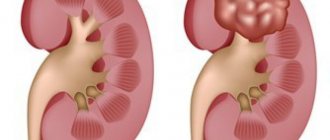
Urological malignant neoplasms during pregnancy are quite rare. Renal carcinoma is the most common urological tumor in pregnancy, followed by benign angiomyolipoma.
Magnetic resonance imaging is an effective diagnostic method for assessing the condition of the urinary organs. Removal of the tumor is carried out after considering the malignant potential of the tumor and fetal survival at different stages of pregnancy. Large tumors should be treated aggressively despite the increased risk of fetal mortality. Smaller tumors may be present until childbirth or until the fetus reaches maturity. The question of when to have surgery is decided by the oncologist together with the obstetrician-gynecologist.
Disease detection
At first, the pathological condition does not manifest itself in any way, so patients usually seek medical help at a later stage. Diagnosis of pyeelectasis is usually made using x-rays and ultrasound. But during pregnancy, the first technique is contraindicated, although it is much more informative than ultrasound.
The doctor collects anamnesis and the results of an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and bladder, on the basis of which an accurate diagnosis is made.
Kidney stones as a factor in the development of pyelectasis
Kidney stones
The main reason for hospitalization of a woman during pregnancy is an acute attack of urolithiasis. Increased progesterone levels and mechanical compression cause bladder congestion. Increased glomerular filtration rate and high levels of circulating vitamin D lead to changes in urine pH and hypercalciuria. Uric acid, sodium and oxalate are lithogenic factors that increase urine output during pregnancy. Such changes promote the formation of calcium phosphate. Up to 75% of pregnant patients with kidney stones have calcium phosphate salts.
Classification
There are the following types of pyelectasis in pregnant women:
- dynamic congenital - a woman has a narrow ureter from birth;
- dynamic acquired – develops after inflammatory diseases;
- organic acquired - among the reasons: mechanical injury, kidney prolapse, hormonal pathologies;
- organic congenital - inflammation during the formation of the kidney led to its structural changes.
With organic congenital pyelectasia in a pregnant woman, renal hydronephrosis in most cases is bilateral.
Clinical picture
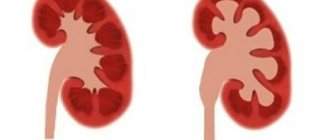
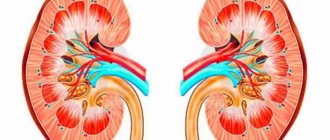
There are three degrees of dilation of the renal pelvis:
Enlargement of the renal pelvis
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
Pyeloecasia usually occurs after the twentieth week of pregnancy. During this period, the patient's uterus begins to actively grow. The severity of pyelectasis depends on how well the kidneys cope with their functions. The mild form is accompanied by a feeling of slight discomfort in the lumbar region. Clinical symptoms of pyelectasis are the appearance of pain in the abdomen and lower back, as well as pain when urinating.
In severe forms of the pathological process, a pregnant woman experiences severe pain in the lower back. There may be severe swelling of the limbs and a feeling of pain during the urination process. This condition is very dangerous and can lead to the development of renal failure, as well as kidney necrosis. Therefore, when the first symptoms of pyelectasis appear, it is necessary not to delay solving the problem and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Types and degrees of disease
Kidney disease of this type in pregnant women is divided into left-sided, right-sided or bilateral pathology. The process of enlargement of the renal pelvis itself is divided into three stages: mild, moderate and severe.
The severe stage of disease progression can result in dangerous complications. Its result can be tissue atrophy, organ sclerosis and renal failure. The stage of the pathology depends on the ability of the kidneys to perform their functions, the presence of concomitant diseases and consequences.
Diagnostics
Methods:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood analysis;
- blood biochemistry;
- determination of electrolytes and GFR to assess the proper functioning of the urinary system.
Diagnosis of pyelectasis during pregnancy is somewhat difficult. This is explained by the fact that the expansion of the renal pelvis is very well visualized during an x-ray examination, however, this examination method is not used during pregnancy.
Diagnosis of kidney condition is also carried out using ultrasound. In this case, the doctor must evaluate the anatomical structure of the collecting system, ureters, bladder and urethra.
MRI
MRI differentiates physiological dilatation of the renal pelvis from pathologies caused by the presence of stones in the patient’s body. This research method shows peripheral edema and expansion of organ structures. MRI in combination with urography is used as an alternative imaging method to standard CT. It visualizes the anatomical details of the urinary tract, but does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, which is an undeniable advantage for examining pregnant women. However, MRI has low spatial resolution and requires long imaging times. The method is low sensitive when it comes to detecting calcifications.
