Why does proteinuria appear in men?
There are plenty of sources for the appearance of protein in the urine of men. Let's consider those that are not causes of disease:
- Stress . It can be one-time or systematically recurring, causing deviations in the normal functioning of organs and other systems.
- Physical stress . Sports activities, difficult working conditions, etc.
- Hypothermia. The human body responds to them especially acutely.
- Transitional age , puberty.
- Excessive consumption of foods high in protein.
The reasons for the increase in protein content in the urine may be pathological changes and diseases. These include:
- pyelonephritis;
- damage to the kidney structure;
- inflammatory processes of the parenchyma;
- nephrosis, hypertension, renal tuberculosis;
- stones, diabetes, prostatitis;
- bacterial infections, urethritis.
Other diseases that affect the performance of the kidneys and ureteral system, which may even include conditions that do not affect the functioning of the paired organ and the ureteral system:
- leukemia;
- oncology;
- consequences after chemotherapy;
- allergy;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- muscle injury;
- burns.
Diagnostics
A general urine test is an initial study, the results of which determine the need for further diagnosis. If protein is detected in a repeated general analysis, a 24-hour urine test is first prescribed. If it confirms proteinuria, then they carry out:
- general blood test (primarily the number of leukocytes and ESR);
- blood sugar test;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (possibly);
- blood test for lipid spectrum (possibly);
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract (required).
Ultrasound with an increased concentration of protein in the urine is very informative.
If pathological changes in the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract are not detected, further searches for the cause of proteinuria continue.
We remind you that proteinuria can signal a developing cancer (leukemia, myeloma).
Pathological proteinuria
A sustained or significant increase in protein content in the male body is considered to be a sign of some disease. Pathological changes develop:
- directly in the kidney ( renal );
- beyond its boundaries, without affecting the organs of the ureteral system ( prerenal or postrenal ).
Renal proteinuria
If protein in the urine rises due to pathological abnormalities in the kidneys, complex inflammatory processes affecting the glomerular apparatus or the kidney membrane are diagnosed. The leading place is occupied by glomerulonephritis, due to which the elasticity of the kidney membrane is impaired and permeability increases. In addition, an increase in protein can occur from pyelonephritis and emerging tumors.
Postrenal proteinuria
Some diseases of the ureteral system, from which an inflammatory process develops in the urethra, bladder or prostate, cause an increase in the protein content in the urine. This is due to the penetration of a product of an active inflammatory process into urine, called “false proteinuria”. When a man’s history contains similar findings as acute or chronic urethritis, cystitis or prostatitis, it is recommended to pay attention and correctly explain the urine analysis.
Prerenal proteinuria
A number of reasons why the level of protein in urine increases is associated with various pathological changes occurring in the body. More likely ones include:
- diabetes;
- damage to blood vessels or heart;
- inflammatory processes of an infectious nature;
- malignant neoplasms;
- epilepsy.
In all diseases, the mechanism of protein formation is different, and its indicators can vary greatly.
Proteinuria during pregnancy
Protein in urine is often elevated during pregnancy. More often the problem appears in the third trimester. If the protein concentration does not differ greatly from the standard values, then this condition is considered natural. Experts explain this fact by physiological changes occurring in the body of the expectant mother.
When protein increases significantly, it becomes a sign of the development of dangerous diseases. If 1 to 3 grams of this substance is detected in urine, the appearance of gestosis is indicated. This pathology is dangerous for the mother and the baby. It can cause premature birth or developmental abnormalities in the child.
Protein detected in urine in the range from 0.3 to 1 grams indicates the development of pyelonephritis. The disease often plagues pregnant women. During this period of life, the kidneys experience increased stress and cannot always cope with it. There is a malfunction in their functioning, as a result of which pyelonephritis arises.
Clinical manifestations
The patient's complaints and research methods depend on the main reason for the appearance of protein in urine.
With pathological changes in the kidneys, patients complain of pain in the lower back, increased body temperature, and disturbances in the emission of urine. Particular importance in determining the diagnosis is given to the interpretation of laboratory and functional studies.
It is recommended to pay attention to the level of creatine, remaining nitrogen and urea. In addition, electrolytes and total protein are assessed. Changes in the structural structure of the kidney are determined by ultrasound.
In the process of inflammatory diseases in the organs of the urinary system that do not affect the kidneys, urine should be correctly collected for analysis so that mucus and purulent accumulations from the lesions do not get into it. The collected urine is conventionally divided into three containers.
When visiting the toilet, the first portion of urine is emitted into the toilet, then the emission of urine is suspended, and the second portion is directed into a jar. Whatever remains after this goes back into the toilet. In the first and last portion there is a chance of “catching” elements that have nothing to do with the kidneys.
Often, the pathological changes that cause proteinuria are quite obvious and can be diagnosed based on a clear clinical picture. Some diseases occur secretly and require a full course of examinations and consultations with specialists.
Collection of urine for analysis
For the laboratory, urine for daily proteinuria is collected in exactly one day, that is, in 24 hours. Thus, starting to collect urine at seven in the morning, you need to fill the jar for the last time at the same time the next day.
In this case, the first portion of urine must be flushed down the toilet, and all subsequent ones, including the morning one the next day, into a jar.
After collection, it is necessary to measure the amount and write it down on a piece of paper or on the direction to the laboratory attached to the urine collection container. This is necessary so that laboratory technicians can calculate the amount of protein in the collected urine based on its concentration per gram.
Norm and diagnosis
Under normal conditions, the permissible norm of protein in a man’s urine is 0.033 g/l.
