Where are the human liver and kidneys located?
The liver and kidneys are important organs of human digestion. They cleanse food of harmful substances and absorb harmful microelements.
The liver is located in the right upper quarter of the abdomen. Its upper edge is located approximately at the level of the right nipple, under the diaphragm, and the lower edge reaches 11-12 pairs of ribs.
The human kidneys are located near the lower back, on either side of the spine. In men, the kidneys are located between 3 and 11 vertebrae, and in women between 2 and 10. The left kidney is located above the right, reaches the base of the spleen and 11-12 pairs of ribs and its upper part is in contact with the diaphragm, and the right one is at the level of the right rib 12 couples.
The distance between the ends of the buds is 8-11 cm.
Video: Kidney treatment - Kidney pain
Video: Human body. Liver (hepar).
The liver is a vital exocrine gland in vertebrates and humans. In this article we will talk in detail about where the liver is located in a person and how it hurts.
Liver, what kind of organ is it?
The liver is the largest digestive gland in animals and humans, which produces bile.
The liver performs a recycling, cleansing function. Removes toxic substances. The gland takes part in vitamin metabolism, as well as hematopoiesis. Pathologies of this organ can lead to disruption of functions important to life. The normal functioning of this organ directly depends on a person’s daily lifestyle.
Almost every person knows in which area of the abdomen this gland is located. On the right side, under the ribs (see photo above). In addition to the gland, other organs are located there, namely the digestive and respiratory systems. How to find out what is bothering the gland specifically?
Important point! The gland itself in the right hypochondrium does not hurt; its membrane or organs, pressure on which is exerted by the enlarged exocrine gland, are disturbing.
Danger of disease
The main danger of hepatic-renal failure lies in the failure of the kidneys and liver due to damage to the tissues of these organs.
The main danger of hepatic-renal failure lies in the following:
- Failure of the kidneys and liver due to damage to the tissues of these organs.
- Due to exposure to toxins, other organs are involved in the destructive process. The respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system may be affected.
- The affected organs begin to accelerate each other’s destructive pathogenic processes. As a result, the disease progresses rapidly and can very quickly lead to the death of the patient if the brain is involved in the process. The mortality rate is approximately 80-90%.
- Those who survive the disease develop postnecrotic cirrhosis of the liver.
Liver diseases: causes of pain
Abscess
A formation with purulent accumulations appears in the tissues of the gland. It appears due to cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. The location of the formation can be determined by pain in one area or another. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, because if the formation breaks through, there will be serious consequences.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammatory process. It can be viral, toxic or autoimmune. It can be determined by the enlarged size of the liver. Due to changes in the structure of the liver, cirrhosis develops.
Cirrhosis
This disease has the potential to be fatal. The gland enlarges due to the proliferation of connective tissue in its structure. And also, the exocrine gland stops functioning. Liver cirrhosis is asymptomatic for a long time. But at the beginning of the development of the disease, minor changes in the person’s condition may appear: fatigue, lethargy, irritability.
Liver failure
With this pathology, the organ is almost unable to fulfill its role. This is fraught with consequences for the functioning of the entire organism.
In addition to these diseases, there are other causes of pain in the liver:
- pregnancy;
- hormonal drugs;
- steroids;
- eating fatty and fried foods;
- daily alcohol consumption.
Let's talk about alcohol separately.
Alcohol and liver (Alcoholic cirrhosis, Alcoholic hepatitis)
Every person knows that alcoholic drinks destroy liver cells, causing alcoholic cirrhosis and alcoholic hepatitis. Since men are exposed to bad habits more often than women, their risk of serious illness caused by alcohol is higher.
However, alcoholism in the weaker sex develops many times faster than in men. Accordingly, diseases of the gland and other organs develop more intensively in women than in men. It is worth emphasizing that female alcoholism is incurable.
With the systematic consumption of alcoholic beverages, gland cells die and are replaced by connective tissue. An inflammatory process develops, in which the organ grows and puts pressure on neighboring organs, which causes pain. It will take a lot of time for the liver to recover and, most importantly, to forget about alcohol forever.
