Symptoms of pyelonephritis in infants
The course of the disease in young children has some differences and depends on the age of the child.
So, in infants, the following symptoms will be noted:
- Increase in body temperature to high values, fever will last for two days or more;
- Complete refusal to breastfeed;
- Frequent regurgitation;
- Urine has an unpleasant odor;
- Vomit;
- Intestinal disorders with a predominance of loose stools;
- During urination, the newborn may show anxiety, which is expressed in crying;
- The child may be extremely sleepy
- Urination occurs in small portions;
- The younger the child is, the faster he will lose weight, especially against the background of a high temperature.
During the newborn period, pathogenic bacteria that provoke pyelonephritis circulate in the child’s blood, so the symptoms of the disease are not specific to this inflammation:
- Body temperature can drop to critically low values, or reach high levels, causing a feverish state;
- Yellowing of the skin is often observed;
- The child refuses to suckle at the breast;
- Repeated regurgitation and vomiting are observed;
- In newborn male infants, hyponatremia and hyperkalemia are detected, although the development of these conditions is also possible in girls;
- The child is delayed in development.
General information about the disease
This is an inflammatory disease caused by infectious microorganisms. Infants are very susceptible to developing this pathology.
It is worth noting that pyelonephritis occurs much more often in girls than in boys. It manifests itself at the age of 5-6 months, when the child consumes various complementary foods in addition to breast milk.
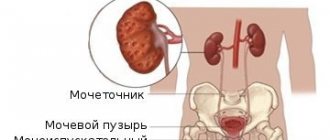
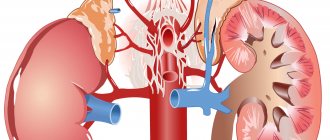
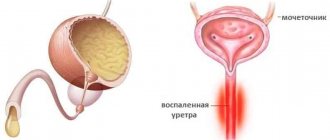
With pyelonephritis, damage occurs to the pelvis, kidney calyces and urethra.
In the presence of constant infectious processes in the baby’s body (tonsillitis, viral diseases, etc.), the risk of developing kidney problems increases significantly.
Doctors note the following trend: the more often a child suffers from infectious diseases, the more often he or she has problems with the urinary system.
Causes of prematurity
All the reasons leading to the birth of premature babies can be combined into several groups. The first group includes socio-biological factors, including too young or old age of parents (under 18 and over 40 years old), bad habits of the pregnant woman, insufficient nutrition and unsatisfactory living conditions, occupational hazards, unfavorable psycho-emotional background, etc. The risk of premature labor and birth The rate of premature babies is higher in women who did not plan pregnancy and neglected medical support for pregnancy.
The second group of reasons is a burdened obstetric-gynecological history and the pathological course of the current pregnancy in the expectant mother. Here, a history of abortion, multiple pregnancy, and gestosis are of greatest importance. hemolytic disease of the fetus. premature placental abruption. The reason for the birth of premature babies can be short (less than 2 years) intervals between births. Often premature babies are born to women who resort to in vitro fertilization. however, this is not due to the very fact of using ART, but rather to the “female” factor that prevents natural fertilization. Gynecological diseases and malformations of the genitals: cervicitis have an unfavorable effect on pregnancy. endometritis. oophoritis. fibroma. endometriosis. bicornuate saddle uterus. uterine hypoplasia, etc.
The third group of reasons that disrupt the normal maturation of the fetus and cause an increased likelihood of having premature babies includes various extragenital diseases of the mother: diabetes mellitus. hypertonic disease. heart defects. pyelonephritis. rheumatism, etc. Often, premature birth is provoked by acute infectious diseases suffered by a woman in late gestation.
Finally, the birth of premature babies may be associated with pathology and abnormal development of the fetus itself: chromosomal and genetic diseases, intrauterine infections, severe malformations.
Causes of pyelonephritis in infants
In most cases, during the newborn period, the cause of the development of the disease is the entry of bacteria into the child’s blood. Circulating through the bloodstream, they reach the kidneys by hematogenous route and cause inflammation of their tissues and systems. Therefore, almost any microbe can lead to the development of disease in a newborn.
As for infants, they are more likely to have an ascending route of infection, when pathogenic microorganisms enter the kidneys from the bladder. In most cases, pyelonephritis in infants is provoked by Escherichia coli (
Diagnosis and treatment methods
Symptoms and treatment of the disease are determined by the doctor. Parents, if they have any suspicions, immediately go to the hospital.
