Reasons for the appearance of protein in children's urine
Protein in a child’s urine in significant quantities clearly indicates serious pathologies.
What diseases does the analysis confirm:
- pyelonephritis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- excess vitamin D3;
- diabetes;
- glomerulonephritis;
- kidney injuries;
- oncological diseases of the urinary system;
- epilepsy.
Elevated protein in combination with increased leukocytes in the blood indicates a severe inflammatory process.
Against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, bronchitis, and sore throats, it is also possible for elevated levels of protein in the urine to appear. They indicate vulvavaginitis or urethritis, depending on the sex of the child.
Diagnostics
Without following strict rules for collecting urine, the results of the analysis may be blurred.
To detect protein in the urine of children, the following studies are used:
- general urinalysis (UCA);
- daily examination of urine for protein;
- analysis according to Zimnitsky;
- rapid test using special diagnostic strips;
- Nechiporenko's method.
Based on a general urine analysis, laboratory assistants calculate the protein level in the morning. How to test daily proteinuria? To establish daily proteinuria, it is necessary to collect urine for 24 hours in one sterile container intended for this procedure. You need to send a complete urine sample or a portion of it to the laboratory. Before this, the daily diuresis in ml should be determined.
To obtain reliable information about protein levels in urine, you must follow the recommendations for urine collection:
- The sample must be collected at the appropriate time of day, which is predetermined by the research method.
- Before urinating, you should wash your baby.
- The jar for collecting urine must be sterile.
- To collect daily urine from children under one year old, urinals should be used, which are sold in any pharmacy.
Additional information on the rules for collecting morning urine to determine protein in the urine, as well as the reasons for its presence in the tests, is provided by a nephrologist in the video:
Decoding the analysis according to the table:
| Protein level in urine | Characteristic |
| Up to 0.033 g/l | Protein is normal |
| Up to 0.099 g/l | Stressed renal function may occur due to stress or hypothermia |
| From 0.099 to 0.3 g/l | ARVI, cold |
| From 0.3 to 1 g/l | Moderate proteinuria. If additional signs appear, then inflammation in the kidneys may develop. |
| From 1 to 3 g/l | Significant increase in protein in urine. In this case, it is necessary to examine the baby in detail to identify the causes. |
If laboratory test results reveal an increase in protein and white blood cells in a child's urine, this may be a sign of serious diseases in the body. An increase in white blood cells is called leukocyturia .
Home testing
Test strips for determining the level of protein in urine can be purchased at pharmacies.
You can determine the level of proteinuria yourself using strips that are impregnated with a special reagent.
To do this, you should collect urine, taking into account all the recommendations, then lower the strip into it for a couple of minutes.
Express test results:
- “-”: protein is normal or completely absent (less than 10 mg per 100 ml);
- “color change”: traces of protein are detectable (10-20 mg per 100 ml);
- “1+”: moderate increase in protein (no more than 50-60 mg per 100 ml);
- “2+”: increased content (up to 100 mg per 100 ml);
- “3+” and “4+”: noticeable renal impairment.
Despite the existence of home testing, a more accurate result can be found using laboratory tests.
Table with the norms of protein in the urine of a child, depending on age:
| Age | Indicators considered normal (mg/l) |
| Up to 30 days (term birth) | 94-456 |
| Up to 30 days (premature birth) | 90-840 |
| Up to 12 months | 71-310 |
| 2-4 years | 37-223 |
| 4-10 years | 32-235 |
| From 10 years | 22-181 |
Symptoms of pathologically elevated protein
An increased amount of protein in the urine associated with diseases is accompanied by swelling of the face and / or legs. The child is pale, lethargic, refuses food and drink.
Parents should also be wary of prolonged unsuccessful attempts to relieve themselves. The baby may urinate frequently, in small portions, and complain of pain and stinging during the process.
With kidney disease, the urine becomes cloudy, its color is darker, and sometimes there is an unpleasant odor. Possible increase in body temperature. It can be either insignificant 37.5º or more critical up to 39º.
Symptoms of proteinuria
Clinical manifestations of proteinuria are nonspecific and are caused by the primary disease. Most often, high protein levels are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- drowsiness;
- poor appetite;
- high body temperature;
- pain of varying intensity in the lumbar region or abdomen;
- nausea, vomiting (babies have frequent and profuse regurgitation);
- fast fatiguability;
- swelling of the face;
- pain when urinating;
- changes in urine (red or brown, cloudy, putrid odor).
