Causes
A genetic change in the gene responsible for the process of collagen biosynthesis is the main prerequisite for the development of Alport syndrome.
A child acquires such a hereditary mutation from his parents: a daughter from her father, and from her mother, both a boy and a girl. A person may have a damaged gene, and the disease does not always develop, but will be inherited by children. One of the three genes responsible for the process of biological synthesis of type IV collagen undergoes a change. It is part of the structure of the basement membranes located in the kidneys, organs of vision and hearing. Basal membranes are special formations - thin boundaries by which some tissues of the human body are separated from each other, support and strengthen their structure. If their composition and integrity are violated, dangerous phenomena arise:
- incomplete and poor-quality filtration of toxic and other substances coming from the blood occurs;
- the composition of urine changes, in which there is a significant increase in red blood cells (hematuria or traces of blood in the urine) and unfiltered protein (proteinuria).
Such changes lead to the development of severe renal failure, in some cases to the complete cessation of organ functions and death.
Alport syndrome and its development can be triggered by several factors:
- severe illnesses caused by bacteria or viruses;
- effects on the body of vaccine components;
- excessive physical stress.
Medical statistics show that every fifth child with a confirmed diagnosis of hereditary nephritis appears in parents who do not have pathologies associated with kidney function. The cause of Alport syndrome in such cases is associated with spontaneous gene mutations.
Symptoms
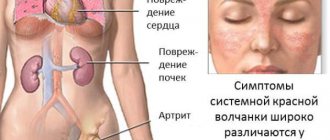
Hereditary nephritis has pronounced clinical symptoms. If we talk about the initial stages of the pathological process, it manifests itself as follows:
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- deterioration of visual function;
- impaired hearing ability, up to the development of deafness.
Clinical symptoms will increase as the disease progresses. Over time, signs of intoxication appear, and anemia develops. The general condition and age of the patient affects the severity of the clinical picture.
Patients do not sleep well at night, so they walk around drowsy during the day
Other characteristic symptoms of the disease are:
- severe headaches;
- muscle pain;
- even slight physical activity quickly tires the patient;
- dizziness;
- arterial hypertension, which is replaced by a sharp drop in pressure;
- dyspnea;
- shallow breathing;
- tinnitus that becomes permanent.
If we are talking about the chronic form of hereditary nephritis, the clinical picture here will be slightly different, namely:
- weakness and general malaise;
- frequent urge to urinate, blood;
- urination does not bring relief;
- nausea and vomiting;
- deterioration of appetite and, as a result, weight loss;
- hemorrhage;
- itchy skin;
- convulsions;
- pain in the chest;
- in severe cases, confusion and attacks of unconsciousness appear.
Symptoms of the disease are discovered purely by chance, during a preventive urine test for a viral disease or upon admission to kindergarten. At first, the general condition of the child is not changed, while the urinary syndrome is persistent and persistent.
Infectious processes of the respiratory tract, active physical activity, preventive vaccinations - all this can provoke increased hematuria. As for the presence of protein in the urine, at first proteinuria is unstable, and then gradually increases and becomes persistent.
Symptoms of intoxication also increase; hearing loss is especially observed in boys; children get tired quickly and suffer from severe headaches. Children are significantly behind in physical development.
Therapy methods
Treatment of Alport syndrome includes diet, medication, and timely sanitation of foci of infection.
Vaccinations for children are contraindicated; vaccination is possible only if there are strict indications.
At the moment, there are no pharmacological drugs that would affect the genetic defect.
Metabolic drugs are widely used to increase... These include cocarboxylase, vitamins A, E, B6. When protein appears in the urine, nephroprotectors (drugs that protect the kidneys) are prescribed.
- Irritable bladder syndrome in women, men and children
These include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril, pyrindopril) and angiotensin receptor blockers (losartan).
The above drugs belong to the group of antihypertensive drugs.
Even with low blood pressure in children, minimal doses of medications should be taken to reduce the rate of progression of kidney failure.
