If protein and leukocytes are in the urine
are in increased content, this may be a sign of the development of serious pathological diseases. Urinalysis is a basic laboratory test designed to diagnose various diseases. From its composition you can read about the functioning of the kidneys and the condition of the urinary tract.
When carrying out the analysis, such features as color, smell, transparency, density, and acidity are taken into account. Each of these indicators has its own norms and deviations. And they also talk about the presence of certain diseases or changes occurring in the body.
Properties of leukocytes and their norm
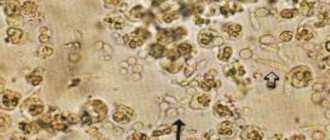
The role of leukocytes in the body cannot be underestimated. These white blood cells are the main defenders of humans. They recognize bacterial flora and neutralize it. A pathological increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine is called leukocyturia in medicine. It develops when there are too many dangerous bacteria in the body. During this period, the synthesis of white cells increases, they quickly move to the site of inflammation, penetrating through the walls of the capillaries. Protective cells absorb foreign bacteria and, after a significant increase in size, are destroyed.
This type of leukocyte is called phagocytes, which translated from Greek means “devouring cells.” The dead white cells turn into pus, causing local inflammation of the surrounding tissues. Elevated white blood cells in urine indicate the formation of a focus of infection in the kidneys or urinary tract. The norms for the content of these cells in the urine differ in different categories of people:
- men, from 0 to 2–3;
- women, 0 to 6;
- girls, up to 10 in sight;
- boys, no more than 7;
- pregnant women, from 0 to 5.
The difference between the values is due to the structural features of the genitourinary system. In women, the risk of urine infection is higher due to the close proximity of the urethra and vagina.
Important! During pregnancy, physiological leukocyturia may develop with an increase in the number of leukocytes to 15 in the field of view. Experts believe that this is due to changes in the woman’s body and should not cause concern, but to exclude pathology, a control ultrasound of the kidneys should be done.
Nitrites
In a healthy person, there are no nitrites in the urine; they are nothing more than nitrogen salts. They are formed from nitrates under the influence of certain bacteria. Nitrates, in turn, appear in the human body through the consumption of food products (cucumbers, tomatoes, grapes). Further, nitrates are decomposed to nitrites with the help of pathogenic bacteria. Thus, if a person does not have pathogens, then there are also no nitrites.
The presence of nitrites in urine indicates the proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the urinary system. The presence of such substances in the ureters is especially dangerous, since it is with this localization that it is difficult to fight them.
Such nitrogen compounds can cause irreparable harm in pregnant women; they have a detrimental effect on the fetus.
The triggering factors for the formation of nitrites are:
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- prostatitis.
The role of proteins and limits of content in urine
Protein (protein) is the basis of life. It is involved in the transport of nutrients, the formation of immunity, metabolic processes and cell synthesis. Without proteins, the body will not receive the necessary amino acids, which are released as a result of the hydrolysis of this component.
Protein enters the urine when the filtering ability of the kidneys is impaired. It penetrates through the affected tubules and glomeruli, which normally should create a natural barrier and return proteins to the blood. When protein in the urine increases, proteinuria is diagnosed.
For women and men, the protein norm is up to 0.033 g/l in a single morning portion of urine and no more than 150 mg in all urine collected per day. In children, the protein norm in the general analysis should not exceed 0.036 g/l, and in the daily analysis 0.06-0.09 g/l. During pregnancy, the norm does not differ from that of ordinary women. But by the end of the third trimester, the level may increase slightly (up to 0.14 g/l) due to increased load on the excretory organs.
Critically elevated protein manifests itself:
- swelling;
- sweating;
- fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- digestive disorders;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- hypertension.
With a simultaneous increase in protein in the urine and leukocytes in the urine, clinical manifestations intensify. Fever of varying degrees, headache, general malaise and body aches develop. This is due to the presence of an inflammatory focus and the development of intoxication against the background of infection.
On a note! Normally, protein leaves the bloodstream in minimal quantities or is not excreted from the body at all. Therefore, the best result of a protein test is a zero value or a mark indicating traces of albumin.
