A story about urolithiasis, about changes in the concentrations of the main substances responsible for the formation of stones will be incomplete if, after uric acid, a story about coral stones, oxalates, the general clinic of urolithiasis, one does not mention the excretion of phosphorus in the urine, and does not tell why phosphates are formed in the urine of adults and children.
Surprisingly, the causes of high phosphate in the urine can be diametrically opposed. For example, if a person has too much phosphorus and its compounds in his blood, then there will be a lot of it in his urine, because the excess phosphorus needs to be eliminated. Healthy kidneys can cope with this. But there is a situation where there is a lot of phosphorus in the urine, but, on the contrary, there is too little phosphorus in the blood, since almost all of it is excreted from the body.
In the first case we are talking about hyperphosphatemia, an excess, and in the second - about hypophosphatemia, a deficiency. And in the urine, in both cases, phosphorus is high. In order to understand the features of these conditions, let us first recall the role of phosphorus in the human body. After this, it will become clear why phosphates appear in the urine and how to deal with their excess.
Why is phosphorus needed?
Unlike oxygen, hydrogen, carbon and nitrogen, which are the main building elements of the body, phosphorus is a microelement. There is not much of it in the body, but without it the human “energy economy” is impossible.
All molecules that store a large amount of energy, “battery molecules,” have special bonds that contain phosphorus residues. ATP, or adenosine triphosphoric acid, and the high-energy compound creatine phosphate can be considered such a universal energy donor. A lot of energy is stored in phosphoric acid residues.
Phosphorus is part of the structure of proteins that form cell membranes; such compounds are called phospholipids. Without phosphorus, the existence of numerous specific membrane receptors, and even nucleic acids that encode hereditary material and are the basis of life, is impossible.
Without phosphorus, the existence of the internal skeleton and teeth would be impossible, since their basis is calcium hydroxyapatite, which also contains phosphorus. Additionally, it can be recalled that some phosphoric acid compounds are involved in maintaining blood pH, that is, the acid-base state due to the work of the phosphate buffer. Therefore, the regulation of the metabolism of this element, with such a large number of diverse reactions and molecules, cannot be considered simple either.
The system for regulating phosphorus metabolism includes parathyroid hormone, which is produced by small parathyroid glands, as well as vitamin D. Without these two substances, proper absorption of phosphorus, its deposition in bone tissue, reabsorption or mobilization, and its return to the blood from primary urine is impossible, or reabsorption in the kidneys. Therefore, phosphorus metabolism is most often disrupted in diseases of the parathyroid glands, kidneys, and bone tissue.
It should be added that the antipode-antagonist, which is closely associated with phosphorus metabolism, is calcium. Therefore, calcium-phosphorus metabolism can be considered a single, inextricable part of metabolism.
Diet
If phosphates are present in large quantities, the diet must be strict. It is mandatory to adhere to the drinking regime - drink at least two liters of clean water during the day. You should not eat food that contains a lot of calcium oxalates - offal, meat and fish broths, herring, jellied meat, lettuce, spinach and sorrel. Minimize in the diet: smoked, spicy, salty foods, vinegar, horseradish, mustard.
Recommended topic:
Treatment and dissolution of oxalate kidney stones
Limit: fried foods, especially meat, eggs, caviar, flour products.
What you can: fresh fruits and vegetables, lemon, mushrooms of any kind.
Be sure to exclude alcoholic beverages, regardless of their origin. Also, do not consume carbonated drinks, lard, or sausages.
As a drink for daily use, you can use the folk recipe for rosehip decoction.
Rosehip decoction
Phosphorus in daily urine
Naturally, phosphorus in urine does not exist in the form of an active element, and urine does not glow from phosphorus, but in the form of phosphoric acid compounds, or phosphates. Phosphates in urine have such synonyms as simply phosphates, inorganic phosphorus or PO4. They are examined by taking daily urine, and an analysis is given in millimoles per day.
The presence of phosphates - crystals in the urine or amorphous phosphates in the urine is examined using the colorimetry method using ammonium molybdate.
The loss of phosphorus by the body must be examined in daily urine, and giving a single portion of urine is completely pointless: phosphorus does not penetrate into the urine in the same concentration throughout the day. Its content in urine varies widely, on average by 50%, and therefore it is possible to make a double error in the final result using only one portion of urine.
In addition, the concentration of phosphates in the urine varies depending on the nature of the diet. If a person consumes a large amount of carbohydrates, then phosphorus is retained in the body, redistributed inside the cells, and its concentration in the blood plasma, and accordingly in the urine, will decrease.
Let's figure out what are the causes of excess phosphates in the urine in adults and children. But first, let's talk about the normal values of urine phosphorus, and when the doctor prescribes this test.