Physical activity
A child with Alport syndrome should refrain from strenuous physical activity. However, he needs daily walking for at least 40 minutes.
This will improve microcirculation in the kidneys and will also promote normal development.
Dietary requirements
Should be excluded from the diet:
- salty, fatty and smoked foods;
- junk food and spicy food;
- Products with a high content of artificial colors.
It is necessary to monitor the amount of protein entering the body; if kidney failure develops, limit liquid to one liter, salt to one gram per day.
A sufficient amount of calories, vitamins, macro- and microelements must be supplied with food.
Surgical intervention
In cases where the kidneys cannot cope with the release of toxic metabolic products, a kidney transplant is performed.
- How to treat bilateral chronic pyelonephritis
Hemodialysis is performed using the kidney apparatus. The essence of the procedure is to cleanse the patient’s blood of toxic substances, which is vital.
The patient also undergoes a kidney transplant, after which immunosuppressive therapy is prescribed to prevent transplant rejection.
ethnoscience
Used in conjunction with traditional methods after consultation with your doctor. The properties of medicinal plants are used to help alleviate the clinical manifestations of the disease.
To improve microcirculation in the kidneys, you can use non-concentrated and.
Juniper fruits and birch buds will help increase the glomerular filtration rate.
How to treat pathology?
To date, the disease cannot be completely cured.
A set of therapeutic measures helps stop the progression of the disease . For this purpose, medications and special nutrition are used, and there is no specific medicine against this disease.
To slow down the development of renal failure, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ATP) inhibitors and angiotensin blockers are prescribed. This reduces proteinuria (protein levels in the urine) and normalizes kidney function.
Additional medications may include Erythropoietin in the presence of anemia and drugs to normalize blood pressure. Peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis are possible. In severe cases, the patient needs a kidney transplant, regardless of age.
As an auxiliary therapy for children, it is important to follow a number of rules:
- reduce physical activity (up to and including exemption from physical education lessons);
- take vitamins A, B6 and E to normalize metabolic processes in the body;
- take walks in the fresh air;
- engage in herbal medicine to improve kidney function and cleanse the blood (use decoctions and infusions of yarrow, chamomile, nettle and chokeberry juice).
Separately, it is worth considering nutrition , which directly affects the kidneys and can both help and harm. The patient is prohibited from eating fatty, fried, salty, smoked and spicy foods. These types of foods overload the kidneys and can cause the disease to progress.
You should also not drink alcohol, with the exception of red wine in small quantities and only as directed by a doctor. Any products containing dyes (colored soda, jelly products with dye, etc.) are hazardous to health.
All food should be nutritious and contain as many vitamins as possible . At the same time, food should be well digested and not overload the digestive system, which affects kidney function. Lean meats (veal, lean beef), fish, seafood, poultry, as well as various vegetables and fruits are suitable for this.
Diagnostics
Several studies, collection and analysis of anamnesis help to make a diagnosis of hereditary nephritis. It is the genetic nature of the disease that requires studying the health characteristics of the baby’s parents and grandparents. An assessment of indicators is necessary; the presence of three of them allows one to diagnose the syndrome:
- signs of hematuria;
- kidney pathologies, renal failure, including death;
- congenital diseases of the organs of vision and hearing;
- progressive deterioration in the quality of visual and auditory perception in the child;
- the presence of changes in the structure of the basement membrane (performed during a biopsy of renal tissue).
To assess the patient’s condition and the development of the pathological process, the doctor prescribes the following studies:
- analysis for Alport syndrome (involves studying blood and urine);
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys and adrenal glands;
- X-ray examination of the organ;
- tissue biopsy;
- DNA test to determine the carrier of a mutant gene.
The patient requires additional visits to highly specialized doctors - nephrologist, geneticist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist.
- What is doubling of the left kidney?