Forms of liver failure
Based on the rate of development of liver cell death, liver failure can be acute or chronic. According to the mechanism of development of the pathology, the following 3 forms of the condition are distinguished:
Hepatocellular failure
It occurs when the cells of an organ are affected by substances that are toxic to them (mushroom poisons, special viruses, poisons from alcohol substitutes). This type of liver failure can be acute, when cells die en masse, and chronic, when poisoning occurs gradually, cells die slowly.
Portocaval form
It is, in most cases, chronic. This name suggests that there is high pressure in the portal vein (called “vena porte” in Latin), which carries blood to the liver for cleansing. In order not to “flood” the liver with blood, this vein “dumps” blood into the inferior vena cava (it is called the “vena cava”) through connecting veins. These veins normally exist to save a life if severe hypertension develops in the portal vein. But if high pressure is maintained in them for a long time, which they are not designed for, ruptures of various sizes periodically occur in them, which leads to bleeding: esophageal-gastric, rectal, retroperitoneal.
Since the blood is shunted bypassing the liver, it turns out that it is not being cleansed of toxins. In addition, the portal vein normally provided part of the liver’s nutrition, that is, with the portacaval form of failure, the liver cells will suffer from hypoxia. The latter will be chronic, since the hepatic artery still remains, which brings blood to the liver directly from the aorta.
Mixed form
This is also a type of chronic liver failure, combining both the suffering of liver cells (hepatocellular failure) and the “discharge” of unfiltered blood into the general bloodstream.
Symptoms of liver disease
The accompanying signals will help prove the fact that the pathology occurs specifically in the liver:
- fast fatiguability;
- weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- constant belching;
- enlarged belly on the right side;
- severe weight loss;
- yellowness of the skin
- discolored urine and stools;
- itching and dry skin;
- swelling.
Liver pathology is visible externally. The quality of hair, nail plates and epithelium deteriorates due to the fact that iron does not cope with complete cleansing; toxins and waste accumulate in the body. The epithelium on the face dries out and becomes dull, rashes form, hair falls out, and the nail plates break and peel.
The most important thing you need to know: if these symptoms appear, you must immediately consult a doctor; self-medication in this situation is strictly prohibited.
Diagnostics
Using laboratory tests of diagnostic procedures, a qualified specialist can identify liver pathology in the early stages of disease development. The treatment system will be determined depending on what caused the pain after diagnostic measures.
Types of diagnostic procedures that a doctor will prescribe for patients with liver pain:
- Laparoscopy;
- Biopsy;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- CT;
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Tests for viral hepatitis and cancer;
- Genetic research;
- Immunological tests.
Treatment is selected individually, based on the results of these tests.
Diagnostic measures
When visiting an experienced specialist, he collects the necessary information. As part of the conversation, the doctor studies the patient’s medical record (it may contain records of chronic diseases), learns about the symptoms that bother the patient, confirms or denies the presence of various types of poisoning.
When, as a medical professional, it becomes clear what pathological process in the human body provoked the development of hepatic-renal failure, he prescribes a series of hardware and laboratory diagnostic tests:
- urine and blood tests;
- taking a biochemical blood test;
- examination of the body using an ultrasound machine;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging examination.
After a qualified doctor receives and reviews the results of the diagnostic examination, he begins to prescribe the most effective and safe treatment method. The specifics of therapeutic measures completely depend on what stage of the disease is progressing in the body, what is the age of the patient who applied, whether he has individual contraindications, and also, to the extent necessary, the age of the patient is taken into account.
Treatment
Most illnesses are treated in a hospital. And many diseases can be treated in simple ways. If this is alcoholic hepatosis, then you should forget about alcohol and choose a diet. In case of toxic poisoning, poisons are removed from the blood through detoxification. Other diseases can be cured by taking antibacterial and antiviral drugs. Surgeon intervention is necessary in the presence of cysts and tumor formations.