Pyelonephritis in children is most often complicated by various pathologies. Therefore, the timeliness of treatment determines the outcome of the disease.
Diagnosis begins with an examination. With the development of pyelonephritis in an infant, attention is drawn to pale skin, profuse sweating, lethargy and apathy.
The doctor prescribes a general analysis of urine and blood, culture on nutrient media. Other diagnostic methods are carried out as needed.
After receiving the results, the attending physician prescribes the necessary treatment. Pyelonephritis in newborns is accompanied by an increase in the number of leukocytes and ESR in the blood.
The number of leukocytes, red blood cells, casts, and protein increases in the urine, and bacterial cells appear. The presence of bacteria in the urine allows a diagnosis of pyelonephritis.
Treatment of pyelonephritis in children is based on adherence to general principles:
- Bed rest during fever.
- Complete refusal to use additional complementary foods. It is recommended to feed only breast milk or formula.
- Compliance with hygiene rules during water procedures of the external genitalia.
- Mandatory use of antibiotics, antipyretics, antispasmodics. Additionally, the body is detoxified.
Pathology in infants is treated using antibacterial drugs. Antibiotics with a pronounced bactericidal effect are used. Prescribed:
- 3rd generation cephalosporins.
- Aminoglycosides.
- Fluoroquinolones.
- Nitrofurans.
From the first days of therapy, the drugs are administered intramuscularly several times a day. The course, dosage and duration are determined only by the doctor. If necessary, vitamin therapy is carried out and probiotics are prescribed.
After recovery, the child is monitored for 5 years. The occurrence of a relapse becomes an indication for constant health monitoring by doctors.
The disease can occur with complications, bacterial sepsis, shock, chronic form. A rule that helps reduce the risks of life-threatening consequences is asking for help. Treatment of the disease is carried out only by a doctor in a hospital setting.
Symptoms
The following clinical picture is typical for pyelonephritis in infants:
- Increased body temperature (39 °C and above) up to the formation of convulsions.
- Chills, fever.
- Weakness, drowsiness and tearfulness.
- The baby refuses to eat.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Frequent regurgitation.
- Possible vomiting.
- Slow weight gain or loss.
- Loose stools, in rare cases constipation.
- Urination is painful, frequent and in small portions. Before defecation, the baby becomes restless, grunts and cries.
- Urine has a dark color and a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Pale or grayish color of the skin, yellowing is rarely observed.
- "Blueness" under the eyes and around the mouth area.
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis in children under one year of age are pronounced. The disease develops gradually, but is severe. The main symptom is an increase in body temperature to 39–40 °C.
IMPORTANT! There are no symptoms typical of ARVI: sneezing, coughing, runny nose.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in newborns are quite specific. Infants cannot indicate pain and describe their sensations. Parents guess about the ongoing pathology only by indirect symptoms.
The most characteristic sign of pyelonephritis is an increase in temperature to 38-39 degrees. In a 3-month-old child, the fever is more pronounced, and the temperature can rise to 40 degrees. The course of the disease without fever is typical for premature babies.
In addition, the baby exhibits severe anxiety. The newborn's skin takes on a sickly pale tint. The baby refuses to eat food and begins to lose weight sharply. The clinical picture may be accompanied by nausea and diarrhea.
In some cases, parents with pyelonephritis in a newborn boy note problems with urination. The stream becomes intermittent and weak.
The disease is also characterized by changes in the quality of urine. A cloudy precipitate forms in it. Urine may also contain minor amounts of blood and have a rather unpleasant odor. Exacerbation of the chronic form of pyelonephritis has exactly the same symptoms as the acute course of the disease. The period of remission is characterized by the complete absence of signs of the disease. Sometimes this pathology is accompanied by a constant slight increase in temperature.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis in infants
As a rule, the first person to diagnose pyelonephritis in infants is a pediatrician, who sends the child and his parents for a mandatory consultation with a pediatric nephrologist or a pediatric urologist. To confirm the diagnosis you will need to do:
- HOW;
- TANK;
- OAM;
- Urine culture for flora with a mandatory antibiogram;
- Biochemical urine analysis;
- The Zimnitsky test is performed in the Reiselman interpretation, when urine is collected not every 3 hours, but in the rhythm in which the child urinates;
- It is possible to detect the disease using PCR and ELISA;
- Assessing spontaneous voiding and monitoring diuresis is important.