Recommended topic:
Pyeelectasia of the kidneys
Intravenous urography is not used during pregnancy, since the main disadvantages of this method are irradiation of the fetus, the need to administer intravenous contrast and various difficulties in its interpretation, because the child’s skeleton is superimposed on the images.
When examining a pregnant woman, it is strongly recommended to avoid radiation exposure, especially in the first trimester of embryogenesis.
If pyeloectasia is suspected, the expectant mother undergoes a urine test to identify proteins, leukocytes, and red blood cells. In order to detect bacteriuria during pregnancy, bacteriological urine culture is necessary.
If a woman is suspected of having a malignant tumor, a biopsy of the tumor is performed.
Symptoms
At the initial stages of the disease, there are no specific symptoms. This is due to the powerful compensatory capabilities of the human body. Especially if only the right or left kidney is enlarged. After all, another organ takes over all functions for a while.
With the progression of pyelocalicoectasia, the likelihood of developing complications sharply increases. This is the addition of a bacterial infection as a result of urine reflux, the development of pyelonephritis. Stagnation of urine occurs, its excretion is impaired, up to acute retention. Local pressure increases, which adversely affects the functioning of the urinary system.
The main symptoms of pyelocalicoectasia:
- difficulty urinating;
- pain during and after bowel movements;
- discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the area of the left or right kidney (on the affected side);
- the appearance of pathological impurities, changes in odor and other indicators of urine.
Treatment
In 70-80% of women with symptomatic hydronephrosis or urolithiasis during pregnancy, therapy is carried out by correcting the water balance, non-narcotic analgesics and antibiotics. Other therapeutic procedures are also acceptable, including an epidural block for pain relief and the use of beta-blockers.
Beta-adrenergic blockers stimulate contractility of the renal pelvis and ureter and thereby can increase the rate of urine flow and also increase renal blood flow.
The main indication for invasive treatment is severe pain that is resistant to pharmacological therapy with the threat of obstruction and infection of the organ.
If the cause of kidney pyeloectasia during pregnancy is a tumor, then consultation with an oncologist and prompt surgical treatment are necessary. During the second trimester, surgical procedures cause contraction of the uterus and provoke spontaneous abortion. Hypotension and bleeding during surgery lead to fetal hypoxia with detrimental effects on the child's brain. In some cases, surgery may be delayed until the baby's lungs mature. This usually occurs in the 28th week of pregnancy or even after childbirth.
Peculiarities
Pyelocalicectasia is not an independent disease. It occurs as the next stage in the development of pyeloectasia, characterized by an increase in only the renal pelvis.
Most often, the disease affects both kidneys at the same time, and the pathological process is complicated by dilation of the ureter. Much less often, pathology is determined only on one side.
It is possible to develop physiological pyelocalicoectasia, when a short-term increase in the lumen of the renal pelvis is observed. This happens with frequent attempts to hold back urination, when a person takes diuretics, and also when drinking a large volume of liquid. This condition is regarded as a compensatory reaction of the body to the action of unfavorable factors. In this case, the person does not need drug therapy, the condition gradually normalizes on its own.
Preventive actions
The main way to prevent pyelectasis is to plan the birth of a child and eliminate all risk factors. The expectant mother should lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, and maintain fluid intake. While carrying a child, you need to give up bad habits and not abuse salty foods.
Recommendations:
- Avoid alcohol and smoking;
- Avoid salty and spicy foods;
- Avoid consuming large amounts of phosphorus in your diet (protein foods contain it);
- Regular exercise and yoga are very beneficial for hydronephrosis. Remember to consult a professional before starting the exercises;
- Contact your doctor if you experience symptoms and signs of renal colic.
Elimination of disease
This process of expansion of the pelvis of the organ often becomes a source of problems during childbirth. Timely treatment of the disease will prevent complications. In most cases, the prognosis is positive.
Therapy for pyeloectasia when a woman is carrying a child depends entirely on the provoking factor. If the pathology is caused by pregnancy, the doctor does not prescribe treatment, monitoring the condition of the expectant mother and fetus. ICD requires surgery and a strict diet. Milk, potatoes, spinach and offal are excluded from the daily menu. Surgical intervention may not be necessary if it is possible to remove the salt compounds using special preparations.