Methods for recognizing hereditary nephritis
Establishing a diagnosis of hereditary nephritis is a complex and multifaceted process. The specialist prescribes a series of tests that should not only confirm the presence of the disease, but also determine how much kidney function is reduced:
- a thorough examination reveals elevated blood pressure, pale or yellowish skin tone;
- The ENT doctor will draw a conclusion about the degree of hearing loss and its nature;
- the ophthalmologist will identify signs of lens clouding, retinal defects and the degree of decrease in visual acuity;
- A complete blood count can reveal signs of infection in the kidney - a high level of white blood cells and an increased red blood cell sedimentation rate (ESR);
- A biochemical blood test is used to study the work of the kidneys to cleanse the body's blood of toxins. High levels of compounds such as urea and creatinine indicate renal failure and death of the vascular glomeruli;
- A general urine test reveals the characteristic features of hereditary nephritis - a high content of red blood cells (hematuria) and protein (proteinuria);
Hematuria is the main manifestation of chronic nephritis - Cumulative tests, in which urine is collected for testing over several hours (up to 24 hours), allow a more accurate assessment of the rate at which the body loses red blood cells and protein. Such research methods include analysis according to Nechiporenko, Amburge and Addis-Kakovsky;
- analysis of fluctuations in the density of urine collected in eight doses per day indirectly confirms the presence of chronic renal failure. In this case, the low density of individual portions of urine and its slight fluctuations during the day are important;
- culture of urine on a nutrient medium is carried out to detect bacteria that often penetrate the kidney affected by hereditary nephritis;
Urine culture allows bacteria to be isolated and examined under a microscope. - ultrasound makes it possible to see a picture of the structure of the kidney and evaluate its size;
- excretory urography is used to create a series of x-rays after intravenous administration of a special drug. Analysis of these images allows the specialist to draw a conclusion about the ability of the kidney to cleanse the body of waste and toxins;
Excretory urography is performed using an X-ray contrast agent. - magnetic resonance (computer) tomography provides valuable information about the internal structure of the kidney, its vessels, urinary tract and neighboring organs;
- audiometry is a specific examination that studies the degree to which the human ear perceives sound vibrations of various tones. The resulting graph confirms the presence of deafness;
Audiometry records the perception of sounds of different pitches - analysis of DNA isolated from blood makes it possible to clarify which chromosome the defective gene is located on.
Differential diagnosis of hereditary nephritis is carried out with the following pathologies:
- infectious inflammation of the kidney - pyelonephritis;
- inflammation of the renal glomeruli against the background of aggressive behavior of the immune system - glomerulonephritis;
- urolithiasis;
- benign and malignant kidney tumors;
- expansion of the cups and pelvis of the kidneys - hydronephrosis.
Hydronephrosis occurs due to obstruction of urine flow from the kidney
Causes and development factors
The DNA molecule is a long chain of chemical compounds that underlies any gene. At the dawn of life, a person inherits many different genes. They are sorted into forty-six chromosomes. Two of them determine gender - X and Y. The cause of Alport syndrome is an incorrect gene, which contains information about the structure of type 4 collagen. There are three copies of this gene, located on the second and X chromosomes.
The Mystery of DNA - video
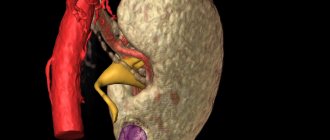
The incorrect structure of the gene leads to the fact that the collagen protein also has a defective configuration. First of all, this leads to changes in the vascular glomeruli. The connective tissue of the renal filter becomes inflamed over time, and hereditary nephritis is formed. With age, the glomeruli die and are replaced by scar connective tissue. Thus, the work of the kidneys in purifying the blood from harmful substances and other toxic metabolic products is significantly affected, and chronic renal failure is formed. The inflamed kidney filter begins to allow red blood cells to pass through, which give the urine a reddish tint (hematuria). Another sign of hereditary nephritis is high blood pressure. This phenomenon is caused by an excess of a special substance - angiotensin, which is released into the blood by the kidneys.