Rules for collecting urine for laboratory tests
To accurately diagnose the parameters of proteins, red blood cells and leukocytes, there is a preliminary stage of urine collection. During pregnancy, monitoring the amount of protein is necessary; testing is prescribed before each visit to the doctor. To get reliable results follow simple rules:
- The day before the test, you should avoid salty and spicy foods, and do not overuse sweet and sour foods. Following a diet will help establish reliable data.
- To collect urine, use only a sterile jar; special containers can be purchased at pharmacies. If this is not possible, then treat the glass jar with boiling water.
- Urine is collected in the morning after sleep; the collection should not contain impurities.
- Doctors recommend taking a shower before getting ready; this approach will reduce the risk of foreign protein getting in.
- The collected analysis is delivered to the hospital no later than 2 hours after the procedure.
- In cold weather, the flask with urine should be wrapped to prevent it from freezing.
The result of the study allows you to monitor the functioning of the kidneys and bladder. The indicators are especially important for pregnant women, whose fetal development increases the load on the genitourinary system.
Causes of increased leukocytes and protein
The etiology of the simultaneous development of leukocyturia and proteinuria most often lies in kidney damage. All inflammatory diseases of this paired organ are called the general term nephritis. Its varieties include glomerulonephritis, pyonephrosis, tuberculosis and pyelonephritis. With nephritis, proteins and leukocytes are found in the urine in moderate or increased quantities, depending on the stage. The diseases differ in clinical presentation and location of the source of inflammation. They can occur in acute or chronic form.
Types of pyelonephritis
Kidney infection or pyelonephritis can be expressed in uncomplicated, complicated or chronic forms. Complicated pyelonephritis refers to diseases that are accompanied by the risk of severe infections and ineffective treatment. Severe kidney damage may occur, including an abscess (suppuration), kidney enlargement or swelling, which can be detected by computed tomography. This type of pyelonephritis is usually caused by urinary tract abnormalities, blockages, and diabetes. In these cases, treatment of pyelonephritis is very difficult.
Chronic pyelonephritis is a condition where the disease constantly returns. This may be the result of kidney stones, blocked ureters, and other structural abnormalities (such as vesicoureteral reflux, in which urine moves back toward the kidneys). Chronic conditions usually present with mild symptoms but last much longer. Evaluating complicated kidney infections or chronic kidney disease usually requires advanced tests and scans, including CT scans and X-rays.
Acute and purulent inflammation of the kidneys
Acute nephritis is the main cause of increased proteins and leukocytes in the urine. This is an intense inflammation of the parenchyma of the paired organ, glomerular vessels and tubules. The etiology of acute nephritis is associated with the penetration of bacteria into the kidneys. Most often, the causative agent is streptococcus, which initially causes a sore throat or flu, and then affects the urinary organs.
Sometimes the infection comes from neighboring areas due to cystitis or urethritis. Less commonly, the cause is pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases and bacteria of the genus pneumococcus and staphylococcus. Foreign flora destroys the structure of the renal tissue, increases vascular permeability and promotes the formation of purulent foci. This explains the penetration of protein and leukocytes into the urine. Purulent lesions can also develop due to urolithiasis. In this case, treatment is only surgical.
On a note! Acute nephritis predominantly affects young patients under 30 years of age and children.
Clinical manifestations
An acute form of inflammation in the kidneys develops over several days, and sometimes hours. Symptoms are always striking and are accompanied by a decrease in the amount of urine excreted.
Among the main clinical manifestations:
- fever up to high levels;
- unbearable pain in the lumbar back;
- swelling;
- chills;
- tachycardia;
- headache.
Urine takes on an unnatural color. May be cloudy, whitish, brown, or contain flakes or streaks of blood. The number of leukocytes increases as it progresses, and the daily loss of protein exceeds 150 mg. With prolonged failure to provide assistance due to the toxic effects of bacteria, symptoms of heart failure (shortness of breath, cyanosis of the lips, pain in the heart) appear.
Classification of proteinuria
There are 2 classifications of this pathology.
Proteinuria is divided into:
- prerenal (associated with increased tissue breakdown);
- renal (due to kidney disease);
- postrenal (the pathological process is located in the urinary tract).