The child is also sent for an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. Cystourethrography is not performed after the first episode of illness in a child; it is performed in cases of repeated pyelonephritis, or if hydronephrosis, sclerosis of renal vessels, and obstruction are detected during ultrasound.
Treatment of childhood pyelonephritis
Based on thorough examinations and diagnosis, the doctor will select an individual course of therapy. As a rule, treatment includes the following medications:
- Initially, strict bed rest is prescribed; when the temperature returns to normal, walks in the fresh air are recommended, but no more than 30 minutes;
- A diet for pyelonephritis in children will reduce the load on the kidneys. The daily salt intake should be kept to a minimum (up to 8 g), drink more water (2 l), avoid fried, smoked, fatty and spicy foods;
- Treatment of pyelonephritis in children with antibiotics is mandatory. The drug is chosen depending on the severity of the disease. As a rule, the following antibiotics are prescribed: Amoxicillin, Cefuroxime, Cefotaxime, Cefepime. The course of treatment lasts from 7 to 21 days;
- Uroantiseptics are prescribed; they effectively disinfect the urinary tract and kill harmful bacteria (Nitroxoline, Nevigramon, Palin). The course of therapy lasts 14 days;
- It is recommended to take medications that reduce unpleasant symptoms (antipyretic antispasmodics, vitamins and anti-inflammatory tablets).
Therapeutic measures
General therapeutic principles:
- Hospitalization of the baby together with the mother. In a specialized hospital, diuresis and the general condition of the small patient are monitored. Based on this, treatment is adjusted.
- Bed rest until fever resolves.
- Elimination of complementary foods. Natural breastfeeding is not limited.
- Maintaining careful baby hygiene. The pediatrician must remind you of the rules for washing your child.
- Cystitis in children aged 2 years: symptoms, causes, treatment options, review of drugs
Drug treatment:
- Antibiotic therapy. Most often drugs of the cephalosporin series.
IMPORTANT! You should not listen to reviews about the dangers of antibiotics for the gastrointestinal tract. It is much easier to restore the intestinal microflora than to cure pyelonephritis.
- Uroseptic drugs (Canephron).
- Antipyretic.
- Antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Nosh-pa).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- If necessary, use antifungal drugs.
- Herbal medicines (horsetail, nettle, St. John's wort, lingonberry leaves).
- Probiotics to restore the balance of normal intestinal microflora (Normobact, Linex for children).
- General strengthening medications: immunomodulators (Viferon), vitamins.
Treatment in a hospital lasts up to 3–4 weeks. Drugs for therapy are selected by a nephrologist or urologist, giving preference to their optimal combinations.
IMPORTANT! It is prohibited to treat pyelonephritis on your own. Reason: many medications are contraindicated in infants or are ineffective when taken at the same time.
Treatment tactics
Timely treatment will avoid complications. The main treatment consists of prescribing broad-spectrum antibiotics: Azithromycin, Flemoxin solutab, Amoxiclav.
Without antibiotic therapy, it is almost impossible to get rid of the disease.
In addition to antibiotics, therapy against pyelonephritis includes :
- restorative drugs in the form of immunomodulators (Viferon), vitamin complexes (Multitabs, Alphabet);
- antispasmodics: Drotaverine, Nosh-pa in an age-appropriate dosage;
- uroseptics: Canephron;
- preparations for normalizing microflora: Bifiform Baby, Normobakt, Linex for children.
A diet with the most gentle nutrition is important; for infants over 6 months of age, complementary feeding is best abolished or limited during treatment of pyelonephritis. Drinking plenty of water in the form of weak chamomile tea, clean water, non-concentrated compotes without sugar and fruit drinks is beneficial
Causes
Primary pyelonephritis in infants occurs in the following situations:
- Insufficient hygiene of the baby’s genitals. For children, the most typical ascending route of infection. Bacteria from the external environment are introduced into the urethra and reach the renal parenchyma through the excretory tract.
- The presence of a focus of inflammation in the body. It could be the flu, a sore throat. Once in the blood, pathogens circulate through the vascular bed and reach the kidneys.
- Changes in intestinal microflora. In case of colitis or dysbacteriosis, comfortable conditions are created for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Subsequently, they are spread throughout all systems by hematogenous route.
- Inflammation of the urinary tract: cystitis, urethritis.
- Pathological conditions caused by imbalance in metabolism: rickets, excess vitamin D.