To determine the level of protein in urine, you need to take a test. As a rule, they collect it themselves. For the result to be correct, the rules for collecting urine must be followed. One of the important conditions is sterility.
The container must be clean; it is recommended to purchase it at a pharmacy kiosk or obtain it from a laboratory. You are allowed to use a glass jar and lid that have been pre-treated in boiling water. It is necessary to stick a tag on the side of the container indicating the patient’s personal data and the time of urine collection.
Before collecting urine for analysis, you must thoroughly wash your genitals. No special preparation is required for the test, but before this procedure you should not drink alcohol, do not overeat, and avoid fatty and aggressive foods that can affect the functioning of the kidneys and organs of the ureteric system. It is recommended to reduce physical activity and avoid stressful situations. Morning urine is tested, because it can provide the most accurate information about the patient’s health.
How to properly collect urine for analysis
Before taking a urine test for protein, you must stop drinking alcohol and diuretics for 2-3 days. If diuretics cannot be discontinued due to medical conditions, this should be discussed with your doctor in advance.
Immediately before the urine collection procedure, the following actions must be performed:
- perform hygiene procedures for the genitals using appropriate means;
- when filling the container, do not touch its edges with your genitals;
- before starting to urinate, spread the labia;
- Use a cotton swab dipped in clean water to wipe the urethral area;
- start urinating into the toilet;
- fill the container with urine;
- complete urination;
- Seal the container with urine hermetically.
In the case of urine collection for analysis according to the rule of three glasses, to diagnose the source of hematuria, steps 5-7 are performed in three different containers
How to reduce protein in urine
The treatment course of the problem depends on the causes of its formation. If an increased content of proteins in urine is detected, specialized treatment is prescribed aimed at eliminating the main problem. Due to the fact that there are many causes for this condition, it is almost impossible to create an accurate list of necessary medications. Most often, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- antibiotics , which are prescribed individually, must fully correspond to the identified problem and be aimed at a specific pathogen;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- drugs that can lower blood pressure;
- antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids;
- cytostatics (if necessary);
- painkillers when signs of pain are felt;
- other medications prescribed by a specialist.
Please note that self-treatment is prohibited, because the causes of the increase in protein in urine can be serious illnesses. The patient is prescribed bed rest and dietary nutrition. Preference should be given to light, easily digestible foods, which include beets, pumpkin, dried fruits, drinks in large quantities, and vitamin decoctions from rose hips.
You should also organize monitoring of emitted urine and pressure indicators in the arteries. In especially severe cases, the man is recommended to undergo urgent hospitalization. The condition accompanied by physiological proteinuria does not require medical therapy. The indicator stabilizes after the cause disappears.
Forecast
In case of various pathological changes during which protein is released, normal nutrition should be provided with foods containing protein in order to promptly replenish it in the body. The prognosis in most cases depends on timely diagnosis and competent treatment course of the underlying disease. The patient must remember that even the slightest hint of proteinuria needs to be referred to a specialist.
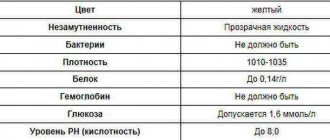
Analysis of urine for the presence of protein allows you to identify kidney pathologies. Based on the results of the study, the doctor identifies the disease and prescribes effective treatment. The normal level of protein in a man's urine is 0.14 g/liter. If this indicator is higher - up to a value of 0.33 g / liter, then they speak of a pathology, a sign of which is proteinuria. It comes in several stages - mild, severe and moderate. The result of the study can be influenced by many factors, so before the analysis it is necessary to avoid certain foods and medications. Let's look at what protein in the urine means in men, and what treatment is required against the background of high levels?
Preparing for analysis
Analysis of the daily amount of protein in urine is carried out quite rarely, in comparison with a general urine test. Therefore, not every person knows how to collect daily proteinuria.
First of all, it is important to prepare a container in which the urine will be collected. The average human diuresis is about two liters, so it is better to take a three-liter glass jar. Before use, it must be thoroughly washed in running water and soap, dried and marked to determine the exact number of milliliters. Instead of a can, you can use a canister.
To carry out the analysis, it is extremely important that the container contains all the urine excreted per day. Therefore, for convenience and to avoid the fact that a certain amount of liquid may spill out, it is better to urinate not into the jar itself, but into a small container, for example, a disposable glass, and then pour the urine into a jar or canister.
What does increased protein in the urine indicate in men?
Protein molecules are characterized by a very small size, as a result of which they cannot pass through the renal corpuscles. In a healthy man, urine does not contain traces of protein even in minimal concentration. If the protein is detected, then this signals a serious impairment of kidney function. To establish the disease, additional diagnostic measures are required.
It is worth knowing: in medical practice, proteinuria is divided into true and false conditions. In the latter version, the results from the laboratory are not related to the disease, but to the characteristics of the patient’s lifestyle and diet. The norm of protein in urine in men is 0.3 to 1000 - in other words, up to 0.3 g of protein components per liter of biological fluid.
Protein in a man’s urine can be a consequence of physiological reasons - in this case, the picture normalizes over time on its own, or pathological conditions - adequate and timely treatment is required.
The increase in protein content is divided into three stages:
- In mild cases, no more than one gram of protein is released per day. The reasons for increased protein in the urine in men may lie in diseases such as urethritis, inflammation in the bladder, etc.;
- During the middle stage, they talk about the release of protein substances up to three grams per day. With this result, the initial stage of amyloidosis, a disease of the renal ducts, is suspected;
- In the severe stage, the daily excretion is more than three grams. They talk about glomerular lesions, nephritis and other diseases that are associated with impaired renal function.