The presence of at least one symptom accompanying an increase in protein in the urine indicates the need for urgent additional examination.
When to call an ambulance
The situation may require urgent hospitalization if:
- the child has a fever (body temperature above 38º);
- severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen (in boys, spasms can radiate to the scrotum);
- the child has not urinated for 24 hours;
- severe weakness, fainting.
Be sure to inform the ambulance crew and hospital doctors on duty about the increased amount of protein in the urine. This will help make an accurate diagnosis and begin timely treatment.
In certain cases, urine becomes a “litmus” to check the baby’s health status - whether the level of protein, acetone or leukocytes is increased in it.
How to detect elevated protein levels?
In order to check whether there is protein in the child’s urine, it is necessary to undergo laboratory tests. Depending on the indications, the doctor may prescribe a general or daily analysis.
General (morning) analysis: execution rules
- The material should be collected immediately after waking up.
You should make sure that the baby does not eat or drink anything.
- Before emptying, it is necessary to perform a hygienic toilet of the genitals.
The child should be washed with warm water, using special detergents intended for children of a certain age.
Washing should be done strictly from front to back (especially for girls!).
- The container in which urine is collected must be sterilized.
It is best to purchase special sterile containers at the pharmacy.
- Urine should be taken to the laboratory no later than 2-3 hours after emptying.
Storage at room temperature longer than the specified period is not allowed!
- It is strictly forbidden to collect liquid from diapers, oilcloths, diapers!
For babies under one year old, you can buy special urinal bags at the pharmacy.
This analysis should be taken according to indications, but at least 1-2 times a year.
Daily analysis: collection rules
- Boil a two-liter jar, as well as a container with a volume of 200-250 ml (for younger children, you can use a plate).
- Explain to your child that you only need to write in a jar during the day, and then give it to your parents.
- Pour all the urine into a large jar.
- It is better to start collecting from 6-7 am. Urine is collected over a 24-hour period.
- After 24 hours, measure the amount of urine in the jar and write down the values.
- Mix the contents of the jar and pour 50-70 ml into a separate container, then deliver the material to the laboratory.
A 24-hour urine test can be prescribed to a child in cases where there are suspicions of certain diseases, for example, tumors, diabetes, pathologies of the cardiac system, etc.
Decoding the analysis according to the table
The protein indicator in the analysis results will be designated by the term PRO. If you don’t want to wait to see a doctor, you can independently determine whether your child has pathological abnormalities. To do this, just look at the values given below.
| Indicator (quantity) of protein, g/l | What does it mean? |
| 0-0,333 | Normal values |
| 0,066-0,099 | The load on the kidneys is increased. Deviation is possible due to unfavorable factors (stress, poor nutrition, etc.). A repeat test is indicated. |
| 0,1-0,2 | Moderate increase. Most often it is a symptom of respiratory infections and colds. |
| 0,25-0,3 | Increased protein content, bordering on the upper levels. An ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urine testing using the Nechiporenko method are mandatory. |
| 0,3-1 | Proteinuria. Consultation with a specialist who deals with kidney problems (nephrologist) is required. |
Home testing
You can also determine the presence of protein in urine at home using special strips soaked in a reagent. To do this, you need to collect urine, following all the rules and recommendations, lower the strip into the container for 1-2 minutes and wait for the result to appear:
- “negative result” - there is no protein in the urine or it is within normal limits (no more than 10 mg per 100 ml);
- “the strip changes color” - the protein content is from 10 to 20 mg per 100 ml, traces of protein are detected;
- “1+” - moderate increase in protein (up to 50-60 mg);
- “2+” – increased content (up to 100 mg);
- “3+” and “4+” - proteinuria, accompanied by kidney disorders.
Despite the widespread popularity of tests for home use, laboratory testing remains the most accurate.
Pay attention to erythrocytes and leucites
Protein and red blood cells. A healthy child should have no red blood cells in the urine. The presence of red blood cells (especially in combination with protein) indicates serious kidney pathologies, including kidney failure.
Protein and mucus. They are a sign of urinary tract infection or infection of the urinary system.