Secondary pyelonephritis is most often a consequence of:
- Kidney underdevelopment.
- Congenital anomalies of the organs of the excretory system: violation of their structure or localization.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in a child of the first year of life
Infancy leaves its mark on the course of any disease. Inflammation in the kidneys is no exception. However, the baby will not be able to communicate about poor health using harmonious phrases. Parents need to very carefully monitor the baby’s behavior, since it is his characteristics that can indicate problems in the urinary system.
The picture of an acute illness is dominated by symptoms that are difficult to attribute to a problem in one or another organ:
- lethargy;
- increased excitability;
- refusal to eat;
- increased body temperature;
Fever is one of the main signs of pyelonephritis - weight loss;
- vomiting of food eaten, including breast milk;
- constipation;
- yellowing of the skin;
- crying and anxiety when urinating;
- the appearance of urine with a pungent odor or discoloration.
High body temperature is dangerous for a child of the first year of life. During this period, the body is not yet able to adequately remove excess heat through the skin into the external environment. Fever affects brain activity the most. Its overheating can lead to the most negative symptom of pyelonephritis - muscle twitching and cramps. In addition, the brain can respond to severe inflammation with excessive muscle tension. This circumstance can lead to an erroneous interpretation of symptoms as a consequence of inflammation of the membranes of the brain - meningitis.
- Pyelonephritis during pregnancy - consequences for the child
Fever may cause a particular posture with the head thrown back
The chronic form of pyelonephritis without exacerbation is manifested by nonspecific signs:
- decreased appetite;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- decreased growth and weight gain;
- delay in psychomotor development. The child masters the necessary skills late: roll over, crawl, walk, talk.
Chronic pyelonephritis can cause delayed psychomotor development
What causes and why is pyelonephritis dangerous in a child: signs, prevention, diagnosis
Pyelonephritis is a dangerous disease in children. Lack of help leads to serious consequences, including uremic coma and death. Treatment of pyelonephritis in children depends on the severity of the disease.
Causes of the disease
Groups of pathogens include staphylococci, streptococci, clostridia, and intestinal flora. There are isolated cases where the pathology is caused by specific pathogens, but this is extremely rare.
The causes of pyelonephritis are often associated with the spread of infection from other foci in the body. Infection occurs:
- Rising. With an ascending route of infection, bacteria spread from the bladder and lower urinary tract. The disease manifests itself as a result of pathogenic microorganisms entering the urethra. This problem is common among children, especially among girls. This is due to the fact that parents do not know how to properly carry out hygiene measures (washing). During this process, intestinal flora is transferred from the anus to the urethra.
- Hematogenous. There are cases when pathology develops in the presence of distant foci of bacterial diseases. Forms as a complication of sepsis, abscesses, and extensive purulent wounds. There are no signs if other anatomical structures of the urinary system are affected.
Acute pyelonephritis develops quickly. This is due to the fact that the urethra and ureters are still short, and the volume of the bladder is insignificant. The bacteria multiply and cause extensive damage to the urinary tract and kidneys.
In addition, it is important to have conditions that promote the activation of bacteria. Among these factors it is worth highlighting:
- Hypothermia. The effect of low temperatures on a child's body leads to poor blood circulation. This is due to the fact that the diameter of the blood vessels is extremely small, and the spasm that occurs in the cold quickly leads to tissue hypoxia. When there is insufficient blood supply, metabolites and carbon dioxide accumulate in the tissues, which become a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Wearing diapers. The cause of frequent diseases of the urogenital complex is the use of diapers. If the replacement is not done in a timely manner, the flora from the feces is carried into the urethra and bladder, from where it spreads to the kidneys. The moist environment in the diaper promotes the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Age 2-6 years. During this period, two immune crises occur in the child’s body. Occurs at the age of 2 years, and the second at 6 years. At 2 years old, the child begins to get acquainted with the outside world, which leads to massive infection of the body with opportunistic bacteria. At the age of 6, the child is sent to a children's group - a school, where mutual infection occurs. Such immune crises are characterized by a sharp decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood, which manifests itself in the form of a predisposition to infectious diseases. At this age, secondary pyelonephritis is observed much more often than at older ages.
The causes are also associated with intrauterine infection. This occurs because at the time of birth the mother has a chronic or acute form of bacterial disease of the vagina, uterus or cervix.
Classification, stages and nature of the course
The classification of pyelonephritis does not differ from that used in adults. It is customary to distinguish between primary and secondary.
