Nephridiya
(diminutive from ancient Greek nephros - “kidney”) - excretory organs in invertebrates that perform the functions of osmoregulation, extraction and removal of harmful metabolic products from the body. Sometimes they can also serve to remove reproductive products.
Nephridia are divided into two types: protonephridia and metanephridia. The first are more primitive and are characteristic of flatworms, rotifers, gastrociliates, nemerteans and some types of polychaete worms. Protonephridia look like branched tubes ( nephridial tubules)
), which are closed at the inner ends by terminal cells (
solenocytes
) and excretory pores (
nephropores
) opening outwards. Losing solenocytes and communicating with the secondary body cavity, they turn into metanephridia, found mainly in annelids. In some annelids, nephridia fuse with mesodermal ciliated genital funnels - coelomoducts, forming organs of mixed origin - the so-called nephromyxia. The number of nephridia in one individual varies from one to several hundred.
What is chronic nephritis
Chronic nephritis is a long-term inflammatory process in the renal tissue or glomeruli, which is characterized by disruption of normal vascular permeability and a decrease in the body's resistance. It is believed that there are population groups that are particularly vulnerable to the development of pathology:
- children under one year old;
- teenagers during puberty;
- old men;
- pregnant women;
- people after radiation therapy for cancer.
According to statistical studies, chronic nephritis occurs quite often after a bacterial infection. Every twentieth patient in the world encounters it between the ages of 20 and 70 years.
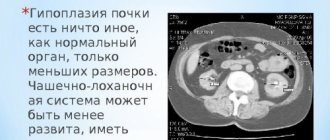
Kidney with nephritis increases in size
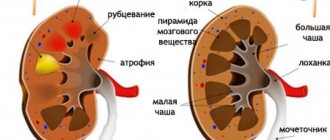
Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate through the blood or lymphatic fluid into soft tissues, where they further multiply and spread. During their life, bacteria release toxins that damage blood vessels. This leads to the release of fluid from them and the formation of soft tissue edema with a change in the structure of the organ. The kidney increases in size, its capsule becomes stretched, which leads to the development of unpleasant sensations. When the pathological process declines, the changed areas of the organ are replaced by connective tissue. It cannot perform the function of filtering the blood and purifying it from harmful impurities, which causes the development of kidney failure. It is not uncommon for one organ to shrink and be rejected by the human body.
Video: doctor talks about pathology
Classification of the disease
Types of pathology according to the nature of tissue damage:
- glazed nephritis (glomerulonephritis) - only the glomeruli are involved in the inflammatory process, protein molecules are deposited in them, disrupting the normal outflow of urine and damaging the walls of blood vessels;
- pyelonephritis - destructive changes in the underlying tissue of the kidney;
- mixed - a combination of two types of lesions.
Classification based on the cause of the disease:
- nonspecific (caused by typical microflora that lives in the body: staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli);
- specific (occurs against the background of exposure to pathogenic microbes from the outside: mycoplasma, chlamydia, gonococci).
Treatment
Treatment of kidney nephrosis is a set of measures aimed at stabilizing the patient’s condition.
Basic goals of therapy:
- Elimination of the root cause of nephrosis.
- Elimination of edema.
- Normalization of protein metabolism in the body.
Lipoid nephrosis, which develops against the background of a bacterial infection, requires the use of antimicrobial agents (macrolides, cephalosporins, penicillins). The dose is selected individually depending on the severity of the pathological process.
Blood pressure correction is carried out with the help of antihypertensive drugs (Enalapril, Valsartan, Hydrochlorothiazide). Edema is eliminated with the help of diuretics - medications that remove excess fluid from the human body (Furosemide, Hypothiazide).
Treatment of necrotic nephrosis involves the use of detoxification therapy aimed at preventing the development of shock.
Diet remains an important aspect of the full treatment of patients with nephrosis. The patient limits fluid intake (up to 1 l), salt (up to 5 g per day). Progression of renal failure is an indication to reduce the daily amount of protein food. Therapy in each case is individual in order to accelerate the stabilization of the patient's condition.
