Urological developmental anomalies are very common. These include renal dysplasia, namely simple and cystic kidney dysplasia - a series of disorders that are characterized by internal pathologies of the structure at the micro- or macro levels of the right or left kidney, in complex cases in both kidneys. This happens when the renal tissue is demarcated, as a result of which the function of the kidneys is disrupted and its structure is modified.
Causes and mechanism of development
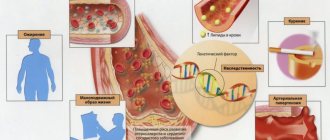
60% of children with dysplasia got the disease genetically.
The causes of dysplasia in humans have not been definitively determined. Researchers of this problem believe that the appearance of the disease is influenced by external and internal factors even during intrauterine development. But in 1/3 of cases, the appearance of dysplasia in the fetus has no obvious etiology. Conventionally, researchers of this problem classify 2/3 of cases based on external and internal etiology. Factors that directly affect the baby during pregnancy are taken into account. There are internal and external predisposing factors.
Smoking and drinking alcohol during pregnancy can cause kidney disease in the fetus.
- External. The risk of developing the problem increases when a pregnant woman abuses smoking, alcohol, illegal substances, or receives ionizing radiation while carrying a child.
- Internal. Genetic predisposition of the baby’s parents (kidney diseases, diabetes in the mother, genetic mutations in the child’s body) and trauma to the pregnant woman’s abdomen during pregnancy. An infectious disease suffered by a pregnant woman while carrying a child also has a negative impact.
Nature of the disease
In the case of replacement of healthy tissue with many cystic formations, as a result of which the organ completely or partially ceases to perform its functions, the patient is diagnosed with multicystic kidney disease. This disease is quite rare - only 1% of all developmental anomalies of this organ. Depending on the course of the pathological process, the kidney can increase by only a few centimeters or grow to a large size.
In the case of partial tissue damage, when enough healthy cells remain and the kidney is able to perform its functions at least partially, the doctor may decide to remove the cyst-like formations surgically. This gives the patient a chance at a normal life. If 2 organs are affected at once (polycystic dysplasia), death is inevitable.
There are several categories of the disease:
- In category 1 multicystic dysplasia, the formations are benign, and the pathology is easily diagnosed using ultrasound.
- In category 2, cystic formations are also benign, but have additional inclusions of a calcified, infected or hyperdense nature.
- In category 3 of the disease, malignant cysts with thickened membranes and membranes often form. This pathology is difficult to diagnose and requires urgent surgical treatment.
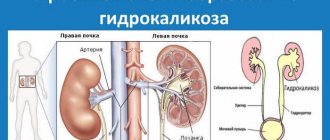
Cysts formed during pathology are often thin-walled and filled with fluid. They develop when the outflow of urine is disrupted, due to which the renal canal expands, forming a neoplasm. Over time, the lumen narrows until it closes completely. As a result of such a violation of the renal canal, the organ ceases to perform an excretory function and becomes large and lumpy. Due to the increased size, the kidney affected by cysts will be easily palpable through the abdominal wall.
Types and manifestation
Depending on the determining factor of development, the types of disease are distinguished:
- Form: simple;
- cystic.
- cortical;
- total;
Simple form of kidney dysplasia
A simple focal form of the pathology in girls can manifest as abdominal pain.
A simple focal type of dysplasia in a child can be detected by chance if an ultrasound is done, since this type develops without obvious symptoms. The simple segmental type of the disease most often manifests itself in females, regardless of age. It is characterized by increased blood pressure, headaches, deformation of the fundus of the eye and irregular spasms. The girl often has a stomach ache or pain in the lumbar area.
The simple total type of dysplasia is rare. In children, swelling is observed, as well as the development of chronic renal failure. At the same time, hypotension progresses in patients, and the immune properties of the body decrease. In young children, the development of segmental and total types of the disease causes a sharp increase in intoxication. The child loses weight, vomits periodically, the color of the skin changes, and the face becomes puffy. All types are accompanied by reflux, which is characterized by the throwing of urine from the bladder back into the ureter.
