If you believe the statistics, more than 35% of congenital anomalies are associated with a disorder of the genitourinary system. This group of diseases includes Frehley syndrome. It was described by an American urologist in 1966. This pathology is not a disease in the sense of the word, but its symptoms lead to the development of other accompanying diseases.
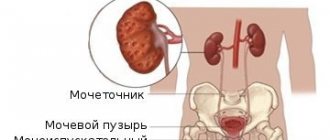
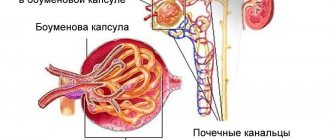
Fraley syndrome is a congenital kidney abnormality that causes the formation of stones and loss of organ functionality.
Symptoms
Frehley syndrome usually makes itself felt at an early age - with enuresis and pain.
The progression of renal vascular disease is indicated by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- pain in the kidney area (colic);
- blood impurities in urine;
- slight increase in blood pressure;
- reduction of urinary secretions.
Diagnosis of DiHS/DRESS syndrome
- maculopapular rashes that appear 3 weeks or more after the start of treatment with certain drugs;
- persistence of clinical symptoms after discontinuation of a causally significant drug;
- fever (the patient’s body temperature is above 38 °C);
- liver pathology (AlAT> 100 U/l);
- the presence of at least one of the following altered hematological parameters: a) leukocytosis more than 11 x 10 (to the 9th degree)/l; b) atypical lymphocytes over 5%; c) eosinophilia more than 1.5 x 10 (to the 9th power)/l;
- lymphadenopathy
- HHV6 reactivation (first degree).
With all seven signs, a typical form is diagnosed; the combination of the first five criteria indicates an atypical form of DiHS/DRESS syndrome. If HHV6 reactivation cannot be determined, the diagnosis of DiHS/DRESS syndrome is considered probable and requires exclusion of other diseases.
Features during pregnancy
After identifying the pathology, it is necessary that during pregnancy and childbirth, the patient be under the strict supervision of a doctor. Women who are sick with Fraley syndrome or any other congenital renal pathology can bear a fetus only after surgery. Surgery is necessary to normalize blood pressure. Without such treatment, pregnancy is very difficult to endure. During the period of pregnancy, a woman must undergo periodic diagnostics.
If complications of Frehley syndrome are observed in a pregnant woman, she will be hospitalized. Most often, complications of the pathology resolve at 15-16 or 26-30 weeks of gestation. At 30 weeks, an exacerbation is caused by the rapid growth of the uterus, which at one time puts pressure on the ureters. Symptoms of exacerbation:
- severe swelling of the limbs;
- retention of urine discharge;
- pain when removing urine from the body.
Childbirth with renal anomaly
In most cases, Frehley syndrome in women in labor indicates a cesarean section. In this case, there is no danger to the child. For pregnant women who have this pathology, special maternity hospitals are equipped, where urologists and nephrologists are required to work. In such a medical institution, a newborn child will undergo a full diagnosis of the body.
Causes of the disease
Causes of Frehley syndrome Since this pathology develops in the womb, it is difficult to talk about the causes of its occurrence. Scientists have only assumptions regarding what may provoke this anomaly:
- genetic factor (presence of Frehley syndrome in one of the relatives);
- other genetic pathologies (failure at the chromosome level, gene mutation);
- the influence of external factors on a pregnant woman (harmful environment, radiation, unsuitable climatic conditions);
- infectious and acute inflammatory processes in a woman’s body during pregnancy;
- taking illegal drugs by a pregnant woman;
- maintaining an inappropriate lifestyle during pregnancy (smoking, drinking alcohol or drugs).
Symptoms of Failey's syndrome
Symptoms of Frailey's syndrome are difficult to associate with the pathology itself - most likely they are a consequence of its effect on the kidneys. Symptoms characteristic of this anomaly are:
- nagging pain in the area of the affected kidney or throughout the lower back (in cases where the pathology is observed in both kidneys at once);
- sharp, shooting pains in the kidneys (renal colic, resulting from the formation of kidney stones);
- the presence of traces of blood in the urine (macrohematurgia - traces of blood are visible to the naked eye, microhematurgia - blood is visualized only under a microscope);
- renal hypertension - increased renal pressure.