The acceptable level of protein in a man's urine is 0.14 g/liter. If the value is higher than this indicator, then the medical specialist must prescribe additional diagnostic measures to identify the disease that provoked this symptom.
Physiological norm of protein
Normally, the protein in urine should not go beyond 0.3 g. This is the upper threshold, because in general there is much less protein. Just some circumstances lead to an increase in protein molecules in the urine:
- Stressful conditions;
- Muscle strain;
- Heavy physical activity.
This explains the fact that in male urine the level of protein is always slightly higher than in female urine. The reason for this is the professional activity and lifestyle of men.
If an increased content of protein molecules is detected in the urine, it is recommended to retake the test. Sometimes the protein enters the urine with sperm or with purulent masses from the genitourinary system.
A man can lose several milligrams (30-70) of protein in urine during the day. In addition to the above factors, the cause of physiological proteinuria can be severe hypothermia, adolescence, etc. Protein in the urine in men may also increase slightly due to excessive consumption of meat dishes and other foods containing large amounts of proteins. Although the protein content in this case will not be particularly high. Physiological proteinuria can also occur during intense training.
Reasons for the increase
Why does protein in urine increase in men? The etiology can be physiological, which does not pose a danger to the patient’s health, and pathological – it is associated with some disease that requires drug treatment. In the latter case, other tests are prescribed to provide a more complete picture.
Physiological pathogenesis of increased protein in urine:
- Age. During adolescence, against the background of intensive growth, various changes occur in the body. As a rule, they do not pose a serious danger. With the end of puberty, the situation normalizes on its own.
- Excessive physical activity - exhausting sports, long hikes, etc. In this situation, the increase is short-term, leveled out on its own within a few days.
- Depressive state, neurosis, severe stress.
- Overstrain of muscle tissue.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Severe hypothermia.
- Intoxication of the body.
Important: against the background of increased protein in the tests and the man’s normal state of health, a repeat test is prescribed. It is necessary in order to exclude a false positive result associated with incorrect testing, for example, if sperm gets into the urine.
Some pathologies remain latent for a long time and do not manifest pronounced symptoms, which leads to a man visiting a doctor at an advanced stage of the pathological process. Often, in addition to protein molecules in the urine, the laboratory technician detects leukocytes and red blood cells.
A persistent and/or significant increase in protein structures in biological fluid is a signal of a disease. It can be localized directly in the male kidney, then they talk about the renal form of proteinuria or beyond it - prerenal or postrenal proteinuria is diagnosed.
The following diseases can increase protein in the urine:
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory process during which the renal membrane is transformed - its permeability increases;
- Kidney cancer, polycystic disease, pyelonephritis;
- Chronic prostatitis, urethritis, bacterial cystitis;
- Diabetes mellitus of any type, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, arterial hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure);
- Infectious diseases, respiratory pathologies (flu);
- Tumor neoplasms;
- Hemorrhagic stroke;
- Epilepsy.
The reasons may not be directly related to impaired kidney function, so an increase in protein in urine may indicate other pathological processes in systems and internal organs. This applies to myocardial infarction, myeloma, muscle injury, oncology, burns, the effects of radiation treatment and allergic reactions.
Pathological causes of increased protein molecules in urine
Typically, various inflammations in the genitourinary system contribute to an increase in protein. Such processes are often caused by functional disorders in the renal filtration system, which arise due to damage to the pelvis. But true proteinuria does not always develop as a result of such lesions. The causes of pathologically increased levels of protein in the urine are:
- Bladder lesions of bacterial origin or various types of cystitis;
- Pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis - these renal pathologies are always characterized by the release of proteins in the urine;
- Renal lesions of toxic or metabolic origin;
- Diabetes. With such a disease, the detection of protein in the urine helps to timely diagnose the pathology at the beginning of its development.
Protein may be released into the urine from the prostate or urethra, then false proteinuria is diagnosed. If a significant excess of the norm of proteins excreted in urine is detected, then the reasons should be sought in the impaired filtering activity of the kidneys, which occurs as a result of nephrosis, tuberculosis, renal hypertension or parenchyma, lesions of the pelvis, glomeruli or calyces.
Normally, a man's urine protein content should not exceed 0.3 g/l. If there is a persistent increase in protein levels, this indicates the presence of a pathological factor.
Proteinuria is not always a consequence of a urological pathological process; often the disease develops as a result of an infectious factor. If the protein excreted in the urine belongs to albumin, then the reason for its release may be:
- Epilepsy;
- Leukemia;
- Allergy;
- Heart failure.
All these factors relate to functionally determined proteinuria. The pathological form of the disease is always of renal origin. If the cause of proteinuria is nephropathy of diabetic origin, then the patient may also be concerned about high blood pressure. An increase in proteins in urine can also be caused by:
- Heart attack;
- Gangrenous processes in the extremities;
- Hypertonic disease;
- Hemolytic anemia;
- Muscle injuries or illnesses;
- Ischemic lesions;
- Oncological processes;
- Cardiovascular disorders;
- Chemotherapy treatment;
- Serious burn injuries, etc.
Each case requires the participation of a specialist to identify the true causes of proteinuria and select the appropriate treatment tactics.
Symptoms and possible complications
When the protein concentration in the biological fluid increases slightly, symptoms are rarely present. Sometimes men complain of slight malaise and fatigue. There are no other signs of a pathological process in the body. A physiological increase in protein molecules has no clinical manifestations at all.
With a significant increase in protein substances, the following clinic is observed:
- Dizziness.
- Chills.