And if pain in the gland is due to injury or physical activity, then you should just rest. No treatment as such is required.
Pain relief medications (first aid for liver pain)
The following special drugs are used to help relieve spasm and severe pain in the liver:
You can take tablets, but it is advisable to administer the medicine intramuscularly, because in this form the drug can relieve suffering in a shorter time than tablets. But we must also forget that No-spa is not used for liver failure.
Its injections are also used to suppress pain. The direct purpose of the drug is to relax the smooth muscles of the digestive and genitourinary systems. But, again, the use of this drug for liver failure is prohibited.
This drug is administered in various ways.
You cannot take analgin yourself, because... it may mislead your doctor by dulling pain or changing signs of pathology. And also, Analgin additionally loads the exocrine gland.
However, the doctor may prescribe injections of this drug if he considers it necessary.
How to cleanse the liver with folk remedies
Although it was indicated that you cannot self-medicate for pain in the liver, it is still worth noting a couple of points about alternative medicine. You can try liver herbal teas, they are sold in pharmacies and do not require a prescription from a doctor.
With all this, you should not abuse traditional medicine. Since inflammatory processes can lead to cirrhosis of the liver.
Diet for liver diseases
Let's start with the fact that it is necessary to eliminate bad habits (smoking and alcohol).
Products whose consumption should be minimized:
- Alcohol. Exceptions may include medications (tinctures, decoctions, etc.);
- Butter. You shouldn’t cut it out of your diet at all, because oil has a beneficial effect on some organs;
- Fast food. Absolutely forbidden. Fast food products contain a huge number of components hazardous to health;
- Pork lard, duck and goose meat are recommended to be consumed in small portions;
- Kiwi. You should also reduce your consumption of this fruit;
- Sweet and rich pastries;
- Hot spices and smoked meats.
To prevent liver diseases at home, you should not suddenly change your diet, because this can have a bad effect on the condition of the liver. All changes in diet must be made gradually.
You should drink no more than three liters of fluid per day. It is advised to eat boiled and steamed food. It is also recommended to consume food before 8 pm.
To prevent liver problems, you need to include a number of foods in your diet:
- Wholemeal breads and pastries;
- Vegetable soups with low-fat broth;
- Fresh vegetables and fruits;
- Dairy products with 0% fat content;
- Boiled and stewed fish;
- Freshly squeezed juices, not strong tea and coffee.
Proper nutrition is the key to a healthy liver.
Kidney cleansing
Kidney intoxication can lead to urolithiasis and kidney failure. But there are several safe methods to reduce the risk of disease.
Apple cider vinegar helps minimize the risk of kidney stones. It is enough to add 4 tablespoons of natural apple cider vinegar to 100 ml of water. The resulting drink should be taken daily before meals.
Ginger is also great for cleansing the kidneys. Grate 2 tablespoons of fresh ginger or take 2 teaspoons of dried ginger, pour boiling water over it, and let the drink brew for 4-9 minutes. You can add a little honey and lemon juice. This infusion should be taken 2 glasses per day for several weeks.
The brightest Baltic actresses who were adored by Soviet audiences
A royal python found on the streets of Prague: the escape of a red-haired friend
I don't like to bake, so I make a quick cookie and white chocolate cake with M&Ms.
Freshly squeezed cranberry juice will remove pathogenic bacteria and toxins from the kidneys.
Active physical activity for at least 30 minutes a day will improve blood flow to the pelvic organs and urinary system and, in addition, will also strengthen the cardiovascular system.
Beets and their juice contain betaine, which has antioxidant properties and increases the acidity of urine. Dissolving calcium in the kidneys reduces the likelihood of developing kidney stones.
Naturally acidic lemon juice increases the level of citrate in urine, which prevents the formation of kidney stones. For a quick and effective kidney cleanse, squeeze 4-5 lemons, combine the juice with a liter of cold water and drink it.