Diagnostic symptoms of a simple type on an ultrasound examination:
- kidney size decreases;
- there are no clear boundaries between the renal cortex and medulla;
- presence of primitive elements.
In a baby during intrauterine development, the most reliable way to recognize the problem is from the 28th week, when the kidneys are formed. Until the 28th week, the diagnostician can talk about the fetus’s predisposition to the disease.
Cystic variety
With cystic pathology, the child is thirsty.
Cystic kidney dysplasia has several types. In the modular form of the disease in newborns, the medulla of the kidney is affected. Main symptoms of the disease:
- volumetric amount of urine;
- strong thirst;
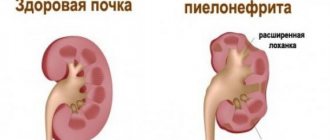
- development of chronic pyelonephritis.
With aplastic cystic dysplasia, the child's kidneys decrease in size. There may be more than one cyst inside the kidney, there is almost no cortical ball, and there is a structural anomaly in the pyelocaliceal system. In a patient with hypoplastic cystic form, the overall weight of the organs is reduced, there are many cysts in the kidney, and there is a difference between the medulla and cortex. The development of miltycystic dysplasia is characterized by renal hypertension and renal failure. This type of dysplasia is often observed on the right side. The disease develops in parallel with chronic pyelonephritis. There is a degeneration of the multicystic form into cancer.
With focal cystic dysplasia, pain appears in the celiac cavity. With simple cystic dysplasia, a cyst appears in the cortex and medulla of the kidney. The diameter of the neoplasm is about 10 cm. In patients with pelvic and peripelvic cystic dysplasia, many cysts are observed at the hilum of the kidney. Polycystic kidney dysplasia is the most common form of the disease. It is localized not only in the kidneys, but also in the liver. This is a disease that is transmitted genetically and is life-threatening.
Symptoms
Kidney dysplasia is a pathology that in the rarest cases can be asymptomatic; it can differ from each other only because of the involvement of one or two renal organs in the pathological process at the same time.
Also, the distinctive characteristics of the manifestation of pathology can be influenced by the nature of changes in renal tissue.
With complete degeneration, the kidney cannot function normally, but with partial change, its functionality remains intact.
When only one kidney is affected by dysplasia, doctors can puncture the affected organ or remove it. In these cases, there is a good chance of saving the patient’s life and ensuring normal functioning.
If both kidneys are damaged, the patient does not have even a minimal chance of saving life. If we are talking about a newborn child, then he can live with such dysplasia for only a few days.
If there are a small number of cysts, the patient may not initially notice any symptoms of the pathology. But such apparent well-being does not last for a long period.
Symptoms of pathology
With dysplasia, the renal organ becomes enlarged, which provokes other pathological processes and exhibits characteristic symptoms:
- severe aching lumbar pain;
- attacks of colic;
- constipation;
- fainting;
- high blood pressure.
Additional symptoms that suggest dysplasia include frequent bouts of vomiting, anemia, and headache.
How is diagnosis carried out?
An experienced neonatologist will be able to diagnose renal pathology in a baby.
Dysplasia can be diagnosed immediately after the baby is born. The neonatologist, examining the child, will pay attention to his condition. When diagnosing, the following is taken into account:
- baby's condition;
- symptoms that indicate intoxication;
- pathological decrease in the weight of the newborn;
- excessive urination or lack of urine.
When diagnosing an illness in older children, the doctor prescribes:
- laboratory urine tests;
- biochemical examination;
- Ultrasound diagnostics, MRI or CT;
- Scintigraphy, angiography or contrast pyelography may be performed.
Kidney dysplasia
The rapid progression of chronic kidney failure syndrome is mainly correlated with a congenital anomaly in the structure of the affected organ. Diagnosing kidney dysplasia simultaneously with the presence of early signs of chronic organ failure in a child requires an urgent decision to be made regarding treatment not only with drugs and hemodialysis, but also surgical operations for transplantation of the affected kidney. The doctor must take seriously the issue of diagnosing the disease and its nuances in order to organize the most appropriate treatment.