In hereditary nephritis, the kidney filter is damaged
Abnormal type 4 collagen causes the hearing organ to suffer. First of all, the transmission of sound through the labyrinth system of the inner ear is disrupted. Over time, connective tissue replaces the nerve endings responsible for producing the electrical signal. Ultimately, these changes lead to deafness.
The lens, surrounded by such collagen, often becomes cloudy with the formation of cataracts. Light through such a modified lens cannot penetrate further and reach the pigment membrane of the eye (retina). The image on it is unclear and blurry. In addition, due to a hereditary disease, the retina itself suffers, which ceases to perceive light. Because of this, black spots appear in the field of vision, which correspond to the affected areas.
The lens is the main component of the optical system of the eye
The role of connective tissue in the body
Connective tissue is perhaps the most common building material in the body. There are many varieties of this tissue: the substance of bones, tendons, muscle sheaths and individual fibers. Many components of various organs are built from it:
- valves and chords of the heart;
- septa between the alveoli in the lungs;
- the basis of the skin is the dermis;
- membranes of the spinal cord and brain;
- kidney filter system;
- shell of the eye lens;
- structures of the labyrinth of the inner ear.
Connective tissue consists of cells and intercellular substance. The latter is formed due to two types of proteins - collagen and elastin. Their long, twisted fibers are strong enough to create frameworks for organs and protect them from a variety of external influences. Collagen fibers are divided into several types. Each is found in strictly defined areas of the body.
Collagen is made up of twisted fibers
Type 4 collagen is involved in the creation of the most important structure of the kidneys - the vascular glomerulus. It is here that the blood is purified through a fine filter. Connective tissue contains microscopic holes that are designed to retain cells in the bloodstream - red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, as well as large proteins. There are a lot of similar vascular glomeruli in the kidney.
There are extremely many collagen fibers in another fine structure - the organ of hearing and balance. The elastic eardrum perceives sound vibrations in the air and transmits them through the auditory ossicle system to the inner ear. It consists of a bony and membranous labyrinth. The movement of a specific fluid inside the labyrinth - endolymph - encourages nerve cells to send an electrical signal to the brain. This is what we perceive as sound.
Type 4 collagen is present in the hearing organ
Type 4 collagen is part of the eyeball. Connective tissue on all sides in the form of a capsule surrounds the natural lens of the eye - the crystalline lens. It is the central structure with the help of which the image of objects is formed on the retina. This is where the path of the electrical signal entering the brain begins. Thanks to these facts, a person has the opportunity to see the world around him.
Alport syndrome is a hereditary disease in which improper functioning of genes leads to changes in the kidneys, deafness and vision problems. According to modern data, the pathology occurs in seventeen cases per hundred thousand newborns. The disease was first described in 1927 by Arthur Alport.
Synonym of the disease: hereditary nephritis with deafness.
Necessary treatment
Treatment of Alport syndrome consists of normalizing kidney function, since there are no special, specific medications to get rid of all the symptoms of the pathology.
The doctor prescribes treatment that reduces the risk of progression of the syndrome:
- drugs that correct the manifestations of renal failure, the level of protein in the urine;
- diuretics;
- means that normalize metabolism in the body, restoring the balance of minerals and vitamins;
- drugs to prevent anemia.
In case of severe renal failure, the use of hemodialysis is indicated. In severe cases of hereditary nephritis, it is necessary to replace the affected organ with a donor one. Kidney transplantation can be performed on patients over 15 years of age.
Features of a child
Hereditary nephritis in children shows the first signs before the age of three, although most often the symptoms are mild and the disease can only be detected by chance. The main symptom is hematuria, a common occurrence in the disease. It intensifies with infectious diseases, with physical exertion or after vaccinations. Proteins are found in the child’s urine, and leukocytes periodically appear. With the further development of the disease, the following signs appear:
- symptoms of body intoxication (pallor, fatigue, headaches);
- developing muscle weakness;
- anemia;
- body weight deficiency;
- hearing loss (usually from 6 to 10 years);
- myopia;
- delayed physical development:
Diagnostic measures
First of all, the doctor studies the medical history of the parents, since the disease is transmitted from parents to children in 4 cases out of 5
. He pays attention to the following details in the child and parents:
- presence of hematuria;
- a kidney biopsy showed abnormalities in the structure of the basement membrane;
- congenital problems with vision and hearing;
- there were cases of renal failure with a fatal outcome in the family;
- There is a constant decrease in hearing and vision in the child.