Phosphaturia during pregnancy
This is a common occurrence for women during this period. Salts in the urine are more often found during toxicosis in the early stages of pregnancy and at the end of the last trimester. With frequent vomiting and nausea, a woman has to reconsider her diet. Often food becomes of the same type, which creates conditions for the precipitation of phosphate salts.
Phosphaturia in pregnant women can occur due to problems with the urinary system. The patient needs to see a nephrologist and have an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder done. It is important to eliminate the inflammatory process in a timely manner in order to prevent the infection from spreading further and not affecting the development of the fetus.
On a note! Pregnancy is accompanied by an increase in progesterone levels. The hormone relaxes muscle tissue, causing urine to stagnate longer in the bladder and increasing salt concentration. Women are advised to move more and strengthen their pelvic muscles with special exercises.
Norm
The concentration of phosphorus in urine varies with age. The lowest value is in infants, and this is understandable, since they have neither teeth nor a well-developed, ossified skeleton, which contains a large amount of hydroxyapatite. That's why:
- in children under one year old, the limit of phosphates in daily urine should not exceed 15 mmol;
- in a four-year-old child – no more than 25 mmol;
- from 4 to 7 years of age, this limit is 30 mmol per day;
- in adolescents under 14 years of age - no more than 40 millimoles per day;
- a person over 14 years of age, and into old age, usually has a constant concentration of phosphates in the urine, which does not go beyond 13 to 42 mmol in daily urine.
Indications for the study
If the study of phosphorus in the blood plasma reveals little of it, then there is the phenomenon of hypophosphatemia. If the excretion of phosphorus by the kidneys is high, this means that the kidneys are sick, and they cannot maintain the normal concentration of phosphorus in the urine, removing it from the blood. At the same time, this study can also exclude dietary phosphorus deficiency if its concentration in the urine is too high.
This study also indicates that there is no tissue redistribution of phosphorus; these last two reasons can only exist with normal values of daily urine phosphate. In a healthy person, the renal tubules almost completely remove phosphorus from the primary urine and return it to the blood. Recall that excess phosphate in the urine is called phosphaturia, and the loss of phosphorus in the urine increases when the renal tubules no longer cope with their function.
Most often, the work of the renal tubules in phosphaturia is affected not by their necrosis or necrosis, but by an excess of parathyroid hormone, which is produced far from the kidneys, in the parathyroid glands located in the neck.
Looking ahead, let's say that the cause of phosphates in the urine in adults is most often tumors of the parathyroid glands, which produce the hormone, or a tumor of another location that produces a special protein, the so-called parathyroid hormone-related protein. For example, with squamous cell lung cancer the phenomenon of phosphaturia can develop precisely for this reason.
It is much easier for a doctor to “miss” chronic phosphaturia in an adult, since there are no special complaints or clinical picture, except for weakness and pain in the muscles, and even then not in all of them.
Phosphaturia in a child is much easier to diagnose. If phosphates are found in the child’s urine in excess quantities, this can ultimately lead to rickets. Therefore, if a pediatrician sees a child’s growth retardation, the presence of bone tissue deformation, insufficiency of ossification nuclei on x-ray, blurring of metaphyses and pathological fractures, then this is also a reason to examine urine for phosphorus, where, most likely, in addition to phosphates, microscopy of the sediment will reveal amorphous crystals in the child's urine.
It has a strong effect on the absorption of phosphorus in the small intestine and vitamin D. Therefore, if a child has already been diagnosed with rickets and has been treated, then testing for phosphorus in the child’s urine is a good way to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for rickets. If phosphates in a child’s urine increase, this means that he is prescribed too much vitamin D, which is in excess, and the doctor can adjust its dose downward.
Agree that urine testing is much more comfortable, convenient and completely non-traumatic for a child, unlike taking blood, which turns into a tragedy every time.
As already mentioned in the preface, there may also be an increased content of phosphates in the blood, that is, hyperphosphatemia. In this case, phosphorus may be excreted in the urine in large quantities, trying to reduce this concentration, which will indicate healthy kidneys working at the limit. But it happens that the kidneys are damaged and they cannot remove phosphorus, and hypophosphaturia occurs. This low urinary phosphorus concentration indicates that extrarenal disease is unlikely to be the cause.
Typically, extrarenal causes of high phosphorus in the blood include massive muscle breakdown, or rhabdomyolysis, prolonged high temperature, fever or hyperthermia, and the development of metabolic acidosis in severe diseases.