- Feverish condition.
- Sleep disturbance – most often drowsiness.
- Weakness, apathy.
- Unpleasant sensations in bones and joints.
- Loss of appetite.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Nausea, and somewhat less commonly, vomiting.
For your information, each symptom indicates a particular disease, which allows the doctor to narrow the “search” and prescribe the necessary diagnostic methods for the patient.
As for complications, a physiological increase does not threaten a person in any way, since it is a variant of the norm. With a pathological increase in protein concentration, negative consequences are associated with the underlying cause. For example, if you have serious kidney problems, kidney failure may develop; hemorrhagic stroke threatens serious disruptions in the functioning of many organs and systems, including death.
Causes of high protein
Increased protein in urine can be caused by a number of reasons.
Physiology
- Powerful physical activity.
- Excessive consumption of foods rich in protein.
- Prolonged stay in an upright position with corresponding disruption of blood flow.
- Late pregnancy.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Active palpation of the kidney area.
- Severe stress, concussions, epileptic seizures.
- Congestion in the kidneys.
- Hypertension.
- Nephropathies of various etiologies.
- Amyloidosis of the kidneys.
- Pyelonephritis, genetic tubulopathies.
- Tubular necrosis.
- Rejection of transplanted kidneys.
- Multiple myeloma.
- Hemolysis.
- Leukemia.
- Myopathies.
- Feverish conditions.
- Tuberculosis and kidney tumors.
- Urolithiasis, cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis, bladder tumors.
Treatment methods
Therapy for proteinuria is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. Only by eliminating the original source of the problem can laboratory test results be normalized. Since there are many pathologies that are accompanied by an increase in protein concentration in the urine, it is impossible to list the entire list of prescribed drugs. The patient can be treated with the following medications:
- Antibacterial tablets are selected individually and must act on a specific pathogen in the male body;
- Anti-inflammatory agents (stop inflammatory processes);
- Medicines that help lower blood pressure. In the presence of protein in urine, a decrease in blood occurs, which leads to swelling and an increase in arterial parameters;
- If there is pain, it is recommended to use painkillers - tablets, capsules or suppositories;
- Glucocorticosteroids, etc.
Often, an increase in protein in biological fluid is caused by a man’s poor diet, so it is recommended to follow a dietary diet. A healthy diet involves the following activities:
- Limit table salt consumption to two grams per day.
- Maintain a drinking regime - up to a liter of water per day.
- Limit consumption of red meat and fish products.
- Include vegetables, dairy products, and rice in your diet.
It’s worth knowing: a decoction based on black poplar, initial cap and tricolor violet helps normalize protein in urine. The components are taken in equal proportions. A tablespoon of the medicinal mixture is poured with 250 boiling water and left for 30 minutes. Take during the day. The duration of treatment is 21 days.
An increase in protein due to physiological reasons does not require treatment. Concentration normalizes over a short period of time, for example, after rest or stress relief. For prolonged emotional overload, sedatives may be recommended. Due to the excessively high content of protein molecules, treatment in a hospital setting under medical supervision is required. After the therapeutic course, a repeat analysis is carried out to determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
The normal level of protein in urine in men is only 0.033 g/l. The detection in tests of a slight excess of the norm of this substance indicates disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys or the negative influence of physiological factors. If the norm is exceeded several times, then the urinary system is in a catastrophic state and immediate help is required.
Treatment method
If protein in the urine is elevated, it is important to begin adequate therapy in time. The following treatment methods are used:
- Use of medications. The choice of drugs will depend on the identified disease. If the infection spreads, antibiotics are prescribed. Antihyperglycemic medications are used to treat diabetes. If hypertension is diagnosed, medications that lower blood pressure are indicated. Diuretics are often prescribed, as well as complex products based on herbal ingredients. They help cope with difficulty urinating and eliminate factors that increase the number of proteins in urine.
- Lifestyle changes. When protein in the urine is elevated, it is important to give up bad habits and adopt a healthy lifestyle. It is recommended to avoid increased physical activity, but this does not mean that you will have to give up sports. It is enough to switch to more gentle sports: athletics, swimming. You need to spend more time outdoors.
- Diet.
Therapy should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. After completing the main course, you will have to undergo the examination again. If the results of general and daily analyzes show a decrease in proteins, then the treatment is considered effective. Otherwise, the program will need to be adjusted.
Diet features
If there is increased protein in the urine, a person will have to follow a special diet. When preparing the right diet, you need to rely on the following recommendations:
- Proteinuria often develops due to the consumption of large amounts of protein foods. This creates an increased load on the kidneys, which causes disruption of their functioning. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to remove proteins from the menu. If you really want milk or eggs, then they must be subjected to heat treatment. Meat and fish are well boiled or baked in the oven. You can eat no more than 19-22 grams of protein per day.
- When choosing meat products, it is recommended to give preference to chicken.
- Semi-finished products, smoked meats, marinades, spices, sweets, as well as products with a high content of chemical additives are removed from the diet.
- To prevent protein concentration from increasing, avoid alcoholic beverages.
- Dishes should be prepared without adding salt. If you can’t give it up right away, then reduce its consumption to 2 grams per day.
- When there is a lot of protein in the urine, the daily menu should mainly consist of vegetables, herbs and fruits. Beetroot and pumpkin are especially beneficial.
- When there is an increase in protein in the urine of women during pregnancy, it is important to organize the correct drinking regime. You can drink not only clean water, but also homemade compotes, fruit drinks and juices. It is better to ask your doctor in what volumes you are allowed to consume drinks.
- Dried fruits and melons will help reduce proteins in urine.