There are acute and chronic stages of the disease, depending on the course. Based on the nature of inflammation, it is customary to distinguish three forms of the disease: serous, purulent and necrotic. Serous and purulent are much more common than necrotic.
Each pyelonephritis begins with serous inflammation. Over time, the disease develops into purulent or necrotizing pyelonephritis.
Starting treatment prevents such processes, and the disease will be easier. Chronic pyelonephritis is diagnosed extremely rarely, since a large number of exacerbations are required to make this diagnosis.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of pyelonephritis tend to progress rapidly. This is due to a deficiency of the immune system, as well as the fact that the size of the affected organ is much smaller.
If the pathology develops in an ascending manner, then bilateral lesions are more often diagnosed.
Bilateral is difficult, since urine output is impaired in two kidneys at once.
If the process is unilateral, then one of the kidneys begins to work more actively compensatoryly, which prevents the development of edema and increased blood pressure. Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis:
- Increased body temperature. Reaches a critical level - 40˚С. In such a situation, there is a risk of depression of consciousness, which leads to hallucinations. This manifests itself quickly, since the amount of blood toxins required for such phenomena is less than in adults. There is a risk of developing toxic shock, which will require emergency care.
- Impaired urination. In childhood, urine production is often disrupted. This is due to the fact that the kidneys are still immature and are not able to fully function. Inflammation is accompanied by a sharp decrease in the amount of urine excreted, which leads to kidney failure. Azotemia appears, blood pressure rises, and swelling quickly increases. This is very noticeable in the first 2 years of life. In children over 12 years of age, the clinical picture does not differ from adults.
The course of the pathology has its own characteristics, but is no different from adults. Diagnosis of the disease in babies in the first year of life is difficult, since the baby cannot express complaints.
In this case, signs of the disease are detected only by parents. Among them are:
- Change in urine color. Pyuria does not cause discomfort. Adults regularly pay attention to the color of their urine. The child's color is checked before throwing out the diaper or emptying the potty. Urine takes on a greenish tint, which is immediately noticeable to adults.
- The child becomes restless. Pain in the projection of the kidneys causes discomfort in the baby, this is manifested by increased irritability or loud screaming. With an increase in body temperature, this state will be replaced by lethargy.
- Profuse sweating. What parents should pay attention to is increased sweating. This occurs due to an increase in temperature and is regarded as a subjective sign of illness. In such a situation, you will need to change the child’s clothes several times within an hour.
- Rare urination. With the disease, insufficient urine production develops extremely quickly, and its quantity will be reduced. This is noticeable in children in the first years of life.
Diagnostic features
Carrying out diagnostic measures in children is difficult. This is due to the fact that it is difficult for children to remain still during instrumental examinations, as well as to follow the rules for collecting material for laboratory tests.
Despite this, the following examinations are recommended:
- Blood and urine analysis. For children, urine is collected for analysis in a clean container to avoid contamination. If a bacteriological study is required, then the urine is collected in a sterile container. Bacteriological analysis is an indispensable diagnostic method, as it helps to accurately determine the species of pathogens. If the child is still too small, then urine is collected using a catheter.
- To conduct an ultrasound of the kidneys and pelvic organs, ensure the child’s immobility. This is achieved by keeping the child in the arms of his mother or father. He feels calm and does not make unnecessary movements.
Excretory urography in children is rarely performed, as there is a risk of developing allergic reactions; it is difficult for children to remain still during x-rays. This study is carried out only in children over 12 years of age.
Additional tests are also prescribed that are aimed at differentiating the disease from glomerulonephritis, since this disease is much more common in children than pyelonephritis.
Treatment of pyelonephritis
You shouldn’t find out how to treat pathology from friends, because each organism has its own characteristics. Treatment of the disease is also difficult.
This is due to the fact that many antibiotics are not recommended for use in childhood, as they have a negative effect on the kidneys, liver, digestive tract, and hearing organs.
Among antibiotics, it is strictly forbidden to use Gentamicin. This drug is ototoxic, that is, it can inhibit the function of the auditory analyzer.
Sometimes it causes complete deafness, which cannot be treated with medication or surgery. For mild forms of the disease, preference is given to herbal remedies such as Canephron or Urolesan.