With low phosphorus in the urine, the most common cause is chronic renal failure. But if we still talk about extrarenal mechanisms, then this is a lack of function of the parathyroid glands, or hypoparathyroidism. A large amount of phosphates in the blood gradually leads to calcium phosphate salts settling in the organs, and various calcifications are formed.
They most often form in the heart, lungs and kidneys. Therefore, if during a standard ultrasound of the patient’s kidneys, or on an X-ray of the lungs, any shadows or stones were detected, then a daily urine phosphorus test should be prescribed automatically.
Naturally, the doctor will prescribe a phosphorus test if there is a suspicion of urolithiasis in the form of renal colic, if visible stones are passed in the urine, and for other similar conditions.
Diagnostics
In order for the analysis to be as accurate as possible, several rules must be followed. So, it is recommended not to eat salty or spicy foods, as well as sweets, alcohol, and smoked foods a couple of days before the analysis. In addition, you should not smoke (dehydrates).
Other tests will also be needed:
- urine culture;
- X-ray;
- ultrasonography;
- blood phosphate test.
Before the tests you need to refrain from serious physical activity. They also affect the composition of urine.
Definition and Causes
In this section we will talk about phosphaturia, that is, excess phosphorus in the urine, and what it can be.
Surprisingly, urine is a unique liquid that cannot be obtained in inanimate nature. Poorly soluble compounds, which include phosphates and phosphoric acid salts, are or can be found in the urine in such a high concentration that several times exceeds their maximum solubility in water. How is this possible? How can urine, being water enriched with salts, deceive nature?
This possibility is associated with the high alkaline reaction of urine, and with the presence of special protective colloidal proteins that can keep poorly soluble lime phosphate salts in dissolved form. But humans are not the leader here, since the greatest ability to dissolve phosphates in urine is possessed by herbivorous ungulates, whose urine is always alkaline. The urine of people who have been on a vegetarian diet for a long time can be compared with the urine of herbivores in terms of alkaline capacity.
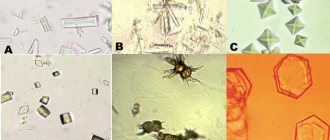
How often does it happen that there is a lot of phosphate in the urine, both crystals and amorphous salts? Here are the statistics. Oxalaturia, or calcium release, is 85% of all cases, and phosphaturia accounts for 10%. However, one should not think that calcium phosphate is released exclusively in pure form. Most patients with excess phosphorus in the urine excrete it not only in the form of calcium phosphate, but also with calcium oxalate, that is, oxaloacetic salt. In the case of high concentrations of uric acid, the remaining small percentages account for, together with cystinuria.
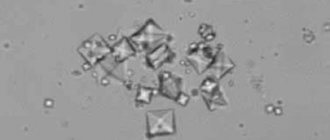
In addition to amorphous phosphates, so-called tripelphosphates can also be observed in the urine. What it is? This is a crystalline phosphate, in which, in addition to calcium and phosphorus, there are also magnesium and ammonium ions, that is, NH4, which give an alkaline reaction to the urine. They are clearly visible under a microscope, and after centrifugation, sometimes the entire field of view is completely occupied by these crystals.
In the previous section it was said that phosphaturia may be associated with changes in the concentration of phosphorus in the blood plasma, or with kidney pathology. Such conditions are called primary, or true phosphaturia. It is quite possible that the parathyroid glands work well, the person does not have any oncology, he does not have kidney pathology, renal failure or tubular necrosis, and he has a lot of phosphorus in his urine. Why?
Urological pathology or a chronic infection of the genitourinary system, for example, long-term chronic pyelonephritis, is to blame. Reproducing microorganisms have high urease activity and produce the enzyme urease. It decomposes urea, and as a result, the urine begins to alkalize. In the article about the dissolution of urinary stones, we wrote that alkalization of urine leads to the dissolution of urates, but if you overdo it a little with medications, the urine reaction will become so alkaline that, despite the dissolution of urates, it will begin to precipitate phosphates, which are even more difficult to dissolve , than urates.
This is precisely the situation, “woe from mind,” that occurs in the case of a chronic infection: the patient does not seem to have any signs of urolithiasis, does not take alkalizing drugs, but microorganisms are to blame for the excess of alkaline urine. It is enriched with magnesium ammonium phosphate, so-called struvite stones, which are markers of kidney infection. If struvite stone combines with carbon dioxide apatite, then the same tripolyphosphate will appear.
How to translate all this chemical wisdom into simple language? Very simple. If we talk about adults, phosphaturia is most often observed in patients with long-term diabetes mellitus, alcoholism and the presence of a chronic urinary infection. Many amorphous crystals in the urine appear as cloudy, milky white urine. These are all salts of phosphate of lime, which, soon after urination, immediately fall out of the urine in the form of sediment.