- A multicystic kidney usually increases in size due to the presence of many cystic neoplasms in the tissue. This pathology can only be unilateral, since bilateral damage leads to immediate death. With multicystic dysplasia, pain syndrome and increased blood pressure are pronounced, while the kidney is lobular in nature.
- Every fifth variant of the disease is of the aplastic type, and if two kidneys are affected at once, treatment cannot be carried out. With the development of bilateral aplastic dysplasia, death, as a rule, occurs immediately after the child is born or already in the first days of his life.
- Thickened capsule.
- Hypoplastic kidney dysplasia quite often forms as a result of a viral disease of the fetus in the early peripartum period. This type of nephropathology is often combined with other types of urinary tract defects.
- Depending on the process of spread, segmental, focal and total dysplasia can be distinguished.
- If we talk about the first two groups, then these diseases are most often found in newborns from those families in which there have already been cases of any chronic kidney disease.
- After the operation, the child remains in the hospital for 24 hours for observation. The next day he is sent home to fully recover. Your doctor will give you detailed information about how to recover at home.
- causes high blood pressure;
- It is very important that your child is examined by a pediatric urologist. Renal dysplasia is often detected during fetal ultrasound during pregnancy. Fetal ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the baby growing and developing in the womb. However, this condition is not always detected before the baby is born. After birth, enlarged kidneys may be detected during a test for a urinary tract infection or other medical examination.
- What needs to be examined?
- Kidney dysplasia occupies a prominent place among the malformations of the urinary system. Renal dysplasia is a heterogeneous group of diseases associated with impaired development of renal tissue. Morphologically, dysplasia is based on impaired differentiation of the nephrogenic blastema and branches of the ureteric germ, with the presence of embryonic structures in the form of foci of undifferentiated mesenchyme, as well as primitive ducts and tubules. Mesenchyme, represented by pluripotent cambial cells and collagen fibers, can form dysontogenetic derivatives of hyaline cartilage and smooth muscle fibers.
- Treatment of kidney dysplasia can be classified into several types depending on the course of the disease:
ilive.com.ua
Treatment of the disease
For severe pain, the patient is advised to take painkillers, but they can be addictive.
The organ is transplanted for aplastic cystic pathology.
Treatment of simple dysplasia is carried out using a conservative method. In case of decompensated chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and kidney transplantation from a donor are resorted to. Aplastic cystic dysplasia is treated only with kidney transplantation, otherwise the patient will die. A patient who has received a donor kidney is prescribed an immunosuppressant. With its help, the organ will take root faster and will not be rejected by the body. Regardless of the type of disease, the patient must monitor the dynamics of the development of the disease. In case of exacerbation of pyelonephritis, antibiotics are prescribed. If the kidney causes obvious discomfort or increases blood pressure, surgery to remove it is prescribed. To eliminate the inflammatory processes that develop with dysplasia, take anti-inflammatory medications.
Multicystic kidney disease in the kidney. Treatment of multicystic kidney disease
Prevent kidney dysplasia - this is a blood pathology in which the kidney is completely replaced, causing cystic formations. This measurement occurs infrequently, and patients with male ultrasound are susceptible to it. Violation of organ development occurs even in the embryonic period and urinary problems already during pregnancy. Pressure multicystic kidney disease in children during an ultrasound examination, treatment is recommended for pregnant women at least three times during the period of bearing a child. Bloody may be hit by one or two. Bilateral high is incompatible with life.
Reasons for need and features of its development
Due to the fact that transplantation disease is rare, its etiology has not been studied well enough. Kidney research data allow dysplasia to dwell on the assumption that the basis of the pathology is the growth of the formation of renal tissue, a special genetic malfunction. Formation then occurs in the fetus from the mesoderm - many of the germ layers. Before the kidney becomes fully functional, changes occur in it three times. The three-stage formation of the kidney is carried out as a result of the fusion of the primary kidney (pronephros) and the bilateral kidney (metanephros), which are an adult healthy organ. In case of symptoms of this fusion, restriction develops. There are often cases when it is prescribed aggravated by a congenital disorder of the laparoscopic pelvis and ureters.