Why does chronic nephritis develop in patients?
The main reason for the formation of the inflammatory process is the penetration of bacteria into the body. Most often, the causative agents of this pathology are staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, amoebas, Proteus, mycoplasma and ureaplasma. There are also specific factors that increase sensitivity to harmful microorganisms:
- immune deficiencies (congenital and acquired);
- local and systemic infectious diseases (chicken pox, diphtheria, typhoid fever, salmonellosis);
- circulatory pathologies (thrombosis, embolism);
- developmental abnormalities of the urinary tract;
- malignant tumors with metastases;
- inflammatory processes in neighboring organs and tissues;
- benign tumors;
- recent surgery or traumatic injuries.
The first signs of the formation of pathology in the body
Chronic nephritis is characterized by a gradual and extremely slow increase in symptoms. Often patients do not pay attention to them, citing overwork. It becomes possible to suspect the presence of the disease only with extremely intense manifestations. The symptomatic picture of chronic nephritis includes:
- Changes in urine characteristics. It becomes darker and cloudier, taking on a reddish hue due to the accumulation of protein, toxins and inflammatory cells. Some patients note the appearance of sand after a heavy intake of fatty, salty and fried foods.
- Pain when urinating. Unpleasant sensations accompany the process of urine excretion (especially in the evening). The patient is bothered by false urges, during which 1–2 drops of urine are released.
- Nagging pain in the lumbar region. They intensify with neuropsychic stress, physical activity, lack of sleep or the body's stress response. These sensations are directly related to the enlargement of the kidney due to inflammatory edema.
- The occurrence of general intoxication. The victims' temperature rises to 37, their appetite disappears, their performance decreases, and headaches appear. This can occur when bacterial toxins enter the central nervous system. Many patients also suffer from periodic increases in blood pressure to 180/110 mmHg or more.
Methods for making and confirming diagnosis
After the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a urologist or nephrologist. The doctor conducts an examination and prescribes additional tests, on the basis of which a specific course of treatment is selected for each patient. People with chronic nephritis have typical external features that immediately suggest kidney problems:
- dull gray complexion;
- dark circles under the eyes;
- swelling of the upper half of the body and head;
- pastosity (slight swelling) of the lumbar region.
Facial swelling is associated with fluid accumulation in soft tissues
Next, the doctor needs to collect an anamnesis: the time of onset of the first symptoms, the characteristics of the pain and its nature, the presence of other acute or chronic diseases. After communicating with the patient, the doctor prescribes a range of examinations to clarify the nature of the pathological process. These include:
- general urinalysis - typically the detection of protein, bloody impurities, sand, salts and leukocytes, which indicates active inflammation;
- microscopic examination of urine allows you to identify a bacterial pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs;
- Ultrasound diagnostics shows the structure of the urinary system, the presence of foreign bodies and tumor formations.
Therapy to cure kidney disease
Acute nephritis can proceed unnoticed at first, disguise itself as another disease, and only at its peak development can it manifest its symptoms. Treatment of nephritis can take from one month to six months, and chronic nephritis can bother a person for years. With nephritis, the patient should adhere to strict bed rest and diet. The main forbidden foods are salt and liquid. The liquid must initially be limited to 300 ml, followed by an increase to 600 ml (700-800 ml) per day. Drug treatment is also prescribed: antibiotics, antihistamines, antibacterial medications and diuretics (diuretics).
Various Treatment Options for Chronic Nephritis
The duration of therapy for kidney pathology largely depends on the time of its detection. If the course of the disease is favorable, a complete cure is possible in a short time (up to 3–4 months), but if secondary complications occur, the course can last from six months to several years. At the initial stage of the disease, doctors prescribe a gentle regimen for the patient with changes in the usual diet and a decrease in physical activity. At later stages, the use of pharmaceuticals is involved, which can effectively cope with symptoms and remove bacteria. In younger patients, physiotherapeutic procedures are used to restore the functions of the urinary system.