- It is forbidden to eat legumes, chocolate, garlic, onions, and mushrooms.
If therapy is carried out using diuretics, then the diet should contain more foods rich in potassium. These include baked potatoes, bananas, dried apricots.
How proteins get into urine
Normally, the proteins necessary for life are in the blood, or rather in its plasma, and are not excreted from the man’s body. The glomeruli are responsible for retaining proteins within the bloodstream. These unique filters do not allow protein molecules to pass into urine, creating a natural barrier.
If small albumins do leak out, the renal tubules come into the fight, absorbing them and returning them to the blood vessels. When the kidneys work well, proteins do not enter the urine even in minimal volumes. If the tubules and glomeruli are damaged, they do not perform their functions, and proteins are removed from the blood through urine. Red blood cells can also penetrate with them. Therefore, increased protein in the urine in men is often accompanied by hematuria.
The cause of damage to kidney tissue is inflammatory and infectious processes in the urinary organs, as well as chronic diseases. Sometimes proteins penetrate en masse into urine due to disturbances in their cellular structure. If there are too many small molecules, the tubules cannot absorb them completely and residual amounts leak into the urine.
Attention! In severe kidney pathologies in men, large protein cells enter the urine, which indicates a complete absence of the glomerular barrier and the development of severe proteinuria.
Neoplasms
The second reason that daily proteinuria exceeds normal levels is cancer. Mainly, neoplasms in the kidneys themselves, and secondarily – bone marrow cancer or myeloma. With myeloma, bone tissue is destroyed, and decay products enter the blood, and through the kidneys into the urine.
Both kidney failure and oncology are very serious diseases that are difficult to treat. You can maintain your health and ability to work only by achieving long-term and stable remission. And it is obvious that it is more likely to achieve it at an early stage of the disease, so it is very important to regularly conduct urine examinations, and if abnormalities are detected, contact a nephrologist.
Normal urine and degree of deviation
For a healthy adult man who leads a normal lifestyle, is not fond of sports and is not engaged in heavy types of physical labor, the optimal protein norm is considered to be its zero value or the detection of traces of the substance (0.033 g/l).
The level of proteins in a man’s urine can often change depending on his current age, lifestyle and diet, but deviations in this case are minor and do not threaten health.
Officially, protein excretion by the kidneys is allowed in the following quantities:
- in the general analysis of the first morning urine no more than 0.033 grams per liter;
- in the average portion of daily urine up to 0.01 grams per liter;
- total loss in 24 hours ranges from 44–50 to 80–100 mg, with an average of 72 mg per day;
- in boys under 16 years of age, the norm is up to 0.9 g/liter.
Proteinuria is said to occur when protein absorption in men exceeds 150 mg in 24 hours. But the doctor pays attention to even a slight excretion of protein (30 mg) and records it as the lower limit of microalbuminuria. The upper threshold for this condition is 300 mg.
If suddenly the protein content in the urine exceeds this limit or reaches 1 gram, a mild stage of proteinuria is diagnosed. Moderate excretion corresponds to values from 1 to 3 grams in daily urine. Analysis results containing information about losses of more than 3 grams of protein fractions in 24 hours indicate severe proteinuria. It is accompanied by impaired renal function and is life threatening.
On a note! The concept of “low protein” does not apply to urine tests and is not considered in medicine. Only a decrease in this substance in the blood, which develops precisely under the influence of proteinuria and other factors, is considered dangerous.
For what reasons does protein appear in urine?
Otherwise, this pathology is called proteinuria. Proteinuria can occur at any age, under the influence of external factors or various diseases. Normally, a slight excretion of protein in the urine is allowed; the levels should not be higher than 0.033 g/l.
The causes of protein in the urine in men can be functional, in which case the kidneys are healthy, and proteinuria is temporary, does not require treatment and can occur with:
- heavy physical activity;
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- eating large amounts of protein foods;
- ARVI or flu;
- overweight.
The severity of proteinuria can be:
- moderate – no more than 1 g of protein per day;
- average – 1-3 g per day;
- severe – more than 3 g of protein per day.
In addition, proteinuria can be renal (associated with kidney pathologies), postrenal (caused by diseases of the urinary system) or prerenal (occurs against the background of other pathologies of organs and body systems).
Thus, if protein appears in a man’s urine, the reasons may be related to:
- Glomerulonephritis is an immunoinflammatory lesion of the kidneys, mainly the glomeruli, and to a lesser extent, the interstitial tissue and tubules of the kidneys. It can occur independently or against the background of certain autoimmune pathologies. With this disease, deposition of antigen-antibody complexes occurs in the capillaries of the glomeruli, which impairs blood circulation and disrupts the production of primary urine. Against this background, salt, water, and metabolic products are retained in the body and the level of antihypertensive factors decreases. Accompanied by increased body temperature, chills, weakness, nausea, decreased appetite, pain in the lumbar region, pallor, swelling of the eyelids. In the first 3-5 days, diuresis decreases, hematuria develops (a characteristic symptom is urine the color of “meat slop”), urine density decreases, and protein is determined. In addition, swelling of the face is pronounced, hypertension develops, and liver enlargement is possible.
- Pyelonephritis is a nonspecific infectious kidney disease that is provoked by various types of bacteria. A fairly common disease, it can occur in acute or chronic form, the inflammatory process can be unilateral or bilateral. The disease develops against the background of diabetes mellitus or urolithiasis, after acute cystitis, and occurs in children due to peculiarities of anatomical development. Accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature to high numbers, sweating, headache, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. In addition, pain in the lower back is noted, the urine becomes cloudy, and sometimes acquires a reddish tint. The tests reveal microhematuria, minor proteinuria and bacteriuria, which means that there is a moderate amount of blood, protein and bacteria in the urine.