There are several indicators that lead to impaired blood supply to the kidneys and the development of the disease:
- heredity along the genetic line - pathologies of the renal vascular system that are transmitted to future generations, abnormalities in the structure of chromosomes, gene mutations;
- congenital abnormalities formed during intrauterine development - the formation of internal organs and systems of the fetus;
- the use of medications during pregnancy, aimed at reducing blood pressure by relaxing the walls of blood vessels, during the formation of the child’s genitourinary system;
- environmental conditions in which the pregnant woman was: elevated air temperature, environmental pollution, hazardous work conditions, prolonged exposure to radiation;
- drinking alcohol, smoking, taking drugs by the expectant mother;
- acute infectious and viral diseases of the mother.
The clinical manifestations of the disease are associated with its pathological effect on the kidneys. The characteristic symptoms of this anomaly are:
- decreased amount of urine excreted;
- nagging pain in the lumbar region on one side with damage to one of the kidneys, girdle pain with pathology of both organs;
- sharp cutting pain in the kidney area due to the formation of stones in them;
- the appearance of blood formations in the urine, which can be quite voluminous, which are visible visually, or very small, which can only be seen under a microscope;
- slight increase in blood pressure.
These symptoms can appear individually or in combination.
Diagnostic measures
Frehley syndrome is confirmed based on the results of a hardware examination of the kidneys.
Symptoms of Frehley syndrome are also inherent in other diseases that may not be related to the urinary system. To determine the disease and determine the cause of development, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis. In addition to the usual tests, you need to carry out a number of other procedures that will help you find out more information about the patient’s condition:
- X-ray of the organs of the excretory system.
- Excretory urography. A study for which it is necessary to inject a contrast agent into the patient’s vein. Next, an x-ray is taken and it is used to determine the functioning of the kidneys.
- Ultrasound analysis. One of the most accurate methods that helps to determine disorders in the structure and functioning of the urinary organs.
- CT scan. Provides a three-dimensional image of the kidneys and blood vessels that belong to the organ.
- Renal angiography. The most effective study that helps clarify the established diagnosis.
- Dopplerography and multislice computed tomography. The research methods that are used in pediatrics are among the most accurate diagnostic measures.
Renal angiography is strictly prohibited for use in children.
Fraley syndrome - kidney anomaly on the left and right: description
Description of Frehley syndrome
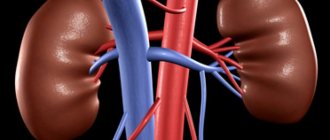
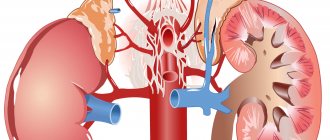
- Fraley syndrome is a pathology characterized by a disorder of the structure of the vascular system of the kidneys.
- This disorder consists of crossing the anterior and posterior branches of the superior renal artery.
- In this condition, compression of the renal pelvis or the ureteropelvic region may occur.
- Compression of the pelvis can lead to overflow of the renal calyces with urine, which subsequently leads to stagnation of urine and various diseases of the urinary system.
- Most often, Frehley syndrome refers to either the right or left kidney. But there are cases when an anomaly is observed in both paired organs.
- The syndrome itself is not classified as any type of disease, but over time it can lead to a number of kidney diseases and pathologies.
- The syndrome owes its name to the American scientist Fraley, who discovered and described this phenomenon in 1966.
Treatment of pathology
Although Frehley syndrome is a congenital kidney defect, it can be cured. It is not enough to relieve the symptoms, because the disease and complications will progress and may become chronic. The most effective treatment method that can ensure a healthy and happy life is surgery. But there are cases when it is impossible to perform a surgical operation due to the age or health of the patient. Then doctors choose other treatment methods.
Drugs for Frehley syndrome
To treat Frehley syndrome, diuretics and vitamins are prescribed.
The most effective medicines include:
- "Dapril" - normalizes blood pressure and improves blood flow in the kidneys;
- "Renipril" - has pronounced antihypertensive and diuretic effects.
There is no harm in taking vitamins A, C, D, and medications that prevent the formation of kidney stones and sand. Doctors recommend being careful when taking vitamin supplements because they can cause kidney stones, especially if the patient is predisposed to the disease.