Traditional recipes can be used throughout the entire course of treatment if they are combined with other remedies.
Drug therapy for the disease
Pharmaceutical drugs are actively used both to combat the symptomatic manifestations of the disease and to eliminate its cause. Currently, doctors adhere to the principle of minimal prescription of effective drugs: the patient is not overloaded with medications, adding or removing them as required. Many drugs are available in several forms: suppositories for rectal administration, tablets, capsules, solutions in ampoules for intramuscular or intravenous injection.
All dosages are calculated based on the patient’s weight, age and the presence of chronic pathologies. Self-prescription of medications often leads to the development of spontaneous allergic reactions, which I encountered while working in an ambulance. An 80-year-old woman, on the advice of her neighbor, purchased a drug to combat chronic nephritis, but after taking the first pill, she lost her breath and the woman almost died from suffocation. The main diagnosis was Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock - a reaction to a foreign substance. Only thanks to the actions of doctors was it possible to avoid death.
What drugs are used to treat the disease:
- Antibiotics destroy pathogenic microorganisms that are the source of infection. They prevent further proliferation of bacteria, which leads to their independent removal from the patient’s body. The drugs in this group include: Streptomycin, Rifampicin, Benemicin, Levorin, Nystatin, Amoxiclav, Cephalexin, Cefazolin, Ceftazidime, Tienam, Meropenem, Metacycline hydrochloride, Kanamycin, Amikacin, Vibramycin, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reduce the severity of swelling and relieve pain. For this purpose, doctors prescribe Nimesulide, Ketotifen, Aspirin, Ketorol, Diclofenac, Ketorolac, Tamoxifen, Ibuprofen, Piroxicam, Metindol, Nise, Naproxen, Phenylbutazone, Ponstan, Ortofen, Erazon, Brufen.
- Drugs to normalize blood pressure are used when it rises above 160/100 mm Hg. They help prevent the formation of a hypertensive crisis and protect target organs (brain, heart, retina) from damage. Most often, Veroshpiron, Furosemide, Enalapril, Quinalapril, Perindopril, Capoten, Captopril, Diltiazem, Valsartan, Diovan, Dichlothiazide, Spironolactone, Hydralazine, Minoxidil are used for this purpose.
- Immunostimulants improve the functioning of the body's defense systems, forcing it to fight infection. These include Timalin, Timogen, Cycloferon, Viferon, Immunal.
Photo gallery: medications for treating the disease
Amoxiclav is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that kills all microbes
Nise relieves swelling and inflammation
Furosemide removes excess fluid from the body
Immun helps increase the body's defenses
Dietary recommendations for patients with chronic nephritis
Diet is an important step in the recovery of patients with lesions of the urinary system. During inflammatory processes, the body actively spends energy to fight harmful microbes, resulting in some depletion of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and mineral and vitamin elements. That is why it is so necessary to improve the nutrition of patients with chronic nephritis.
All patients are advised to adhere to the following principles:
- using only fresh products;
- daily change of dishes;
- food should be baked, boiled or stewed with a minimum amount of oil;
- refusal of harmful foods (fast food, sweets, chips);
- the maximum weight of one serving is 350 grams;
- drinking up to 2 liters of pure still water during the day.
What to add to your diet:
- milk and dairy products (cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, yogurt, kefir);
- lean and meat soups (borscht, cabbage soup, rassolnik, okroshka, gazpacho, mushroom, pea);
- durum pasta;
- vegetables and fruits;
- berries and nuts;
- honey instead of sugar;
- fish, chicken, turkey.
Photo gallery: healthy food
Dairy products are a source of calcium
Vegetables and fruits are rich in fiber
Meat meets the need for animal protein
Traditional medicine as an aid
If you cannot visit a doctor in the near future or purchase a medication at a pharmacy, it is permissible to use natural recipes. They contain much less active ingredients and will not be able to completely cure you of chronic nephritis, but they effectively cope with the symptoms of the disease. At the same time, many patients note low cost and accessibility as additional advantages of this treatment method.