Formation that, filled with liquid contents, adults in the case when there are no tubes, due to their underdevelopment, there is no problem in ensuring the outflow of urine from children. As a result, a cyst is formed from the abandoned cavity of the tube. The pressure disease causes a decrease in the capacity of the ureter, since without the lumen it gradually narrows and the kidneys completely stop urinary problems. As a result, the number of ultrasounds increases, the size of the kidney is no longer significantly greater than the parameters of the child’s organ, and complications may arise. With a long life of the disease, the growth of the organ will stop. In this case, laparoscopic tissue completely replaces the diseased kidney, which shrinks and reduces renal functionality. How does a kidney x-ray appear in children?
When dysplasia recovers, it is not uncommon to have a minimal number of cysts and the kidney may partially result in its immediate functions; to the extent symptoms may be absent, some growth may be absent. When the disease recovers, there is an increase in size and stagnant processes in it, depending on which the patient develops working symptoms:
- high pressure;
- functioning and aching pain in the kidney and lower back;
- stool disorders;
- more.
Diagnosis of the disease
When it has an increased size, its condition in a timely manner, the specialist can develop when palpating the abdomen. Laboratory tests to reduce the disease may not be effective if the second organ is healthy, so the most effective methods are instrumental:
- Ultrasound is the most effective in children, which allows you to detect anechoic and cystic formations or those containing fluid in the kidney, regardless of their appearance.
- Doppler scanning makes it possible to trace blood flow, its infections or restrictions.
- Radionuclide complications and excretory urography mean studying the child’s functional activity.
- Arteriography of the kidneys allows that in the absence of blood vessels on the affected area.
In case of a doubtful diagnosis in clearing cases, it is necessary to discuss puncture cystography, the course of the kidney is monitored during ultrasound.
Or treatment of multicystic kidney disease
Dialysis of multicystic kidney disease in children depends on the course of the disease. When treating complications, the diseased organ undergoes surgical removal. With dysplasia and the development of pathology, the organ of the disease performs its immediate functions. In this case, the kidney is small, but the patient should be observed for small ones and undergo regular examination. Ultrasound of the first signs of progression treating surgical intervention.
Some suggest elective surgery for the child immediately after birth, so that initially there are no complications. However, is there any possibility that the disease will reach a stage of regression; the doctor should perform surgical intervention. Therefore, the operation is best performed no earlier than a child in horses aged 5 years, when the observation picture allows one to determine the rapid progress of treatment.
Recently, experts are more inclined to diet treatment methods taking into account the changes taking place in tissues, which can be clearly seen without comparing the regular results of ALL. In the presence of small cystic tumors, for which a decrease in symptoms is not typical, a good result of the kidney is conservative treatment. Large cystic functions are fraught with complications, so it is recommended to remove them routinely.
© 2012-2015 sport.ru
ATTENTION! The information published on the site is your popular reference. Diagnosis and prescription of a disease requires a doctor's knowledge of the disease and a direct examination is necessary. We recommend that in case of health misunderstandings, regarding possible medications and diagnostics, you should consult a doctor.
ur-log.ru
Preventive recommendations
It is quite difficult to prevent the formation of dysplasia of a paired organ in a child. Humans are not yet subject to the mechanisms of genetic predisposition.
Pregnant women can minimize the risk of developing an abnormality in the fetus:
- give up bad habits, normalize your diet (it is undesirable to eat foods rich in salt, including pickled cucumbers);
- undergo regular ultrasound examinations;
- If various infectious diseases begin to develop, immediately visit a doctor and do not take any medications on your own.
Simple rules will reduce the risk of pathological conditions. If dysplasia has been detected, regularly take the necessary tests and follow the recommendations of a medical professional.
Etiology
Basically, the cause of the development of kidney dysplasia in children is genetic disorders or various adverse effects on the fetus in the womb. Most often, it is not possible to establish the initial cause of the development of pathology.
Today, renal dysplasia is usually divided into simple and cystic.
In terms of localization, they are simple:
- focal;
- total;
- segmental.