If the effect of the drug is not enough, then antibiotics are prescribed. Among them are cephalosporins, this group with the least pronounced side effects. Among the drugs, Ceftriaxone is distinguished, which is prescribed most often. Treatment of acute pyelonephritis does not exceed 14 days.
During this period, the bacteria die with adequate therapy.
Treatment of chronic pyelonephritis is carried out from 12 years of age, when relapses and exacerbations are already observed. The duration of treatment for the chronic form is longer than for the acute form.
Since the intestinal microflora in children is not fully formed, preference is given to parenteral methods of administering antibiotics.
Thus, the negative impact on the digestive tract is reduced, which reduces the risk of developing dysbiosis.
Sulfonamides or nitrofuran derivatives are predominantly prescribed, since drugs of these pharmacological groups have fewer side effects and a wide spectrum of antimicrobial effects.
Diuretics should be used with caution before reaching 12 years of age. Prescribed only in cases where there is a risk of developing septic complications.
This is due to the fact that diuretics in children provoke water-electrolyte imbalance in several doses.
If such medications are prescribed, intravenous drips of saline solutions are indicated, which helps maintain electrolyte levels within normal limits.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for children are prescribed only in the form of rectal suppositories. An ulcer forms on the fragile mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum even after a short course of treatment.
Among antipyretics, preference should be given to NSAIDs rather than aspirin derivatives. This is due to the fact that acetylsalicylic acid derivatives cause Raynaud's disease. Most people prescribe Paracetamol or Nurofen.
Several doctors treat chronic pyelonephritis: a urologist, a pediatrician and an immunologist.
Disease prevention
Prevention includes the following points:
- avoid hypothermia;
- observe the rules and regulations of intimate hygiene;
- strengthen the immune system;
- adhere to the principles of healthy eating.
It is better to prevent a disease than to start treatment. All possible measures are taken for prevention.
Pyelonephritis is a dangerous disease that leads not only to serious complications, but also to death.
Emergency treatment is required, which means hospitalization of the child in the intensive care unit.
( 1 rating, average 5 out of 5 )
Classification
The types of this disease in infants are varied. There are several criteria for determining them.
By etiology:
- Primary. It occurs without any prerequisites or previous urological diseases. The infectious process develops in an initially healthy organ. The frequency of occurrence is about 10%.
- Secondary. The pathology develops against the background of previous inflammation of the urinary tract. A more common type of pyelonephritis.
By stage:
- Infiltrative.
- Sclerotic.
By localization:
- Unilateral.
- Bilateral.
According to the course of the disease:
- Spicy. Lasts less than six months. Vivid clinical picture of inflammation.
- Chronic. It is a consequence of untreated acute pyelonephritis. Characteristically, symptoms persist for more than 6 months and at least two relapses occur during this time.
- Latent. It occurs in a latent form and is characterized by a long absence of signs of pyelonephritis in infants. Urinary syndrome is slightly manifested.
REFERENCE! The famous doctor Komarovsky states that the most insidious type of pyelonephritis is hidden. After all, it is almost impossible to detect it in time.
According to the conductivity of the excretory tract:
- Obstructive. Formed as a result of organic or functional disorders of urodynamics. In this case, the outflow of urine is disrupted.
- Non-obstructive. Associated with dysmetabolic changes in the renal parenchyma, inadequate blood supply, immunodeficiency conditions and endocrine pathologies. There are no obstacles to the exit of urine.
Why does the disease occur?
The reasons why primary pyelonephritis occurs in a child are as follows.
- Changes in microflora in the intestines.
- Intestinal dysbiosis, which mainly develops against the background of colds or intestinal infections.
- Flu, sore throat caused by coccal pathogens.
- Inflammation of the bladder (cystitis).
Secondary kidney inflammation in a child can occur due to the following disorders.
- Congenital anomaly of the urinary organs (disturbances in the structure and location of the kidneys and bladder).
- Underdevelopment of the kidneys.
The reasons why pyeloectasia develops in infants are as follows.
- Hereditary factor.
- Infection in the urinary tract.
- Prolapse of the kidneys.
- Incorrect location of the pelvis.
- Inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
Carrying out prevention
The occurrence of pyelonephritis and its complications is quite possible to prevent; the most important thing is to follow certain preventive measures, in particular:
After previously suffering from pyelonephritis, the child should be registered with a urologist. Consultations and examinations with a nephrologist will also be required. Particular care should be taken when administering vaccinations. If acute pyelonephritis occurs in a child, vaccination until the age of one can be postponed until the child’s health is completely normalized.