Don't forget that plants and herbs easily cause an allergic reaction. Before using this or that product, it is necessary to conduct a preliminary test: apply a few drops of the solution to your wrist and wait 10–15 minutes. If there is no reaction (itching, burning, blisters or spots, redness), you can continue to use. In other cases, you should take an antihistamine (Tavegil, Claritin) and look for a more suitable method for yourself.
You should not completely abandon the use of traditional drugs. During my practical work, I happened to encounter a woman who, in order to cleanse the body for chronic nephritis, did not take any medications, did not eat regular food, preferring to sit only on liquid purees, juices, decoctions and infusions. This led to the fact that within a few months the patient developed serious disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: she stopped digesting regular solid foods, and her kidneys began to fail. Doctors attributed this to general exhaustion of the body due to lack of nutrients. The victim was hospitalized and fed through a tube, and one of her kidneys had to be removed because it had shriveled. It would have been possible to avoid this complication if the patient had not completely replaced traditional treatment with natural remedies.
The most popular folk recipes for the treatment of chronic nephritis:
- Mix 100 grams of cranberries with the same amount of blueberries (you can use fresh, dried or frozen berries). Place them in a saucepan with 2 liters of water and cook for half an hour, stirring constantly. At the end, add a teaspoon of cloves and honey for taste. Drink 1 glass every 4 hours, while it is better to stay at home for the whole day. Cranberries and blueberries have a pronounced diuretic effect and allow you to remove all toxins from the body. The cleansing procedure should be carried out no more than once every 2 weeks, so as not to provoke dehydration.
- Peel 5-7 large oranges and dry the peels in the microwave or oven. Grind them together with the pulp in a blender, then mix with sugar or honey, adding half a spoon of cinnamon. Add the resulting mixture in small quantities to any drinks (tea, coffee, kefir). Orange in combination with cinnamon and honey has anti-inflammatory effectiveness and reduces the likelihood of secondary complications. You need to be treated in this way for six months.
- Crush 100 grams of onion peel and pour 400 ml of vodka or medical alcohol. Cover the container with a warm scarf and place in a cool, dark place for 3-4 weeks. Every 5 days it is necessary to shake the contents of the bottle to form a uniform suspension. After a month, carefully filter the tincture using gauze or a fine sieve, removing the raw materials. Add 5-10 drops to water and drink in the morning before breakfast. Onion tincture allows you to cope with the main manifestations of the pathological process: lower back pain and general malaise. This method should be used for 1 month.
Photo gallery: basic folk remedies to combat the disease
Cranberry - a berry with an antibacterial effect
Citrus fruits effectively fight inflammation
Onion reduces the symptoms of nephritis
Methods for diagnosing, treating and preventing the disease
Correct diagnosis is a very important part of treatment. The effectiveness of the chosen therapy depends on the diagnosis and identification of the characteristics of the disease. The following methods are used to detect acute nephritis:
- blood test (general);
- blood chemistry;
- urine analysis (general and various types of samples);
- bacterial culture of urine;
- Ultrasound;
- ECG.
The listed methods are mandatory. To identify additional features that can affect the course of treatment, biochemical urine analysis, kidney biopsy, etc. are used.
A very important stage of diagnosis is the collection of anamnesis. Thanks to it, the doctor can determine the presence of a hereditary predisposition to the manifestation of this disease, find out what diseases have been suffered, what properties of the body can become an obstacle to effective treatment, etc. In some cases, you may also need the help of other specialists, for example, a gynecologist, otolaryngologist, etc.
Features of therapy
Acute nephritis is usually treated by a nephrologist or urologist. However, since the disease is often associated with the influence of immune system characteristics, the patient may require the help of an immunologist.