The couple decided to separate and did not see each other for 2 years. But one day everything changed
No photos together. Why Hermione's boyfriend left social networks
Renowned plastic surgeon notes growth in his clientele of people aged 40+
Watermelon juice is a source of potassium. It helps remove toxins from the body. Combine watermelon pieces and peeled lime in a mixer. Add honey to the resulting juice and mix well. This delicious drink also cleanses the kidneys.
Videos on the topic
Often people begin to think about the location of their kidneys only when they begin to hurt. But relying solely on pain, it is quite difficult to determine where the kidneys are.
Pain syndrome in various nephrological diseases is diffuse, sometimes it can indicate dysfunction of internal organs or diseases of the musculoskeletal center.
Ignorance of the anatomical location of the kidneys, as well as the nature of the pain, complicates early diagnosis. Therefore, for timely treatment, it is necessary to know the physiology of the organ, as well as the principles of first aid in the event of kidney pain.
Content:
Where are the kidneys located?
The kidney is an important paired bean-shaped organ. It is located on the surface of the posterior wall of the peritoneum on either side of the spinal column. The location of the kidneys corresponds to the level of the XII thoracic and three upper lumbar vertebrae.
Normally, the kidneys are reliably isolated from other organs by a connective membrane (fascia), which attaches them to the diaphragm. Their fixing apparatus is additionally represented by a fatty capsule, a bed of abdominal and back muscles, and vascular pedicles.
The right organ is projected onto the anterior wall of the peritoneum, its membrane is in contact with the duodenum and liver. Left - located in the projection of the epigastric region. The spleen hangs over the left kidney, the organ is covered from behind by the colon, and the anterior wall borders the pancreas, the middle section of the small intestine.
The location of the kidneys depends on gender and age category:
- in men they are slightly larger, the height of their projection in the lumbar region corresponds to the level of the XI thoracic and second lumbar vertebra;
- in women they are slightly lowered, but only by half a vertebra;
- in childhood, the kidneys, despite their large size, occupy a low position in the extraperitoneal space. Closer to 10 years, they rise to the third lumbar vertebra.
Related article - Axillary muscle strain
The kidney is a mobile organ and changes its location when the body posture changes. Relative to the sacrum, the kidneys can shift by 2-4 cm. If this figure is higher than 5 cm, then we are talking about the “wandering kidney” pathology.
In addition, with the help of palpation during examination, ultrasound or radiography, an abnormal location of the organ can be detected. If pathological prolapse of one kidney is noticed, a diagnosis of unilateral dystopia is made, but if both organs are displaced and are located on the same side of the spinal column, then we are talking about cross dystopia. Fusion is less commonly diagnosed: one-sided, two-sided or in the form of the letter “S”.
Structure and functions of the organ
In cross-section, the kidney is represented by a yellow-red cortex (outer layer), located on the periphery of the organ, and a lilac-red substance (marrow). The approximate weight of the organ is 130-200 g. The average size is 10-12 cm in length, no more than 5 cm in width. The thickness can be about 4 cm.
The parenchyma (internal tissue) of the kidney is densely dotted with renal tubules covered with an epithelial layer. They interact with the capillary network of the organ, creating a functional renal unit - the nephron. It filters primary urine from the plasma. One organ can have more than 1 million such structural units.
The dimensions, location and structure of a person’s kidney may differ slightly. But exceeding the statistical average can affect the functionality of the organ, and is considered a pathology. As for kidney function, it is vital, and without kidneys the body cannot exist. In addition to performing a cleansing function, they actively maintain the acid-base balance, take part in hematopoiesis, and maintain blood pressure. The functioning of the endocrine system and the regulation of the balance of micro- and trace elements depend on their work.
Kidney pain: causes and symptoms
Discomfort in the lower back is a common symptom of diseases of the urinary system. But only a doctor can determine exactly what is hurting, the kidneys or another organ. Therefore, it is important to know how kidney pain differs from other pathologies.
Where and how do the kidneys hurt?