- Renal amyloidosis refers to a manifestation of systemic amyloidosis, characterized by a malfunction in protein-carbohydrate metabolism and extracellular deposition of amyloid in the kidney tissue, which disrupts the normal functioning of the organs. The disease is accompanied by nephrotic syndrome (proteinuria, edema, hypercholesterolemia, dysproteinemia or hypoproteinemia) and leads to chronic renal failure. Renal amyloidosis can occur in an idiopathic, familial, acquired, senile or local tumor form. The reasons for the development of the disease are unclear; in some cases it develops with multiple myeloma. Secondary amyloidosis is often associated with chronic infectious pathologies, intestinal lesions, purulent destructive processes, autoimmune disorders and tumors.
- Acute tubular necrosis - with this pathology, damage and dysfunction of tubular cells occurs. Why does this violation occur? Most often after hypotension or sepsis, in which renal hypoperfusion is observed, after extensive surgery, 3rd degree burns, and also after treatment with nephrotoxic drugs. Most often, the disease is asymptomatic; oliguria, the appearance of granular casts in the urine, moderate proteinuria and a small number of leukocytes and red blood cells may be observed.
- Toxic nephropathy - develops from poisoning with nephrotoxic substances: mercury, lead, oxalic acid, copper sulfate, acetic acid, etc. The pathogenesis is related to the etiology, depending on the substance, swelling of the nephrons, release of free hemoglobin and blockage of the nephrons, damage to the nephrons by myoglobin may occur. The disease has three degrees; in mild cases, casts, blood cells and protein in the urine are observed. The average degree, in addition to these disorders, is accompanied by a decrease in diuresis, a slight increase in creatinine, urea and potassium. Severe degree is characterized by manifestations of acute renal failure.
- Nephrotuberculosis - the disease is an extrapulmonary infection, the causative agent is Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which affects the kidney parenchyma. This form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis is the most common and accounts for about 30-40% of cases. The progression of the disease is accompanied by tissue breakdown, cavities and cavities form in the renal parenchyma, and the functioning of organs is disrupted. In more severe cases, purulent melting of the kidney tissue may occur; the pelvis and ureters, bladder, and genitals may be involved in the process. Over time, genital tuberculosis develops, which affects the epididymis, testicles and prostate. Quite often, the disease has a latent course or is accompanied by a slight disturbance in health: low-grade fever, fatigue, sudden weight loss. A urine test determines protein, leukocytes and red blood cells, pyuria and acid reaction.
- Urolithiasis – accompanied by the formation of stones in various parts of the urinary system. The most common occurrence of stones is in the bladder and kidneys. Stones can appear at any age; what causes them is not reliably clear; at the moment, only predisposing factors are known: disturbances in calcium-phosphorus metabolism, a sedentary lifestyle, occupational hazards, abnormalities in the development of the urinary system, chronic gastrointestinal diseases, etc. With urolithiasis, sharp or dull pain may occur, moderate proteinuria, pyuria and hematuria are observed. Renal colic and anuria may appear due to blockage of the ducts with stones.
- Diabetic nephropathy is a common complication of diabetes mellitus, which is asymptomatic for a long time and can lead to absolute dysfunction of the organ. With diabetic nephropathy, kidney tissue is damaged and nodular or diffuse glomerulosclerosis forms. The pathology is characterized by a triad of symptoms: the presence of protein in the urine, hypertension and kidney damage. There are stages of development in which: at stage 1, hyperfunction of the kidneys is observed, at stage 2, structural changes in the kidney tissue begin, at stage 3, nephropathy develops, stage 4 is characterized by severe nephropathy, and stage 5 is terminal and is accompanied by obvious arterial hypertension, glomerular dysfunction. filtration and nitrogen excretion function.
- Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland, which can occur in acute or chronic form. It develops against the background of a sedentary lifestyle, hypothermia, disturbances in the rhythm of sexual activity, frequent constipation, against the background of previous urological diseases or STDs, as well as in the presence of chronic diseases of other organs. Accompanied by frequent painful urination, pain in the perineum and lower back. Sometimes, on the contrary, it causes urinary retention, dysuric disorders, and increased body temperature. When OAM is detected, the presence of protein, blood, changes in the acidity and color of urine.
In addition, the appearance of different amounts of protein in the urine in men is possible due to allergic reactions, hypertension, hemolytic anemia, heart attack or heart failure.
Also in men, proteinuria can occur with:
- Injuries - in this case, muscle cells die in large numbers, and they contain protein.
- Chronic and acute inflammatory processes - the body produces antibodies, which are protein substances and can be detected in the urine.
- Malignant formations in the decay stage - protein appears in a urine test due to massive cell destruction and the release of free protein into the blood.
As we can see, protein can appear in the urine of men for many reasons. Many of them can lead to impaired kidney function and require serious treatment.
Note! Some pathologies in the initial stages occur without obvious clinical symptoms, but changes in the tests are present. By regularly visiting specialists, serious health problems can be prevented.
Low back pain accompanies most kidney diseases
Renal dysfunction affects both the patient’s condition and test results
The pathological process may affect one or both kidneys
Morning urine is required for analysis.
The analysis result is ready the next day
A specialist will decipher the results of a urine test
How to detect protein in urine?
If any complaints arise, the patient consults a doctor, after which the specialist takes an anamnesis and examination, and, based on the information received, prescribes the necessary tests. Instructions in urological practice indicate that the presence of protein in urine can be detected using a general urine test.