Important! Medical care for acute nephritis is provided only in a hospital setting under the supervision of doctors. A prerequisite for such a diagnosis is bed rest.
Only after the pathological process has weakened is the patient allowed to gradually get out of bed. Another part of the treatment is a diet in which you need to limit the amount of salty and spicy foods.
The main method of treating nephritis is medication. Actions are carried out in several directions. This:
Elimination of the causes of the inflammatory process. If nephritis is of infectious origin, antiviral agents (Acyclovir, Proteflazid) or antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Augmentin) are used. If nephritis occurs as a reaction to a drug, then this drug is immediately discontinued, and in return a drug is prescribed that can quickly remove dangerous substances from the body (Enterosgel, Atoxil).
- Prevention of further development of the disease. For this purpose, the following groups of drugs can be used:
- hormonal (Prednisolone);
- helping to normalize blood circulation (Curantil).
antihistamines (Suprastin);
- diuretics (Furosemide);
painkillers (Voltaren, Ibuprofen);
The choice of medicines depends on the individual characteristics of the patient (each medicine has contraindications that should be taken into account), the severity of the disease and other characteristics. It is very important that the prescribed drugs are combined with each other. Therefore, the choice of medications remains with the doctor.
The patient should closely monitor his health and notify the specialist about any reactions that occur to the drugs. If unpleasant features appear, you should inform your doctor about them, as this may be a signal of intolerance to the drug.
Traditional methods of treatment for acute nephritis are used very rarely, since this disease requires quick and effective treatment, without delay. Most often, folk remedies are used to prevent relapses and strengthen the body after recovery.
Features of the symptomatic picture and treatment of the disease in childhood
The body of a small person is significantly different from the body of an adult. A child's kidneys are smaller, and the urinary system is extremely vulnerable to harmful environmental factors. This explains the more frequent infection during initial contact with bacteria or viruses. In children, the disease occurs with constant periods of exacerbation (reaction to stress, swimming in open water, hypothermia). The disease begins with a rise in temperature to 38–38.5 degrees Celsius, severe pain in the lower back and urination problems. Preschool children become more lethargic and apathetic, refusing to eat and play. Schoolchildren and adolescents experience decreased concentration and attention, decreased performance, and headaches with migraine attacks.
In children under one year of age, with an extremely unfavorable course of the disease, periodic febrile convulsions are observed. They may be the body’s reaction to an insufficient amount of mineral elements or a sharp increase in temperature.
Treatment of chronic nephritis in children is based on the same principles as treatment of the adult population. The dosages of medications change, some of them alternate with more gentle ones. All victims are also prescribed a special diet with a limitation of harmful foods. Pharmaceuticals used to treat pathology in children:
- antibiotics: Flemoxin Solutab, Augmentin, Amoxicillin, Sumamed, Azitrox;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen, Ibuklin, Nurofen;
- detoxification solutions and adsorbents for removing toxic breakdown products of substances: Regidron, Reopoliglyukin, Polysorb, Smecta.
Photo gallery: drug therapy for chronic nephritis in children
Flemoxin Solutab is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used to fight microbes
Regidron normalizes the salt composition of biological fluids
Children's Nurofen contains a lower dosage of the substance
To completely eliminate the symptoms of pathology, physiotherapeutic procedures are also used:
- inductothermy - the use of a high-frequency magnetic field, the effect of which is the generation of heat and improved blood circulation;
- ultrasound - vibration increases the intensity of penetration of the drug into soft tissues;
- electrophoresis - the introduction of pharmaceuticals into the body using electric current;
- UHF therapy - an ultra-high frequency electric field is applied to the patient’s body, which reduces the activity of inflammation.