Protein and leukocytes. Leukocytes appear if inflammatory pathologies occur. For example, with infections of the bladder or kidneys, the number of white blood cells will exceed the permissible norm. Consultation with a nephrologist in such a situation is mandatory!
Does protein in urine always indicate pathology?
The protein is slightly elevated and we are not talking about pathology. But what does it mean? Pediatricians agree that the increase in indicators within acceptable limits occurs for the following reasons:
- prolonged stress, emotional overload;
- neuroses, psychoses;
- dehydration;
- excess protein food;
- allergies, frequent dermatitis;
- increased physical activity, active training;
- long-term use of certain medications.
If protein values are at the acceptable limit and tests detect them regularly, additional ultrasound is required.
Diagnosis of proteinuria
In young children and adolescents, the amount of protein in urine is assessed using a general urine test. It often happens that proteinuria is discovered completely by accident during a routine examination. This helps to promptly suspect a particular disease and select the appropriate treatment.
Detection of the disease at an early stage gives every chance of its rapid cure without the development of any complications.
Norms of protein in children's urine
For this analysis, the complete absence of protein is considered normal. But there are acceptable deviations. Their values depend on the age of the child.
Average values of protein levels in urine
| Values, g/l | Degree of concentration | Conclusion |
| up to 0.336 | Minimum | No treatment required, you can retake the test |
| from 0.5 to 1 | Average | Need additional diagnostics |
| from 1 to 3 | High | Treatment and full examination required |
Analysis control
It is important to be sure that the obtained analysis result is reliable. For this purpose, there are various systems for checking the quality control of laboratory research, including at the Russian level.
The test consists of determining the concentration of protein in urine with an already known concentration. The result obtained is compared with what should have happened. And a conclusion is drawn about whether it is possible to use this method for use in determining protein in urine.
Elevated protein in infants
80% of newborns have increased protein in the urine; this is associated with physiological immaturity. The phenomenon is not considered a pathology if the values do not exceed 1 g/l.
In infants, slightly elevated values are often associated with overeating. An excess of mother's milk or formula, or, at an older age, vegetable or meat complementary foods provoke the situation. It is important to adjust your diet.
Protein in the urine of a baby may appear during increased emotional stress, fear, or hypothermia, but in small quantities. In this case, you need to adjust your daily routine.
It is important to understand that indicators above 1 g/l indicate pathology and additional examinations are necessary.
Kidney disease is common in infants if:
- pregnancy proceeded with complications;
- there is a hereditary predisposition to pathology;
- birth injuries, hypoxia during childbirth.
Infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy also increase the risk of kidney pathologies.
The most convenient way to collect urine from infants is to use a urinal. A special sterile bag is attached to the child’s genitals. The pharmacy sells universal models or special ones for girls and boys.
How to collect the analysis correctly?
Capacity
To collect urine, you need to prepare a sterile, dry container. A container from a pharmacy is ideal for this. If it is not possible to purchase it at the pharmacy, a glass baby food jar will do, which must first be sterilized.
A urinal bag is suitable for babies. It is convenient to collect urine in it without waiting for the moment of “starting the stream”.
Diet
To avoid the effect of a high-protein diet on the level of protein in the urine, you need to monitor your diet for a couple of days. There are specific standards for protein consumption depending on a person’s body weight, level of physical activity and other criteria.
Maintaining hygiene
Before collecting urine, it is important to observe hygiene measures. Thus, toileting the external genitalia will prevent protein from getting into the urine, for example, from the vagina.
Deadlines for delivery of collected material
Once the urine is collected in a container, it must be transported within two hours to the laboratory. Prolonged standing of urine can lead to distortion of test results.
Increased protein in the urine of a teenager
In adolescents, a slight increase in protein levels (up to 1 g/l) is considered acceptable. This is due to increased physical activity and age-related changes in the body.
Why does protein increase in the urine of teenagers?
This is due to physiological changes in the body and high physical activity. During the day, while the child moves and is in an upright position, protein enters the urine, but at night this does not happen.
This condition is called orthostatic proteinuria. To detect it, you need to take several urine samples. In the evening, the child must urinate. In the morning, before he gets up, it is necessary to collect the night portion of urine. On the container with it they put a mark - night. During the day, so-called active urine is collected. The container with it is marked as daytime.
If the protein in the urine is associated with the physiological characteristics of growing up, the “night” sample will not contain “active” protein, its amount should not exceed 1 g/l.