It is enough to have 3 signs
to almost certainly make a diagnosis. Further additional studies will be prescribed in the form of:
- kidney,
- biopsy of collagen structures,
- radiography,
- urine and blood,
- consultations with a geneticist and nephrologist.
General information
Alport's disease was first described in 1927 by British scientist Arthur Alport. The syndrome is rare. Statistics show that in 3 children out of 100 it is the cause of borderline renal failure in children, and less often in adults. This syndrome is the most common type of nephritis. There are different types of heredity, but the most common is the X-linked dominant form. It causes severe kidney failure in male children. It begins to appear in the first years of life, problems with hearing and vision develop later. Loss of vision and hearing precedes the development of severe renal impairment and occurs in late childhood or adolescence.
Diet food
When diagnosing hereditary nephritis, great importance is given to switching to a special diet. The Alport syndrome diet involves the complete exclusion of “wrong” foods:
- containing preservatives and unnatural food additives;
- spicy and salty dishes;
- fatty ingredients;
- high in protein;
- any alcoholic drinks.
The diet uses products individually recommended by a doctor. Their list is formed taking into account the functional abilities of the kidneys of each patient. It is proposed to introduce into the diet components that provide the patient with the necessary energy, vitamins and microelements, as well as those with sufficient calorie content - veal, lean beef, poultry, fish, fruits and vegetables.
Clinical picture
Manifestations of Alport syndrome differ in the severity of manifestations . , progressive nephropathy comes to the fore .
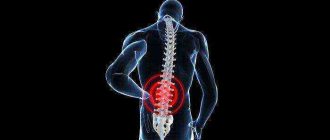
The patient may complain of prolonged pressing pain in the lower back. The pain is constant and can radiate to the groin area or leg. The use of painkillers reduces the intensity of pain, but does not completely remove it. Episodes of pain may worsen after hypothermia or significant physical exertion.
- Swelling of the face in the morning appears as the disease progresses. The face becomes pasty, bags appear around the eyes. In the afternoon, swelling decreases, sometimes disappears completely.
- Increased amount of urine . Often, patients with nephropathy note that the amount of urine excreted is even greater than the amount of fluid drunk.
- Visual impairment . Occurs in half of patients with Alport syndrome. It can manifest itself as cataracts at a young age, dislocation of the lens of the eye.
- Hearing impairment . In 25-30% of cases, sensory deafness occurs, which tends to progress. More often the process is bilateral and symmetrical. Only in rare cases does it lead to complete hearing loss.
Treatment
Alport syndrome is an incurable disease. The following expert recommendations will help slow down the development of kidney failure:
- Rational and fortified diet,
- Optimal physical activity
- Frequent and long walks in the fresh air,
- Sanitation of foci of chronic infection,
- Prevention of infectious diseases,
- Ban on routine vaccinations for sick children
- A herbal collection of nettle, yarrow and chokeberry is indicated for sick children with hematuria,
- Vitamin therapy and biostimulants to improve metabolism.
Proper nutrition consists of eating easily digestible foods with sufficient amounts of essential nutrients. From the diet of patients, salted and smoked foods, spicy and hot dishes, alcohol, and products with artificial colors, stabilizers, and flavors should be excluded. In case of impaired renal function, it is necessary to limit the intake of phosphorus and calcium. Such recommendations should be followed by patients throughout their lives.
Drug symptomatic therapy:
- To eliminate hypertension, ACE inhibitors are prescribed - Captopril, Lisinopril and angiotensin receptor blockers - Lorista, Vasotens.