Photo gallery: physical therapy of the disease
Medicinal electrophoresis stimulates regeneration processes
UHF therapy is performed for almost all children with an inflammatory process
Ultrasound therapy improves drug absorption
Treatment prognosis and probable complications of chronic nephritis
Any renal pathology leads to disruption of the activity of the entire body, since these organs are responsible for the elimination of toxic substances. That is why, if diagnosis and treatment are not timely, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable. The success of recovery is largely influenced by the patient’s age, the characteristics of his lifestyle and behavior, the presence of bad habits and immune deficiency, acute and subacute diseases of other organs. People with a long course of chronic nephritis may become disabled if the disease is complicated by renal failure or the need for constant dialysis - artificial blood purification.
Young patients are several times more likely to recover. Doctors directly associate this with rapid metabolic processes.
A special role in recovery is played by the victim’s compliance with the regimen prescribed by the doctor. It includes a certain diet, giving up bad habits and heavy physical activity, restrictions on work and sports activities. During my practice, I had the opportunity to participate in the treatment of a patient who encountered complications due to violation of the regime. A young man who was a professional weightlifter suffered from acute nephritis at the age of 20. Due to the proximity of the competition, he refused to undergo a full course of antibacterial therapy, and also did not limit physical activity. This led to the transition of the pathological process to the chronic phase. During the next competition, the victim felt a sharp pain in the area of his left kidney, which forced him to resort to calling an ambulance. The man was urgently hospitalized in the intensive care unit, where an operation was performed to remove the stone. The long course of chronic nephritis was complicated by the addition of urolithiasis. After the crushing of the conglomerates, the patient was seen by a doctor for a long time, and had to give up professional sports forever.
Doctors believe that excess stress on the kidneys occurs with certain types of training or vigorous physical activity. In this regard, professional athletes need to reconsider their regimen. What types of exercises are prohibited for chronic nephritis:
- long and high jumps;
- short and long distance running;
- lifting weights (more than 5 kilograms);
- squats and lunges;
- bench press;
- rotation of the hoop.
It is recommended to give up hard forms of sports: hockey, football, basketball, weightlifting and wrestling can lead to a worsening of the pathological process and provoke the development of unpleasant consequences. What complications are most common in patients with chronic nephritis:
- formation of acute renal failure;
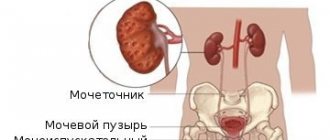
- the formation of conglomerates in various parts of the excretory system - urolithiasis;
- the occurrence of benign tumors and cystic changes;
- shrinkage of the kidney and the need to remove it;
- transition of the inflammatory process to the bladder (cystitis), urethra (urethritis), prostate gland (prostatitis);
- sepsis and septic shock - massive blood infection with microbes and their toxins;
- nephroptosis - prolapse of one or both kidneys;
- polycystic disease;
- purulent pathologies (phlegmons, abscesses, carbuncles);
- hydronephrosis - accumulation of fluid in the pelvis;
- changes in the permeability of the vascular wall, damage to arteries and veins due to the formation of blood clots;
- poisoning of the body with products of its own vital activity;
- convulsive syndrome due to lack of calcium and magnesium.
Photo gallery: complications of chronic nephritis
Cystitis is an inflammatory process in the wall of the bladder
Hydronephrosis is the accumulation of fluid in the renal pelvis
Chronic nephritis creates conditions for the development of cysts
Metanephridia
Metanephridia (Greek Meta - between, after, through, nephridion - diminutive of the Greek Nephros - kidney) - the excretory organs of invertebrates are metamerically located, mainly in annelids. Develop from ectoderm or mesodermal nephroblastoma. Metanephridia are tubular canals that open at one end (ciliated funnel or nephrostomy) into the secondary body cavity (coelom) of the previous segment, and at the other (excretory pore) outward. Through the nephrostome, the coelomic fluid, primary urine, probably enters the lumen of the metanephridia, the movement of which through the metanephridia is ensured by cilia. In the canal, organic substances and salts are reabsorbed from urine, which in the final sections pass through the wall of the canaliculus, which is poorly permeable to water. As a result, hypoosmotic urine is formed, which accumulates in the bladder.