Old doctors have noticed that such phosphaturia can occur after the release of a large amount of acidic gastric juice, for example, when studying stimulated secretion.
Phosphaturia occurs after numerous vomitings of acidic masses, due to the loss of hydrochloric acid. Accordingly, if the body loses its acid potential, its alkaline reserve increases, and alkalization of urine leads to increased excretion of phosphates. Such frequent vomiting occurs in patients with chronic alcoholism.
In order to detect phosphates and crystals in urine, or more precisely to suspect their presence, you can carefully examine your own urine in a jar after it has completely cooled. It is then that a whitish cloudiness can be noticed, and this will be enough to collect daily urine and take it to the laboratory. How daily urine collection is carried out, and according to what rules - a separate article is devoted to this.
Also, old doctors knew the sign of phosphaturia in the form of the appearance of a very light, whitish, slightly greasy-looking, opalescent film that appears at the point of contact of the surface of cooled urine with the wall of the vessel. This film indicates a high concentration of phosphates, and its visibility increases as the sediment increases.
Let us remind you once again about the primary causes of high phosphorus in the urine, which are not related to urinary infection and poor kidney function. This:
- hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands, including their adenoma;
- metabolic acidosis, which develops with any severe multiple organ pathology, for example, with diabetes mellitus;
- bone fractures, characteristic, among other things, of multiple myeloma and oncohematological pathology;
- significant excess of vitamin D;
- Fanconi syndrome, in the case of familial hypophosphatemia;
- due to taking certain medications. These include, in addition to vitamin D, furosemide, parathyroid hormone, glucocorticosteroids, and other urine alkalizing substances, for example, excess regular baking soda to combat heartburn.
Treatment
How to treat phosphates in urine? First of all, you need to eliminate or eliminate the cases described in the previous paragraph, and then phosphorus in the urine will return to normal.
But if we are talking about symptomatic, secondary forms of phosphate crystalluria, then the treatment should be the opposite of the treatment of urate stones. Then the urine had to be alkalized, but now it needs to be acidified. For this purpose, treatment with mineral waters is used, the drugs prescribed are Cystenal, Methionine, and ascorbic acid.
It is quite possible to reduce the absorption of phosphorus and calcium in the intestine by prescribing antacid drugs, for example, Almagel is used.
If tripelphosphates or struvite stones are found in the urine, then it is imperative to treat the secondary urinary infection and sanitize the lesions in the urinary system. Rational diet therapy can be considered the basis of treatment.
Diet therapy
A diet with phosphates in the urine necessarily requires limiting the diet containing excess calcium.
- It is necessary to exclude spicy snacks, all drinks and spices that stimulate the digestion and nervous system, remove from the diet everything that causes excessive stimulation of the secretion of gastric juice and pancreatic juice. It was said above that the loss of acidity increases the alkaline reserve.
- If there is an excess of phosphorus in the urine, it is recommended to drink a large amount of liquid and administer it in the form of weak tea, fruit and berry juices.
- Limit eggs and egg dishes, as well as bread.
- Various soups, dough products, meat and fish are allowed. Vegetables should only be eaten that are low in calcium and do not contain an alkaline reserve. These include: asparagus, pumpkin, Brussels sprouts.
- Many fruits and berries, which are so useful for many diseases, should be limited, since they are precisely the source of alkalization. Perhaps the patient should be recommended red currants, sour apples and lingonberries.
However, a long and constant diet low in calcium can also be harmful. Therefore, it is still necessary to periodically add foods containing excess calcium to it for a short time. For example, break up the monotony with dairy or cottage cheese dishes, or eat cheese.
Let us once again name those products that are strictly prohibited for phosphaturia.
- This is any alcohol, both high and low strength.
- These are various sweets, candies, marmalade, chocolate.
- These are pastries and cakes, cookies and confectionery.
- All stimulating seasonings, smoked and canned foods, marinades and pickles are prohibited.
- It is necessary to limit table salt and exclude high-fat foods - fatty meats and fish, lard, cream.
- Dairy products are excluded for a time and limited due to their high calcium content.
However, it is necessary to control the amount of urine pH by periodically checking its reaction using test strips.
If a person can control the process of acidification of his own urine, then this is much better than doing it blindly. However, if a patient has phosphate kidney stones, phosphate sand is secreted, then even a single intake of sharply acidic food brings relief to such a patient, stopping an attack of phosphaturia and even renal colic.
The above-described diet, together with drinking plenty of water, warm baths, and drinking low-mineralized water such as Essentuki No. 20, helps eliminate phosphaturia and normalize the excretion of phosphorus in the urine.