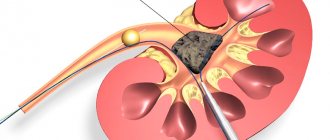
Surgery
Surgical operations that are used to treat Frehley syndrome are classified as plastic procedures performed on the upper urinary tract:
- infundibuloplasty;
- infundibuloanastomosis;
- infundibulopyeloneostomy;
- calikipyeloneostopia.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
To relieve renal colic, which occurs due to kidney stones, you should take hot sitz baths and place a warm heating pad on the lumbar region. All procedures must be performed under the supervision of the attending physician. It is forbidden to use this method for patients with acute kidney inflammation. For pain relief, you can resort to electropuncture and acupuncture. In the fight against high blood pressure, inductothermy, galvanization, magnetic therapy and amplipulture therapy will be effective.
Recipes from the people
Infusions and herbal decoctions improve the condition of patients with Frehley syndrome.
To combat high blood pressure in the kidneys, it is recommended to take an infusion of dill seeds.
To prepare the drink, grind the plant and pour in 1 teaspoon of seeds and 300 ml of boiling water. Should be consumed 3 times a day before meals. For inflammatory processes, it is useful to take a decoction of nettle, plantain, chamomile, St. John's wort and other plants. To forget about renal colic, you need to make lotions and compresses from an oil solution of mint, lemon balm and chamomile. Flax seed tea will help in the fight against kidney stones. To prepare you need to pour 1 tsp. a glass of boiling water and take half a glass every 2 hours for several days.
What to do?
What does all this mean for parents and their children? Should they avoid not only aspirin, but also other medications for the flu? Should this also be done for other viral infections?
First of all, there is no need to panic. Apparently, the likelihood of getting Reye's syndrome is not for everyone, but for those who have congenital problems with mitochondria. True, in victims of this disease they were usually hidden before its development. Is it possible to somehow identify them in this state? No, but there are signs that make them more likely. This happens if blood relatives in the family had or have congenital problems with metabolism or mitochondrial dysfunction. In the same way, special care should be taken if among such relatives there were hereditary encephalopathies (brain diseases) or other brain diseases. Many of them can be accompanied by problems with mitochondria.
Article on the topic
And wash, and lose weight.
Non-standard ways to use aspirin Secondly, the use of aspirin and other antipyretics in children is best avoided and non-drug methods of reducing fever are used more often. To do this, it is often recommended to wipe the skin under the arms and in the popliteal fossae with vinegar. But the famous pediatrician, advisor to the director of the National Medical Research Center for Children's Health, Professor Vladimir Tatochenko has a different opinion on this matter: “Under no circumstances use vinegar, forget about it, there will definitely be some mother who uses vinegar essence instead, and there will be a burn.” .
Ordinary lukewarm water is much more effective than vinegar. And you need to wet the entire surface of the body. At the same time, the child must be kept open in a room without drafts and with normal air temperature to avoid hypothermia. You can lubricate your skin with vodka in the same way. The treatment is based on the fact that alcohol and water, evaporating from the skin, take away heat and thereby reduce the temperature.” Thirdly, if the child tolerates the temperature satisfactorily, then it does not need to be reduced to 39 degrees. If it does come down to the need to take antipyretic drugs, then it is better to give children drugs with ibuprofen or paracetamol.
Classification
The syndrome has 4 main forms depending on the course:
- chronic;
- acute;
- full;
- partial.
Determining the disease by its source of formation, doctors identified congenital and acquired forms.
Rotations and fixations of the intestine are divided into three main types of pathology:
- nonrotation - intestinal volvulus;
- incomplete rotation – intestinal volvulus, duodenal obstruction and internal hernia;
- incomplete fixation – internal hernia, inaccessible intestinal volvulus.
Differential diagnosis of DiHS/DRESS syndrome
The diagnosis of DiHS/DRESS syndrome depends on the stage of the disease. In her debut it is carried out with:
- viral and bacterial diseases (infectious mononucleosis, measles, rubella, infections caused by enteroviruses, adenoviruses, HHV6, HHV7, EBV, CMV, parvovirus B19, acute febrile phase of HIV infection, scarlet fever, secondary syphilis, etc.);
- various manifestations of drug hypersensitivity (serum sickness and serum-like syndrome, exudative erythema multiforme and other drug maculopapular exanthemas, with Stevens-Johnson syndrome, drug-induced erythroderma, acute exanthematous pustulosis);
- graft versus host reaction.
At the stage of multiple organ symptoms and high blood eosinophilia, the differential diagnosis must be made with:
- idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome;
- Charge-Ostrich vasculitis;
- lymphomas.