If a child has already suffered from the disease once, then it is necessary to take preventive measures to prevent relapses. To prevent the development of chronic pyelonephritis, it is extremely important:
Pyelonephritis is a very serious disease, especially for infants. If the acute form is treated incorrectly or untimely, the disease can progress to the chronic stage, which is fraught with dangerous complications and frequent relapses.
Complications
In the first month, a baby's kidney size is about 5 cm, by the year it reaches 6 cm. Bacteria very quickly completely infect the small organ. Therefore, pyelonephritis actively progresses, increasing the risk of complications.
Consequences of kidney inflammation:
- The transition from an acute form of the disease to a chronic form, which is difficult to get rid of.
- Hydronephrosis. Due to the obstructed outflow of urine, the load on the pyelocaliceal system increases, which leads to atrophy of the renal parenchyma.
- Arterial hypertension. The work on the heart increases, and cranial pressure rises.
- Necrosis of the tubular system.
- Sepsis.
- Formation of apostematous nephritis (multiple kidney abscesses).
To prevent complications, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician for any increase in body temperature.
Popular about pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis. Who is to blame, what to do and how to live further?
Pyelonephritis is a bacterial inflammatory disease that affects the pyelocaliceal system and the parenchyma (tissue) of the kidneys.
Acute and chronic. Acute pyelonephritis - everything is clear from the name itself, we lived - we didn’t bother, and then bam bam and everything is bad.
Chronic - like any chronic disease, it proceeds quietly, not typically and in every way unusual.
But there is also primary pyelonephritis: there are no anomalies in the development of the kidneys or urinary tract, but the disease has developed.
And there is secondary pyelonephritis, which occurs against the background of the presence of pathologies in the structure of the kidneys and urinary tract, which, in turn, are often detected at an early age. And this disease is concomitant.
All relatives will immediately say that it is the mother’s fault, who did not notice, caught a cold, and also Komarovsky - the villain with his bare legs and walks without hats! (4).
The causative agent is a bacterium. Therefore, herbs, drops, peas, etc. are not treatment. Treatment with antibiotics only.
To choose the right antibiotic, you need to have your urine tested for sterility (urine culture tank). But not everything is so simple: in many countries it is believed that this test has diagnostic value only when urine is collected through a catheter! (2)
The drugs of choice for the doctor are (1):
– II-IV generation cephalosporins (cefuroxime, cefotaxime, cefoperazone, ceftriaxone (this drug can cause jaundice), cefepime).
– co-trimoxazole (in regions where the level of E. coli resistance is less than 10%.)
The course ranges from 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity and related data. Determined only by a doctor.
If treated incorrectly, pyelonephritis can become chronic (advanced, untreated disease). Therefore, treatment must be taken seriously! And strictly follow the doctor's instructions. With the right treatment, the child’s condition should improve within 24 to 48 hours, and on the third day there should be an improvement in urine and blood tests. I hope that all parents understand that self-medication in this case cannot be done.
How to live further?
I would like to focus on lifestyle! In any case, only a doctor prescribes treatment, but the parents organize the life of the child. Therefore, the lifestyle of a child who has suffered pyelonephritis should be as opposed to popular opinion as possible (4). This child vitally needs strong local immunity - any acute respiratory infection can trigger a relapse. Many medications pass through the kidneys. And strong local immunity, as everyone knows, can only be achieved by: frequent walks, swimming in cool water, barefoot walking, gymnastics, drinking plenty of fluids, and cool and humidified air. As for sitting on the floor and ground. Sitting on a cold surface for a long time is prohibited for everyone. If a child in a diaper sits on a tile for 10 minutes, this is not the case. And a very important point is hygiene. To do this, review the episodes on the hygiene of boys and girls from the program of the School of Doctor Komarovsky. The main thing with hygiene is not to overdo it! But follow it regularly!
Diagnostic methods
To identify pyelonephritis in infants and differentiate it from glomerulonephritis, the following examination methods are necessary:
- Collection of complaints from the mother.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the kidneys and bladder.
- Blood pressure measurement.
IMPORTANT! Cystourethrography is prescribed only for repeated exacerbations of pyelonephritis and when hydronephrosis, sclerosis and obstruction of renal vessels are detected.
Laboratory research:
- Blood tests: general, biochemical. Inflammation is characterized by: leukocytosis, increased ESR, neutrophilia, decreased hemoglobin and red blood cells, the appearance of C-reactive protein, creatinine and urea.