In order to pass the test correctly, you need to prepare for it. Various medications and foods affect the composition of urine, so it is better to check with your doctor what needs to be limited before the test (alcohol, vitamins, protein foods). It is also recommended not to overheat, avoid stress and physical activity.
The material is collected into a sterile disposable container. Before this, it is necessary to toilet the genitals, and flush the first portion of urine into the toilet to avoid bacteria from the genitals getting into the sample.
The analysis requires fresh urine, so it must be delivered to the laboratory within 1-2 hours. The cost of the study is minimal, and in most medical institutions the analysis is carried out free of charge.
Based on the results of urine analysis, volume and color, transparency, odor and foaminess, acidity, density and the presence of bilirubin, protein, red blood cells, salts or casts, leukocytes, ketone bodies, bacteria and fungi are assessed. The presence of formed elements is normally allowed in small quantities, in other cases this indicates pathological processes in the body.
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment
From the photos and videos in this article, we were able to find out for what reasons protein may appear in the urine of men, what symptoms accompany these conditions, and how, if necessary, to identify proteinuria.
Pathological causes
Constantly high protein in the urine means that the kidneys are not doing their job. The reason for this may be diseases of the urinary organs and other life support systems. Regardless of the factors that caused high protein, the condition can be complicated by nephrotic syndrome and severe renal failure, including failure of the paired organ. Diseases that contribute to proteinuria in men can be divided into certain groups.
| Category | Structure |
| Pathologies of the genitourinary system. | Urolithiasis, prostatitis, urethritis, adenoma, tumors, glomerulonephritis, chronic renal failure, urinary inflammation, pyelonephritis, injuries in the kidney area and specific lesions of tuberculosis. |
| General infections and febrile conditions. | Acute respiratory infections, flu, pneumonia, severe bronchitis, purulent tonsillitis. |
| Oncological diseases, including the effects of chemotherapy. | Malignant lesions of the skin, blood, internal organs and lymphatic systems. |
| Systemic pathologies. | Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis, vasculitis. |
| Chronic diseases of the heart, metabolism, blood vessels and endocrine system. | Heart failure, varicose veins, hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis and severe obesity. |
A temporary cause of protein in the urine in men is also appendicitis, but in this case the number of leukocytes simultaneously increases.
What does mucus in urine mean?
The entire length of the urinary tract (ureters, bladder and urethra) is lined with epithelium, among which there are goblet cells that secrete mucus. The main function of mucus is to protect the inner lining of the urinary tract from the irritating effects of urea and the acidic reaction of urine.
Normally, just enough mucus is released to neutralize aggressive influences. When urinating, a very small amount of it is released into the urine, which cannot be seen with the eye, but can be determined by laboratory testing of urine.
Normally, when describing a urine test, a note will be made: “mucus in a small amount,” which means that there is no need to worry about this.
If there is increased mucus in the urine
With inflammatory changes that occur in the urinary tract, their mucous membrane becomes congested, swells, and goblet cells begin to actively produce an increased amount of mucous secretion, as if trying to protect the ureters, bladder and urethra from the aggression of bacteria, fungi or viruses. A lot of mucus in a urine test appears with urethritis, cystitis or urinary tract infection.
- Urethritis
This is an inflammatory disease of the urethra, which can occur as an acute or chronic process. Most often, urethritis is provoked by a saprophytic bacterial infection (Escherichia coli, staphylococci) or specific flora of sexually transmitted infections (gonococci, mycoplasma, trichomonas, gardnerella).
Thus, mucus in the urine of men, in combination with leukocytosis and the appearance of blood, usually appears with specific acute urethritis (see urethritis in men). Less commonly, the cause of inflammation of the urethra is fungi of the genus Candida albicans or viruses. The clinical picture of urethritis boils down to pain at the beginning of urination, itching and burning in the urethra, and frequent urge to urinate.
- Cystitis or inflammation of the bladder
This is a more polymorphic acute or chronic disease, the main cause of which today is generally recognized as E. coli (see cystitis in women). For hemorrhagic forms of the disease, a viral origin is more typical. Clinical manifestations of cystitis are reduced to heaviness and pain in the suprapubic region, increased frequency of urination, false urge to urinate, pain in the middle and end of urination and pathological changes in urine analysis in the form of the appearance of abundant mucus, bacteria, leukocytes and red blood cells (with hemorrhagic cystitis).
- Urinary tract infection
This is a transient condition associated with inflammation of the urinary tract against the background of increased aggressiveness of saprophytic microflora. It can occur with the clinical picture of urethritis or cystitis, but during instrumental studies there are no morphological changes in the mucous membrane of the urinary tract.
The infection clears up fairly quickly with antibacterial treatment. Women of reproductive age are most susceptible to this pathology. On the one hand, the structural features of the perineum and the proximity of the external urethral opening to the genital tract determine the association of urinary tract infections with sexual life, when in addition to their own microflora, saprophytic microbes of the partner can also enter the urinary tract of a woman.
On the other hand, women have an increased risk of introducing E. coli into the urethra from the anal area. The risk of infection reaches its greatest peak during periods when women have a reduced immune response: during menopause or pregnancy. A small amount of mucus in the urine during pregnancy is considered normal.
But mucus and bacteria in the urine in combination with leukocytosis, red blood cells or protein is a reason to conduct a more thorough examination of the urinary tract.
A large amount of mucus in the urine of women may also indicate an inflammatory process in the genital tract, so an examination by a gynecologist if there are changes in urine tests is mandatory.