There are two types of renal proteinuria:
- tubular (based on a change in the normal process of reuptake of low molecular weight protein units);
- glomerular (if the filtration system of the glomerulus of the kidney is damaged).
Chronic nephritis
It is distinguished by the presence of an erased form and the need for long-term therapy. It occurs with periods of remissions and exacerbations. During an attack, the clinical picture corresponds to acute nephritis.
After relief of inflammation, most patients retain a number of symptoms:
- persistent hypertension;
- loss of appetite;
- nagging pain in the lower back;
- low-grade fever (not higher than 37.9);
- evening swelling.
Over time, complexion changes. The skin becomes dry, acquires an earthy tint, and there are dark circles under the eyes. Urine tests retain a moderate amount of protein and leukocytes, and red blood cells are periodically detected.
Attention! Chronic nephritis most often results from insufficient treatment of the acute form, with incomplete destruction of the infectious agent.
Indications for protein testing
The doctor will recommend this study when the following clinic appears in an individual:
- abnormal swelling;
- chronic anemia;
- pain in bones and joints due to protein loss;
- sudden attacks of loss of consciousness and dizziness;
- drowsiness, lethargy, constant weakness;
- cramps, muscle spasms;
- numbness of fingers, tingling;
- nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, loss or, conversely, increased appetite for no reason;
- attacks of chills or fever;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- pain, discomfort, itching, burning during urination.
In addition, a general urine test for protein is indicated for:
- Diabetes mellitus (diagnosis and treatment monitoring).
- When registering at a dispensary, including during pregnancy.
- Diagnosis of the genitourinary system, multiple myeloma.
- Prolonged hypothermia of the body.
- Oncology of the genitourinary system.
- Systemic diseases of acute and chronic nature.
- Extensive burns and injuries.
Changes in characteristics such as sediment, daily volume of urine, density, odor, sediment, transparency, and the appearance of blood are also indications for this study.
Treatment tactics
If a urine test reveals a lot of proteins and at the same time leukocyturia is diagnosed, the doctor prescribes an additional examination. The cause is usually identified after an ultrasound scan of the kidneys and a 24-hour urine sample. It is also necessary to decipher the leukocyte formula of the blood to exclude appendicitis and systemic diseases. After the diagnosis is established, antibacterial drugs are prescribed in combination with vitamin therapy and physiotherapy.
Patients are advised to maintain fluid balance and a low-salt diet. This regime must be maintained for at least a month after the tests become normal. In the future, you need to avoid hypothermia, try to get rid of bad habits and not drink alcohol. In children, the disease can be prevented by thoroughly sanitizing foci of infection and hardening the body.
The detection of protein and leukocytes in urine does not always mean pathology; it all depends on the number of cells. Slight shifts in the direction of increase without clinical manifestations may be a consequence of the influence of physiological factors. These changes are temporary and do not threaten health. You need to be alarmed if the level of protein and proteins is significant and is accompanied by characteristic symptoms of inflammation in the kidneys.
Treatment, stabilization of general indicators
The content of red blood cells in the urine and the detection of protein require further treatment and correction by the attending physician. It is unacceptable to treat abnormalities at home if there are abnormalities in the tests; for a pregnant woman, the protein level is a decisive indicator for the development of the unborn child. Traditional methods of treatment without consultation with a therapist can only do harm; to eliminate deviations, it is important to determine the cause and treat the disease.
The treatment consists of a set of procedures, which the doctor will help you combine:
- create the right diet;
- use physiotherapy;
- treatment with medications;
- surgical intervention.
The presence of bacteria in the urine indicates the need for antibiotics. The presence of oncology means immediate hospitalization and surgical intervention. Pain in the lower abdomen, changes in urine density and color indicate dysfunction; after detailed diagnosis and determination of the causes of this condition, treatment and correction of indicators follows.
How to diagnose the presence of nitrites?
If everything is clearer with the diagnosis of leukocytes and proteins, then the issue of nitrites is not so transparent. The standard method for determining such substances is a general urine test. But besides this, there is also a home method using litmus strips, which give a reaction to nitrites. They are very easy to use, just dip them in urine and watch the paper change color. There are also disadvantages to this method: it cannot determine the localization of bacteria and reacts exclusively to strains that form nitrites.