If protein is present in both portions or the amount of protein in the daily portion is high, an ultrasound will be required to identify the pathology.
Why protein is exceeded - reasons
There are a number of factors that cause the appearance of protein in the urine of children. These are mainly infectious pathologies of the genitourinary system - cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis in boys, vulvovaginitis in girls. Viral diseases - ARVI, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, otitis media, sinusitis - lead to an increase in protein content in urine.
Other reasons:
- stressful situations, strong feelings;
- allergic reactions and atopic dermatitis;
- overeating protein foods (meat, fish, eggs, cottage cheese and other dairy products);
- inadequate drinking regime - low fluid intake;
- high physical activity and increased stress;
- hypothermia;
- various injuries, including serious burns;
- long-term use of medications that affect the condition of the kidneys.
There are often no symptoms indicating the presence of protein in urine. A child may look healthy and cheerful, even if there are abnormalities in the urine test. But sometimes the appearance of protein can be indirectly indicated by:
- poor appetite;
- slight swelling on the face - in the eyelid area;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- nausea;
- poor skin;
- fatigue;
- change in the color of urine, formation of foam in it;
- subfebrile temperature - 37-37.3°.
Treatment of pyelonephritis in children
The disease occurs in acute and chronic forms. In medical practice, after the first attack, a diagnosis of chronic pyelonephritis is often made.
In the acute form, the child requires hospital treatment. Its duration is about three weeks. But much depends on the specific case, the individual characteristics of the course of the disease.
After discharge from the hospital, children are treated at home under the supervision of a pediatrician and nephrologist. It is necessary to follow a diet that limits the amount of salt, spices, and fatty foods. Be sure to drink plenty of fluids.
The child will have to visit a nephrologist every two or three months and undergo regular urine tests. Every six months, do an ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract. If the disease does not manifest itself within two years, he is removed from the nephrologist’s register.
If protein is elevated in the urine due to diabetes or other diseases. Therapy will be aimed at the root cause.
In some cases, it is enough to follow a diet for two or three months and regularly take a urine test.
How are proteins and leukocytes related?
Leukocytes are formed elements of blood that prevent the development of pathogenic microflora in the body, namely viruses, fungi and bacteria. In a healthy child, these particles are absent in a urine test or are present in an amount of no more than 3 units in the field of view.
You may be interested in: Glomerulonephritis in a child
If white blood cells and protein are elevated in a urine test, this may indicate the following diseases:
1246847579
- Diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract - pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis, urolithiasis and more.
- Diseases of the genital organs - venereal pathologies, cervicitis, cervical erosion, colpitis.
- Allergic reactions in the body.
- Development of internal bleeding.
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
- Inflammation of the appendix.
If a child has an increased number of leukocytes and protein, we are most likely talking about an infectious disease that requires timely diagnosis and competent treatment.
Basic nutritional recommendations for children with increased protein in the urine
Eating errors can lead to increased protein in the urine. Most often, young children from 3 to 7 years old suffer from this.
To correct the situation, limit protein foods - meat, fatty fish. Salt and spices are prohibited, as they also increase the load on the kidneys.
The child is recommended to eat more fiber-rich foods - fresh vegetables, fruits, whole grain bread. In order not to completely exclude protein from the diet, it includes a sufficient amount of cottage cheese and fermented milk products. It is important that they do not have a high mass fraction of fat.
- There should be up to 6 meals a day. Portions should be small. Apples and bananas are suitable for snacks.
- Sweets, especially chocolate, should be limited. Berries and honey can be an alternative.
- Drinking should be plentiful. The doctor will set the norm depending on age.
The child is recommended to drink more herbal teas, such as chamomile or lemon balm, with a small amount of sugar. Cranberry and currant fruit drinks, compotes made from dried fruits, fresh or frozen berries are useful. Mineral water without gas is allowed.
Dietary recommendations for children with elevated protein in urine
| Allowed | Prohibited |
| Stewed potatoes, zucchini, pumpkin | Legumes |
| Fresh beets, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers | Fatty meat and fish, rich broths made from them |
| Boiled eggs (but not soft-boiled) | Canned food, mayonnaise, ketchup, other sauces |
| Cereals, pasta | Baking, sweet |
| Two day bread | Mushrooms and broths made from them |
| Dairy products | |
| Light vegetable soups or low-fat chicken or turkey broth |
A nephrologist or pediatrician will provide more complete dietary recommendations.