The location of the kidneys most often contributes to the appearance of pain in the back, where the organ is projected. However, the lesion is accompanied not only by pain, but also by weakness, problems with urination, and other symptoms.
Kidney pain is mainly concentrated in the lower back. But its localization may be on the inner thighs or along the ureter. Also, a painful lumbago can radiate to the perineum and navel.
The cause of lower back pain can be two diseases with similar clinical manifestations - kidney inflammation and rheumatism. At the first stage of the disease, you need to be able to distinguish kidney pain from rheumatic pain.
This is done according to three criteria:
- With an exacerbation of rheumatism, the pain is aching, shooting, aggravated during movements, which are often constrained. Kidney pain is sharp, impulsive, and does not depend on body position.
- Inflammation is accompanied by fever and pain, nausea and vomiting. With rheumatism, this picture is absent.
- When the organ is diseased, pain occurs when urinating, the color of the urine changes, and sediment, flakes, and threads of mucus appear in it.
Other symptoms of kidney damage include:
- general weakness;
- sleep disturbance (kidneys begin to hurt more at night);
- swelling of the limbs, face (mainly in the morning);
- hypertensive crisis;
- increase or decrease in daily diuresis;
- headache.
If on the eve of the onset of pain there was an injury to the kidney area or severe hypothermia, you can be sure that this is definitely kidney pain.
What causes kidney pain
- The provocateurs of kidney pain in humans can be infections and injuries, as well as congenital pathologies and oncology. Common causes of organ damage are:
- Inflammation of tissues, for example, pyelonephritis, exacerbation as a result of the formation of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, inflammation of the urethra.
- Congenital anomalies that lead to inadequate outflow of urine (enlarged pelvis).
- Neoplasms of various etiologies (cysts, oncological tumors, polyps).
- Dysfunction of internal organs causing insufficient kidney function.
- Trauma (blood appears in the urine, colic, blood pressure drops).
First aid for kidney pain
The sudden appearance of pain in the kidneys is a reason to immediately seek medical help. And if the outflow of urine is disrupted, there is a high temperature, or renal colic, especially if the child is sick, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Before visiting the doctor, you can take any drug with an analgesic and antispasmodic effect: Spazmalgon, No-Shpa, Maxigan, Drotaverine.
In some cases, soaking in a hot bath can help relieve pain. But until the diagnosis is clarified, you should not resort to this method.
Features and phases
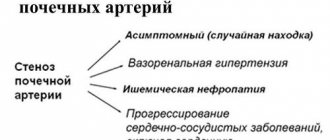
This dangerous condition is characterized mainly by a sharp narrowing of the vessels of the kidneys , especially pronounced in the cortical areas. At the first stage, damage to the liver and biliary tract occurs.
Later, the kidneys begin to become involved in the pathological process, taking on that part of the functions of removing toxic substances from the body, which is completely unusual for them.
As a result, irreversible loss of functioning parenchyma . At the same time, the amount of fluid released from the kidneys quickly decreases (oliguria). It can reach a complete absence of its entry into the bladder (anuria). Urine accumulates inside, poisoning and destroying the body.
There are usually four clinical phases that progress rapidly:
- The first degree is initial, which is very difficult to detect, since it is characterized by common symptoms similar to many diseases - severe irritability, persistent loss of appetite, poor sleep
- The second is accompanied by significant deterioration - weakness increases, dizziness and nausea appear, often accompanied by vomiting and fainting, periodic disturbances in coordination of movement and speech, and a distinct smell of acetone from the mouth when exhaling.
- In the third phase, the state of health worsens even more and a serious threat to life already appears. The patient experiences unbearable pain, behaves quite restlessly, screams loudly, cannot fall asleep, and if he falls asleep, he does not wake up for a long time, and is constantly delirious in his sleep.
- In the last fourth stage, uremic coma occurs. There is no longer any response to stimuli - pain is not felt, there is no pupillary reflex to light. Frequent paroxysmal involuntary muscle contractions—convulsions—appear.