- Pyelonephritis develops as a result of infection. In this case, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory medications are used.
- To correct disturbances in water-electrolyte metabolism, Furosemide, Veroshpiron, intravenous saline, glucose, and calcium gluconate are prescribed.
- Anabolic hormones and iron-containing drugs are indicated to accelerate the formation of red blood cells.
- Immunomodulatory therapy - Levamisole.
- Antihistamines - Zirtec, Cetrin, Suprastin.
- A complex of vitamins and medications that improve metabolism.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has a positive effect on the severity of hematuria and kidney function. When renal failure progresses to the terminal stage, hemodialysis and a kidney transplant are required. Surgery is performed after the patient reaches the age of fifteen. There is no recurrence of the disease in the graft. In some cases, nephritis may develop.
Gene therapy for the syndrome is currently being actively developed. Its main goal is to prevent and slow down the deterioration of kidney function. This promising treatment option is now being introduced into medical practice by Western medical laboratories.
Causes and mechanism of development of Alport syndrome
Alport syndrome is caused by mutations in the COL4A4, COL4A3, COL4A5 genes, which are responsible for collagen biosynthesis. Mutations in these genes disrupt the normal synthesis of type IV collagen, which is a very important structural component of the basement membranes in the kidneys, inner ear and eyes. Basement membranes are thin film-like structures that support tissues and separate them from each other. When type IV collagen synthesis is impaired, the glomerular basement membranes in the kidneys are unable to properly filter toxic products from the blood, allowing proteins (proteinuria) and red blood cells (hematuria) to pass into the urine. Abnormalities in the synthesis of type IV collagen lead to renal failure and kidney failure, which is the main cause of death in Alport syndrome.
Video: What you need to know about hereditary diseases
Useful information about hereditary diseases, which will help avoid the development of many diseases in the unborn child. If you take these tips into account, the likelihood of having a child with hereditary disorders will be significantly reduced.
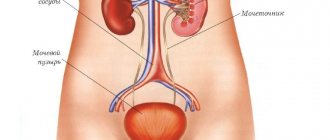
The kidney is a paired organ that performs the function of urine formation, regulation of blood pressure, mineral metabolism and hematopoiesis.
The formation of kidneys in the fetus occurs already at 4-5 weeks of pregnancy.
If there is a defect in the gene responsible for the synthesis of type 4 collagen, the vascular system of the kidneys, the lens capsule, and the organ of Corti (located in the area of the inner ear) suffer.
This hereditary disease is called Alport syndrome.
Classification
There are three types of hereditary nephritis
- Option I - clinically manifested by nephritis with hematuria, hearing loss and eye damage. The course of nephritis is progressive with the development of chronic renal failure. The type of inheritance is dominant, linked to the X chromosome. Morphologically, a violation of the structure of the basement membrane, its thinning and splitting is revealed.
- Option II - clinically manifested by nephritis with hematuria without hearing loss. The course of nephritis is progressive with the development of chronic renal failure. The type of inheritance is dominant, linked to the X chromosome. Morphologically, thinning of the basement membrane of the glomerular capillaries (especially laminadensa) is revealed.
- Option III - benign familial hematuria. The course is favorable, chronic renal failure does not develop. The type of inheritance is autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. With an autosomal recessive type of inheritance, women have a more severe course of the disease.
[9], [10], [11], [12], [13]
Kinds
Experts distinguish three types of alport syndrome:
- pronounced symptoms and rapid progression of acute renal failure;
- the disease progresses rapidly, but there is no visual or hearing impairment;
- benign course of the disease, in which there are no clinical symptoms and progression. In this development scenario, the prognosis is favorable. If a woman has an autosomal recessive type of inheritance, then a more severe course of the disease is observed.