Treatment
Before starting treatment, a comprehensive examination is required to identify the causes of proteinuria. The doctor (nephrologist or pediatrician) gives the child’s parents general recommendations that should reduce the load on the kidneys:
- refusal to eat salt;
- sufficient fluid intake;
- control over the rhythm of urination;
- optimal intake of proteins from food;
- organization of rational nutrition for the baby.
Therapeutic treatment of proteinuria is always complex. They influence the underlying pathological process and relieve symptoms. The following groups of drugs can be used for this:
- diuretics;
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- hypoglycemic;
- antihypertensive;
- immunosuppressants – drugs that suppress immune damage to kidney tissue.
In addition to official drugs, it is possible to use some traditional medicine. The following homemade recipes are easy to prepare and safe for children.
Recipe 1
Rose hips 1 tbsp. (you can use filter bags) pour boiling water, bring to a boil over low heat and leave to cool for 30 minutes. Take the decoction three times a day.
Recipe 2
Dried and crushed bearberry leaves 1 tbsp. add water, cover with a lid. After 20 minutes, you can take half a glass of infusion.
nephrologinfo.ru
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion on the problem
Many mothers trust the advice of a nationally known pediatrician, TV presenter, and author of books, Evgeniy Komarovsky. In his opinion, small amounts of protein in a child’s urine are not always a sign of serious illness.
In infants, this indicator indicates overfeeding; the specialist recommends not to rush into complementary feeding, but to introduce it according to the individual.
Often traces of protein are the result of poor hygiene of the baby before urine collection. It is imperative to wash your child with soap. It is unacceptable to pour urine from a pot into a sterile container.
Dr. Komarovsky advises to retake the test if the readings are elevated. If the amount of protein is increased again, this is evidence of pathology of the genitourinary system, at a minimum.
About the causes of pathology
Protein in a child’s urine (proteinuria) does not always indicate pathology. In newborns this is not considered a pathology; during lactation it may indicate overfeeding. In addition, reasons include:
- allergies;
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- dehydration;
- intoxication of the body due to infectious diseases.
Typically, specialists prescribe dietary nutrition that neutralizes provoking factors. The child’s body recovers after a certain period of time, and the readings return to normal. But there are other reasons why proteinuria levels deviate from the norm. This is typical:
- malignant neoplasm in the kidneys;
- pyelonephritis;
- kidney injury;
- glomerulonephritis;
- thrombosis of renal vessels;
- the presence of stones in the bladder;
- kidney amyloidosis;
- congestive kidney;
- interstitial nephritis.
In addition, an increase is possible if the patient is predisposed to hypertension, blood diseases, diabetes mellitus, and autoimmune pathologies.
Differences in data for children of different ages
After a year, the information differs only in some respects.
Urine output per day increases with age:
- 3 years – 600-900 ml;
- 5 years – 700-1000 ml;
- 5-7 years – 1100-1200 ml.
Color change:
- 3 years - light yellow;
- 5 years – from light yellow to moderate yellow;
- 7-10 years – rich yellow color.
The remaining indicators become stable after a year and change only when the child is not healthy.
If abnormalities are detected in the analysis, then, as a rule, the doctor prescribes a repeat collection. Poor performance is sometimes caused by non-compliance with urine collection rules. This is directly related to childhood. To carry out the procedure, special tools are provided to help parents. If the second analysis, when carefully collected, shows an unsatisfactory result, the doctor will prescribe a general blood test. The result will confirm or refute the guesses, after which additional examinations will be prescribed or a treatment regimen will be selected.
Classification
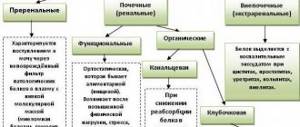
If proteins are detected in the urine, the specialist always suspects a decrease in kidney activity. This paired organ is designed to remove various wastes and toxins from the body. When excreted, the protein must be absorbed back into the blood. If this process is disrupted for some reason, proteinuria develops. Doctors divide pathology into several types:
- Perenal - develops due to excess protein in the circulatory system.
- Renal - occurs due to the fact that the nephrons cannot cope with the absorption of large molecular proteins.