- General urine analysis. With pyelonephritis, the appearance of bacteria, protein and red blood cells is noted.
- Zimnitsky's test, Nechiporenko.
- Culture of urine for pathogenic microflora with identification of the pathogen.
- Determination of bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics.
Sources used:
- https://www.ayzdorov.ru/lechenie_pielonefrit_grydnichek.php
- https://urohelp.guru/pochki/pielonefrit/u-grudnichka.html
- https://1opochkah.ru/deti/pielonefrit-u-grudnichka.html
- https://creacon.ru/bolezni-pochek/pielonefrit-u-grudnichka-simptomyi.html
- https://grudnichky.ru/zdorove/pielonefrit-u-grudnichka.html
- https://tvoyapochka.ru/bolezni/pielonefrit-u-grudnichka
Popular about pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis. Who is to blame, what to do and how to live further?
Pyelonephritis is a bacterial inflammatory disease that affects the pyelocaliceal system and the parenchyma (tissue) of the kidneys.
Acute and chronic. Acute pyelonephritis - everything is clear from the name itself, we lived - we didn’t bother, and then bam bam and everything is bad.
Chronic - like any chronic disease, it proceeds quietly, not typically and in every way unusual.
But there is also primary pyelonephritis: there are no anomalies in the development of the kidneys or urinary tract, but the disease has developed.
And there is secondary pyelonephritis, which occurs against the background of the presence of pathologies in the structure of the kidneys and urinary tract, which, in turn, are often detected at an early age. And this disease is concomitant.
All relatives will immediately say that it is the mother’s fault, who did not notice, caught a cold, and also Komarovsky - the villain with his bare legs and walks without hats! (4).
The causative agent is a bacterium. Therefore, herbs, drops, peas, etc. are not treatment. Treatment with antibiotics only.
To choose the right antibiotic, you need to have your urine tested for sterility (urine culture tank). But not everything is so simple: in many countries it is believed that this test has diagnostic value only when urine is collected through a catheter! (2)
The drugs of choice for the doctor are (1):
– II-IV generation cephalosporins (cefuroxime, cefotaxime, cefoperazone, ceftriaxone (this drug can cause jaundice), cefepime).
– co-trimoxazole (in regions where the level of E. coli resistance is less than 10%.)
The course ranges from 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity and related data. Determined only by a doctor.
If treated incorrectly, pyelonephritis can become chronic (advanced, untreated disease). Therefore, treatment must be taken seriously! And strictly follow the doctor's instructions. With the right treatment, the child’s condition should improve within 24 to 48 hours, and on the third day there should be an improvement in urine and blood tests. I hope that all parents understand that self-medication in this case cannot be done.
How to live further?
I would like to focus on lifestyle! In any case, only a doctor prescribes treatment, but the parents organize the life of the child. Therefore, the lifestyle of a child who has suffered pyelonephritis should be as opposed to popular opinion as possible (4). This child vitally needs strong local immunity - any acute respiratory infection can trigger a relapse. Many medications pass through the kidneys. And strong local immunity, as everyone knows, can only be achieved by: frequent walks, swimming in cool water, barefoot walking, gymnastics, drinking plenty of fluids, and cool and humidified air. As for sitting on the floor and ground. Sitting on a cold surface for a long time is prohibited for everyone. If a child in a diaper sits on a tile for 10 minutes, this is not the case. And a very important point is hygiene. To do this, review the episodes on the hygiene of boys and girls from the program of the School of Doctor Komarovsky. The main thing with hygiene is not to overdo it! But follow it regularly!
Urine analysis is very capricious, and it must be collected correctly!
Basic rules for collecting analysis:
– Wash well with running water;
– Delivery to the laboratory within 1.5 hours.
So pyelonephritis is not a death sentence for an active and busy life, but a reason to be more attentive to the family’s lifestyle.
This article and its discussion in ClubCom.
published 30/10/ 14:28
SEE ALSO:
Comments 3
To leave a comment, please log in or register.
Xeona Russia, St. Petersburg
Helena Ukraine, Odessa
Helena Ukraine, Odessa
“Children’s question” - a new section in the “School of Doctor Komarovsky”
Ask questions and get answers!
Measles vaccination: who is protected and who needs vaccination
Hand-foot-mouth disease:
how to avoid getting an enterovirus infection (Library)