Pathogenesis
Pathogenetic links of the syndrome:
- violation of collagen biosynthesis or its deficiency,
- destruction of the basement membrane of the kidneys, inner ear and ocular apparatus,
- sprouting of collagen fibers types V and VI,
- damage to the renal glomeruli,
- immunonegative glomerulitis,
- glomerular hyalinosis, tubular atrophy and renal stromal fibrosis,
- glomerulosclerosis,
- accumulation of lipids and lipophages in the renal tissue,
- decrease in the blood level of Ig A, increase in IgM and G,
- decreased activity of T- and B-lymphocytes,
- impaired renal filtration function,
- dysfunction of the organ of vision and hearing,
- accumulation of toxins and metabolic products in the blood,
- proteinuria,
- hematuria,
- development of acute renal failure,
- death.
The disease develops gradually with renal symptoms. In the early stages of pathology, the kidneys work fully, and there are traces of protein, leukocytes and blood in the urine. Pollakiuria and nocturia are accompanied by hypertension and other signs of urinary syndrome. In patients, the calyces and pelvis of the kidneys dilate, and aminoaciduria occurs. After some time, hearing loss of neurogenic origin occurs.
Men are most susceptible to developing kidney dysfunction. If left untreated, death occurs between 15 and 30 years of age. Women usually suffer from a latent form of pathology with signs of hematuria syndrome and slight hearing loss.
Classification of the disease
There are 3 main forms
diseases:
- Dominant type of inheritance associated with the X chromosome. Thinning and splitting of the basement membrane in the kidneys, consisting of collagen, develops. Symptoms: hearing loss, decreased vision, nephritis and hematuria. Constantly evolving.
- Autosomal recessive type of inheritance. The clinical picture is similar to the previous type, but without hearing impairment.
- Autosomal dominant type of inheritance. Called benign familial hematuria. Renal failure does not develop, the course of the disease is favorable.
Aneurysm - aorta, brain and cerebral vessels, symptoms, treatment with surgery
Published: 11/08/2017
Aneurysm is an enlargement of an artery caused by weakness in the arterial wall or damage to it. Often the disease is asymptomatic, but rupture of an aneurysm can lead to complications and even death. What is an aneurysm? An aneurysm weakens the walls of the artery, which creates a bulge, or rupture, in the artery. The bulge can take two main forms: Fusiform aneurysms of the arches of all sides of the blood vessel. Saccular aneurysms
no comments yet
Diagnostics
Hereditary nephritis is rarely diagnosed after birth, usually the first signs appear only by 3–5 years of age.
A comprehensive examination of children with Alport syndrome includes collecting a life history, hereditary and clinical history, and studying complaints. Given the hereditary nature of the disease, cases of renal failure in close relatives are important. To clarify the diagnosis, a number of studies are carried out:
- general clinical laboratory tests, including Alport syndrome;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and renal structures, organs of the genitourinary system;
- X-ray contrast research methods (excretory urography);
- DNA test;
- kidney biopsy.
Diagnosis requires additional consultation with a nephrologist, urologist, geneticist, ophthalmologist, cardiologist, and otolaryngologist. The disease is differentiated from other genomic mutations, in particular, from the “cry of the cat” syndrome - a disorder of the structure of chromosome 5, when typical signs are expressed in hearing and vision impairment at an early age.
Sources used:
- https://prosindrom.ru/genetic/sindrom-alporta.html
- https://shango.ru/sindrom-alporta-u-detei-simptomy-sindrom-alporta—bolezni-organov/
- https://lechenie-simptomy.ru/sindrom-alporta-u-detey
- https://medbe.ru/news/meditsina/sindrom-alporta-prichiny-i-simptomy-diagnostika-i-lechenie-sindroma-alporta/
- https://sindrom.info/alporta/
- https://ilive.com.ua/health/nasledstvennyy-nefrit-sindrom-alporta-u-detey_107170i15937.html
- https://m.baby.ru/wiki/sindrom-al-porta-u-detej-osobennosti-razvitia-simptomy-metody-diagnostiki-i-lecenie/