- Postrenal – observed, as a rule, due to the presence of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system.
Adolescents are often diagnosed with an orthostatic increase in protein levels in the urine, which is explained by hormonal instability. This condition most often does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
Norms of urine parameters in children
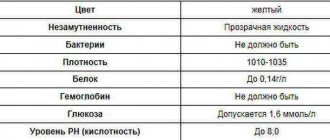
A general urine test contains a fairly large number of various indicators that may indicate certain problems with the child’s body. The table below shows the norms for such basic urine indicators in a child as protein, leukocytes, red blood cells, bilirubin and other components.
The norms of indicators and the interpretation of a general urine test in a child are presented in the table:
| Indicator (international classification) | Decoding the indicator | Norm for children under 1 year | Norm for children over 1 year |
| PRO | Protein | From 0 to 0.002 grams per liter | From 0 to 0.036 grams per liter |
| BIL | Bilirubin | Absent | |
| LEU | Leukocytes | No more than 3 in sight | No more than 6 in sight |
| BLD | Red blood cells | None | Up to 2 in sight |
| URO | Urobilinogen | Absent | 5 to 10 milligrams per liter |
| pH | Acidity | From 4 to 7.5 | From 4.5 to 8 |
| S.G. | Density | From 1001 to 1005 grams/liter | Up to 2 years – 1002-1015 g/l; From 2 to 3 years – 1010-1016 g/l; From 4 years – 1010-1025 g/l |
| COLOR | Color | Straw yellow | |
| KET | Ketone bodies | None | |
| G.L.U. | Glucose | Absent | |
| NIT | Nitrites | None | |
| CR | Cylinders | None | |
| LMS | Slime | In trace amounts | |
| BKT | Bacteria | None | |
| SLS | Salts | Single crystals | None |
| T.E. | Epithelial cells | Up to 2-3 in sight | Up to 8-10 in sight |
| P.R.S. | Transparency | Transparent |
Brief description of individual components:
- Bilirubin. The main component of bile, formed as a result of the breakdown of proteins containing hemoglobin, cytochrome and myoglobin. Mainly circulates in the blood, both in free and bound states. Its appearance in the urine indicates the presence of pathology;
- Red blood cells. Human blood cells that are saturated with oxygen in the lungs and distribute it throughout the body. It is a red blood cell with an elastic, biconcave disc-shaped structure. In the urine of a healthy child it occurs only in small quantities, no more than a few units;
- Protein. These elements are high-molecular structures that are part of a number of enzymes and are involved in a large number of biological and chemical processes in the human body;
- Leukocytes. Provide comprehensive protection of the body from internal and external pathological agents. Normally they may be present in urine in small quantities. The norm of leukocytes in a child’s urine is presented in the table above;
- Urobilinogen. It is the end product of the reduction of bilirubin, which is formed mainly under the influence of various intestinal bacteria, both beneficial and opportunistic. After its formation, it is converted into urobilin, which is found in urine. A high concentration of a component in biological material indicates the presence of serious diseases and pathologies;
- Acidity. It is a relative indicator that serves as an indicator of the acid-base properties of substances excreted from the body along with urine. Deviations from the norm are considered to be too acidic or alkaline, and the norm is neutral acidity;
- Epithelial cells. Urine, as a biological fluid, passes through the kidneys, ureters, and other components of the urinary system and always comes into contact with the inner layers of the epithelium. Sometimes individual cells break away from the structure and end up in the urine. A significant increase in the number of epithelial cells in urine can be observed in a number of serious pathologies with the body;
- Ketone bodies. They are the end product of the metabolism of a number of substances formed in the liver, in particular beta-aminobutyric acid, acetone, and acetoacetic acid. Normally, they are present exclusively in the blood in small quantities, and their presence in the urine indicates a number of problems with the child’s body.
Traditional treatment
Alternative treatment cannot replace full-fledged drug therapy, but it is quite acceptable as an auxiliary treatment. The following natural recipes are used to treat proteinuria:
- Fruit drinks prepared with cranberries and lingonberries.
- Pumpkin juice with pulp.
- Rose hip tea.
- A decoction of parsley and birch buds.
- Infusion of fir bark.
When using traditional treatment, it is important to consider whether the patient is allergic to the products used. Therapy should be started with small doses. This will help prevent possible side effects.