Mucus in a child's urine
Caution should always be present when mucus is found in a child’s urine. Features of the structure of the urinary system in children:
- imperfection of innervation
- weaker muscle layer
- incomplete development of the kidneys before the age of three, their increased mobility
- wider ureters with less contractility than in adults
- thinner and more vulnerable urethral mucosa predisposes to the easy development of urinary tract infections
At the same time, girls get sick more often than boys due to the shorter and wider urethra and the proximity of its external opening to the anus, which creates more favorable conditions for ascending infection. When a child has increased mucus in the urine, the causes should be sought according to the same principle as in adults, excluding inflammation of the urethra, bladder, ureters and kidneys.
- As a rule, a general urinalysis is prescribed again (it is replaced with a Nechiporenko analysis if they want to clarify the nature of the urinary sediment), in addition, clinical blood and kidney tests are examined in biochemistry.
- According to indications, a Zimnitsky test, urine culture, cystoscopy, ultrasound of the kidneys or excretory urography are prescribed.
Moderate mucus in combination with leukocytes, bacteria and protein is always indisputable evidence of problems in the child’s urinary system.
Author:
Postnova Maria Borisovna general practitioner
Therapy methods
Treatment of pathological albuminuria consists of prescribing specific drugs. Antibacterial therapy is used to relieve inflammation in the urinary system and in chronic foci of infection. Somatic pathologies are monitored, followed by the development of an individual treatment regimen. Systemic diseases require long-term hormonal therapy, and sometimes the use of cytostatics.
It is possible to reduce the manifestations of physiological proteinuria without the use of drugs. First of all, a man should give up alcohol and pickles and normalize his water balance. Without enough liquid, proteins are poorly broken down into amino acids, but this does not mean that you can drink without measure. In the presence of edema, excess fluid is contraindicated. Therefore, it would be ideal to consume an average of 1 liter of clean water per day; in the absence of edema, you can increase the volume to 1.5 liters.
You should eat rationally and in moderation, especially if you are obese. You can’t completely exclude protein foods, you just need to reduce their predominance. It is useful to include dried fruits, nuts and seeds in your daily diet. They will not only reduce protein, but also increase male strength.
Professional athletes and bodybuilders, in order to reduce the pathological level of albumin, will have to wait a bit with exercise and switch to a more gentle exercise regime. A minimal amount of protein or traces of it are normal for them and do not require specialist intervention.
For men, as well as for other categories of patients, moderate proteinuria is the norm only if it develops against the background of physiological factors and in the absence of clinical manifestations. In other cases, this is a pathology that definitely needs to be treated.
Frequently asked questions to the doctor
Unknown reasons
Hello. I gave birth less than a week ago, the baby had a urine test and an increased amount of protein was determined. Tell me, why is there increased protein in a child’s urine?
Good afternoon. This phenomenon occurs among newborns and is not a pathology. This occurs due to the fact that the permeability of the epithelium of the glomeruli and tubules of the kidneys increases, against the background of the hemodynamics of the newborn. If proteinuria persists after the first 7-10 days of a child’s life, it makes sense to consider it pathological.
Many diseases of the urinary system are characterized by the appearance of pathological impurities in the urine, as evidence of inflammatory changes in the urinary tract or kidneys. The most characteristic components of urinary sediment are mucus, white blood cells, red blood cells and protein. Let's consider situations that are characterized by two of them: mucus and protein in the urine.
What do proteins do for the body?
Proteins in medicine are also called albumins or proteins; they are biological macromolecules that can independently form and maintain a spatial structure. This is the basis for the functioning of polypeptides. Proteins are divided into 2 groups, complex (proteids) and simple (proteins). When interacting with water, they break down into a number of amino acids necessary for humans. These substances are called the basis of human life. They participate in the following processes:
- metabolism;
- transportation of nutrient media in the body;
- support of cell structure and participation in its division;
- protection of the body and formation of immunity;
- synthesis of hormones and enzymes.
An increased content of any protein inclusions in urine is a sign of a pathological loss of these substances. More often, simple forms penetrate into the fluid secreted by the kidneys. In this case, proteinuria is diagnosed.
On a note! The excretion of proteins in the urine is not only a sign indicating pathologies of organs and systems, but also the threat of developing a deficiency in the body of this important substance for men.
High protein concentration
Normally, there should be no protein in a urine test. After all, protein in urine is, most often, casts from the kidney tubules. If there are no inflammatory changes in the kidneys or urinary tract, then there is usually no protein in the urine. That is, protein is most often lost due to pathologies of the urinary system. This is the so-called pathological proteinuria.
But there are also conditions when a healthy body loses protein in the urine, for example:
- athletes undergoing heavy physical activity, during which the body breaks down not only sugars and fats, but also protein to obtain energy
- a similar situation occurs during prolonged fasting, when the body does not have enough energy resources and it utilizes its proteins
- When dehydrated, exposed to a hot room or elevated body temperature, protein can also penetrate the kidney membrane and be excreted in the urine.
- physiological protein losses in men with urine, which contains prostatic secretions, are about one hundred and fifty milligrams per day.
Normally, a urine test may contain up to 0.033 g/l of protein. Daily loss normally does not exceed 30-50 milligrams. Depending on the volume of protein excreted in the urine, proteinuria is divided into three subtypes.
- Microproteinuria is considered to be a daily loss of 150 to 500 milligrams per day.
- Moderate protein loss is considered to be between 500 and 2000 mg per day.
- Macroproteinuria (protein flakes visible in the urine with the eye) is a loss of more than 2 grams of protein per day.